Kaarten: Cell Biology - Chapter 2: Cell Chemistry and Bioenergetics | Quizlet
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
noncovalent attractions
- hydrogen bonds
- electrostatic attractions (ionic bonds)
- van der Waals attractions
- hydrophobic force
effect of water on noncovalent bonds
presence of water REDUCES strength of ion and hydrogen bonds
acids
substances that release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
bases
proton acceptors
buffers
mixtures that can react with acids or bases to keep the pH within a particular range
four major families of small organic molecules
sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotides
sugars form
polysaccharides
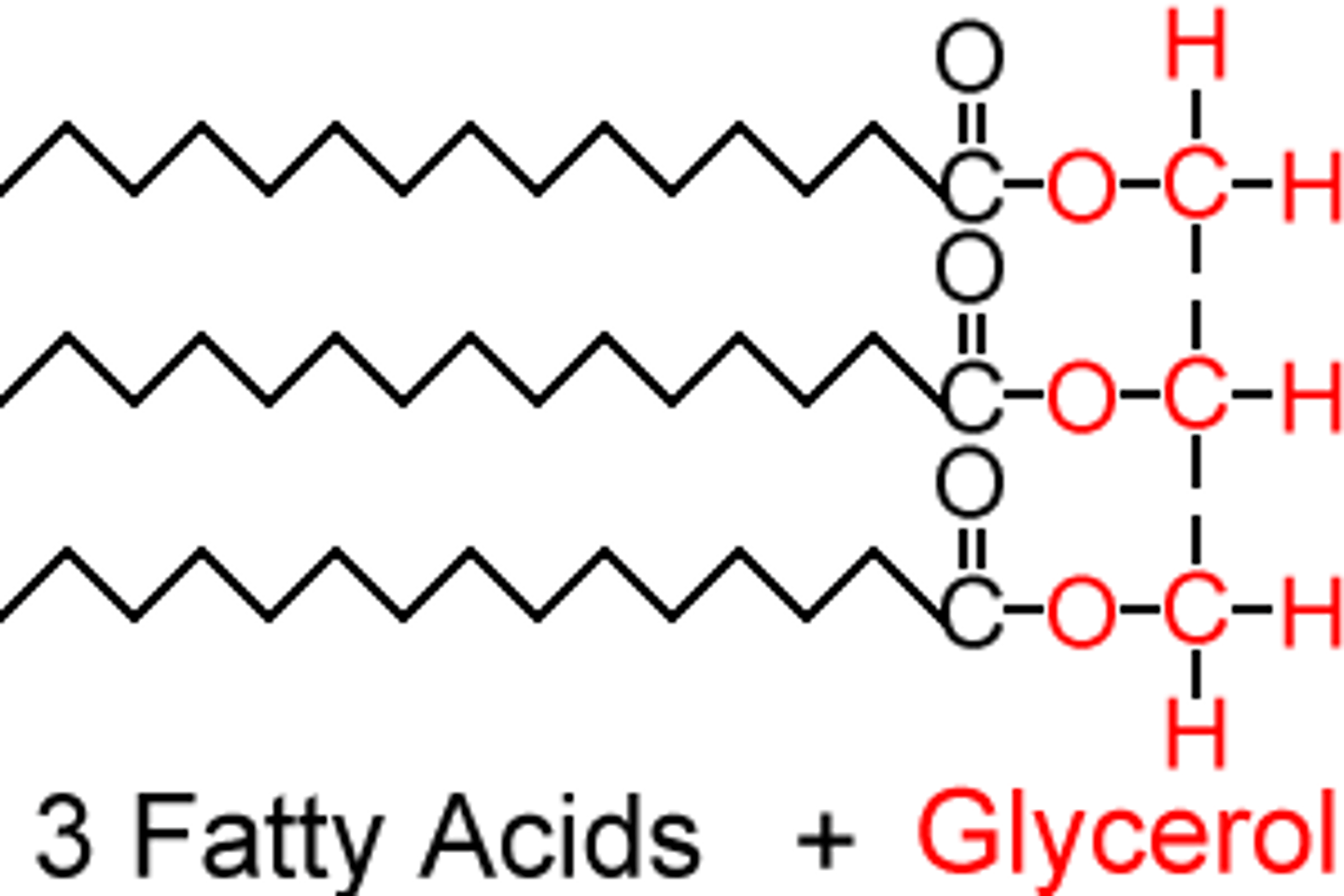
fatty acids form
lipids
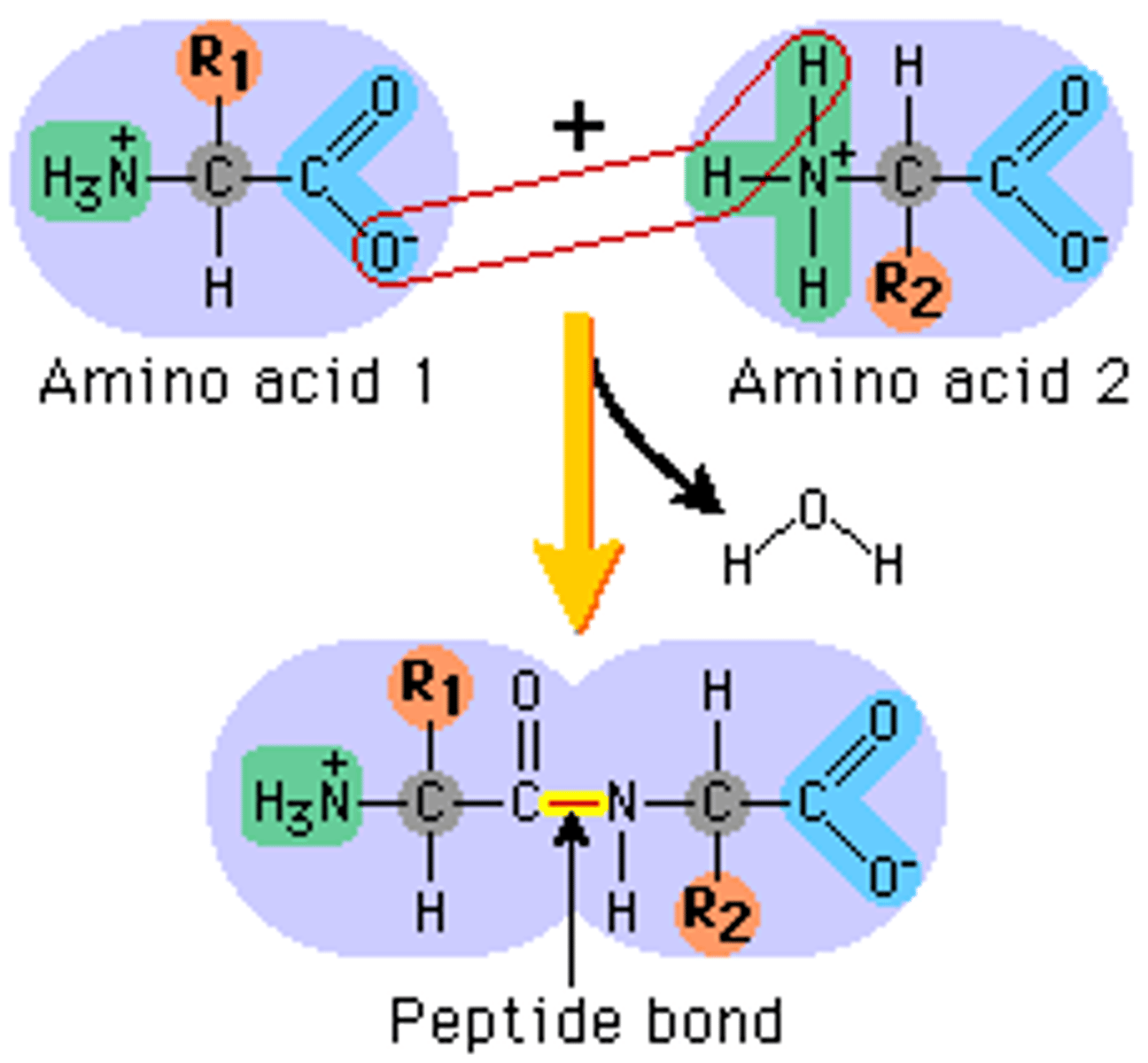
amino acids form
proteins
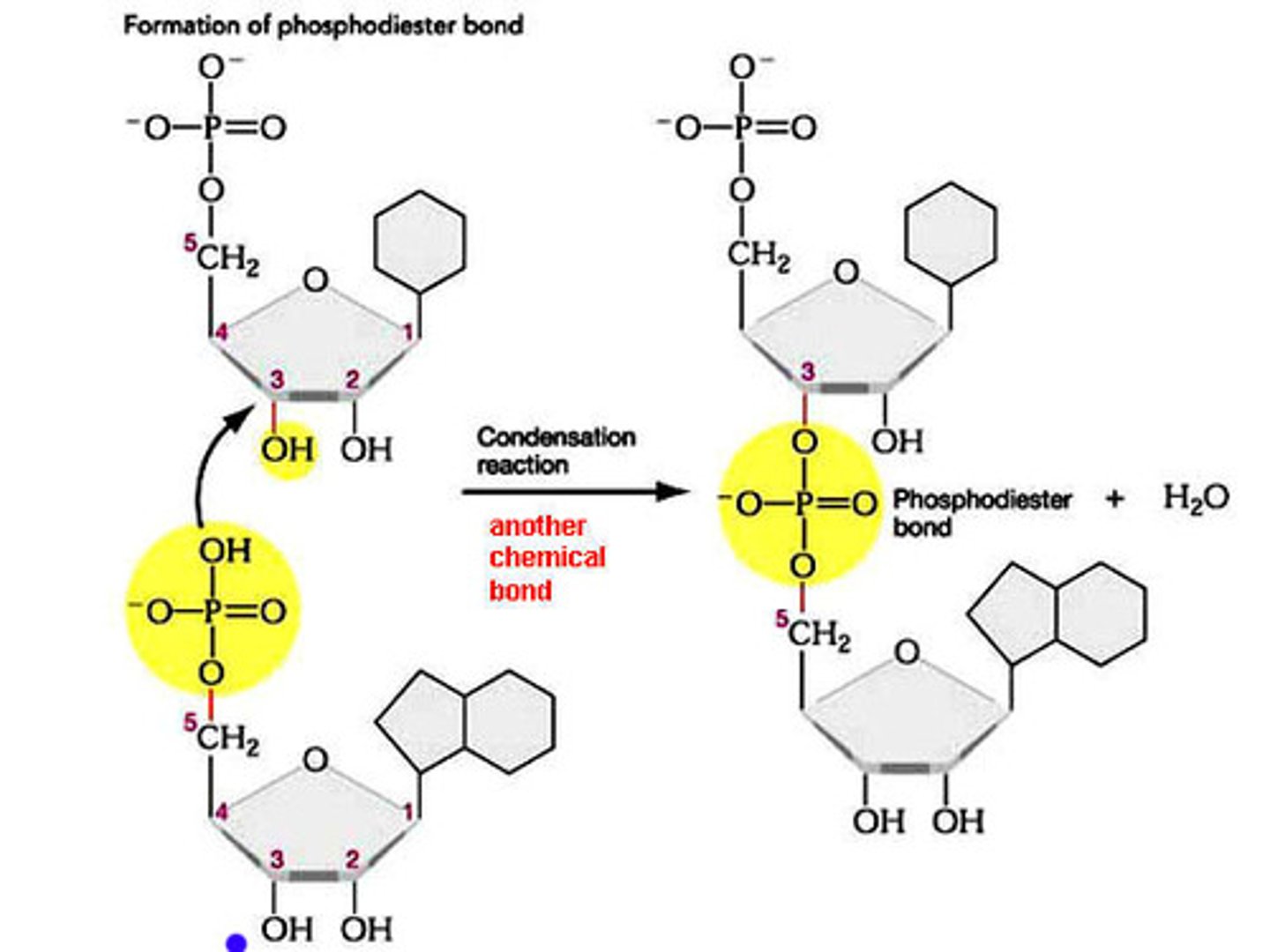
nucleotides form
nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
condensation reaction
a reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water; also called dehydration reaction
hydrolysis
breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
covalent bond gives
flexibility to the molecule (many conformations)
noncovalent bond gives
one preferred conformations (thus specifies binding to other molecules)
catalysts
substances that speed up chemical reactions
enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts
ribozymes
RNA molecules that function as enzymes
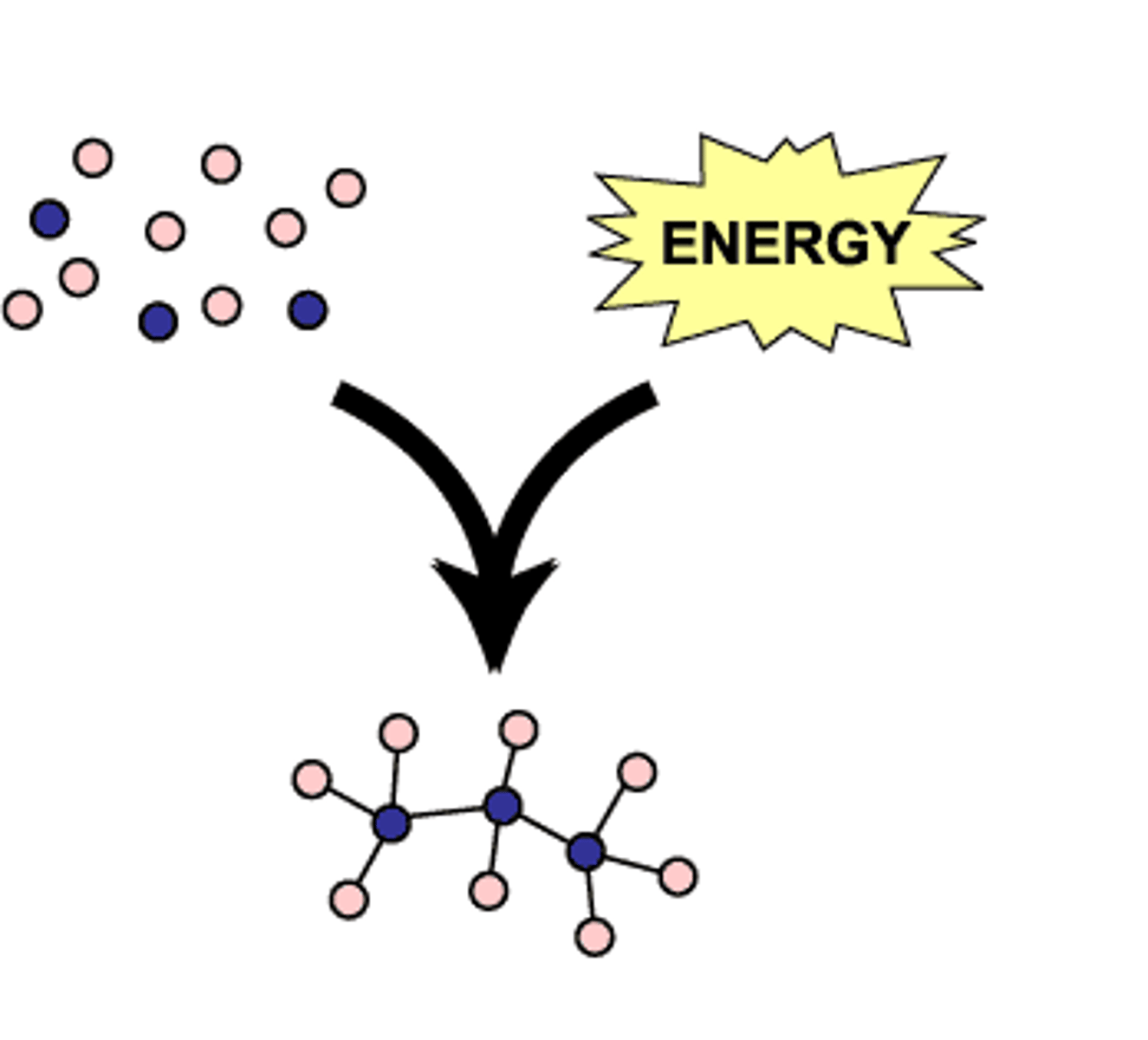
catabolic pathways
release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds (oxidation)
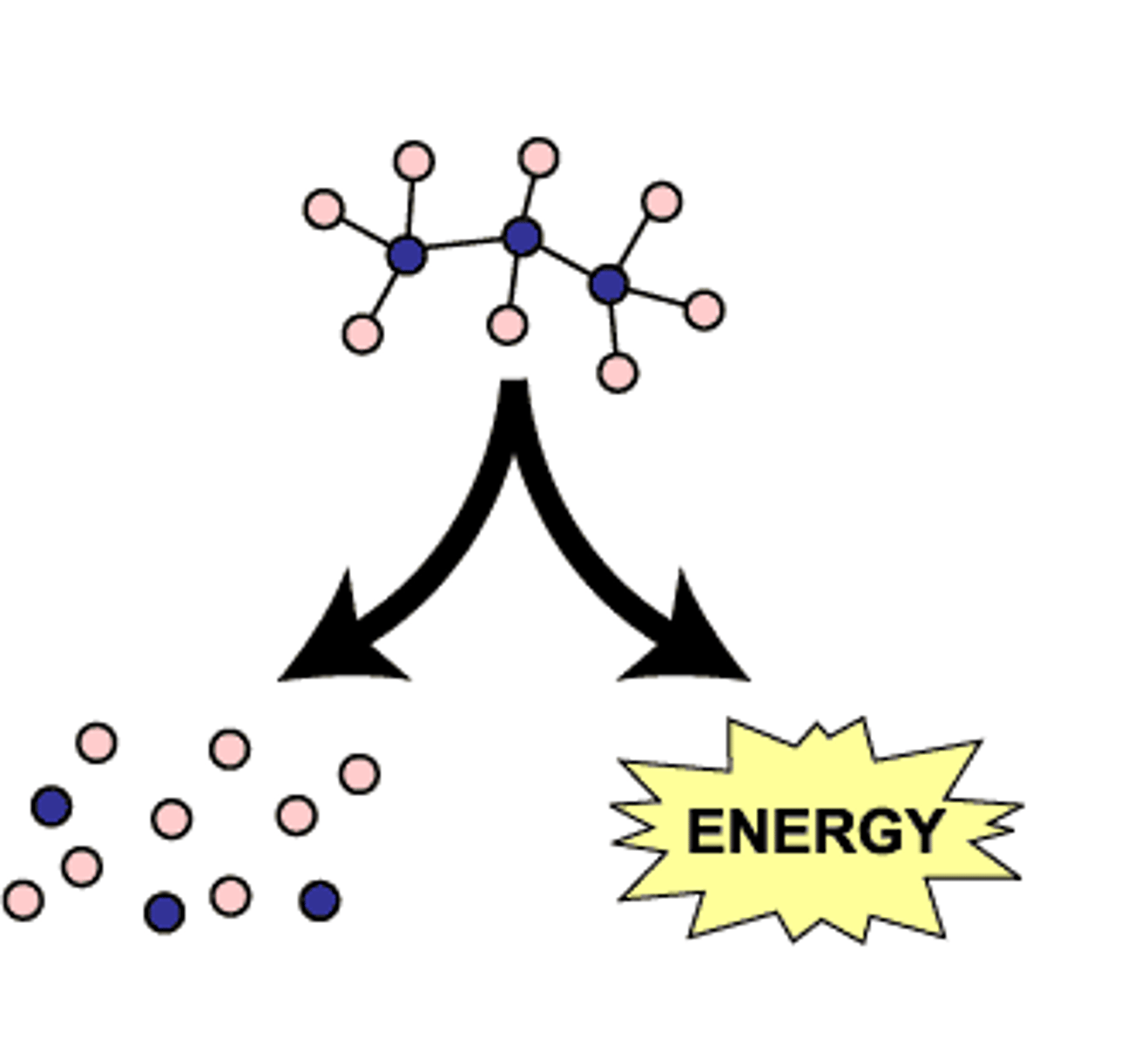
anabolic (biosynthetic) pathways
consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones
metabolism
catabolic and anabolic reactions in a cell
aerobic respiration
cell obtains energy from sugars
complementary process to aerobic respiration
photosynthesis
substrates
the specific reactants that an enzyme acts on
diffusion
movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
change in free energy equation
ΔG = ΔG° + RTln([X]/[Y])
ΔG less than 0
favorable reaction
ΔG bigger than 0
unfavorable reaction
overall free energy change of the reaction must be
negative
carrier molecules (coenzymes)
store energy in energy-rich covalent bonds
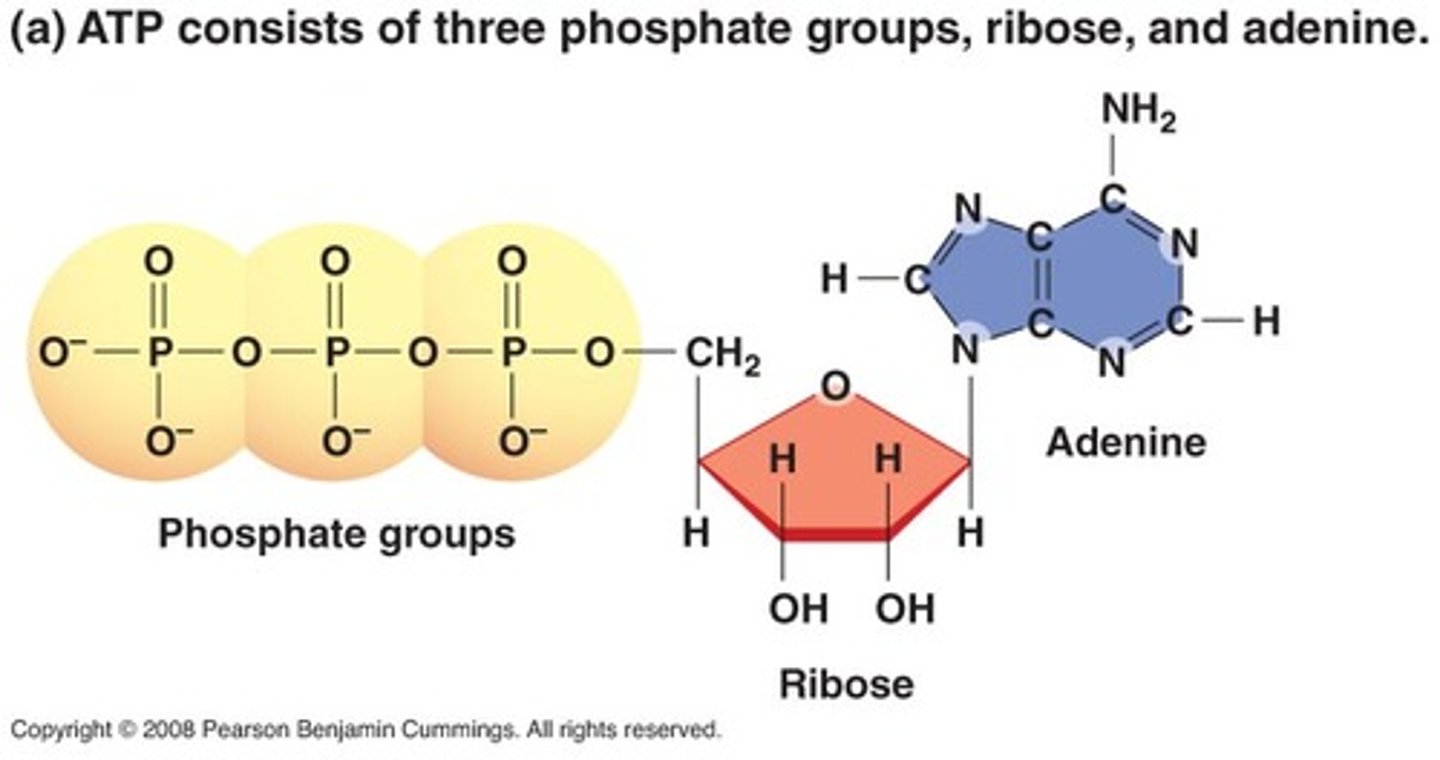
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
high-energy phosphoanhydride bond
ADP to ATP (energetically unfavorable)
phosphorylation - binding of an inorganic P
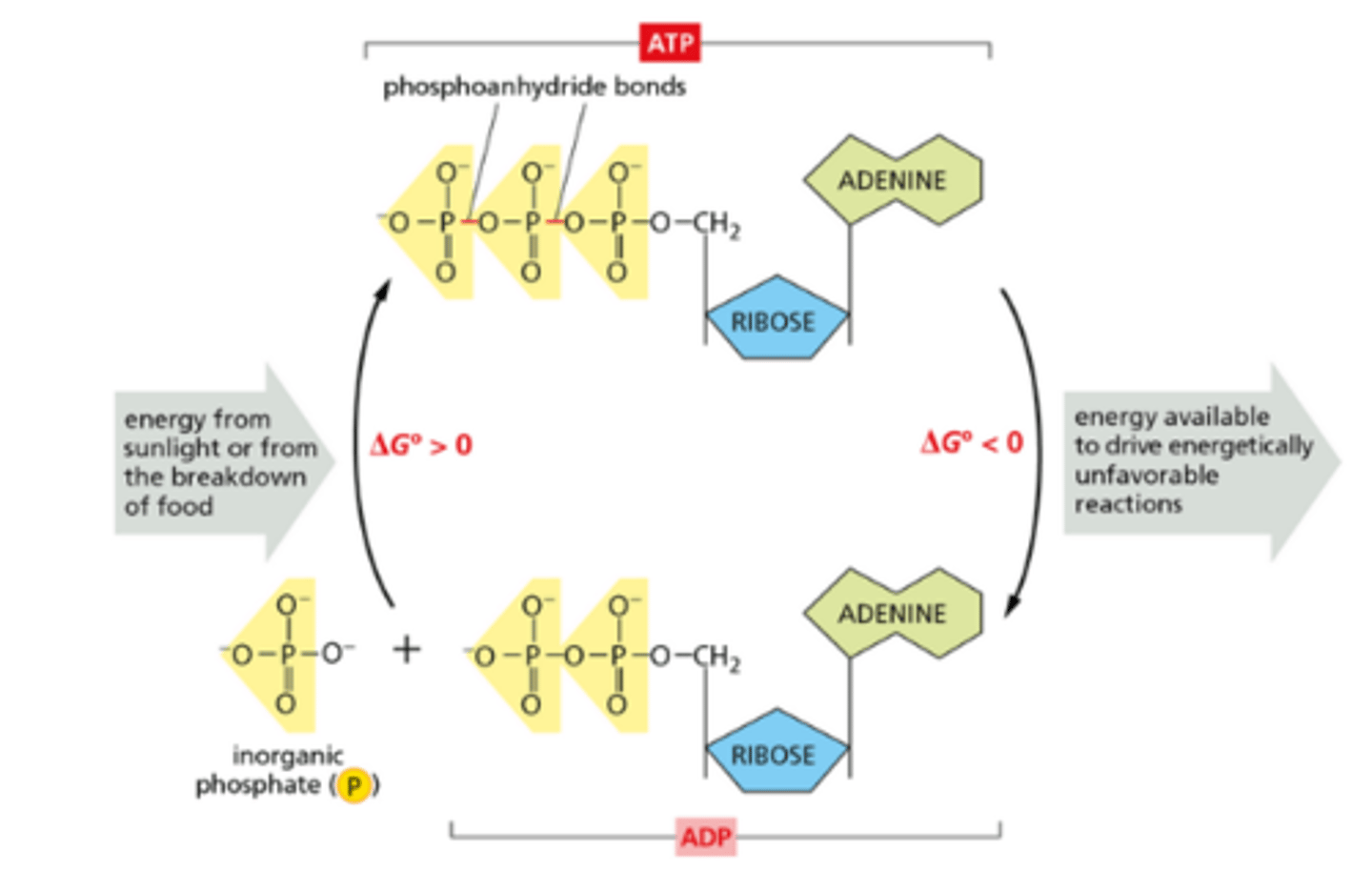
ATP to ADP (energetically favorable - no repulsion between adjacent negative charges)
hydrolysis - loss of an inorganic P
condensation reaction with ATP makes
a high-energy intermediate compound
high energy electron carriers
NADH, NADPH
NAD+
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NADP+
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
NADH
the reduced form of NAD+; an electron-carrying molecule that binds to enzymes that catalyze catabolic reactions
NADPH
the reduced form of NADP+; an electron-carrying molecule that binds to enzymes that catalyze anabolic reactions
other activated carrier molecules
coenzyme A, FADH2, carboxylate biotin, S-Adenosylmethionine, uridine diphosphate glucose
alternative pathway of ATP hydrolysis
ATP ---> AMP + pyrophosphate ---> AMP + 2 Pi
head polymerization
proteins and fatty acids; each monomer carries a high energy bond that will be used for the addition of the NEXT monomer
tail polymerization
DNA, RNA, polysaccharides; each monomer carries a high-energy bond for its OWN addition
glycolysis
oxidation of sugars; net products are 2 ATP and 2 NADH
aerobic cells transport pyruvate to
mitochondria (oxidation to CO2 and H2O)
glycolysis reaction
glucose + 2 NAD+ 2 ADP + 2 Pi ---> 2 pyruvate (3C) + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 net ATP
fermentation (anaerobic respiration)
pyruvate and NADH stay in the cytosol ---> ethanol + CO2 (yeasts) or lactate (muscle)
triacylglycerols
storage form of fatty acids
adipocytes
fat cells storing fatty acids in the form of triacylglycerols in their cytosol
glycogen
storage form of glucose in animals (short term storage)
starch
storage form of glucose in plants
Fat and starch are both stored in _______ in plants.
chloroplasts
degradation of pyruvate (by dehydrogenase complex)
CO2 + NADH + acetyl CoA
oxidation of fatty acids (takes place in mitochondria)
acetyl CoA + FADH2 + NADH
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
complete oxidation of acetyl groups' carbon atoms in acetyl CoA into CO2
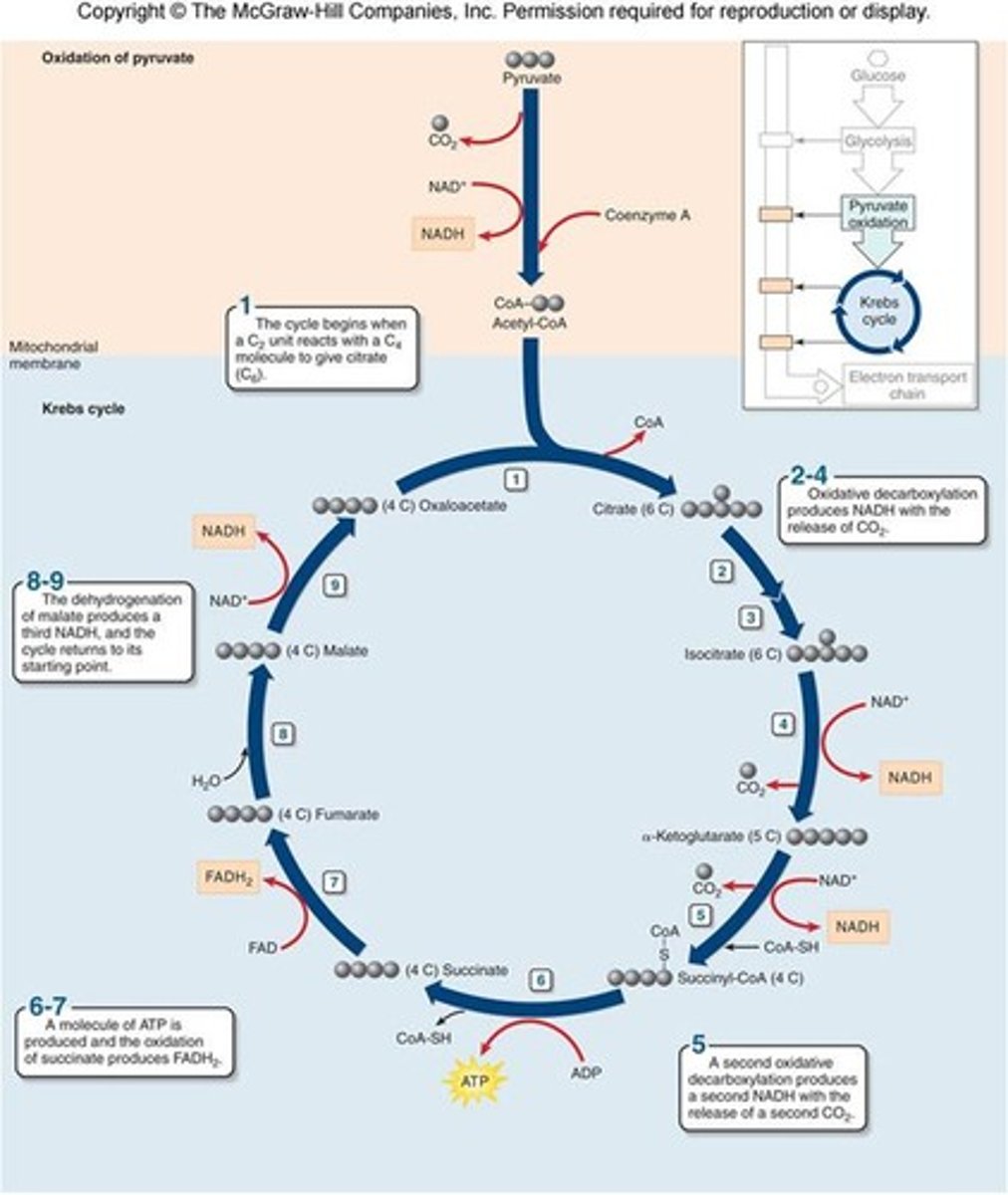
oxaloacetate and alpha-ketoglutarate
vital intermediates produced in the citric acid cycle and glycolysis
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
nitrogen cycle
the transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere
animals acquire sulfur through
diet
plants, bacteria, fungi can _________ sulfate
reduce