The Cardiovascular System and Blood Composition
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the main components of the cardiovascular system?
Blood
heart
blood vessels.
What is the primary function of the cardiovascular system?
transport of nutrients, waste products, and cells within the body.
What are the main functions of blood?
Distributes nutrients, oxygen, and hormones
carries metabolic wastes to the kidneys
transports white blood cells
maintains homeostasis.
What are the two main components of whole blood?
Plasma and formed elements.
What does plasma contain?
Dissolved proteins and serves as the liquid matrix of blood.
What are the formed elements of blood?
Blood cells and cell fragments suspended in plasma
rbc
wbc
platelets
What is the role of red blood cells (RBCs)?
To transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What is the lifespan of red blood cells in circulation?
Approximately 120 days.
What protein is primarily responsible for the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in RBCs?
Hemoglobin (Hb).
What are the two major classes of white blood cells (WBCs)?
Granular leukocytes and agranular leukocytes.
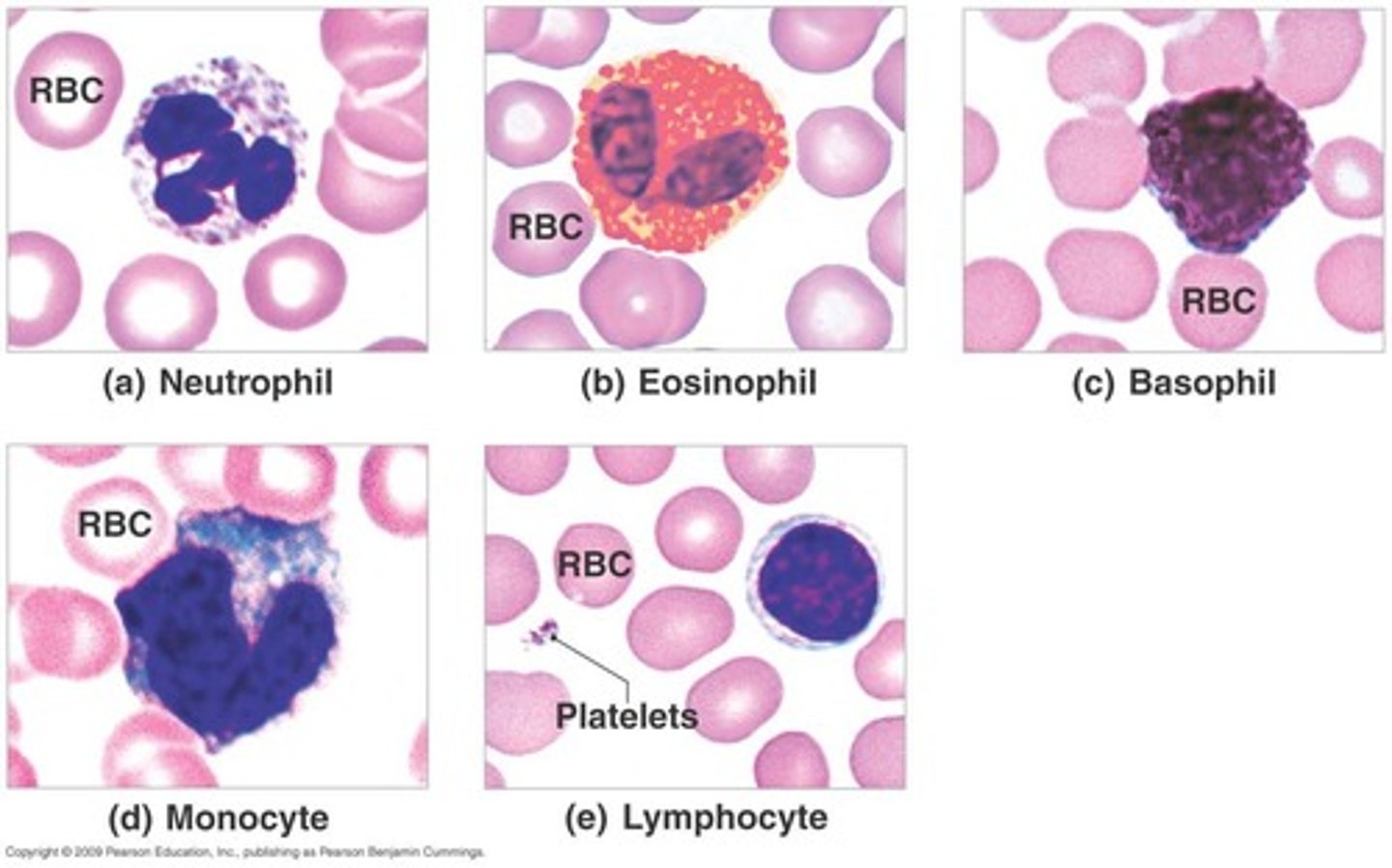
What are the types of granular leukocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils (acidophils), and basophils.
What are the types of agranular leukocytes?
Monocytes and lymphocytes.
What process do WBCs use to move through vessel walls?
Diapedesis.
What are platelets and their primary function?
transport chemicals important for clotting
temporarily patch the walls of damaged blood vessels
causing contraction after a clot has formed to reduce the size of the break in the vessel wall
How long do platelets circulate in the blood before being removed?
10 to 12 days.
What is hemopoiesis?
The process of blood cell formation.
What types of stem cells give rise to blood cells?
Myeloid and lymphoid stem cells.
What is normovolemic blood volume?
normal
what is albumins
a major contributor to the osmotic concentration of plasma and transport some lipids
What is the normal blood volume in an adult man?
5-6 liters.
What is the normal blood volume in an adult woman?
4-5 liters.
What is the pH range of blood?
7.35 to 7.45.
What is the normal temperature of blood?
100.4°F.
What are the three major classes of plasma proteins?
Albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen.
What is hypovolemic blood volume?
Low blood volume.
What is hypervolemic blood volume?
High blood volume.
what is globulins
transport ions, hormones, and lipids
What is fibrinogen
An essential component of the clotting system, and can be converted to insoluble fibrin
rbc
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
wbc
Defends the body against pathogens, removes toxins, waste, and damaged cells
platelets
participates in clotting respone