ARC 1013 - Briar Jones/MSST - Test 2, Architecture Appreciation Test 2
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
"Dead" Load
forces from all the "immovable" elements of a building (weight of building materials, walls, floors, etc)
"Live" Load
forces from all the "movable" elements of a building (people, equipment, furniture, etc)
Compression
capacity to resist being pushed together
Tension
capacity to resist being pulled apart
Post & Beam/Lintel
1. wood beam, steel cupping post
2. steel beam, welded steel post
3. 2 steel beams welded together
Frame
wood
steel (tall buildings; light weights; thin walls; take veneers of brick, stone, stucco, etc)
Masonry
brick
concrete
stone (heavy, thick walls, costly (today), good insulation)
Freedom Tower
David Childs, FAIA (SOM), & Lubscilm
Menhirs
single stone standing upright
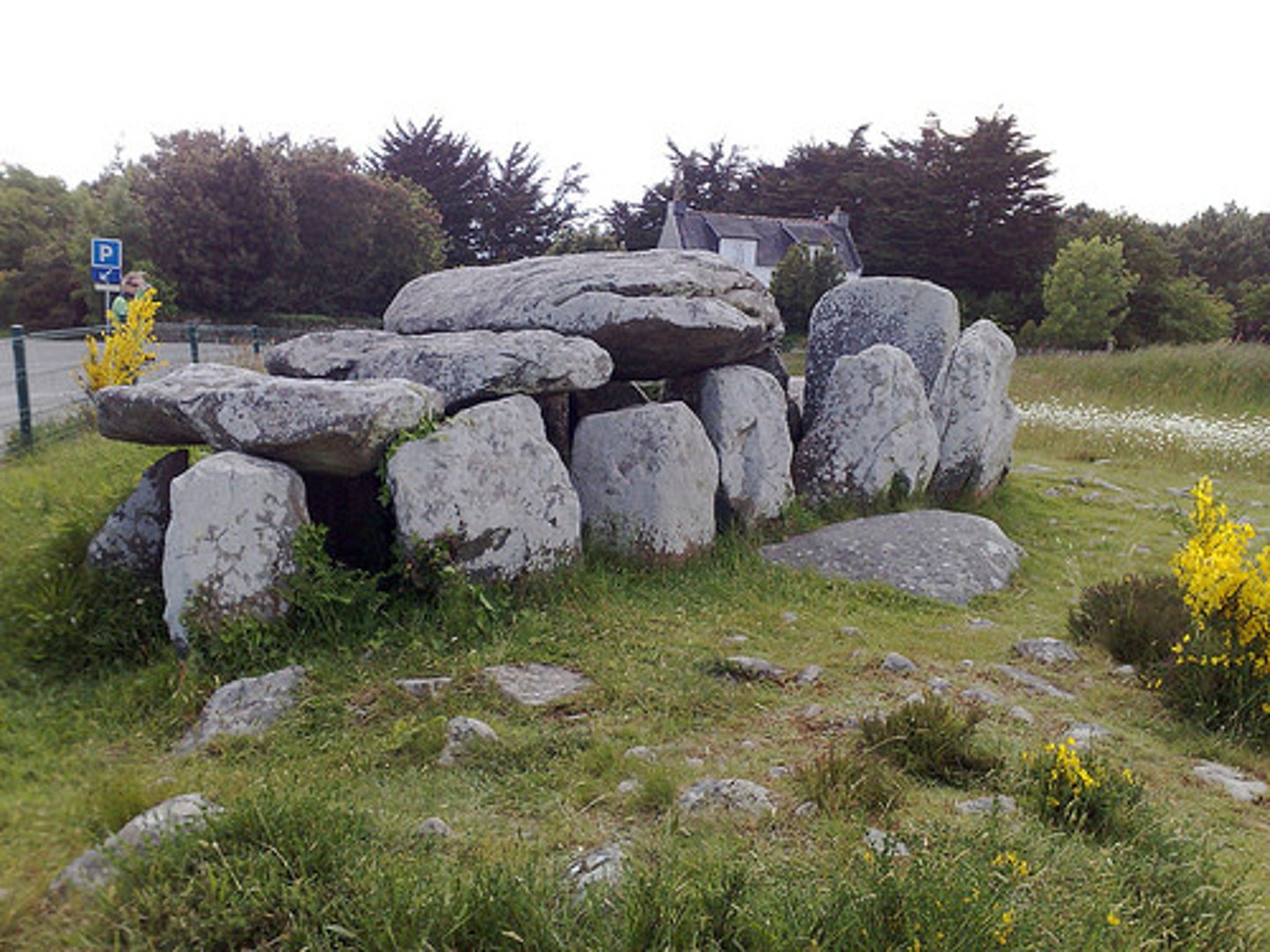
Dolmen
several stones supporting a stone slab
Henges
circular ditches around which some Megalithic monuments are arranged
Cromlech
circle of stones
Trabeation
post & lintel
Stonehenge
most famous Neolithic monument
built 3000 BC - 2100 BC
tops of stones/columns - mortise and tenon

3 Types of Pyramids
1. step - Saqqara: Doser's Step Pyramid
2. bent - Sneferu's South Pyramid; Dahshur, Egypt
3. straight - Cheops' Pyramid; Giza, Egypt
Ziggurat
stepped structure (mud brick)
some of oldest pyramids (2125 BC)
7 Wonders of the Ancient World
1. Great Pyramid
2. Hanging Gardens of Babylon
3. Temple of Artemis @ Ephesus (Fire)
4. Statue of Zeus (Fire)
5. Mausoleum of Halicarnassus (Earthquake)
6. Lighthouse of Alexandria (Earthquake)
7. Colossus of Rhodes (Earthquake)
First Recorded Architect
Imhotep
- born a commoner
- b/t 2700-2600 BC Zoser hired Imhotep to design his tomb
- "translated" traditional building materials of mud, wood, & reeds into stone
- also an astronomer, magician, & doctor
- later worshiped as a god
Pyramids of Giza - 2550 BC
Cheops - "Great Pyramid"
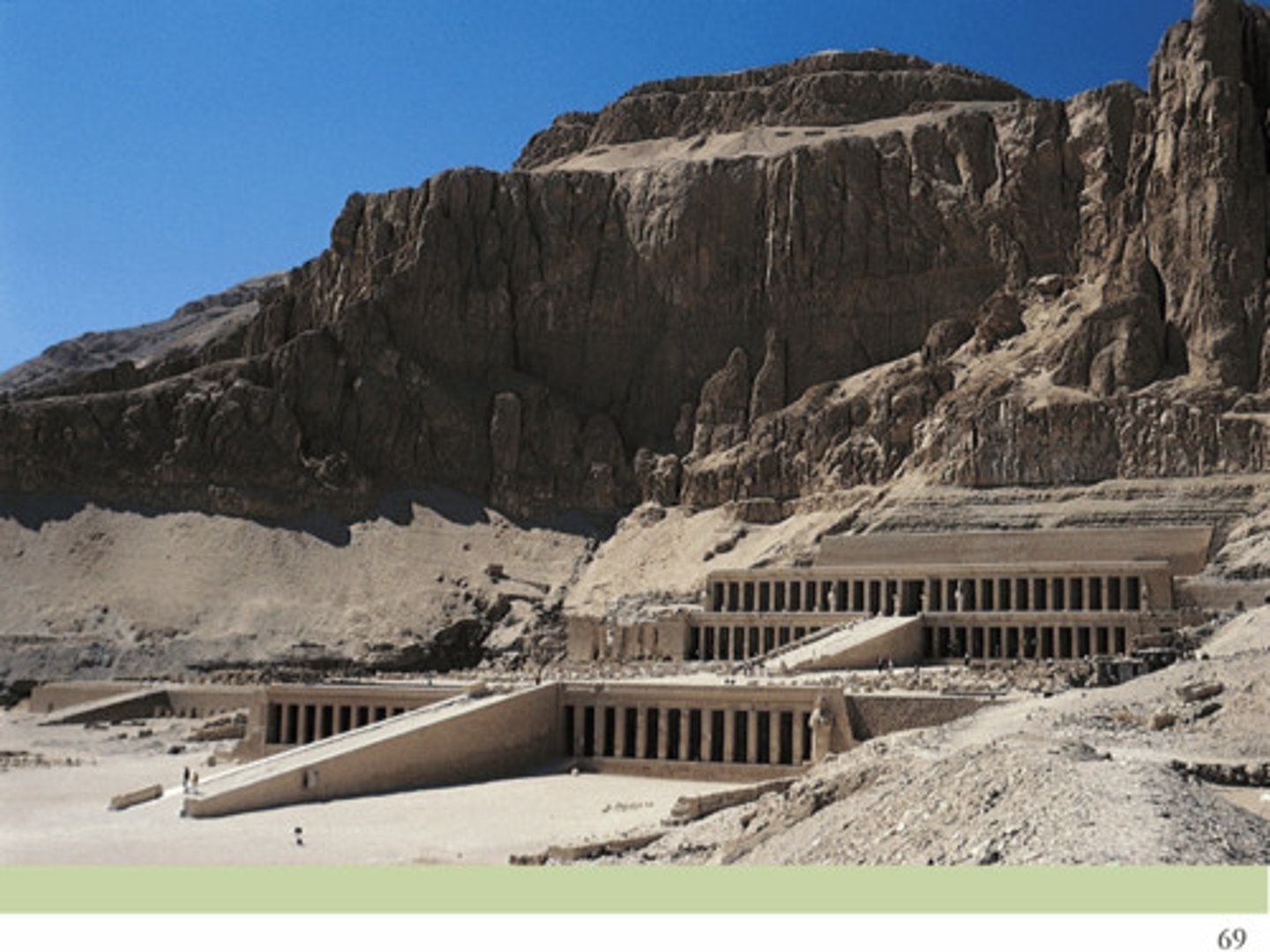
Mortuary Temple of Queen Hatshepsut
first tomb built into mountain; help stop looters

Hypostyle Halls
large space w/ flat roof supported by rows of columns (ex: Temple of Luxor & Temple of Amun @ Karnak)
When was the Egyptian revival?
mid 19th century
Pyramids in Central America
used as temples
ziggurats
often added onto over time (new temple over old)
Minoans in the Aegean
Palace @ Knossos
Mycenae
Lion Gate, precursor to Greek Arch (forerunner to post & lintel)
sense of structure was inheritance from Neolithic Period
lion element from Egypt
Greek will refine post & lintel
Greek Architecture
united by language
founded on: private property, individual freedom (less than 35% weren't slaves), democracy
Colonnade
series of regularly spaced columns supporting an entablature & usually 1 side of a roof structure

Why were temples built?
housed gods
impress non-Greeks (vivid color, floral design)
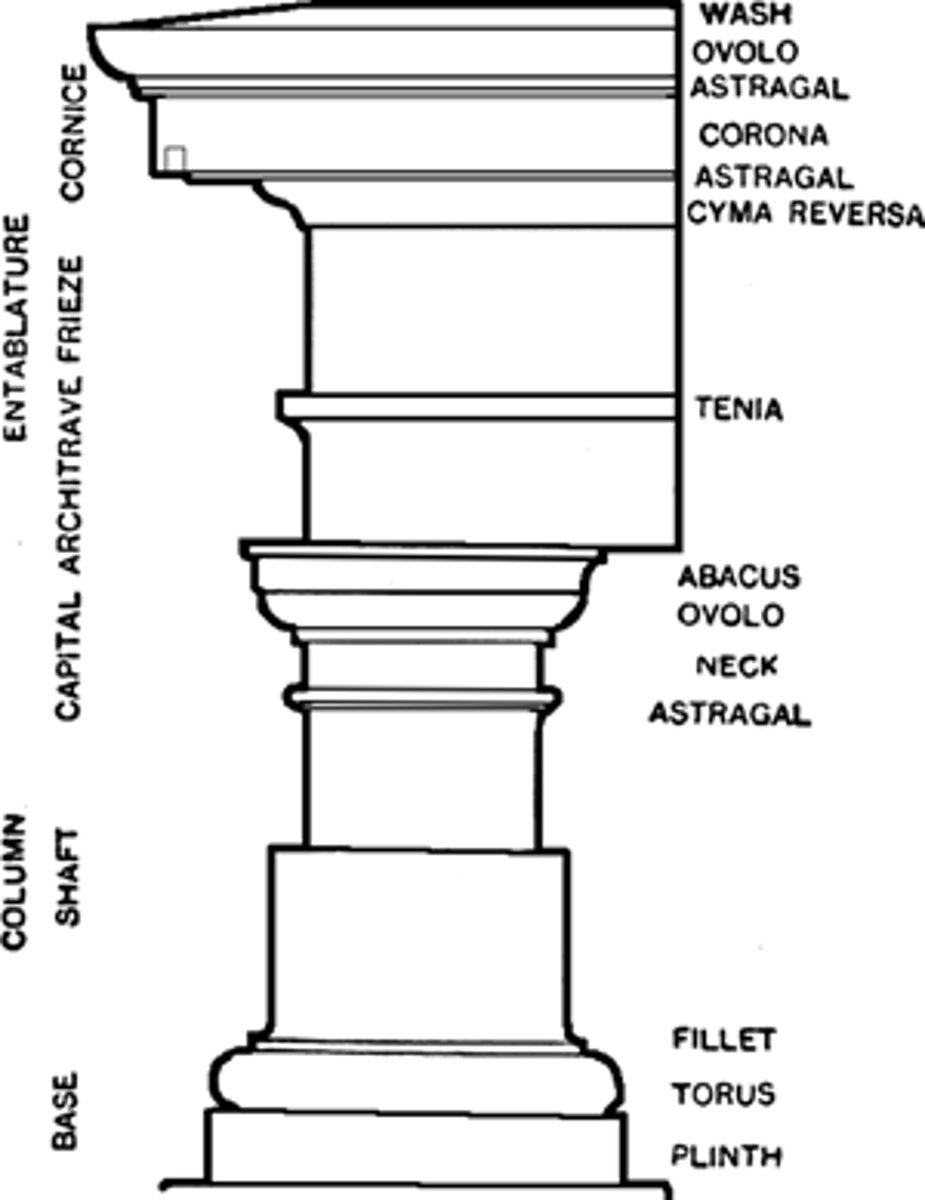
3 Orders
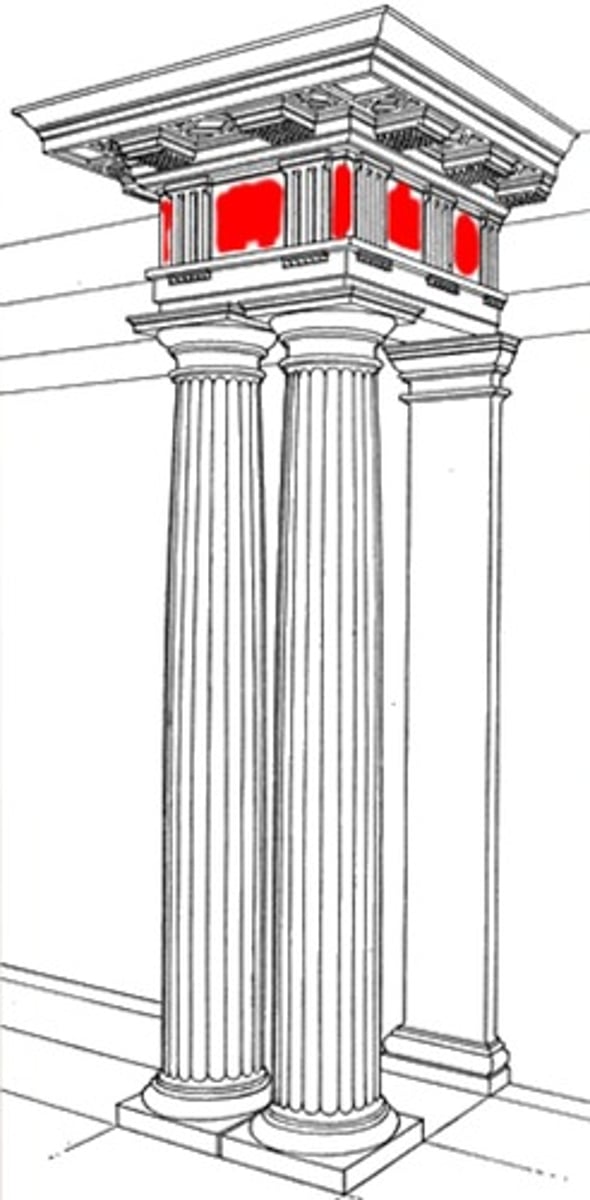
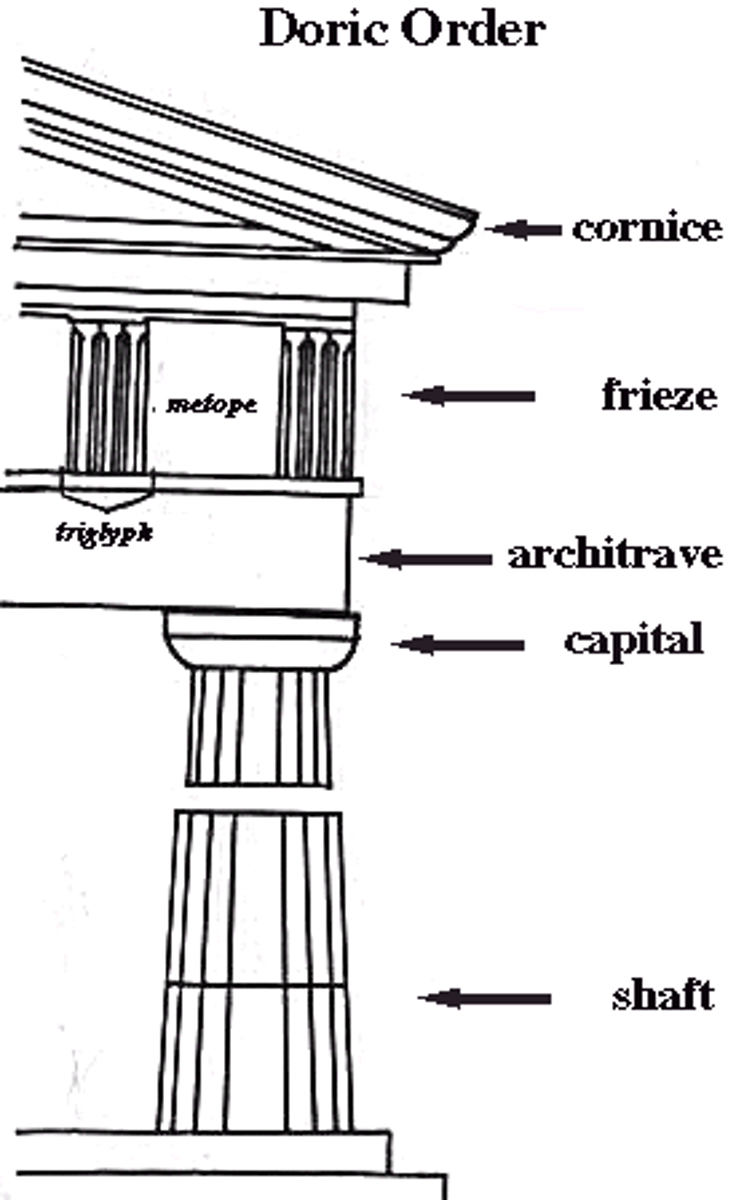
1. Doric - oldest, simplest, most massive
2. Ionic - "feminine", Ionian Islands developed it
3. Corinthian - variation of Ionic
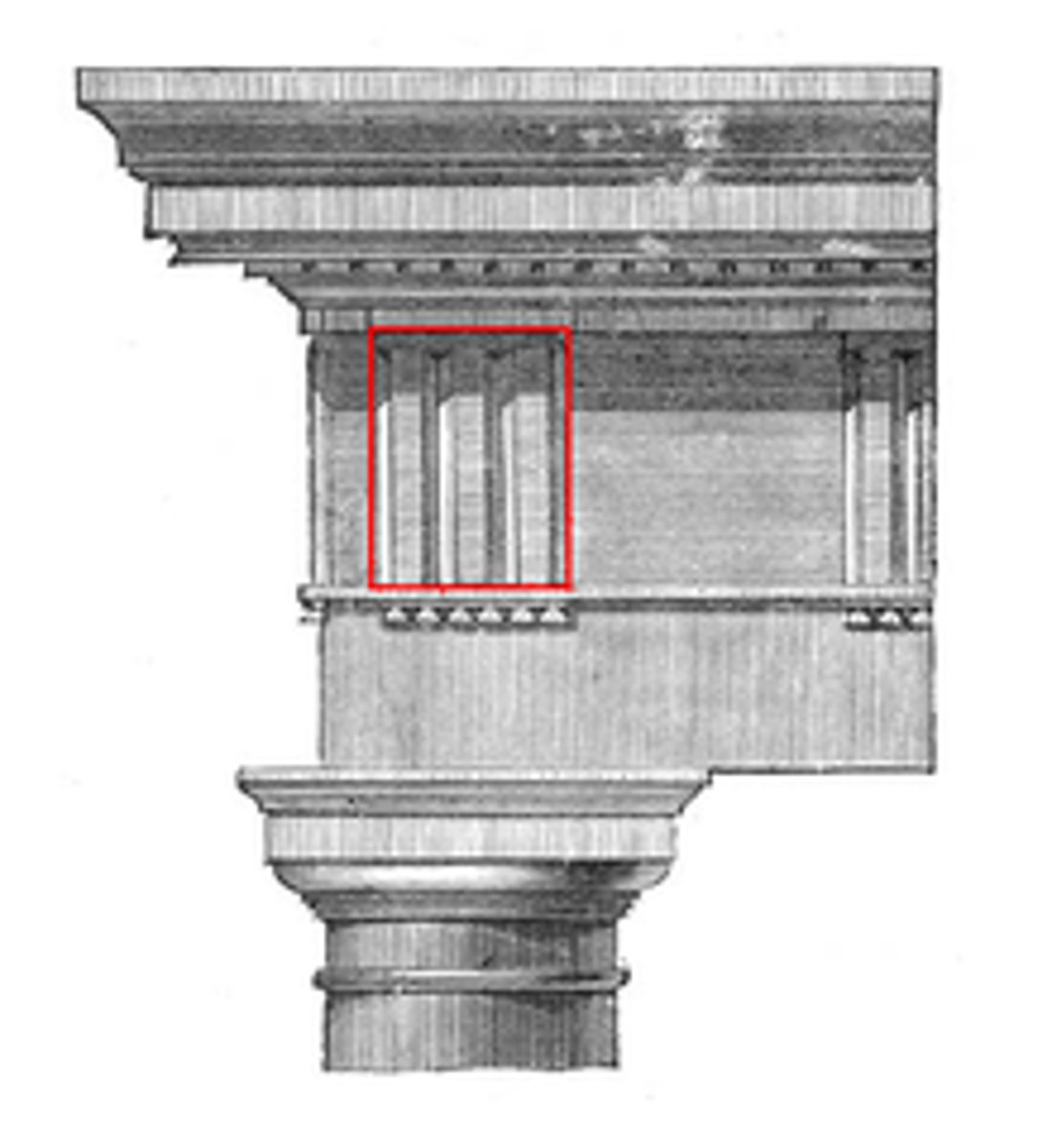
Metope
any of the panels, either decorated or plain, b/t the triglyph on a Doric frieze
Triglyph
1 of the vertical blocks separating the metopes on a Doric frieze
Doric Order
columns placed close, no base
plain capitals
metopes & triglyph
perfection of Doric - Parthenon
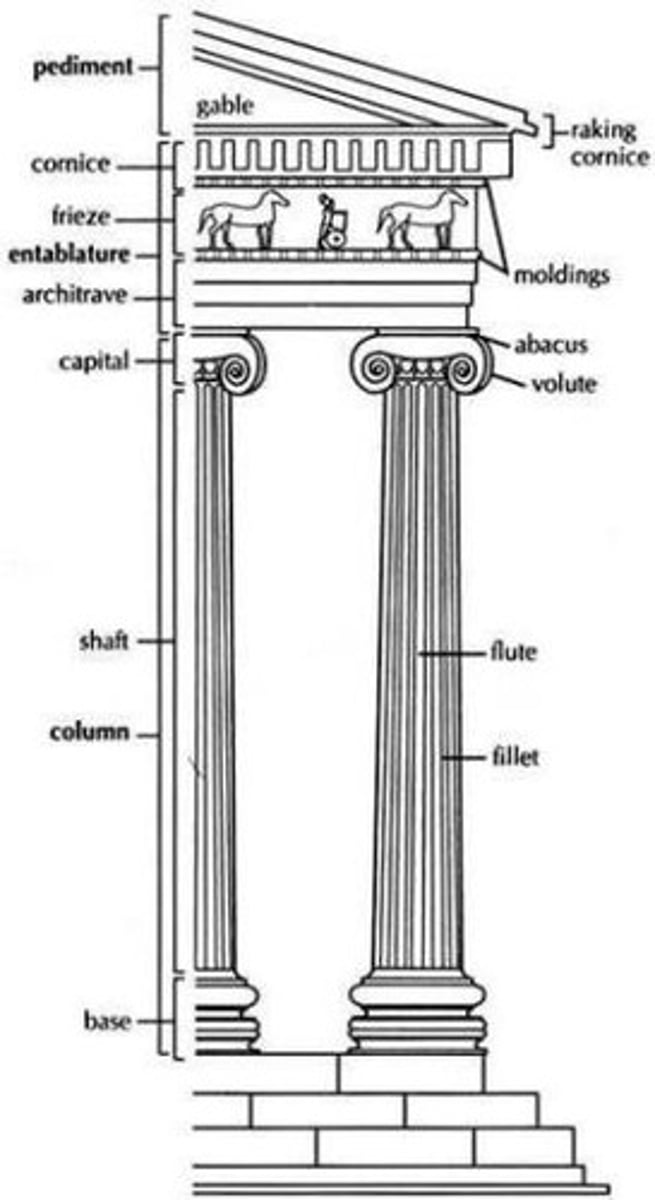
Ionic Order
smaller buildings & interiors
recognizable by capital
perfection of Ionic - Temple of Athena Nike
Corinthian Order
different capital from Ionic (leaves)
found on interiors
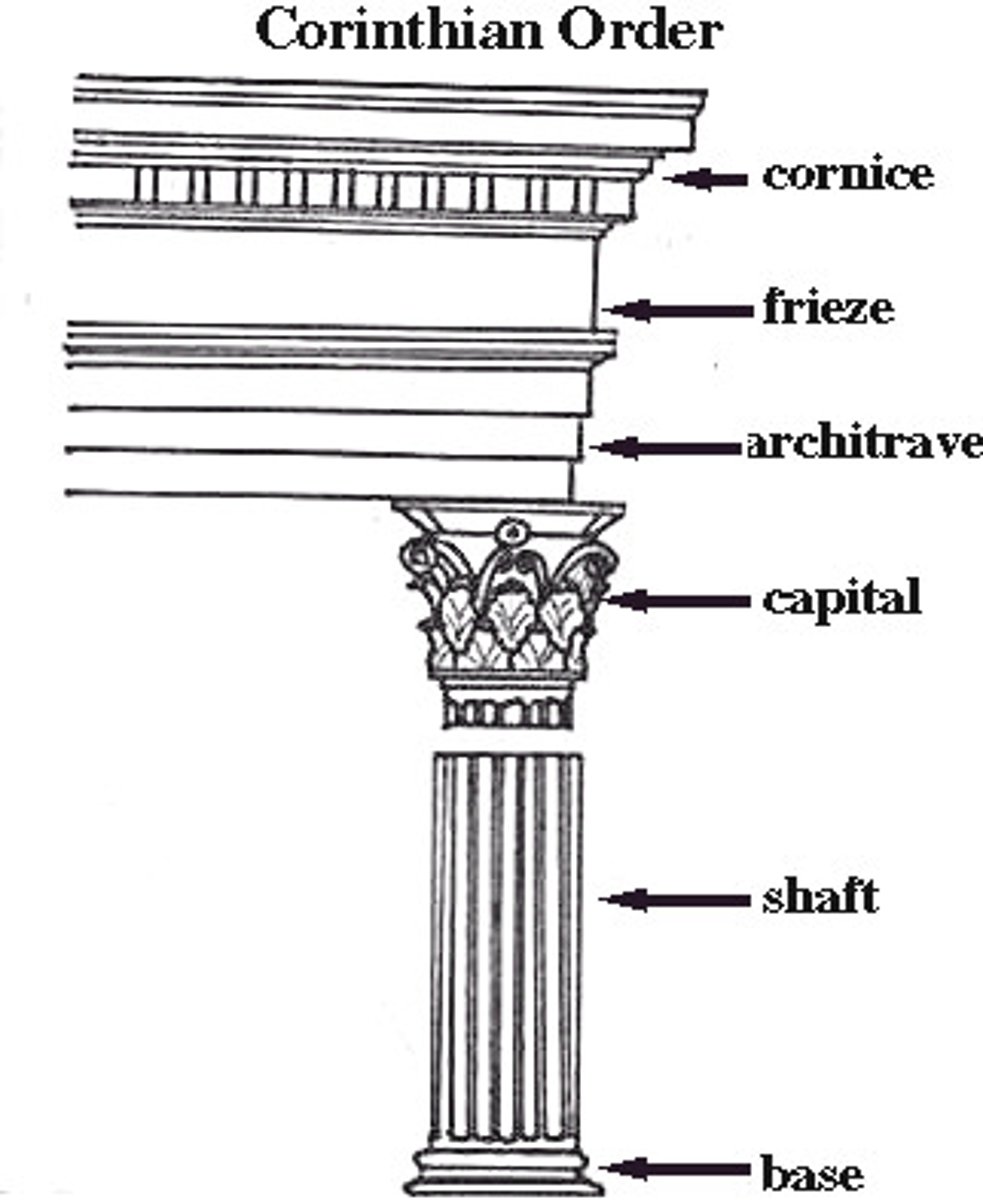
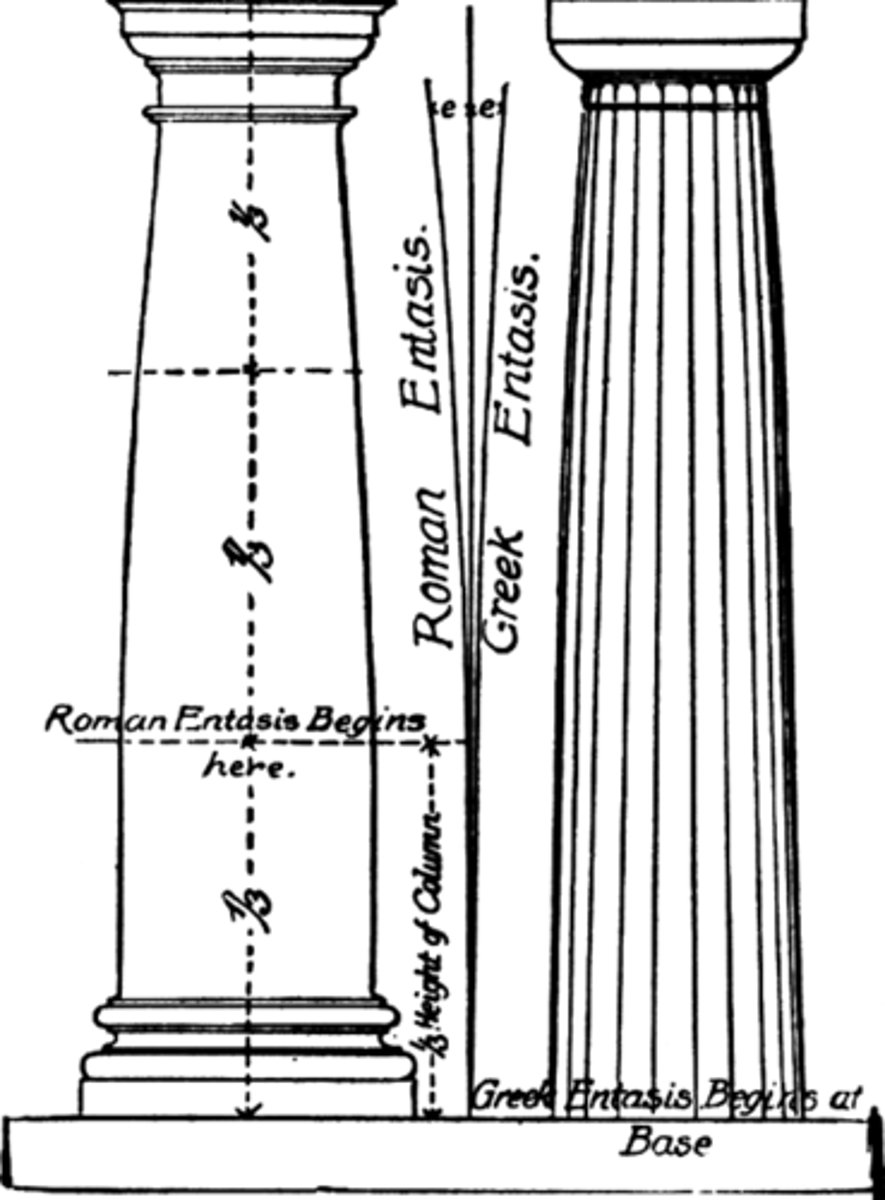
Entasis
slight convex bulge given to a column to offset the optical illusion that it is thinner in the middle
The Acropolis - Athens, Greece; 448-432 BC
Agora - open meeting place or market
Erechtheion (421-407 BC)
Caryatids - sculpted female figure used as a column
Atlas - sculpted male figure used as a column
Tuscan Order
unlike Doric, supports an entablature w/ no decoration (wooden temple w/ pitched roof)
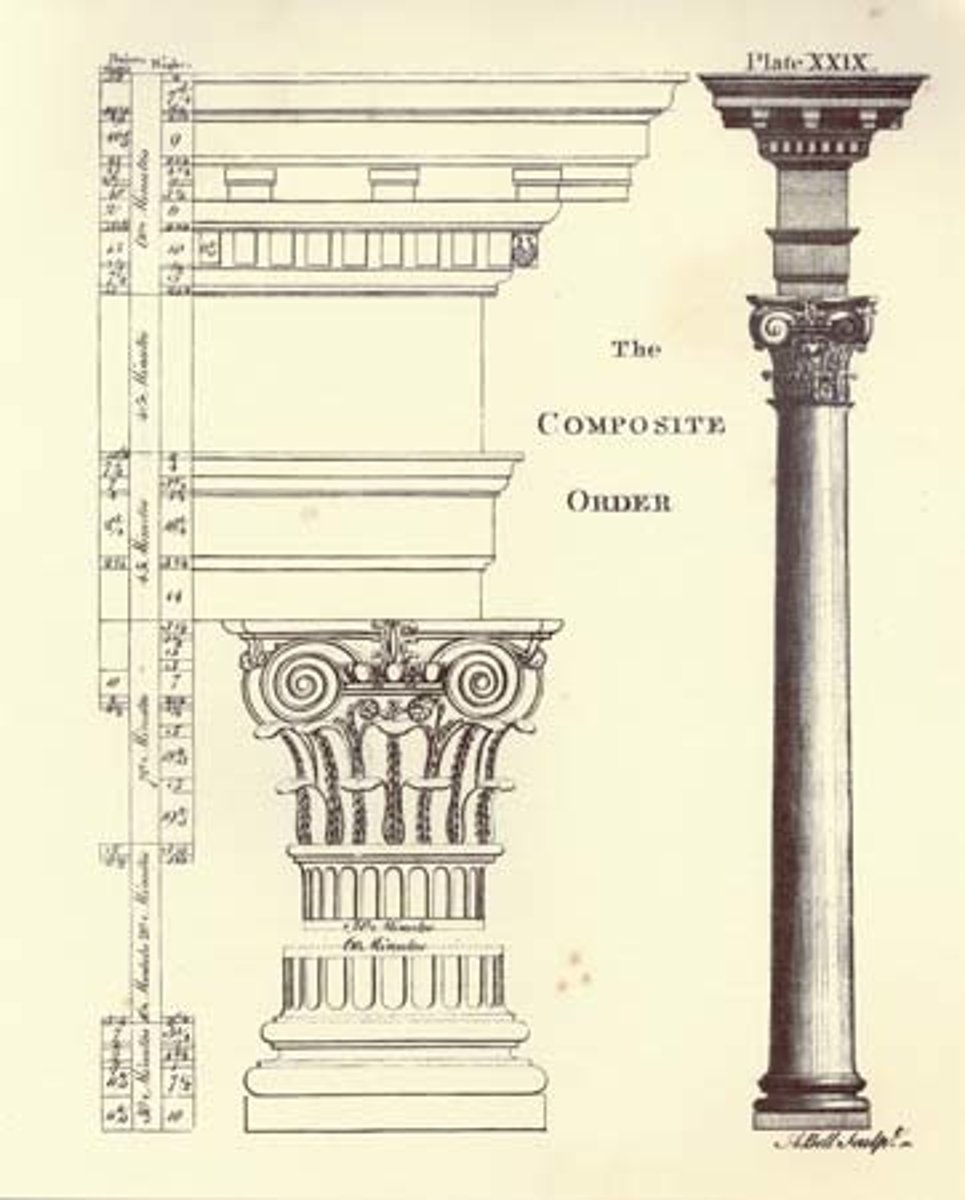
Composite Order
Ionic and Corinthian; roman innovation
Greeks v. Romans
G: objects in landscape (balance harmony refinement of form, not structure), post and beam
R: made space (images in context), the arch, vault, dome, concrete
Barrel Vault
extending an arch along its depth

Groin vault
2 intersecting barrel vaults in 4 directions, used in huge interiors (gyms and baths)

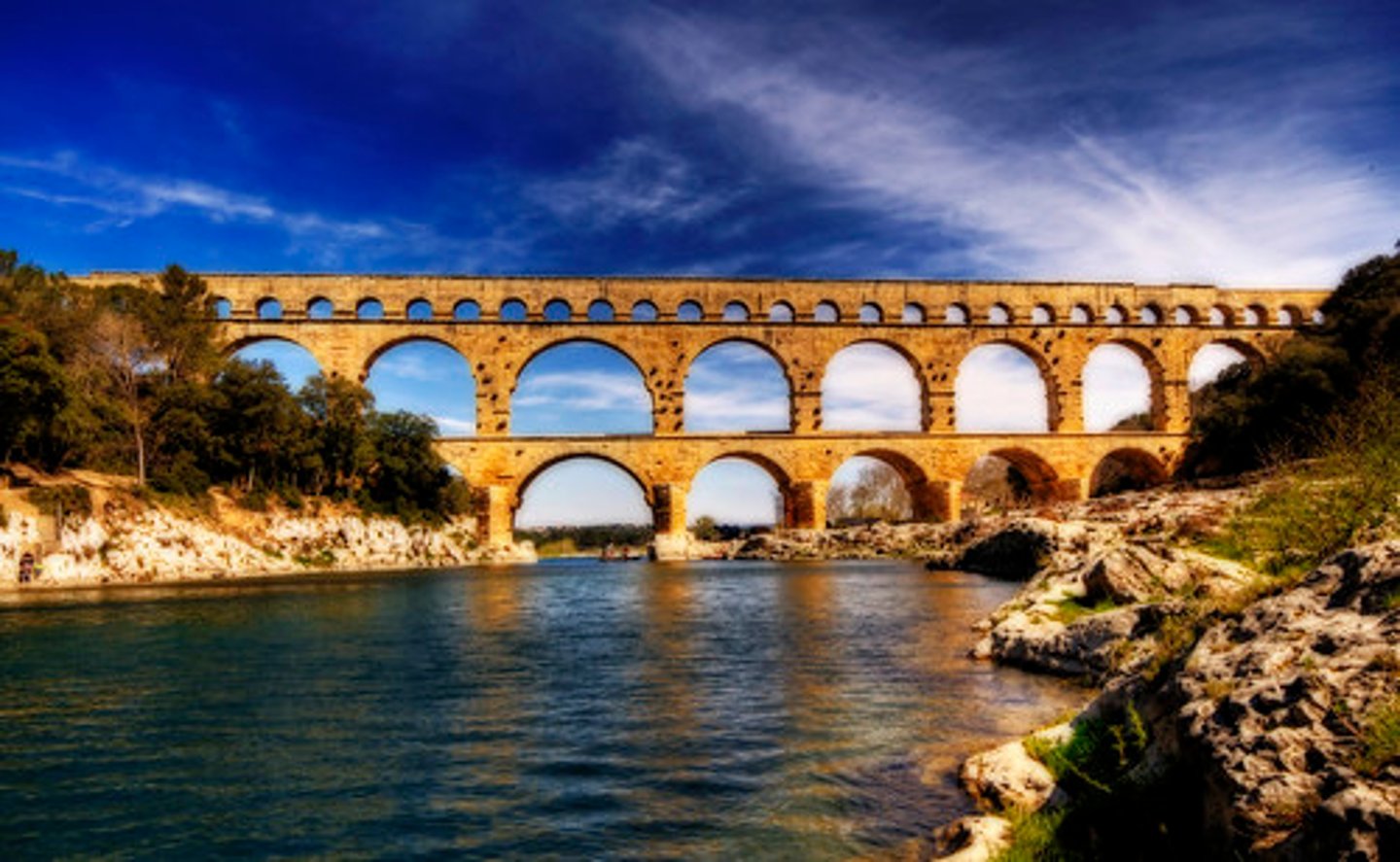
Pont Du Gard
Nimes, France (20-16 BC)

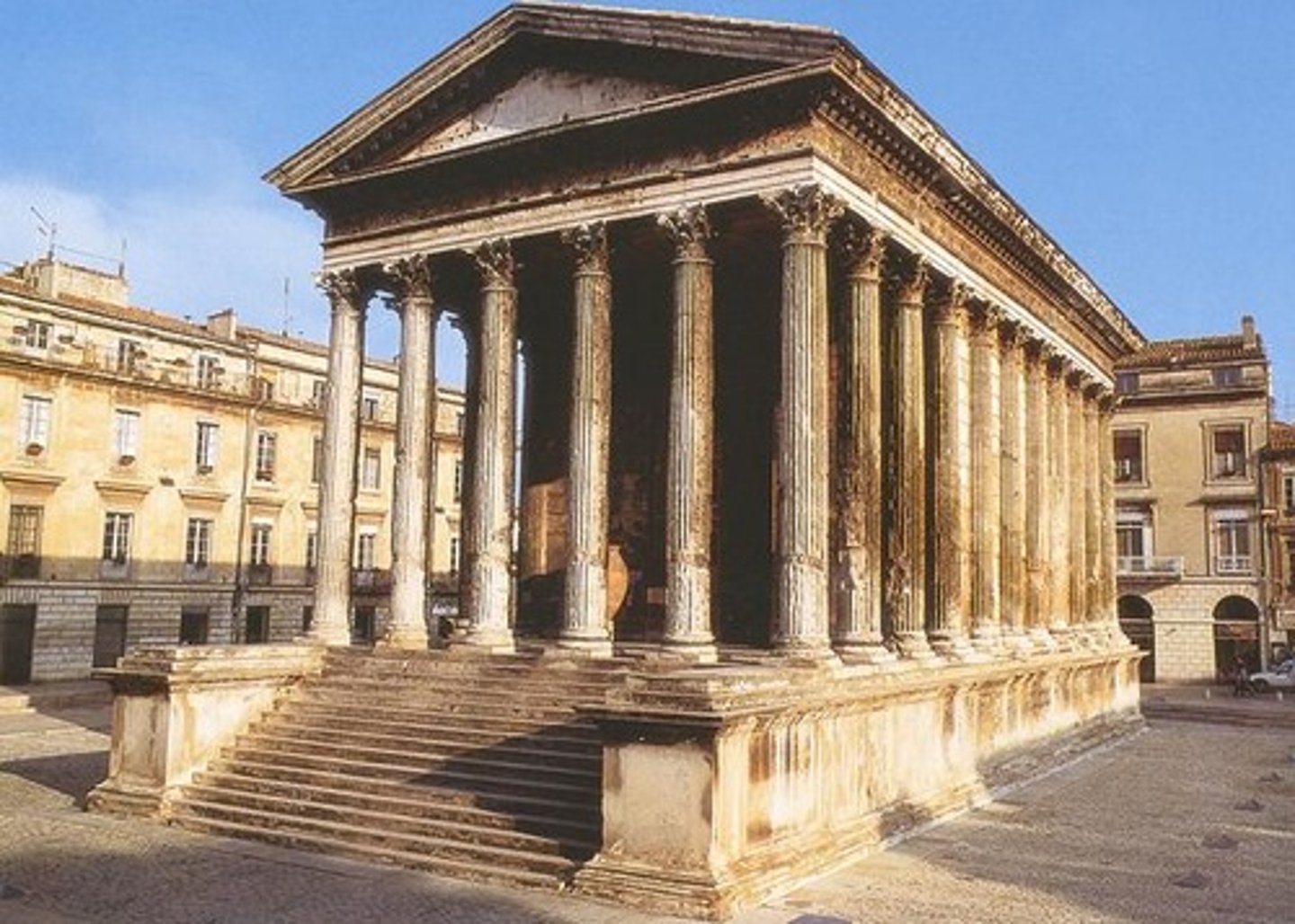
Maison Carree
Nimes, France (10 ACE)

Concrete
volcanic ash, lime ash, sand, water, and gravel
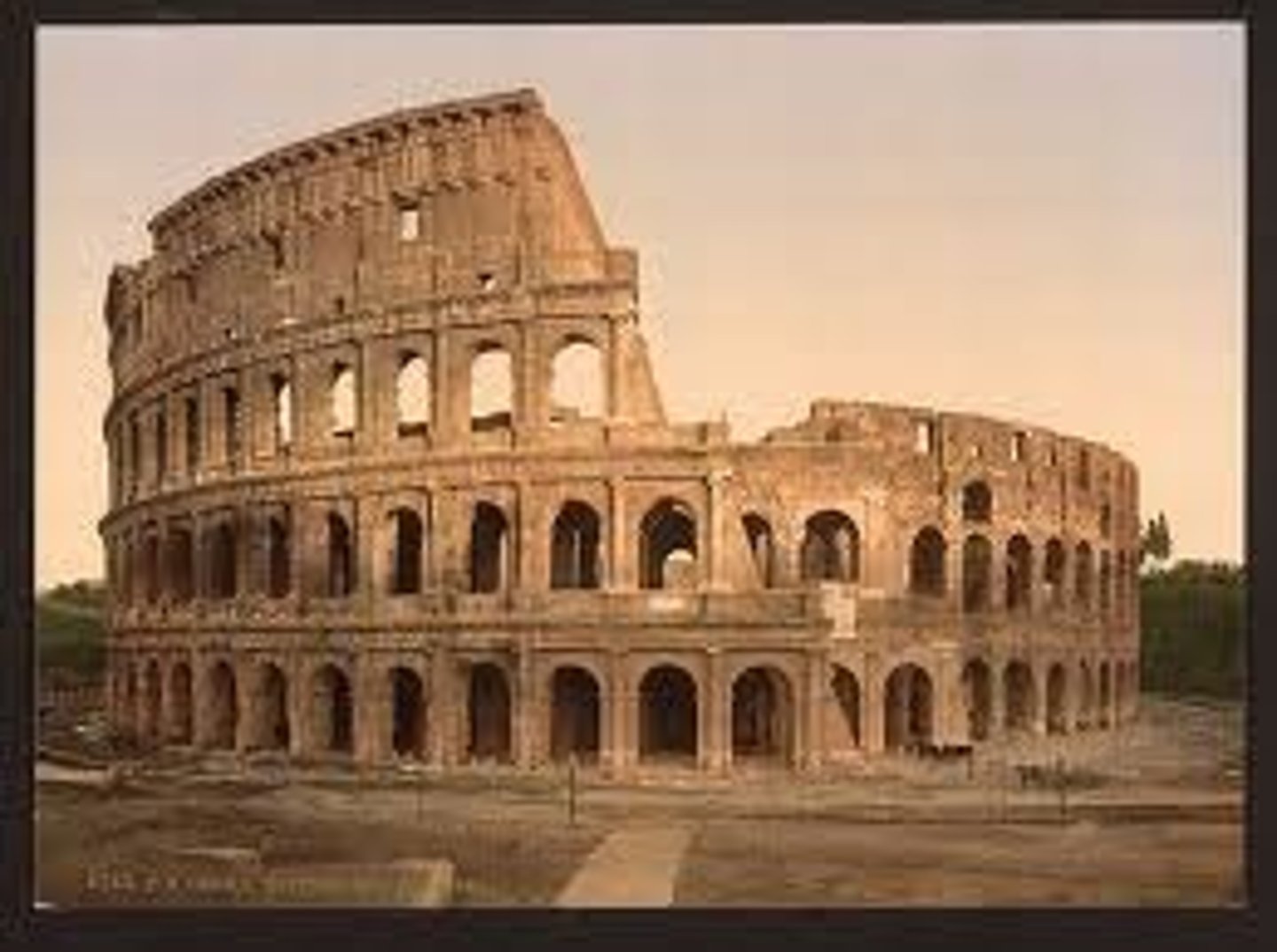
Coliseum in Rome
completed around 80 ACE, seats 50k, orders differ by levels

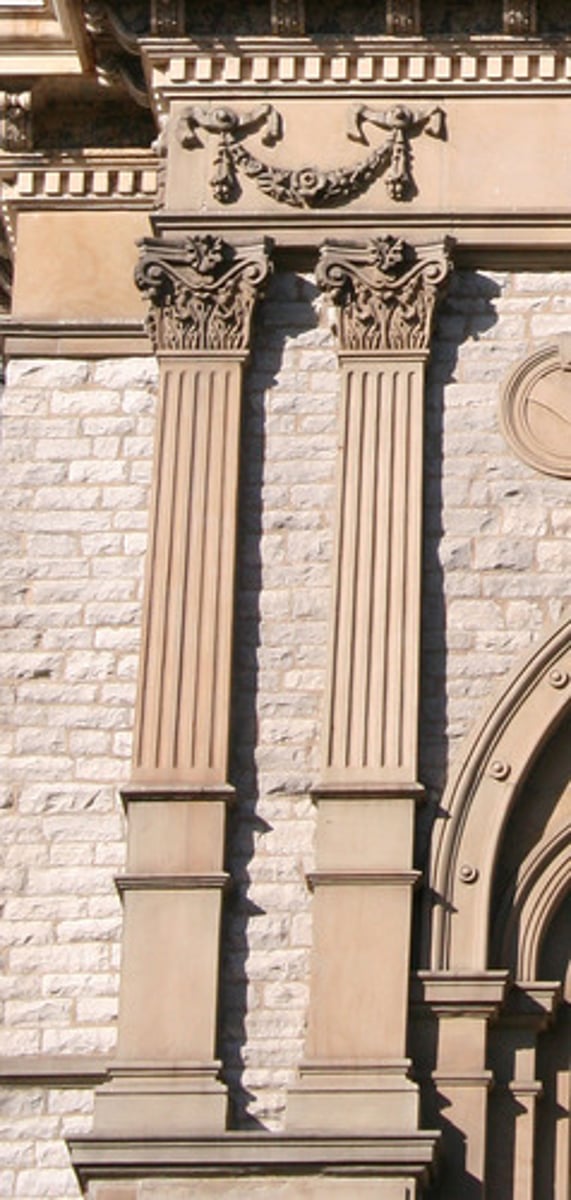
Pilaster
column in wall

Circus Maximus
seated 250k; precursor to NASCAR

Pantheon (125 CE)
double pediment, oculus, built under Hadrian (117-138 ACE)
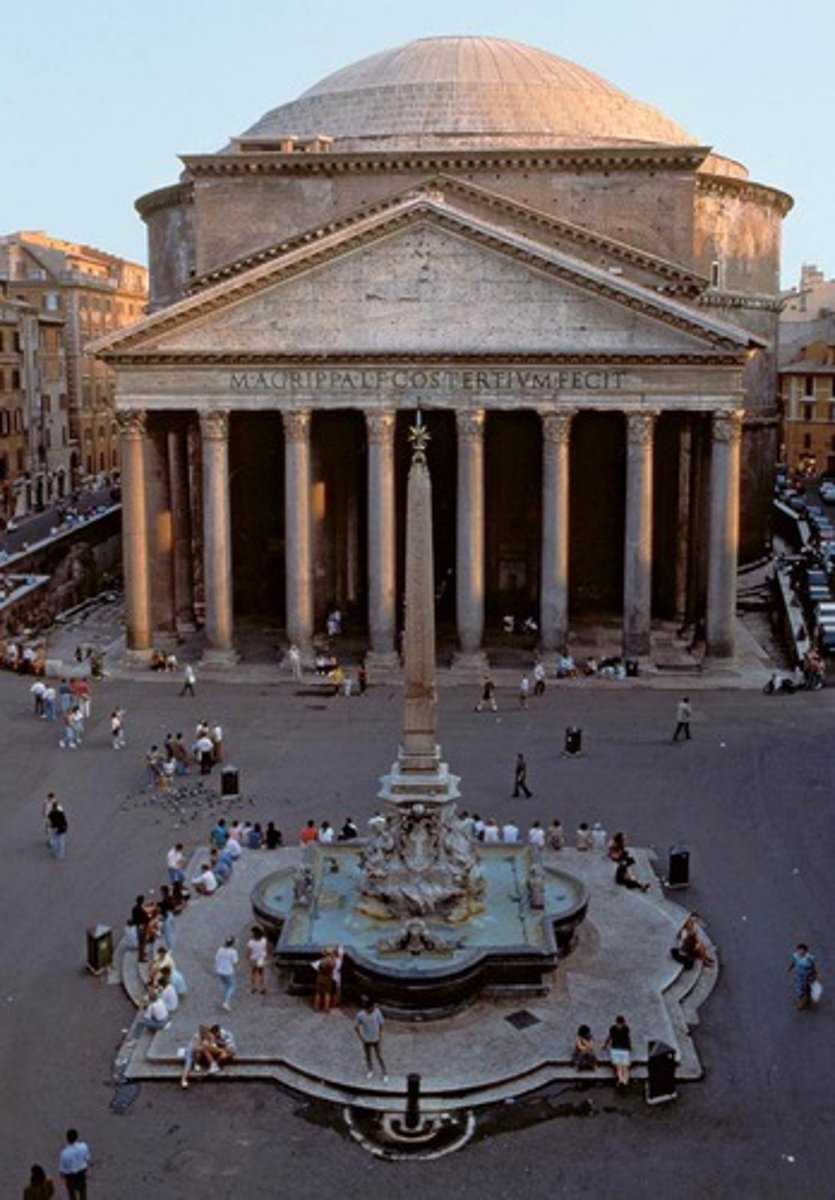

Pediment
triangle shape over colonnade
Portico
a colonnade space forming an entrance or vestibule
Constantine I (306-337 ACE)
Edict of Milan (313) - proclaimed tolerance of all religions which gave Christians authority to build churches
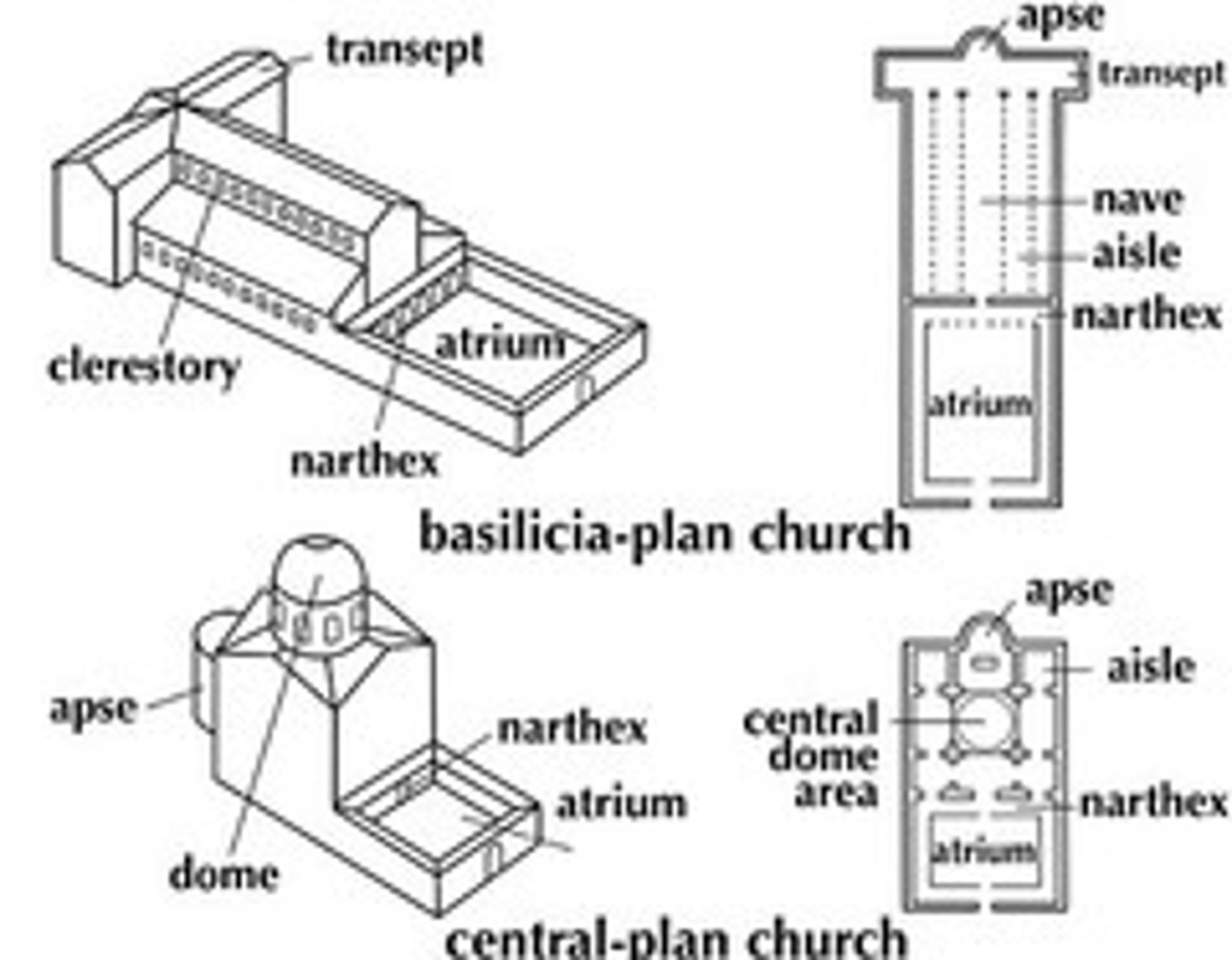
Early Christian Churches
Basilica Plan
Pendentives
curved triangular panels which hold the load of a dome
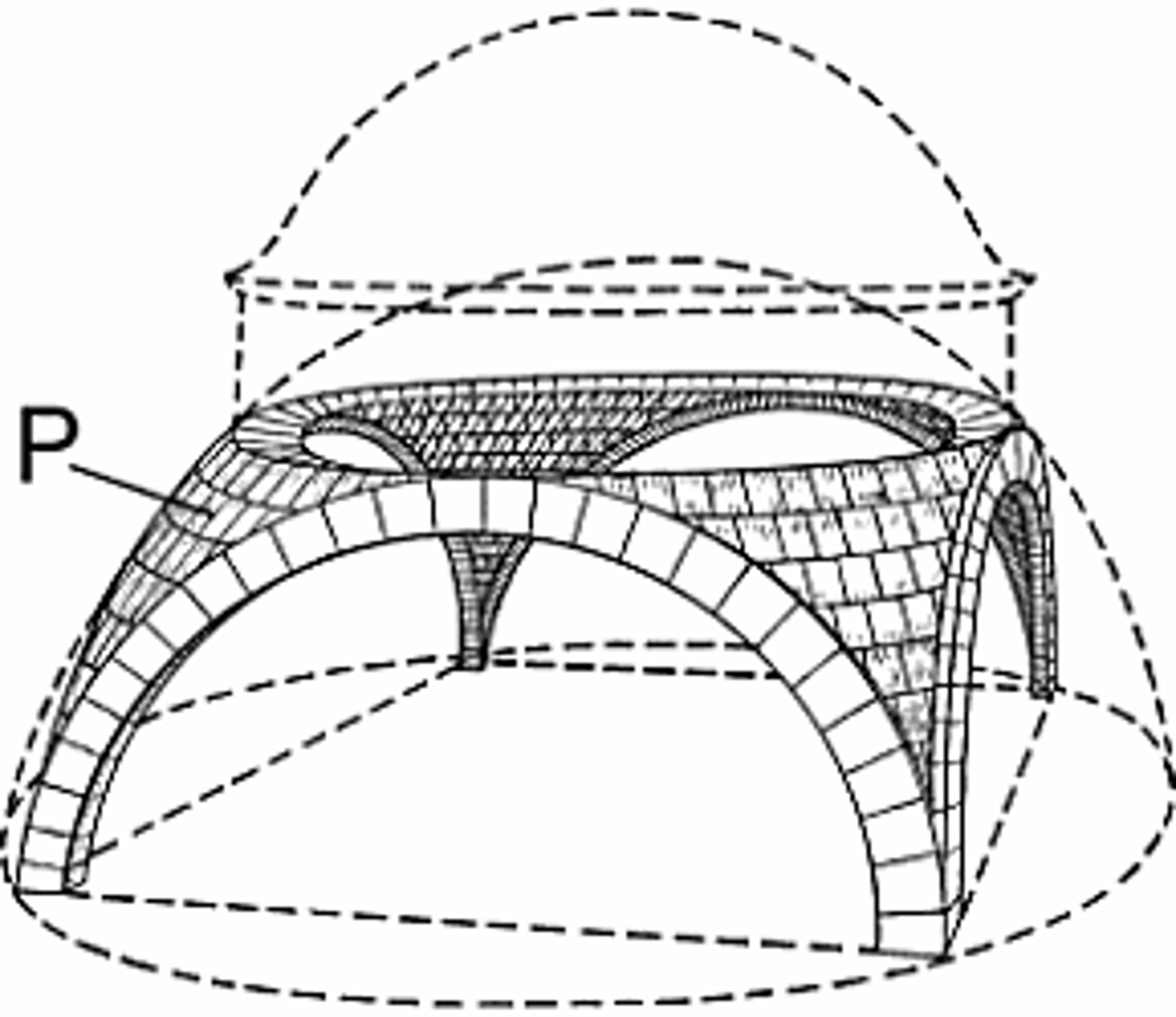
Hagia Sophia
built by Justine
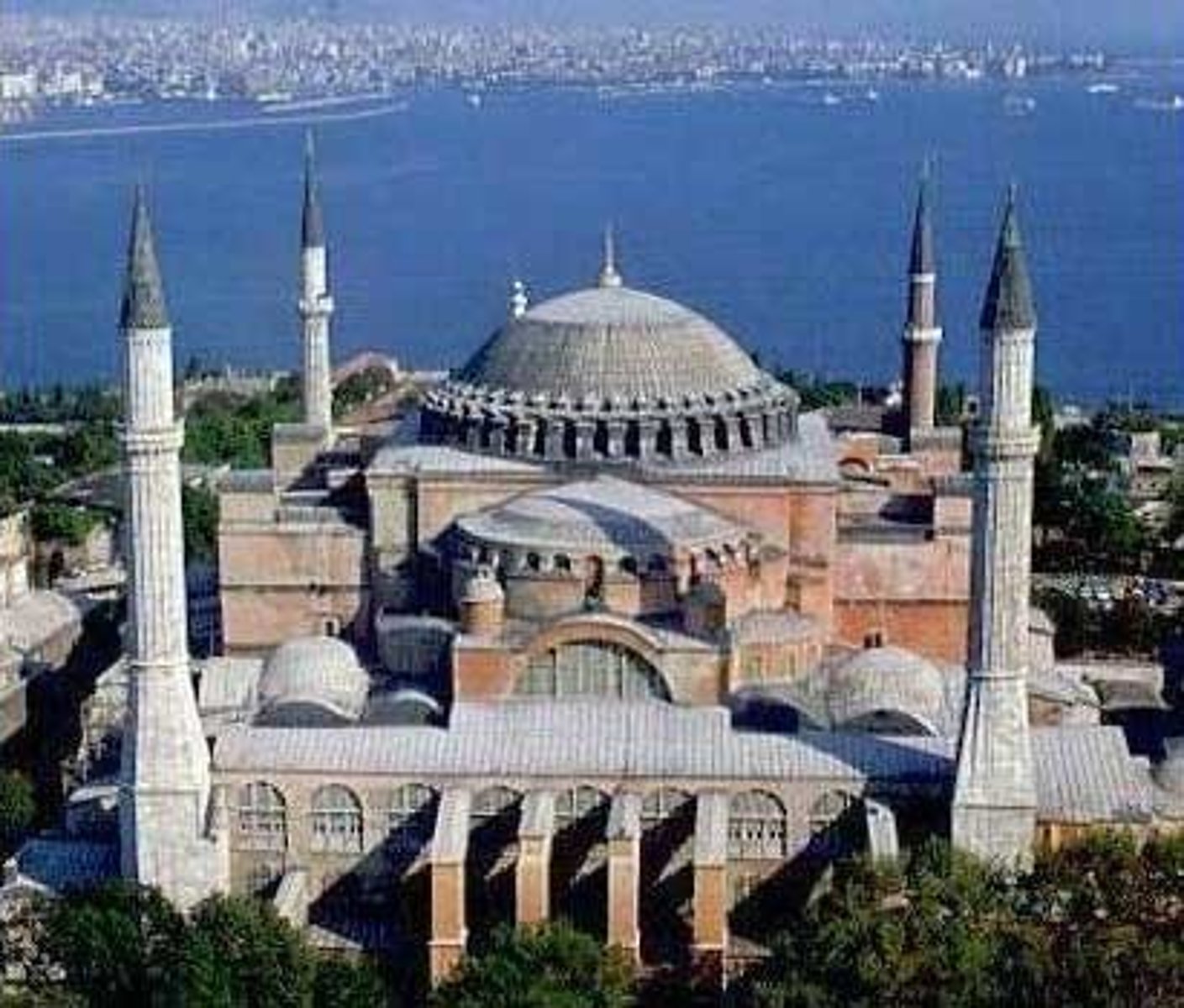

Byzantium
new Roman capital
changed to Constantinople (Constantine I)
now Istanbul, Turkey
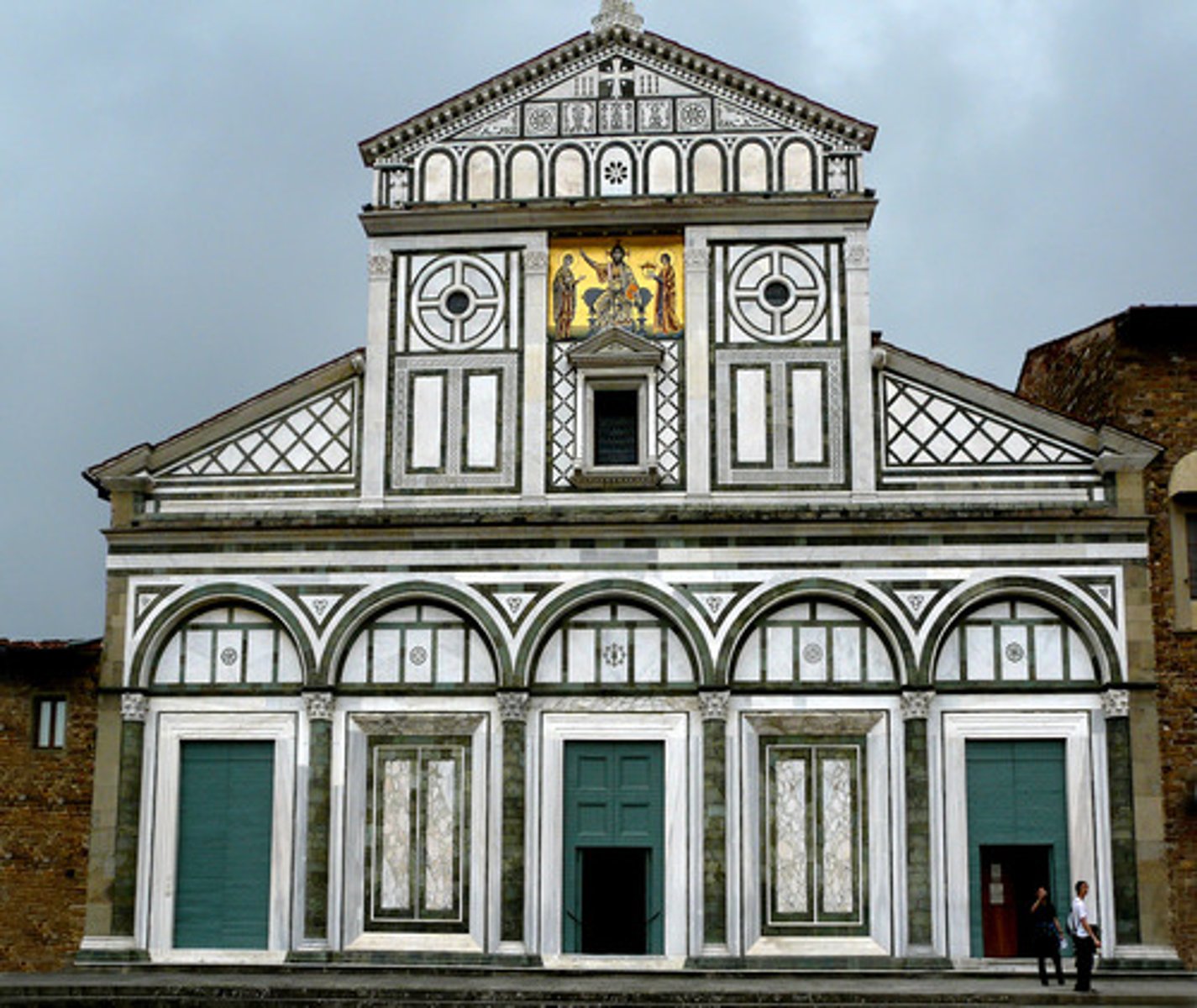
St. Miniato al Monte
Florence, Italy (1062-90)

Pisa Cathedral & Campanile
Pisa, Italy 1063, 1089-1272

Gothic Architecture
structure is also ornament (like Greeks)
not thick walls; use buttresses @ 90 degree to take collected pressures of ribbed vault and arch
Ribbed Groin Vault
groin vault + pointed arch
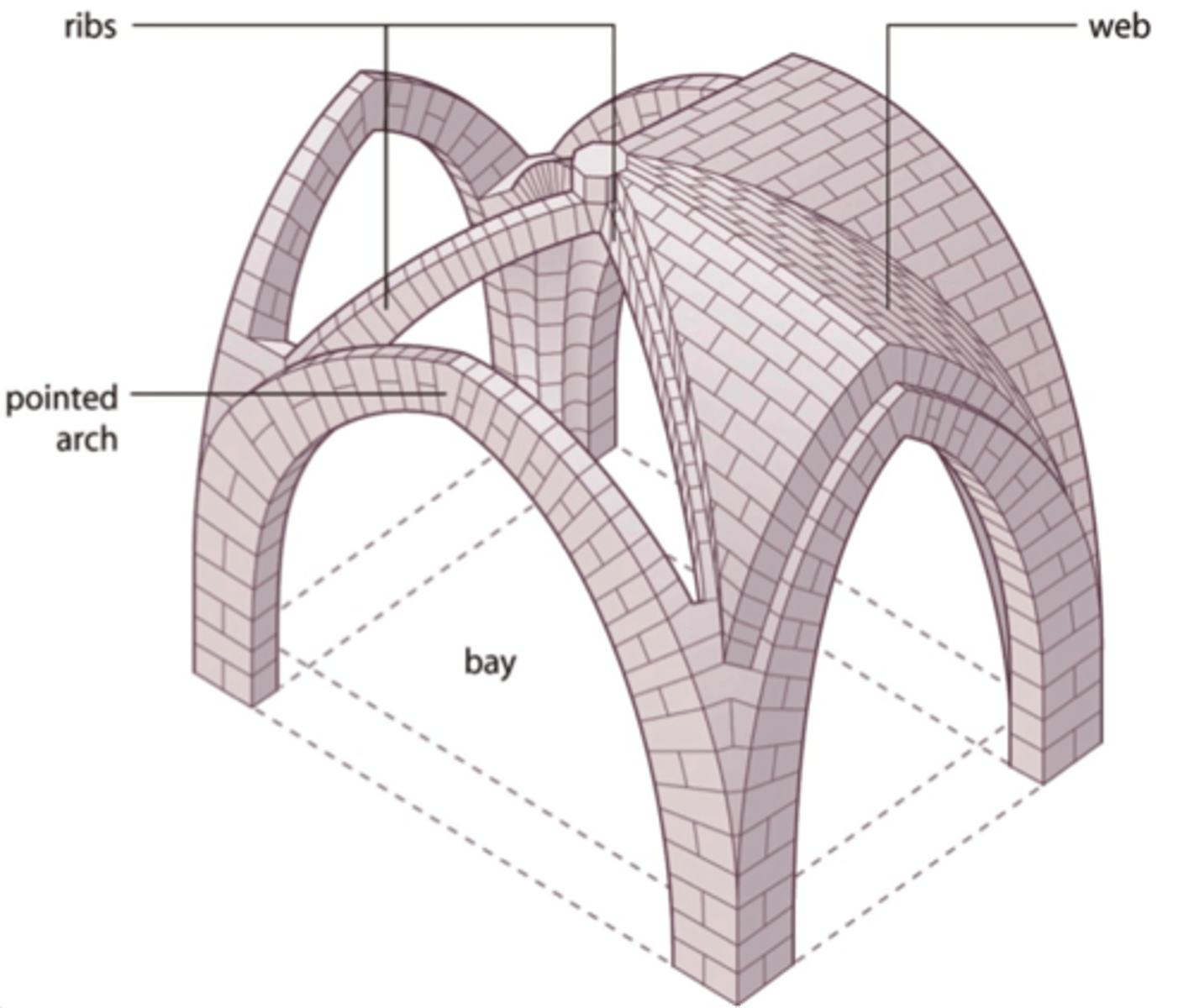
Pointed Arch
signals gothic architecture/style
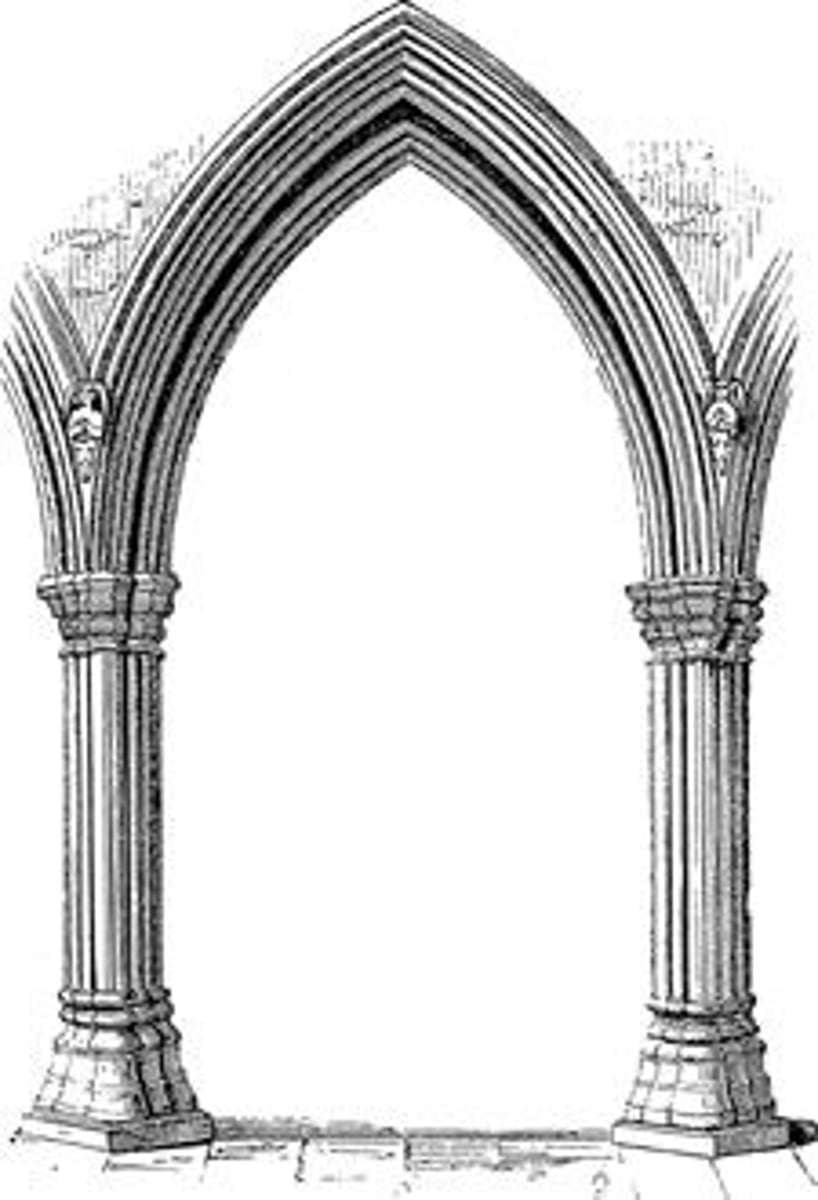

Buttresses & Pinnacles
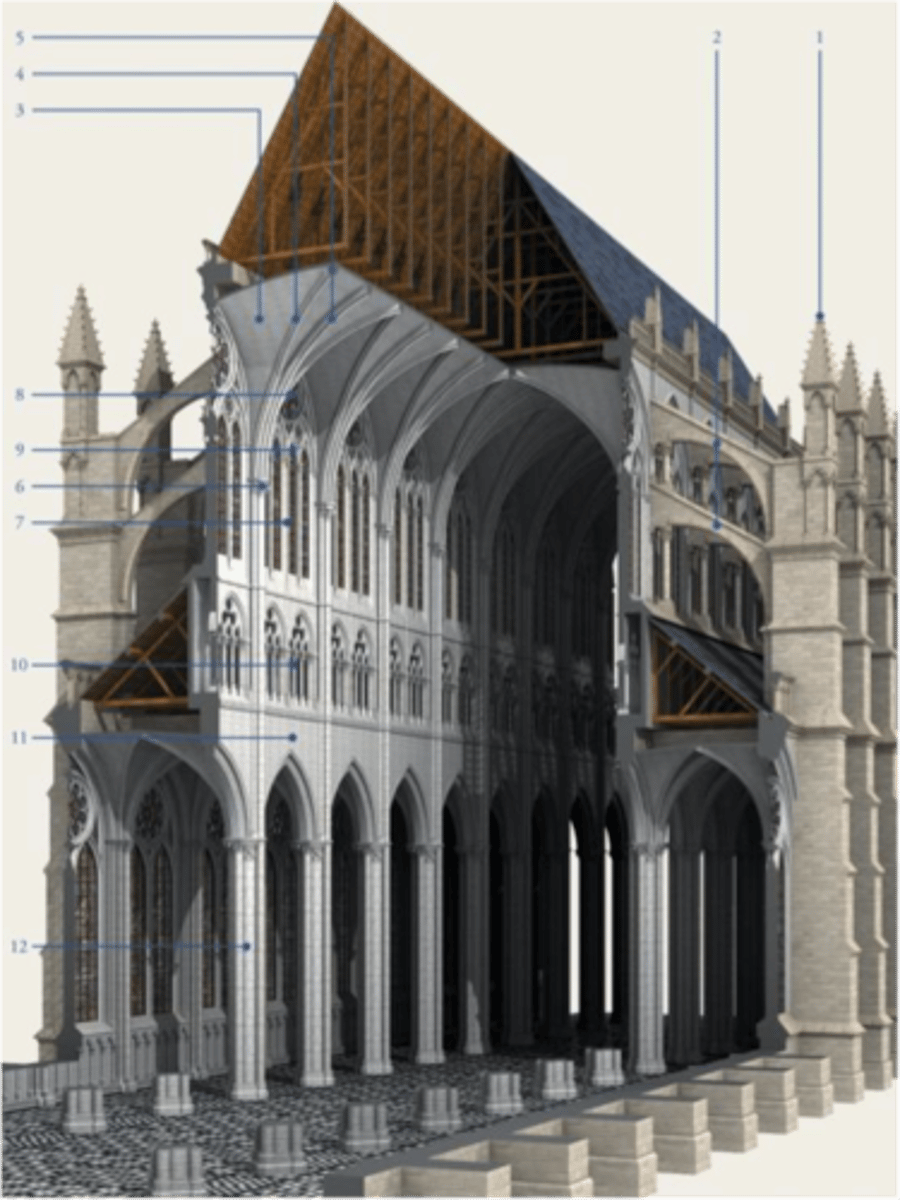

How does English gothic architecture differ from French gothic architecture?
English is more rectangular (churches)
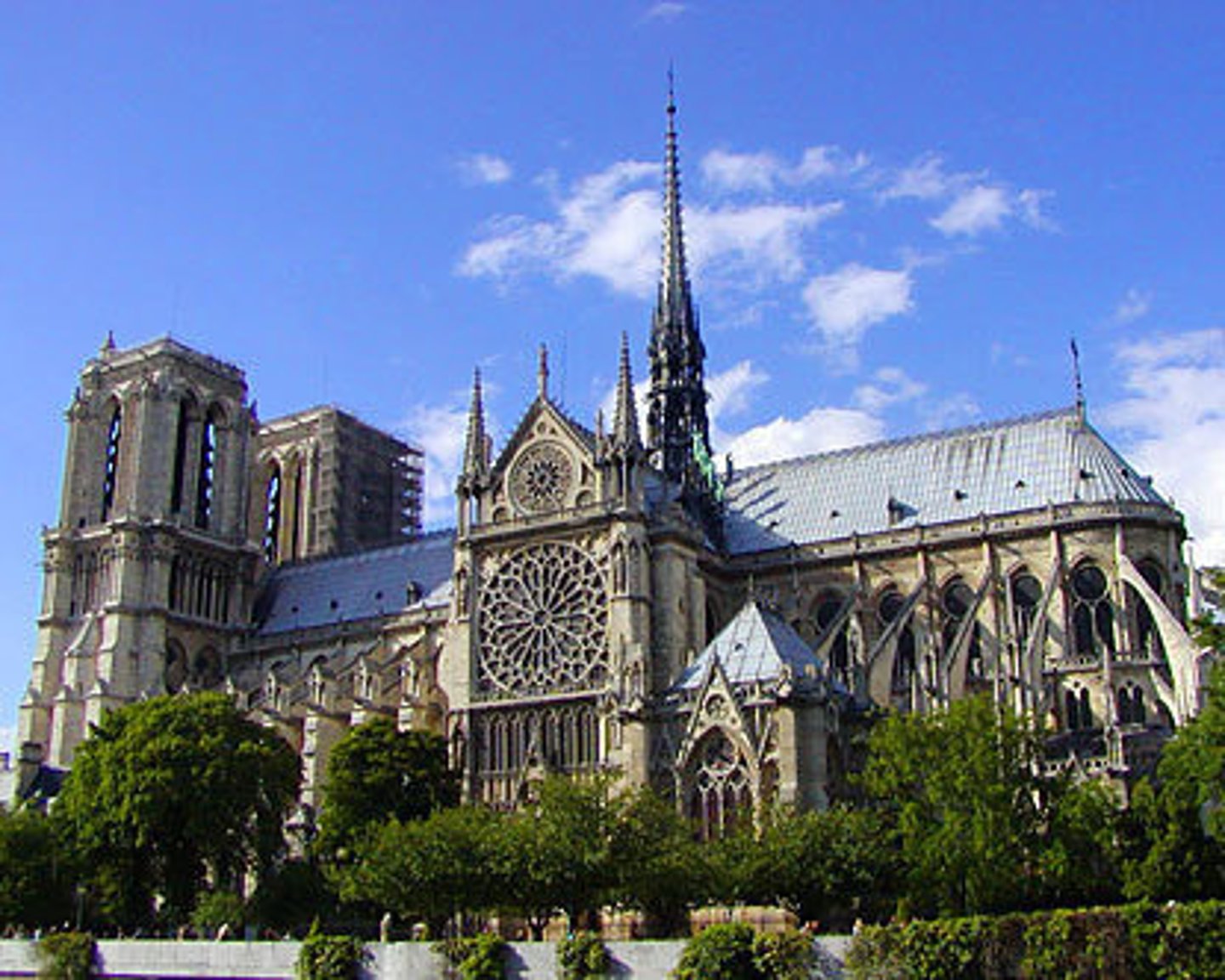
Notre Dame de Paris (1163-1250)

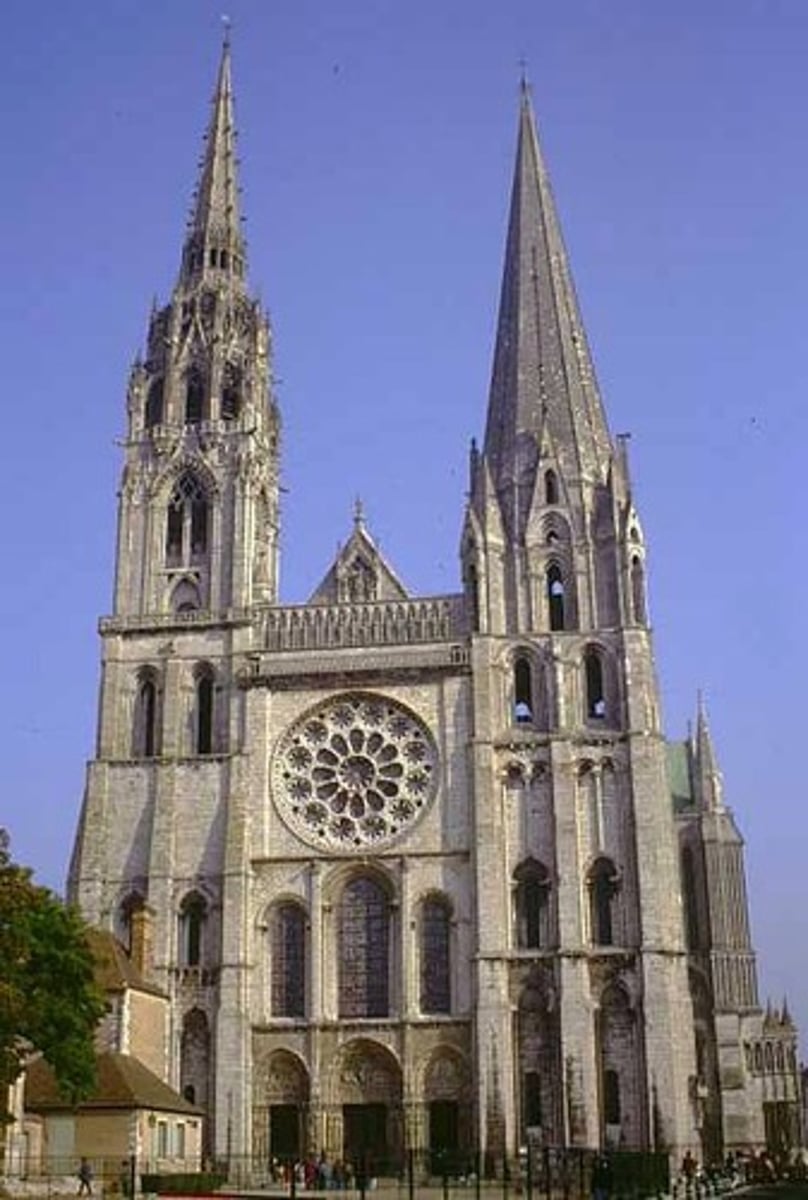
Chartres Cathedral (1130-1260)

Apse
semi circular projection, containing an altar
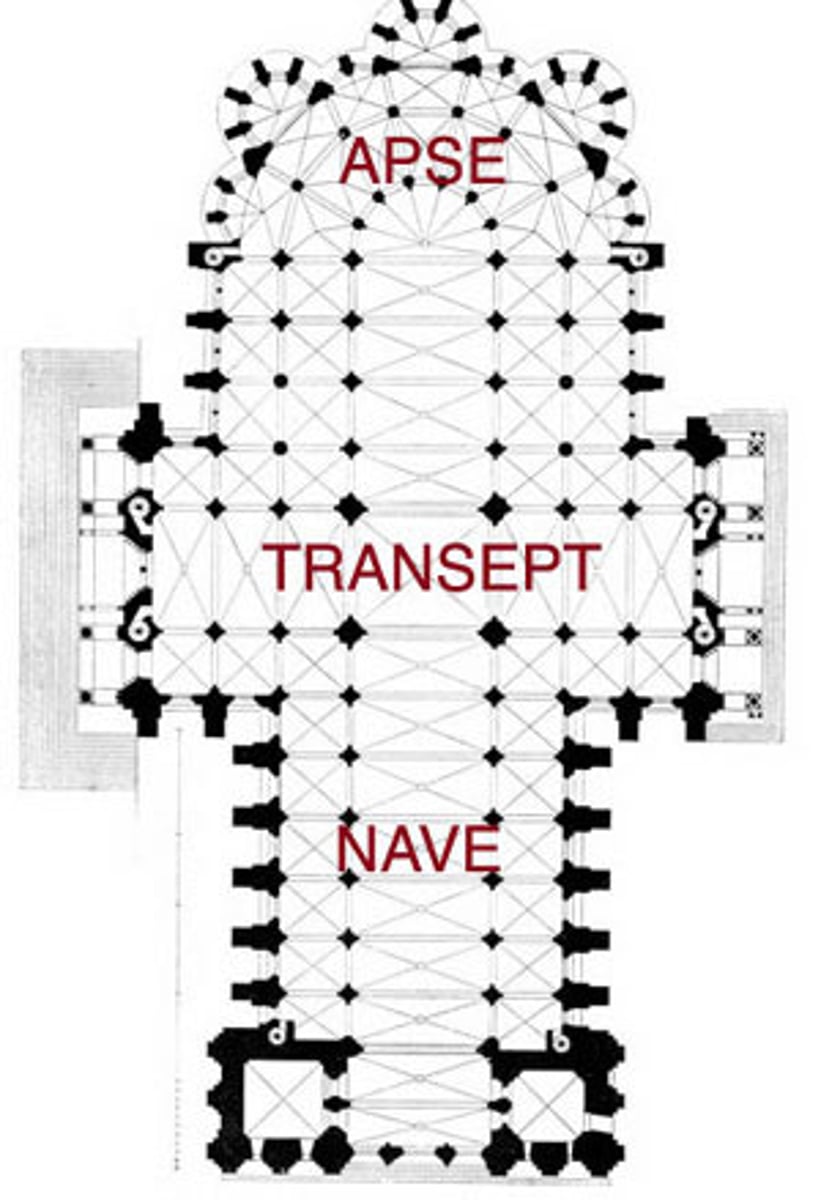
Transept
2 arms in a "Latin cross" plan
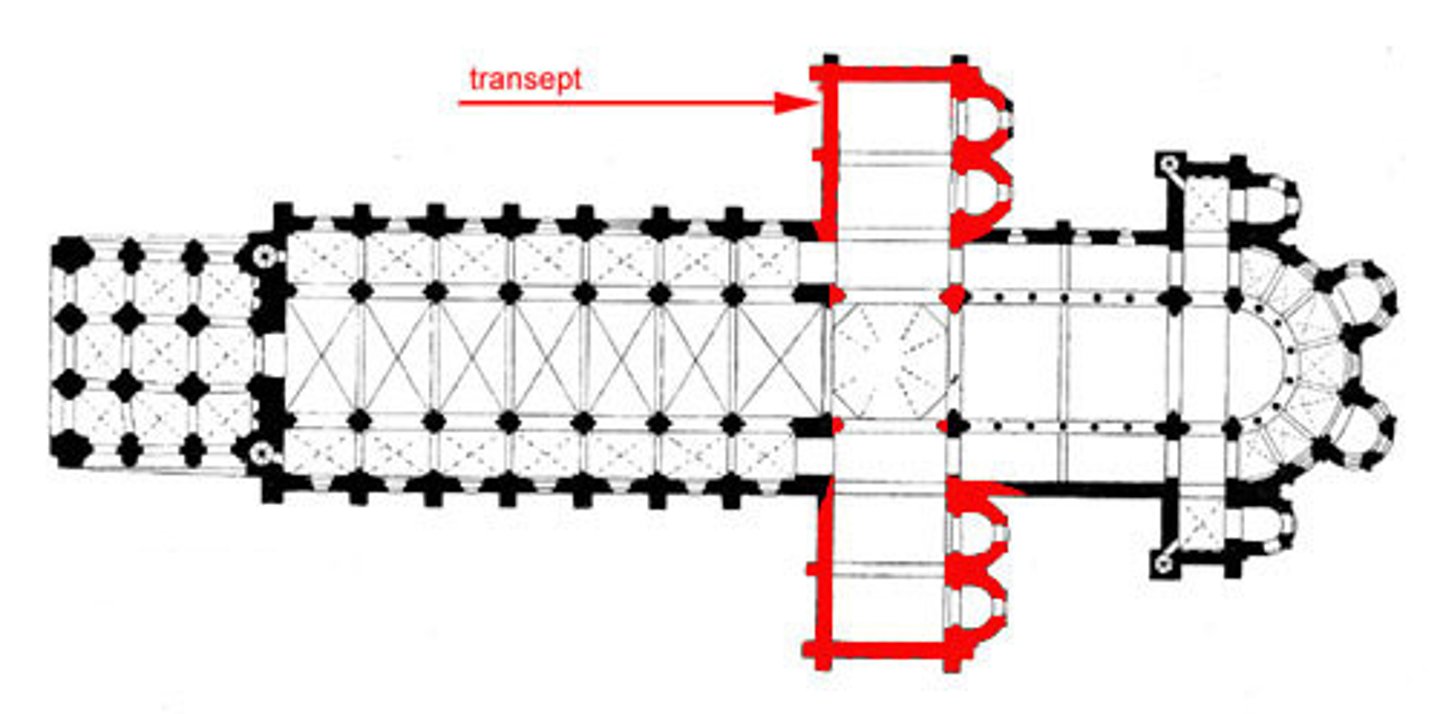
Nave
space beyond transept crossing toward west/"front" of church
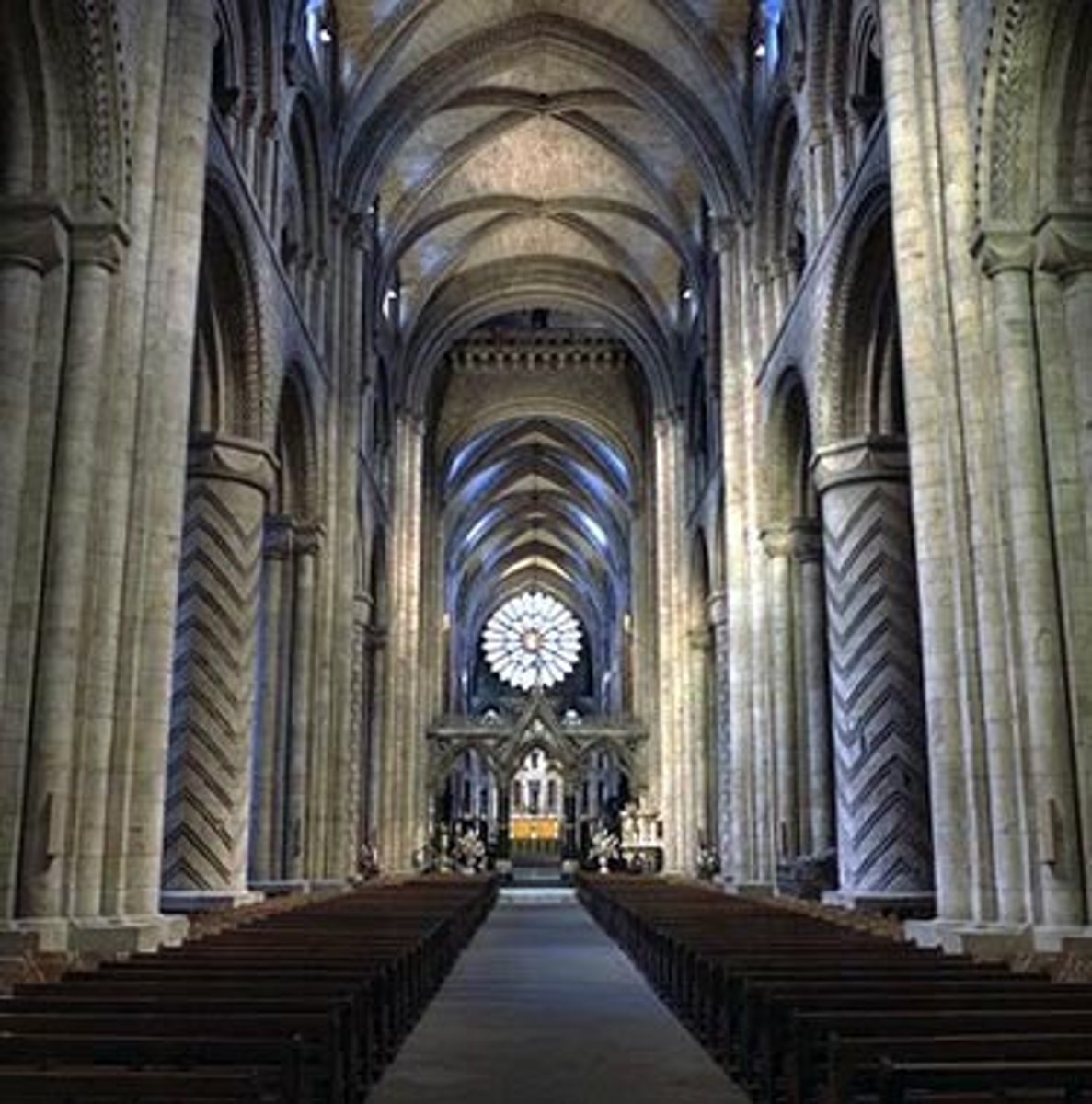

Choir
where monks sit

Structural Failure of Twin Towers
1. The Planes crashes into the buildings, damaging or destroying many outer columns. Some interior columns are also damaged, but the building still stands
2. Fire erupts instantly and is spread by jet fuel down the core
3. Temperature reach as high as 1600 F, weakening steel columns until they can no longer support the building weight. Interior columns essentially melt and collapse, buckling the exterior columns.
4. Added weight of each collapsed floor causes a pancaking effect- called progressive collapse- and the building came down.
Freedom Tower
memorial for twin towers

What are dead loads on a building?
forces from all the "immovable" elements of a building (weight of building materials, walls, floors, builtins, etc)
What are live loads on a building?
forces from all the "moveable" elements of a building (people, equipment, furniture, etc)
Where would be somewhere that has a great amount of live loads?
the library
What is the force of Compression?
the capacity to resist being pushed together
What is the force of Tension?
the capacity to resist pulling apart
What is post and beam trabeated?
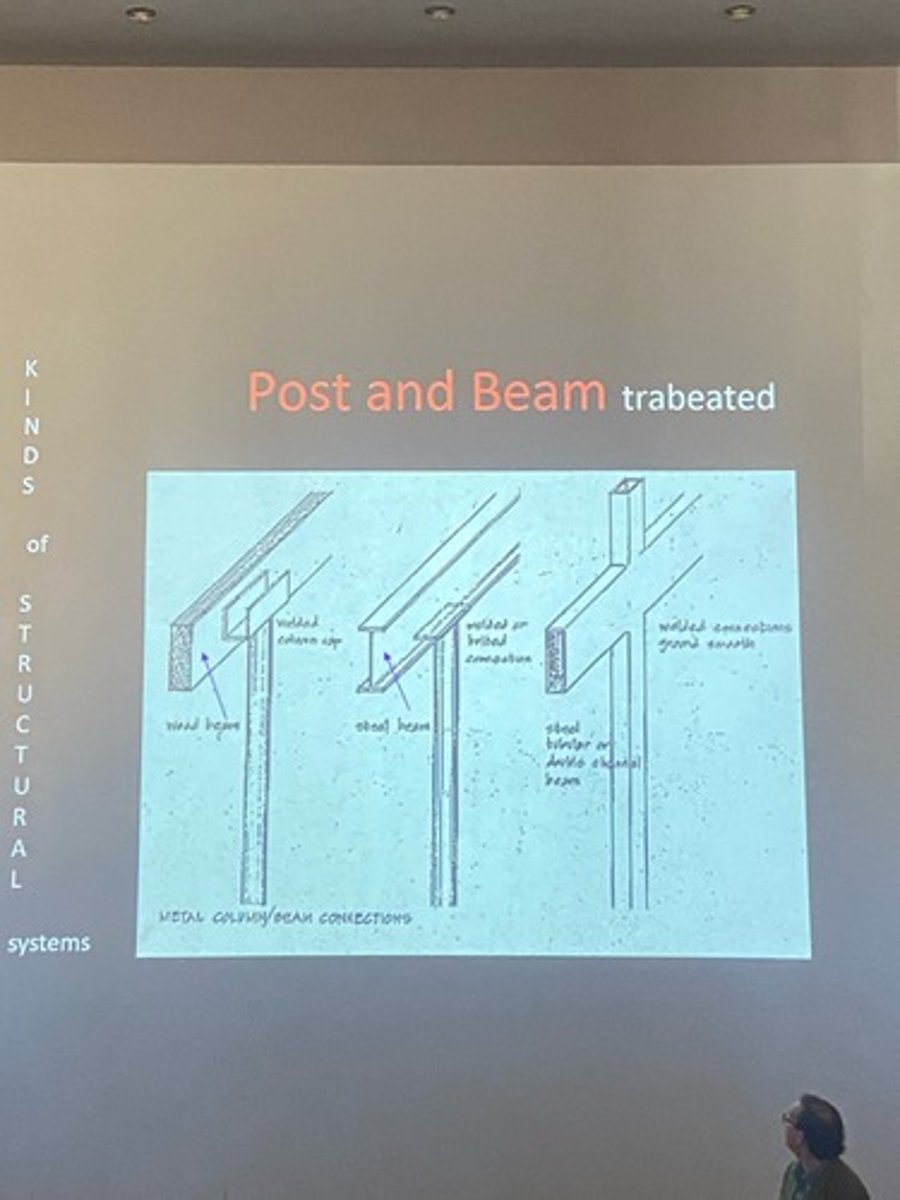
What are Frame Structures?
trabeated; wood or steel, lightweight, thin walls, tall buildings
What are Masonry structures?
arcaded; brick or concrete or stone, heavy, thick walls, costly, good insolation
What are things that are not used to make enclosures, but to mark location from great distances?
Menhirs, Dolmen, Henges, and cromlech
Menhirs
single stone standing upright
Dolmen
several stones supporting a stone slab
Henges
circular ditches around which some megalithic monuments are arranged
Cromlech
circle of stones
Dolmen Examples
several upright stones supporting a horizontal stone slab

Stonehenge
most famous Neolithic monuments; built 3000-2100 B.C.

Trabeation
post and beam structure
Remarkable joinery
mortise and tenon
The tree types of pyramids
Step Pyramid
Bent Pyramid
Straight-sided Pyramid
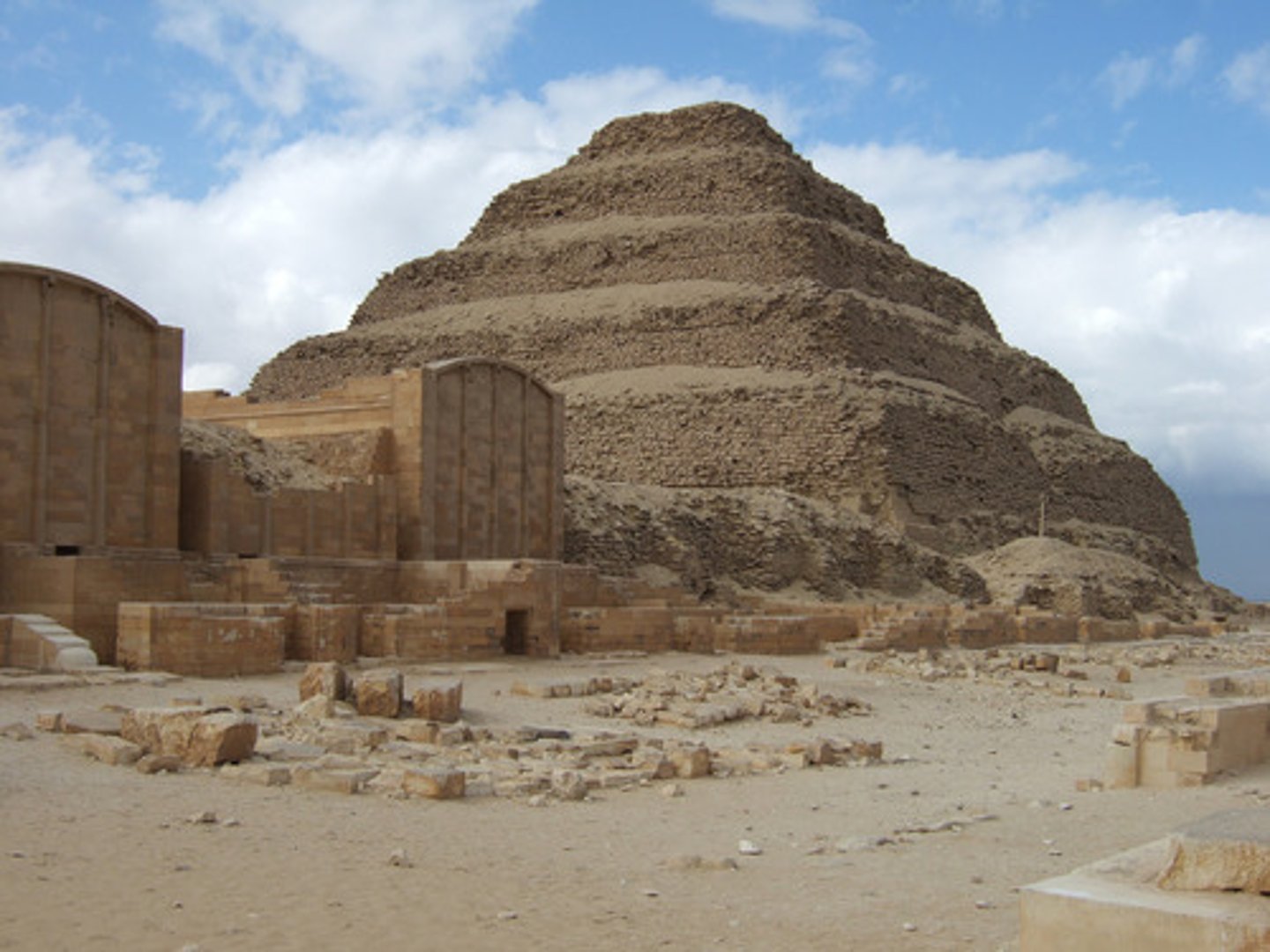
Step Pyramid
Saqqara: Doser's step pyramid

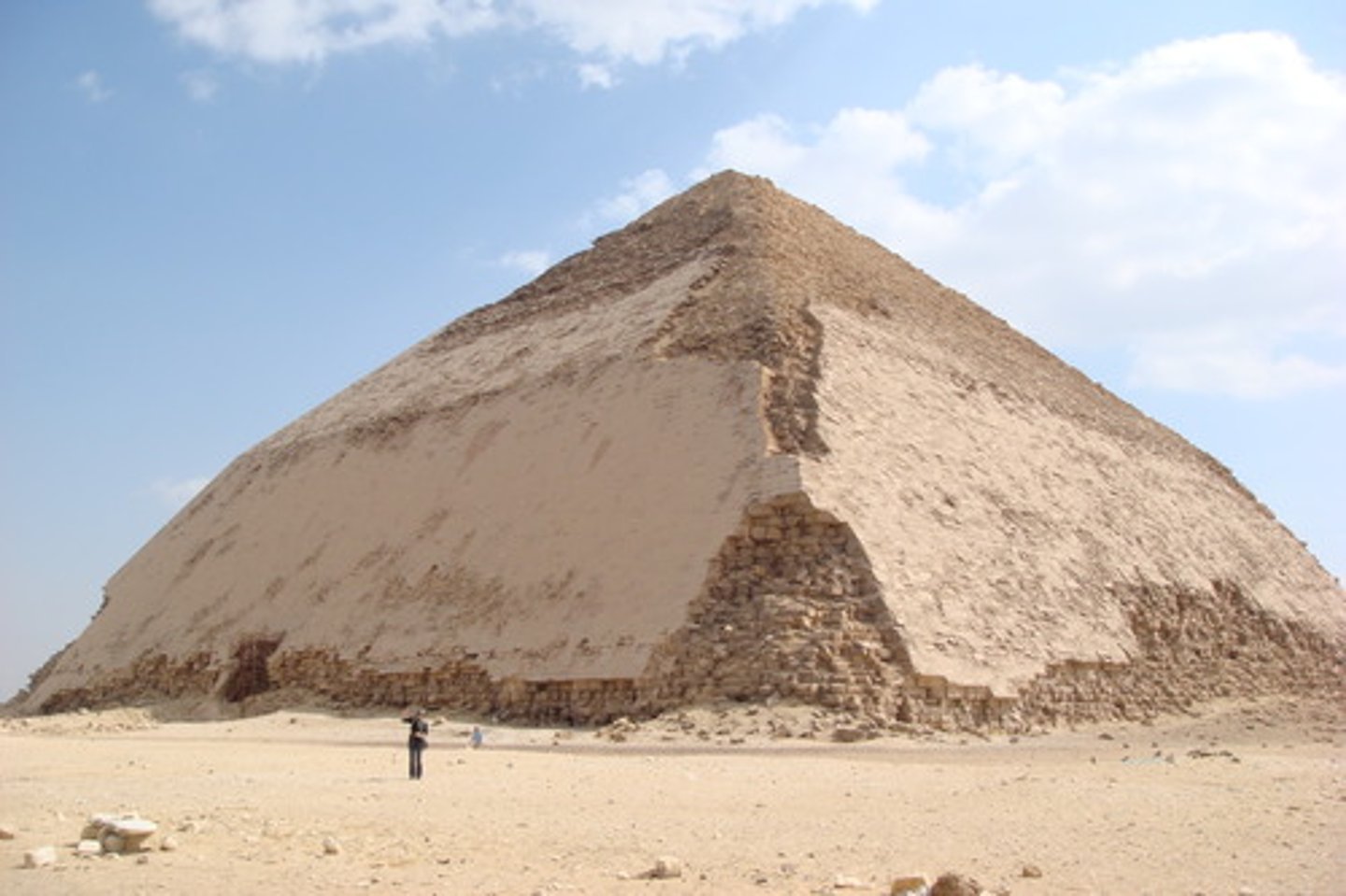
Bent Pyramid
Sneferu's South Pyramid, Dahshur, Egypt

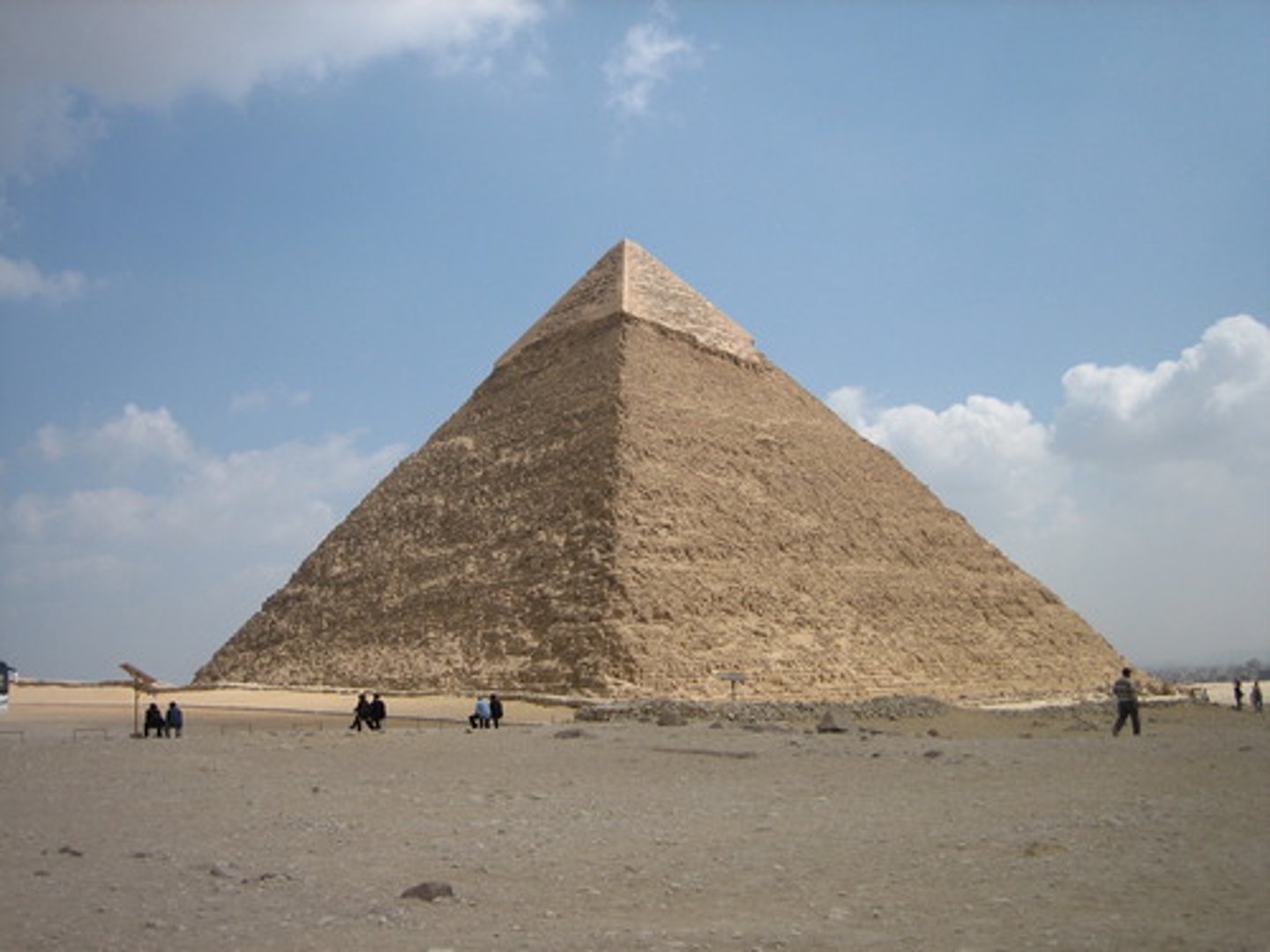
Straight Sided Pyramid
Cheop's Pyramid, Giza, Egypt

Ziggurats
stepped pyramids
Some of the oldest pyramids; 2125 BC
Built from mud bricks

What are the seven wonders of the ancient world?
Great Pyramids of Giza
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Temple of Artemis at Ephesus
Statue of Zeus
Colossus of Rhodes
Lighthouse of Alexandria
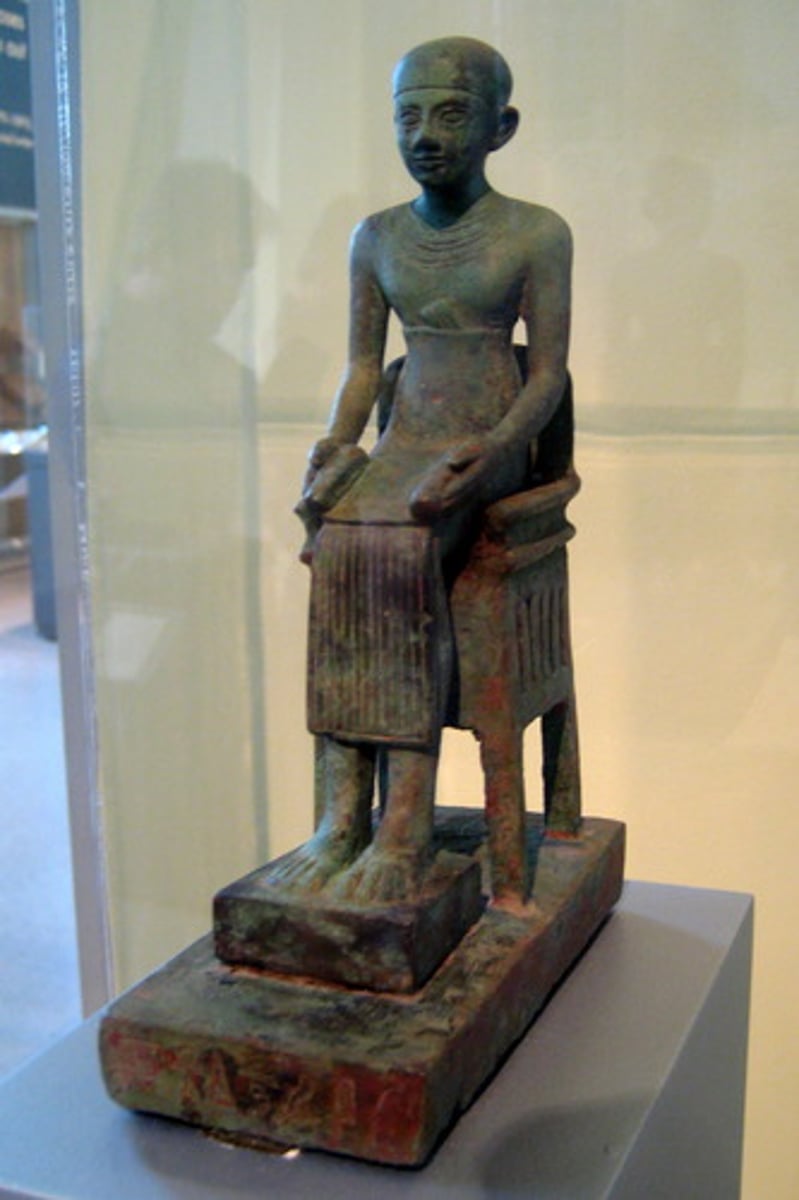
First Recorded Architect
Imhotep
What does Imhotep mean?
the one who comes in peace
Who was Imhotep?
-born a commoner
-between 2,700 and 2,600 Zoser hired Imhotep to design and build his tomb
-He "translated" traditional building materials of mud, wood, and reeds
-Imhotep was also an astronomer, magician, and doctor
-He was later worshiped by the Egyptians as a god

What were pyramids?
tombs for pharaohs (kings) that were built on West Bank of the Nile River
What were pyramids covered in?
covered in reflective limestone- quarried/east bank
What is found at the top of pyramids?
gold veneer
What did the people of Egypt think about the King?
thought the king would walk on sun rays to eternity. If the king lives forever, the people do too