Dental Anatomy Lecture 1: Dental Anatomy
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Specialties of dentistry we will be studying
-operative
-prosthodontics
-endo
-pens
-oral surgery
-perio
Why do we need to know this?
Foundational building blocks for other dental knowledge
3 planes of orientation
-coronal
-median/midsagittal
-transverse
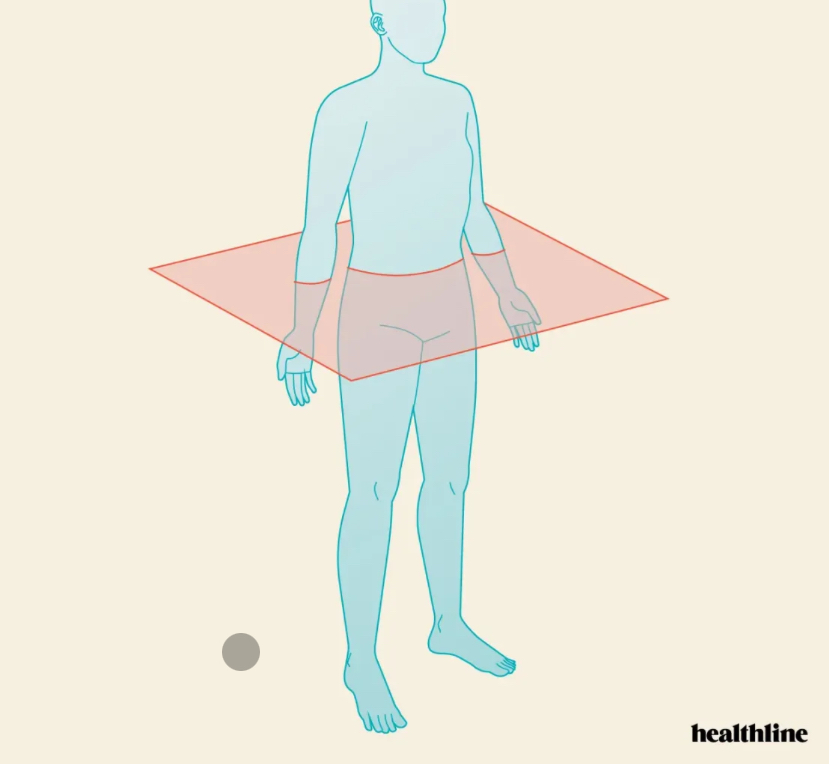
What plane is this?
Transverse
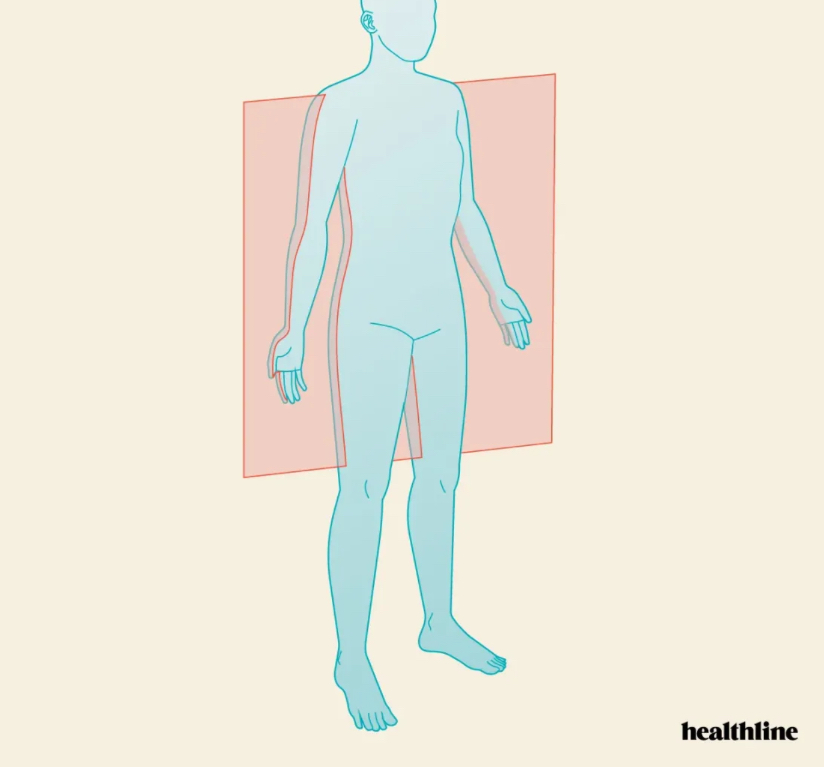
What plane is this?
Coronal
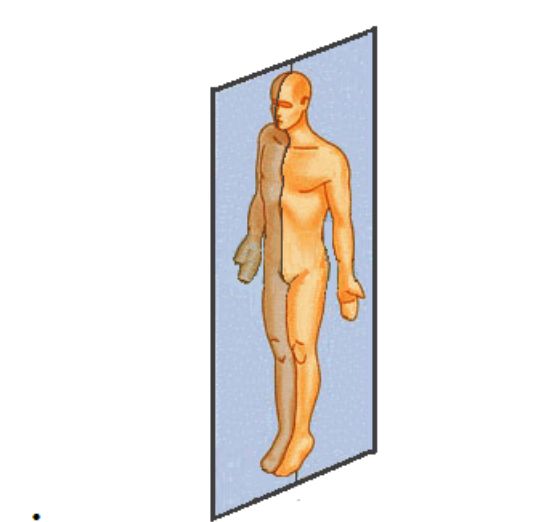
What plane is this?
Median/sagittal/midsagittal
What two planes do we use in the mouth?
Transverse and Median
What does the transverse plane separate in the mouth?
Maxillary and Mandibular
What does the median plane separate in the mouth?
Left and right sides
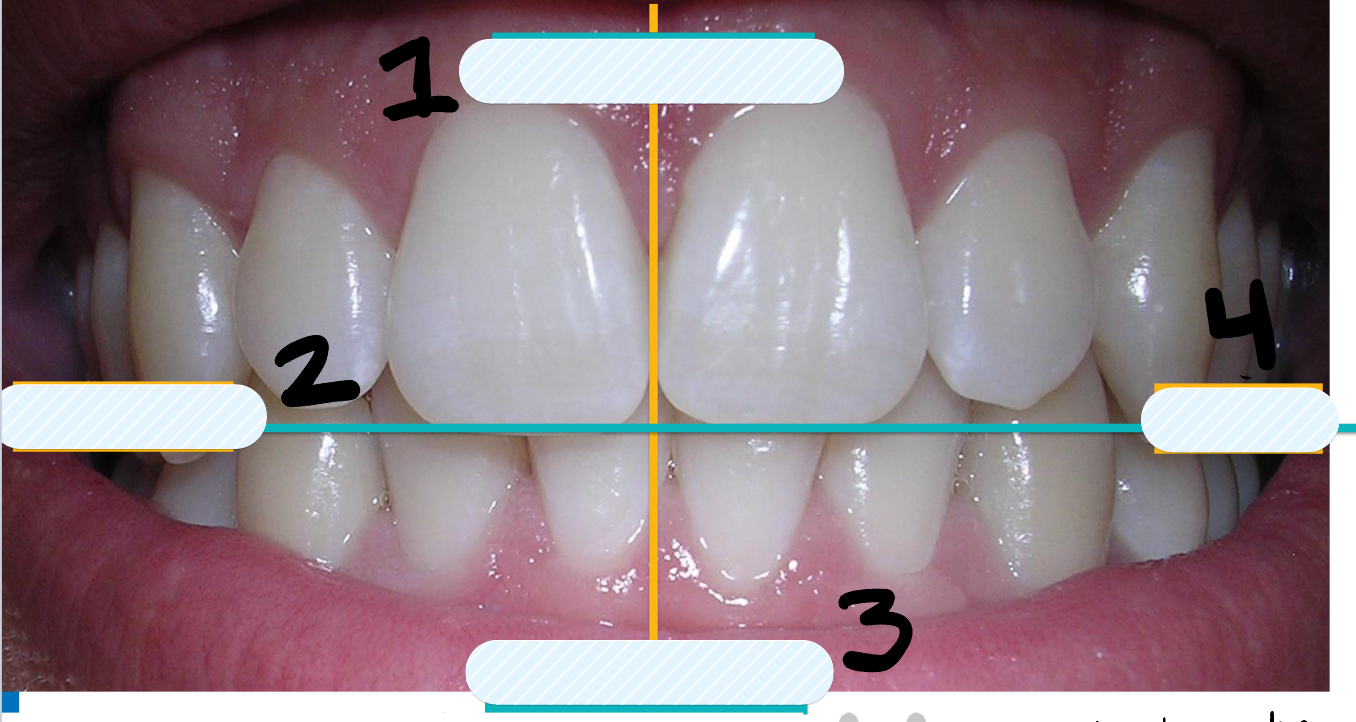
What side is labeled number 2?
Right side
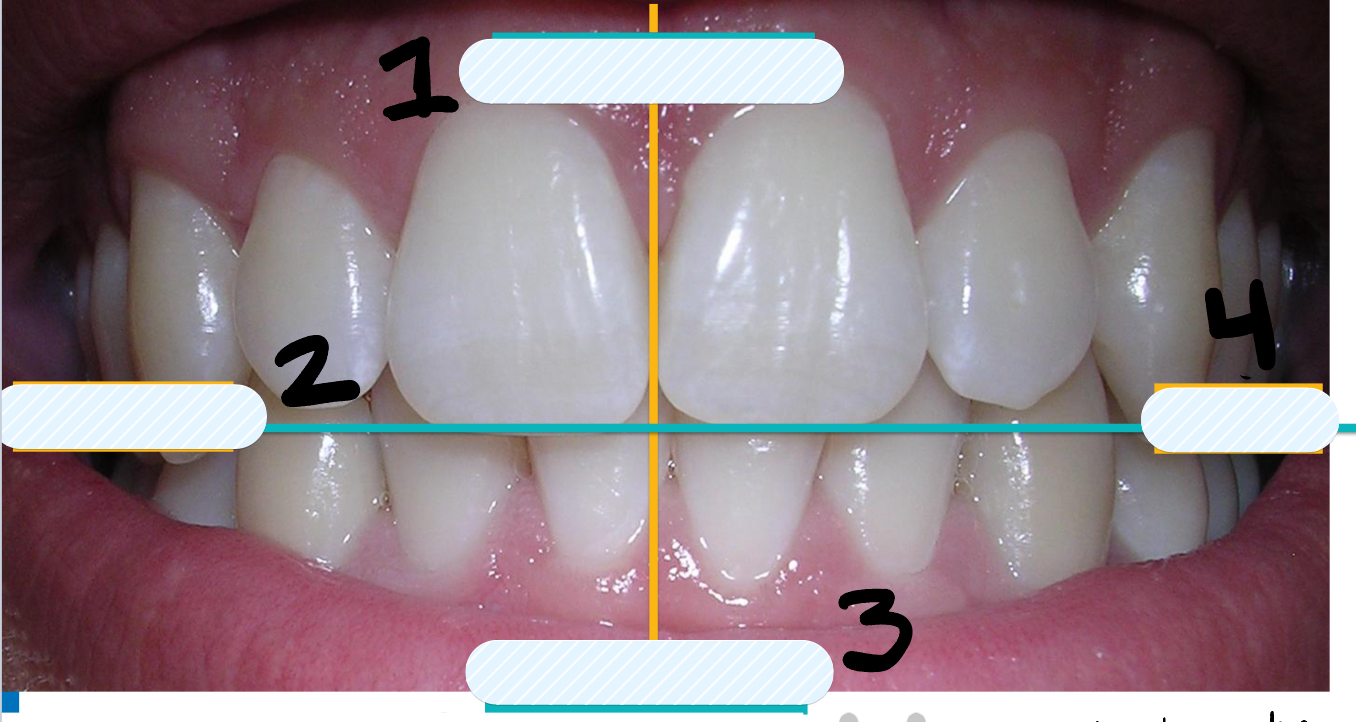
What side is labeled number 4?
Left side
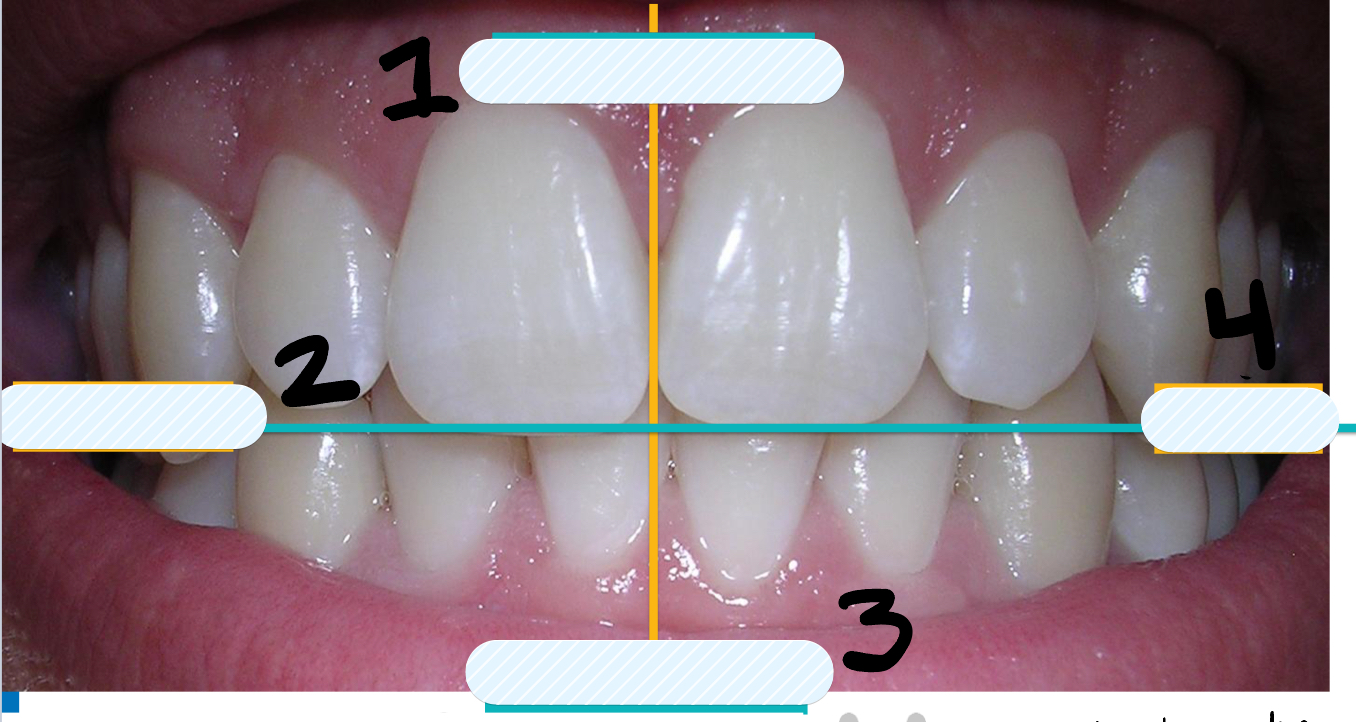
What arch is labeled number 1?
Maxillary
What arch is labeled number 3?
Mandibular
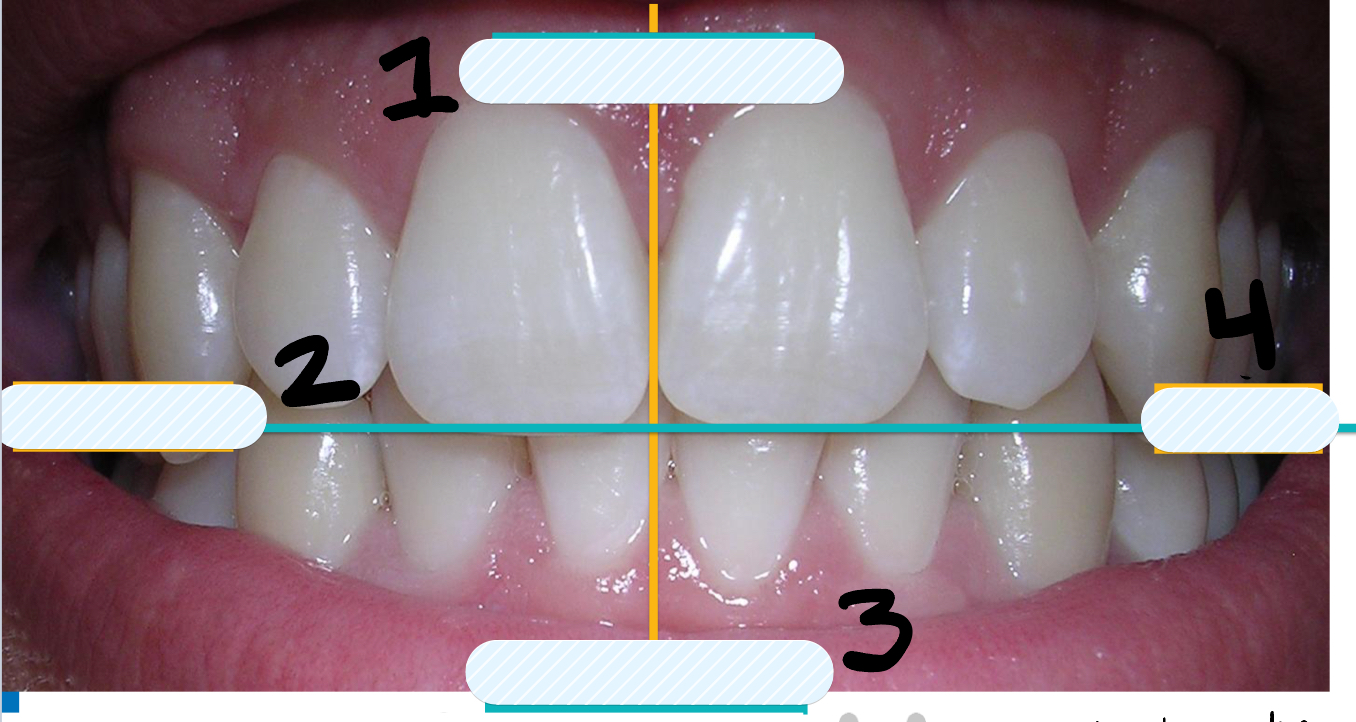
Where is quadrant 1 located?
Right maxillary
Where is quadrant 2 located?
Left maxillary
Where is quadrant 3 located?
Left Mandibular
Where is quadrant 4 located?
Right Mandibular
What are the two front teeth called?
Central Incisors
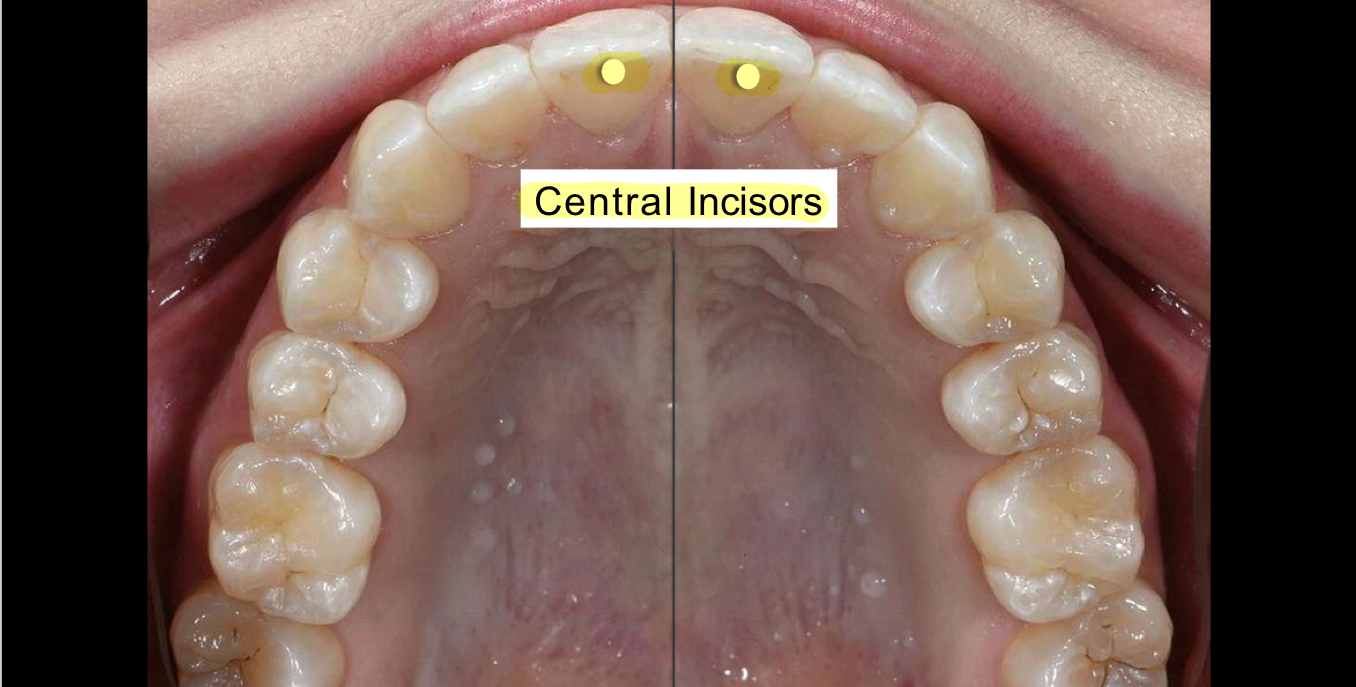
What two teeth are next to the central incisors?
Lateral incisors
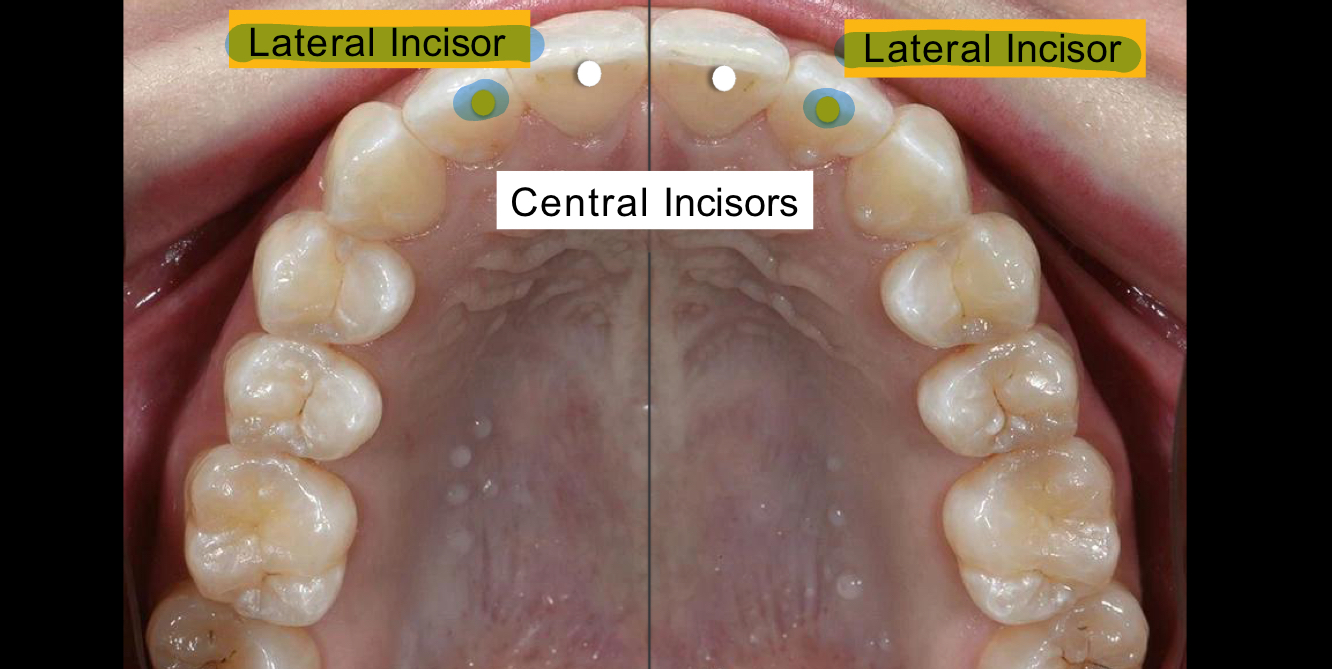
What are the teeth between the lateral incisors and premolars called?
Canines/Cuspids
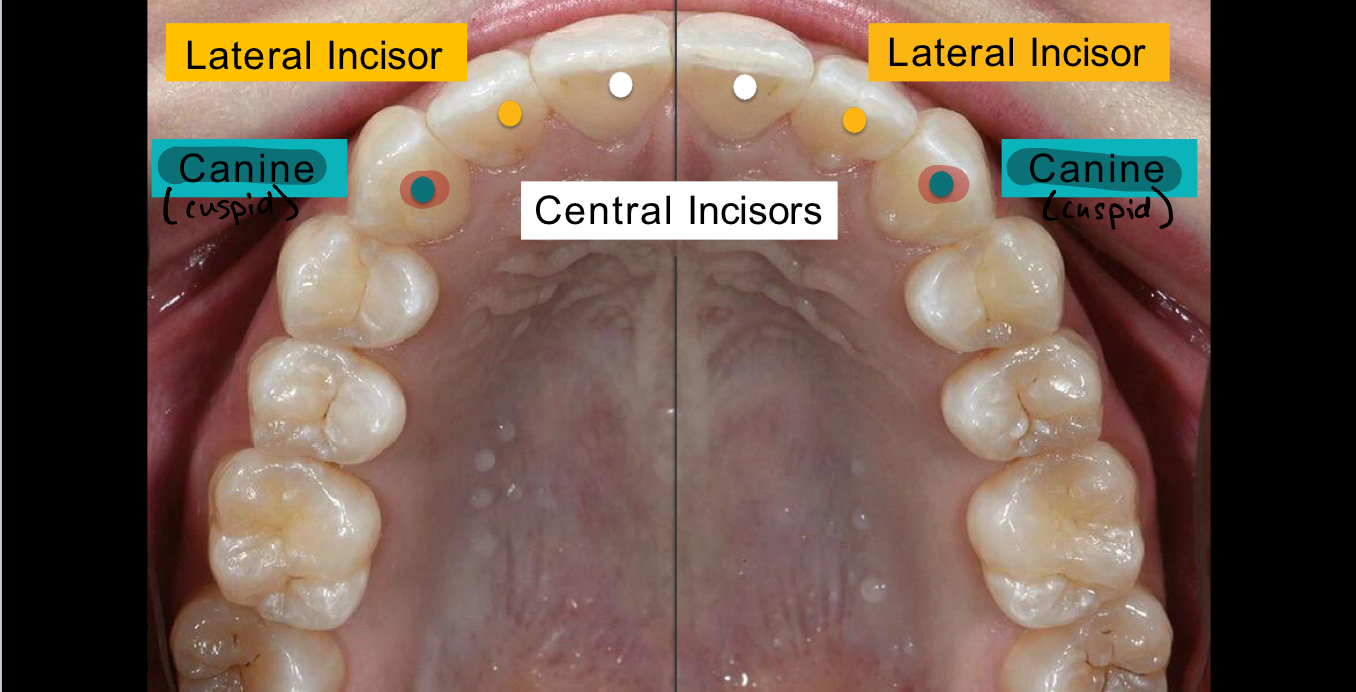
What are the front 6 teeth called?
Anterior
What are the back 10 teeth called?
Posterior
What are the teeth in front of the molars called?
Premolars/Bicuspids
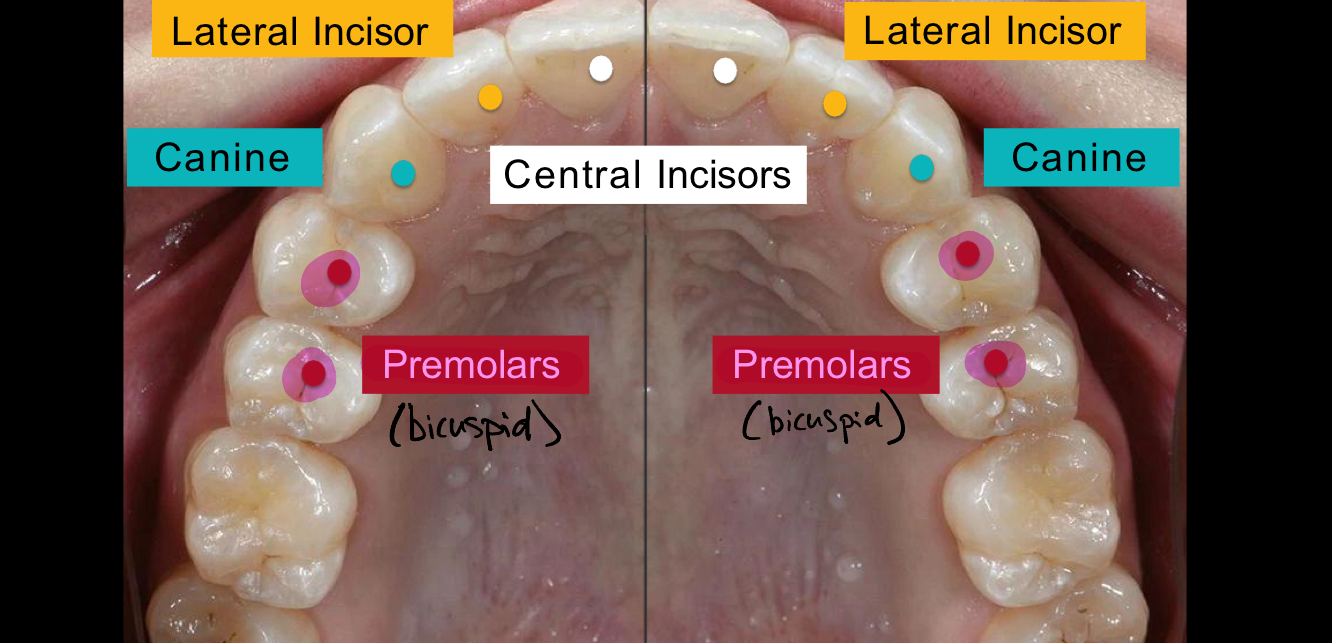
What are the very back teeth called?
Molars
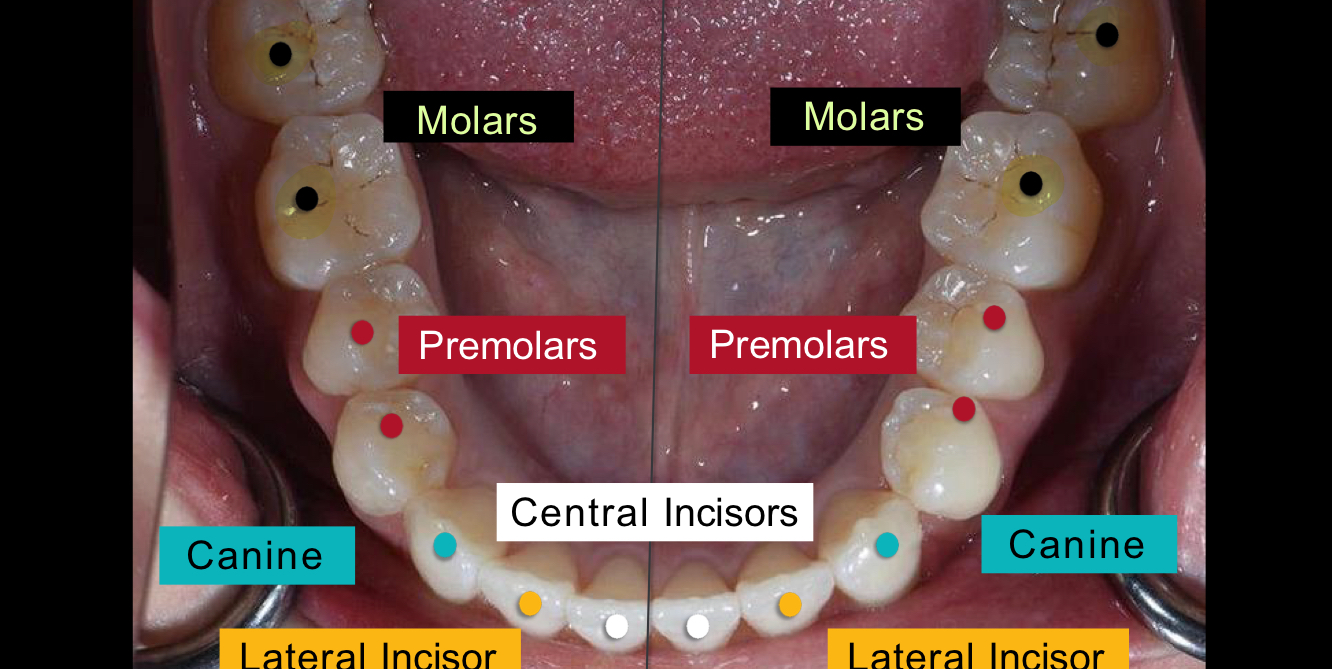
What is the function of the central and lateral incisors?
To cut
What is the function of the canines?
To pierce and to hold
What is the function of the premolars and molars?
To chew
Tooth positions used in nomenclature
-maxillary
-mandibular
-anterior
-posterior
2 sequences of eruption
Primary and Secondary Dentition
Another name for primary dentition
Deciduous
Another name for secondary dentition
Permanent
How many primary/deciduous teeth?
20
How many secondary/permanent teeth?
32
What teeth do primary dentition lack?
The 8 premolars and wisdom teeth
What is the order for ID/naming a tooth?
1) Dentition: permanent or deciduous
2) Arch: Maxillary or mandibular
3) Side: Left or right
4) Tooth name: Canine etc.
What is the universal numbering system for permanent teeth?
1-32
What is the universal numbering system for deciduous teeth?
A-T
In what order are teeth numbered?
Quadrants 1-4, starting on the right maxillary side
What teeth are in quadrant 1 for permanent teeth?
1-8
What teeth are in quadrant 2 for permanent teeth?
9-16
What teeth are in quadrant 3 for permanent teeth?
17-24
What teeth are in quadrant 4 for permanent teeth?
25-32
What teeth are in quadrant 1 for deciduous teeth?
A-E
What teeth are in quadrant 2 for deciduous teeth?
F-J
What teeth are in quadrant 3 for deciduous teeth?
K-O
What teeth are in quadrant 4 for deciduous teeth?
P-T
Where is the Palmer ID System used?
Orthodontics
How many different bracket shapes in the Palmer System?
4
Permanent Dentition for Palmer System numbering
1-8
Primary Dentition for Palmer System numbering
A-E
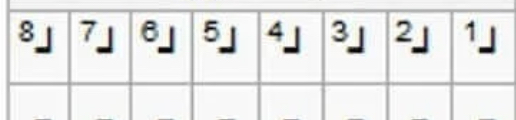
What quadrant of the palmer system is this?
Upper Right
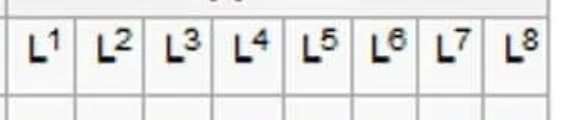
What quadrant of the palmer system is this?
Upper Left
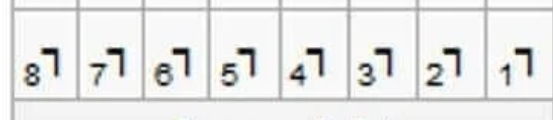
What quadrant of the palmer system is this?
Lower Right
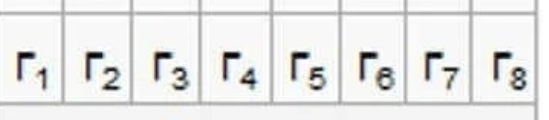
What quadrant of the palmer system is this?
Lower Left
Two main parts of a tooth
Crown and Root
Two parts of the Crown of the tooth
Enamel and Dentin
Parts of the Root of the tooth
Pulp and Cementum
Do baby teeth have more enamel or dentin?
Enamel
What percentage of calcium hydroxyapatite in the enamel
95%
What is the hardest substance in the body?
Enamel
What makes the tooth white?
Enamel
What is the external surface layer of the crown?
Enamel
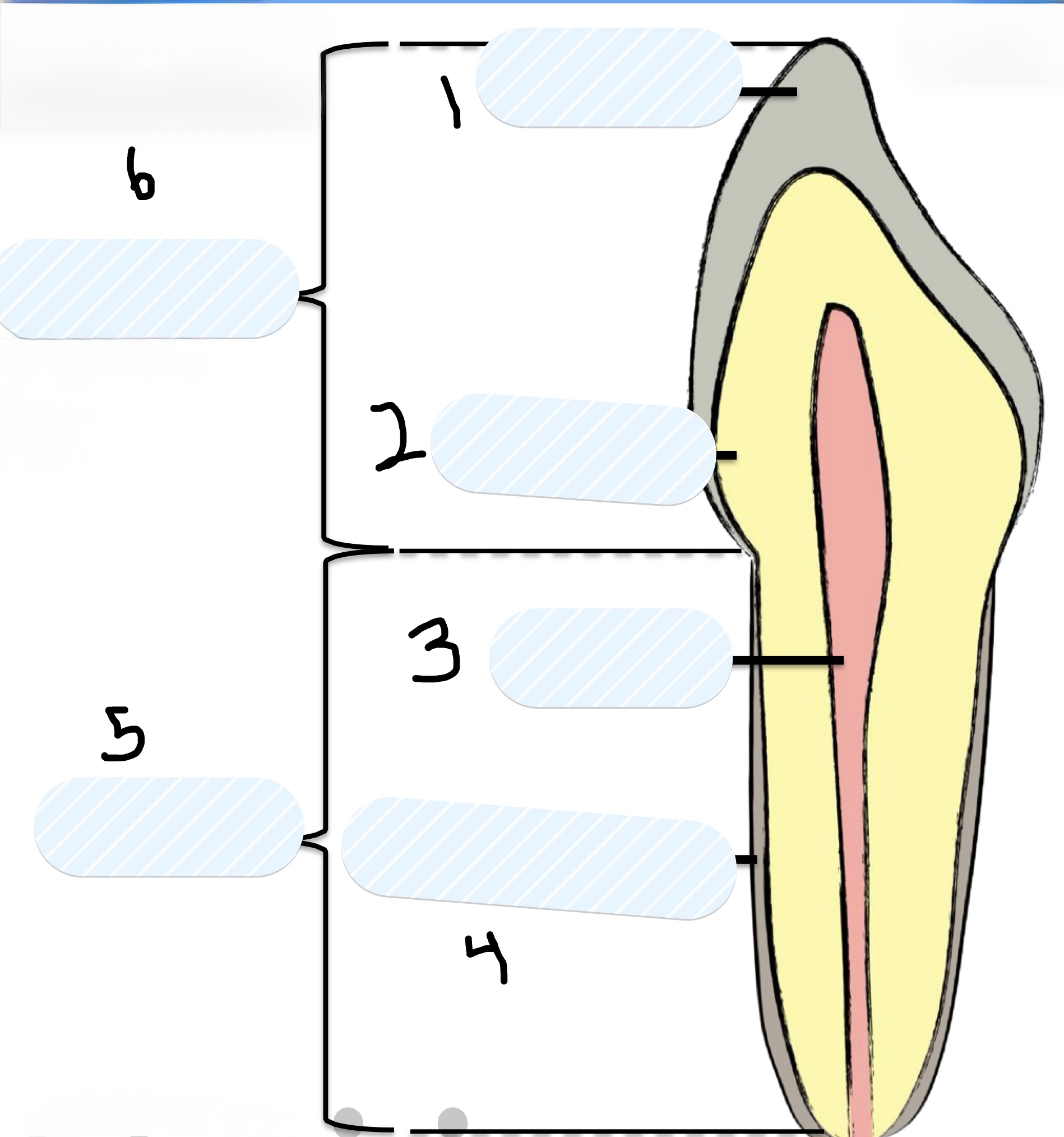
What is number 1?
Enamel
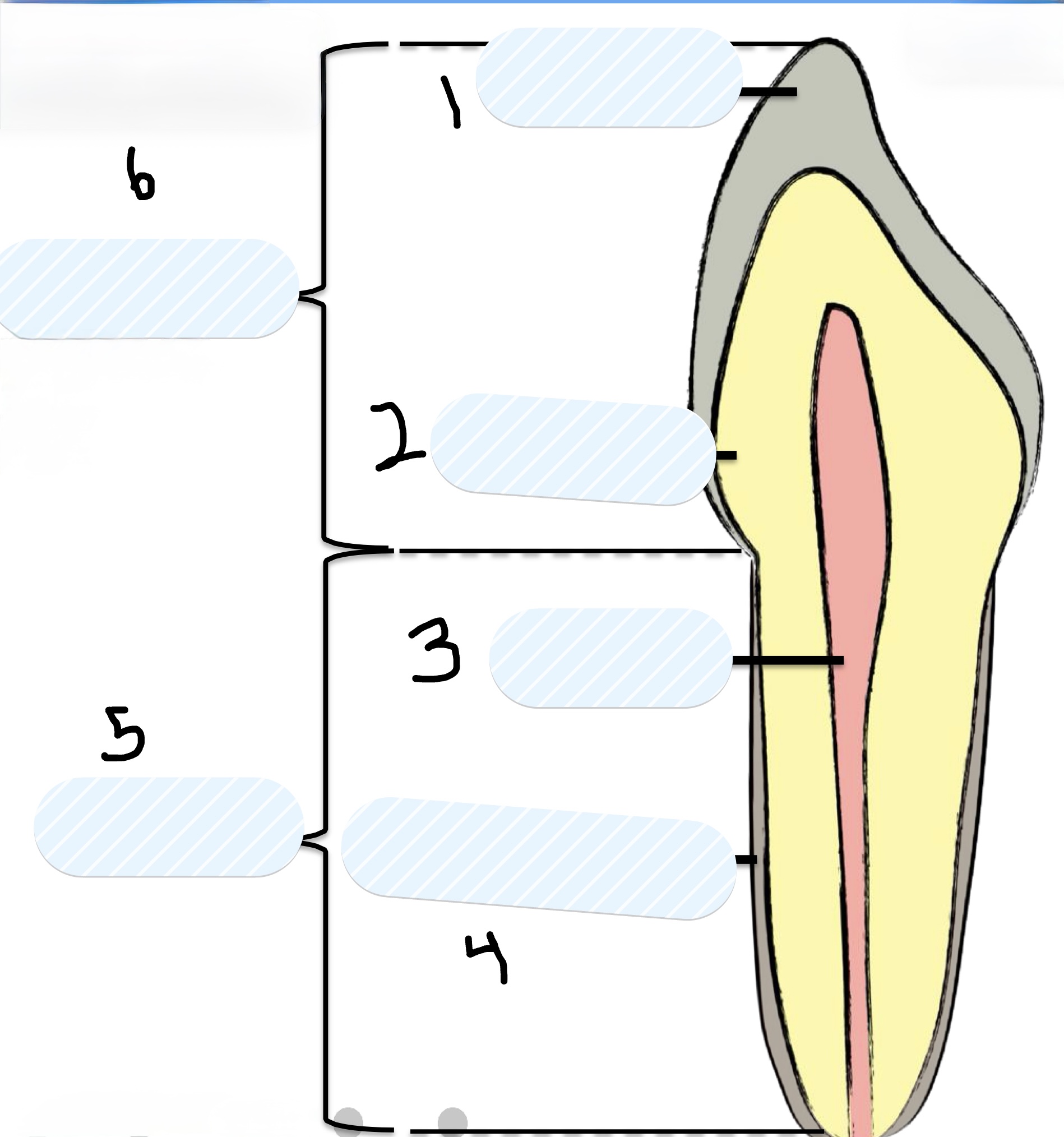
What is number 2?
Dentin
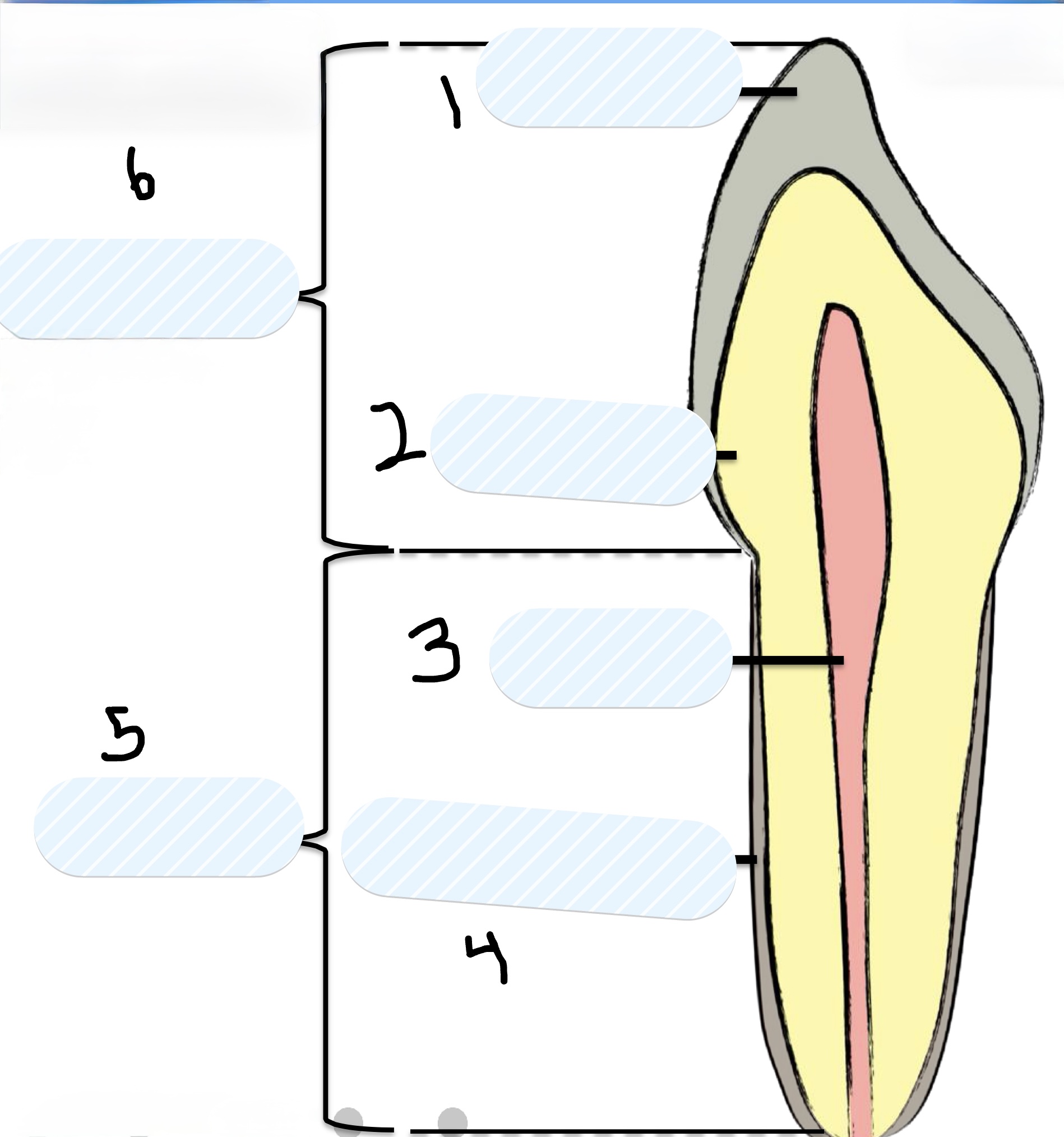
What is number 3?
Pulp
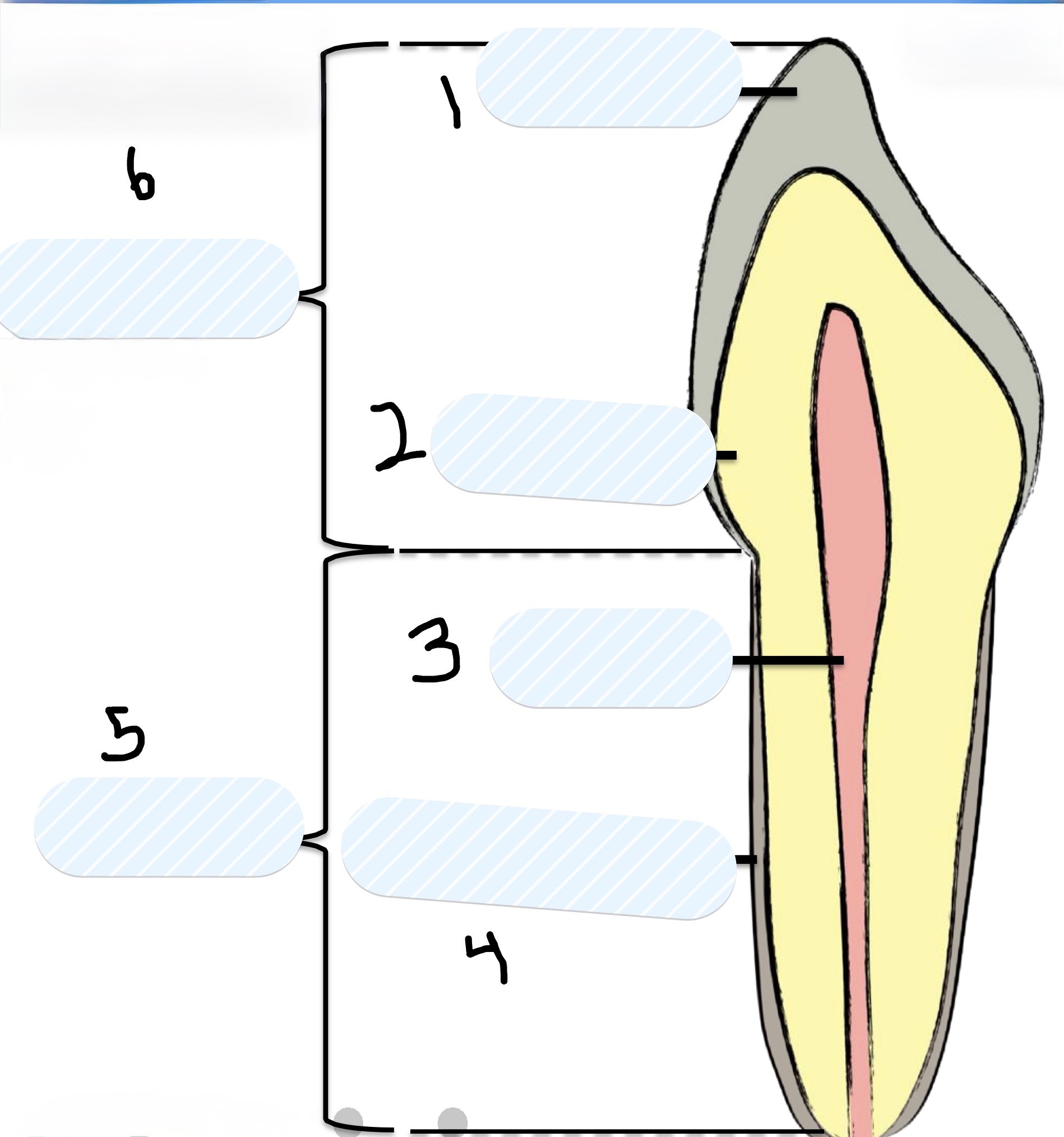
What is number 4?
Cementum
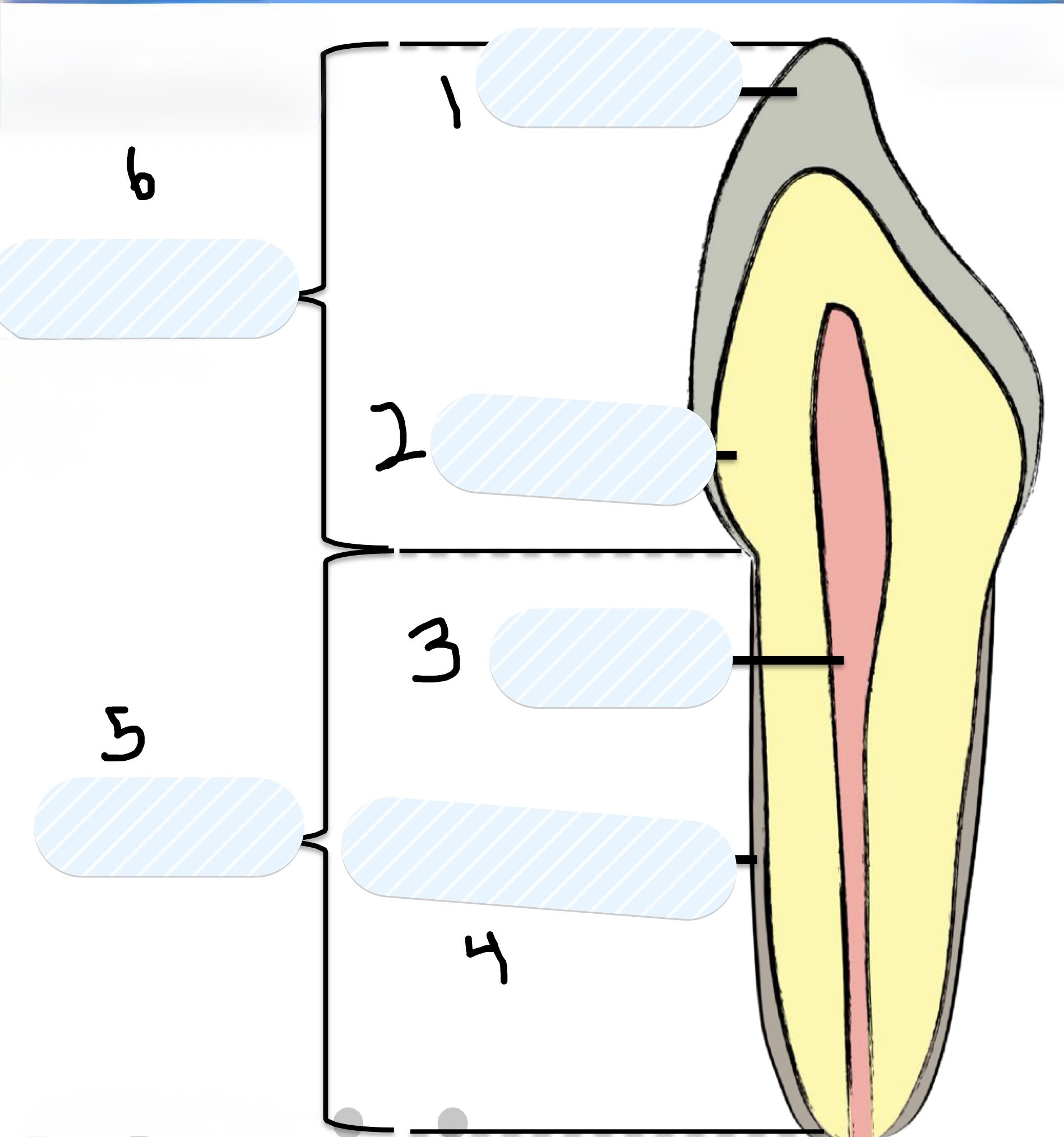
What is number 5?
Root
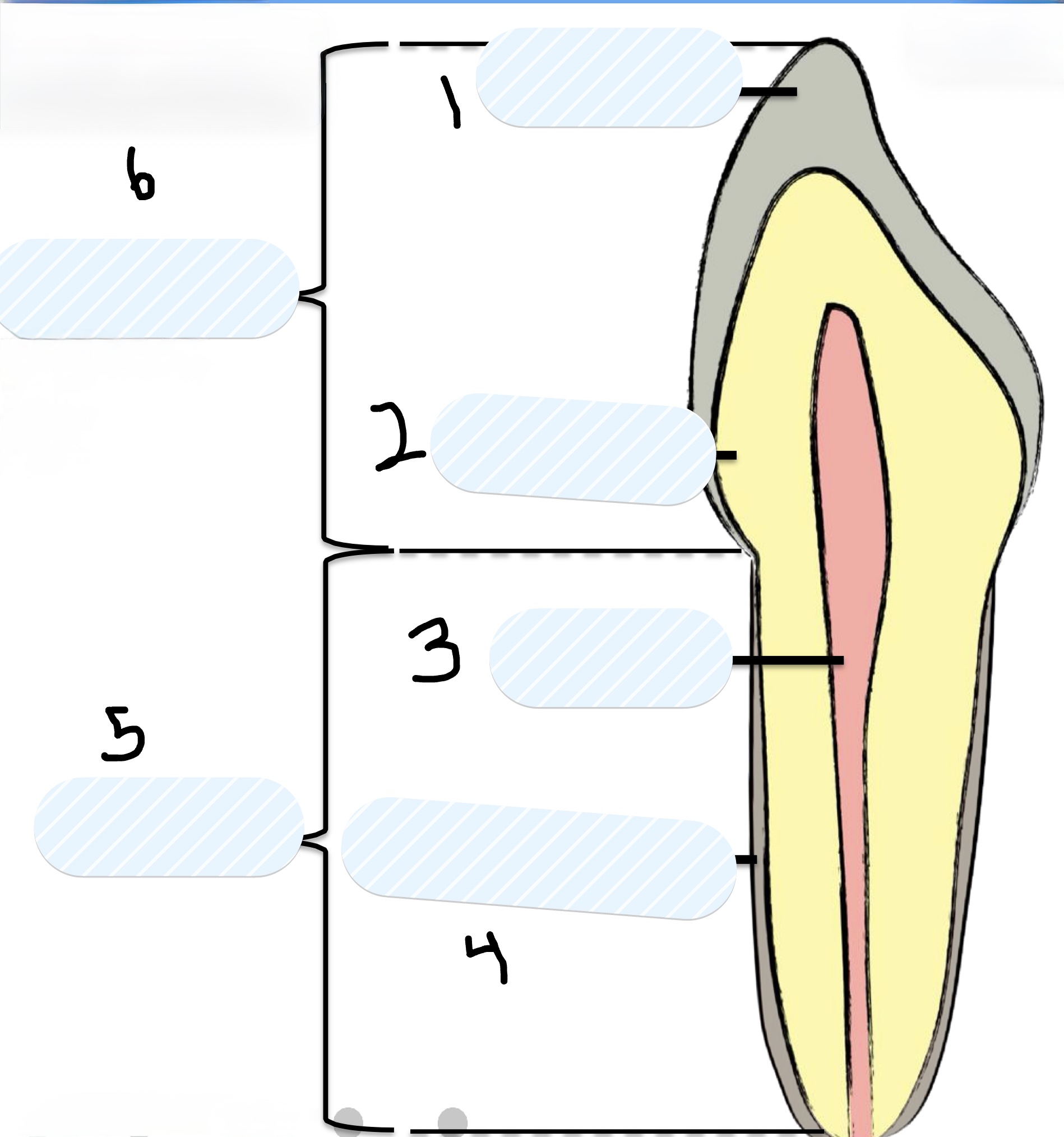
What is number 6?
Crown
Is dentin sensitive?
Yes!
Percentage of calcium hydroxyapatite in Dentin
70%
Is dentin visible?
Not normally, can appear with grinding, etc.
What directly underlays the enamel and cementum?
Dentin
Percentage of calcium hydroxyapatite in cementum
65%
What is the external layer of the root?
Cementum
Is the cementum thick or thin?
Very thin
Where is the cementum located?
Covering the root, under the gum and bone
How many junctions are there?
3
What is the junction where the enamel meets the cementum?
Cement enamel (CEJ) or Cervical Line
What is the junction where the cementum meets the dentin?
Cementodentinal
What is the junction where the enamel meets the dentin?
Dentinoenamel
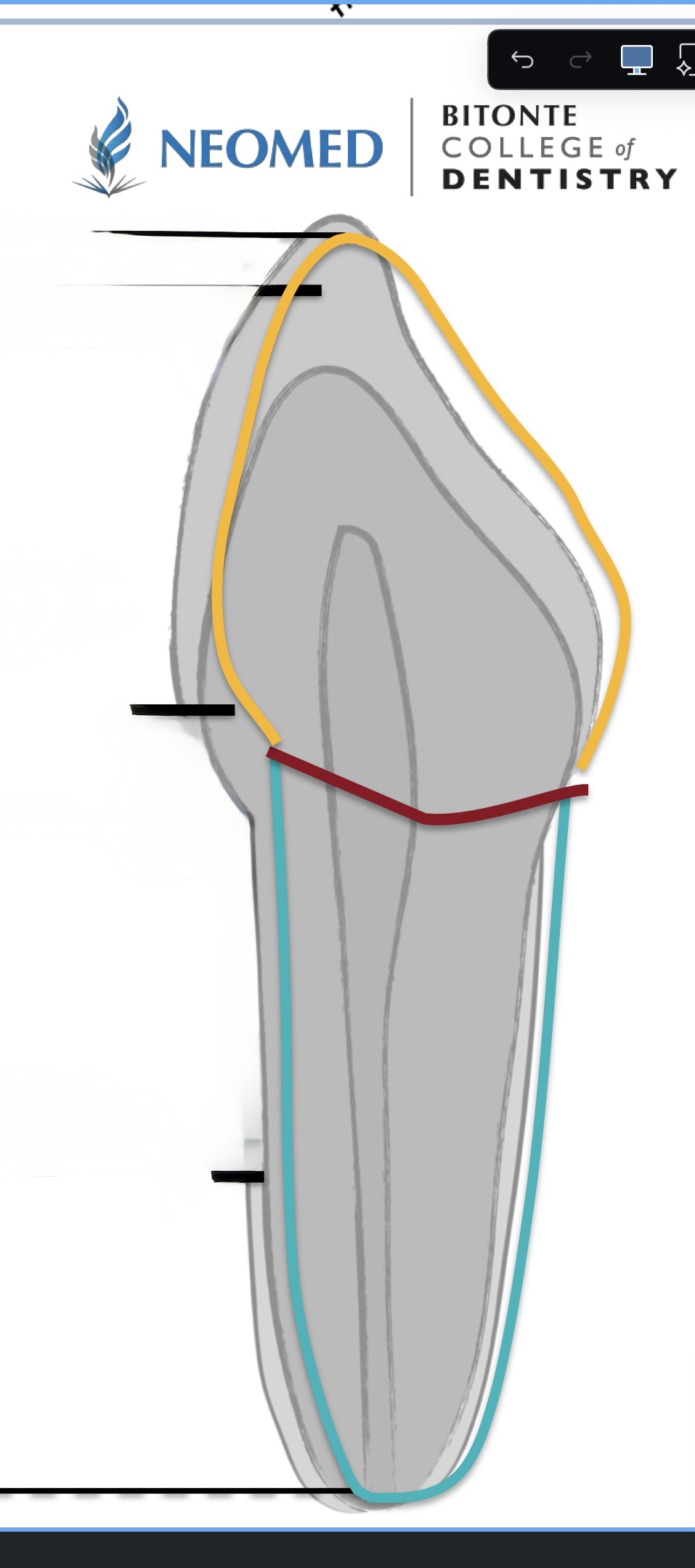
What junction is red?
Cementoenamel (CEJ), or cervical line
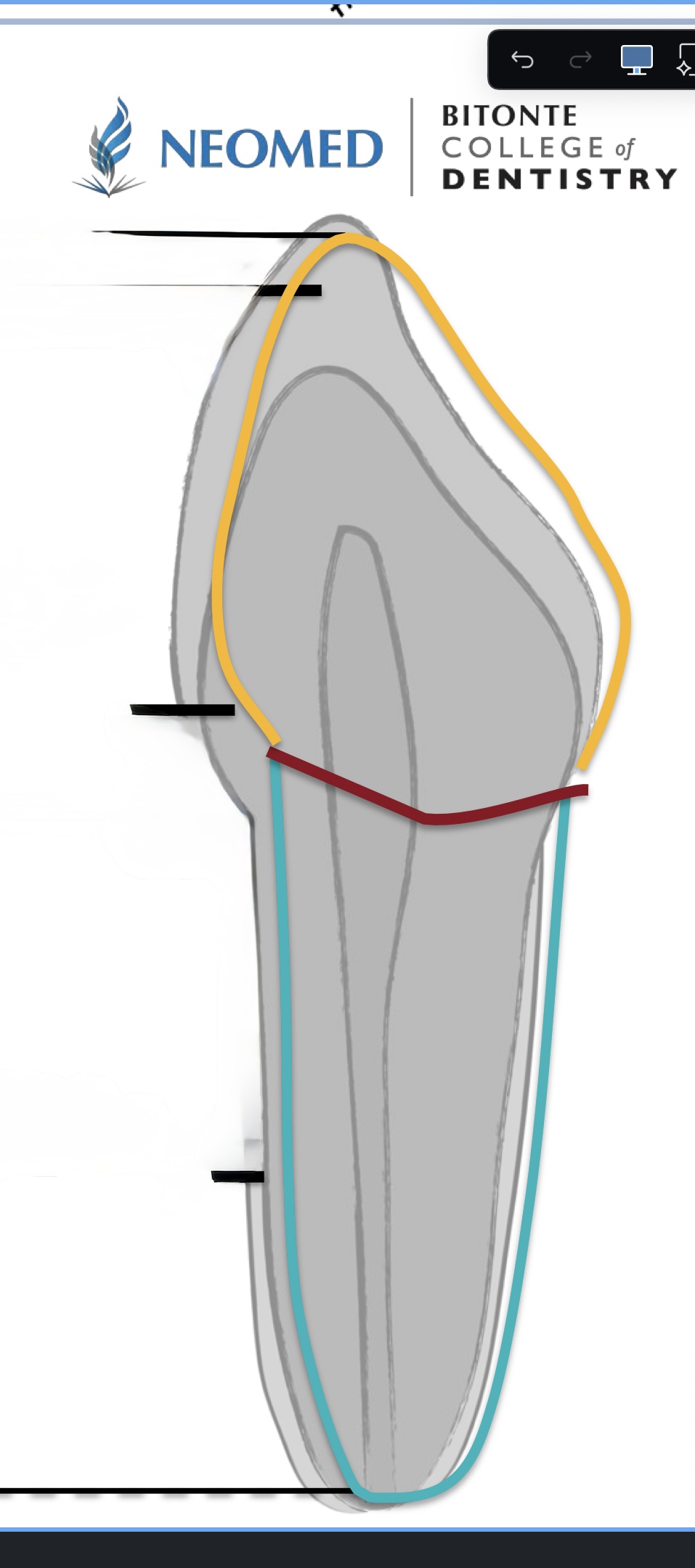
What junction is blue?
Cementodentinal
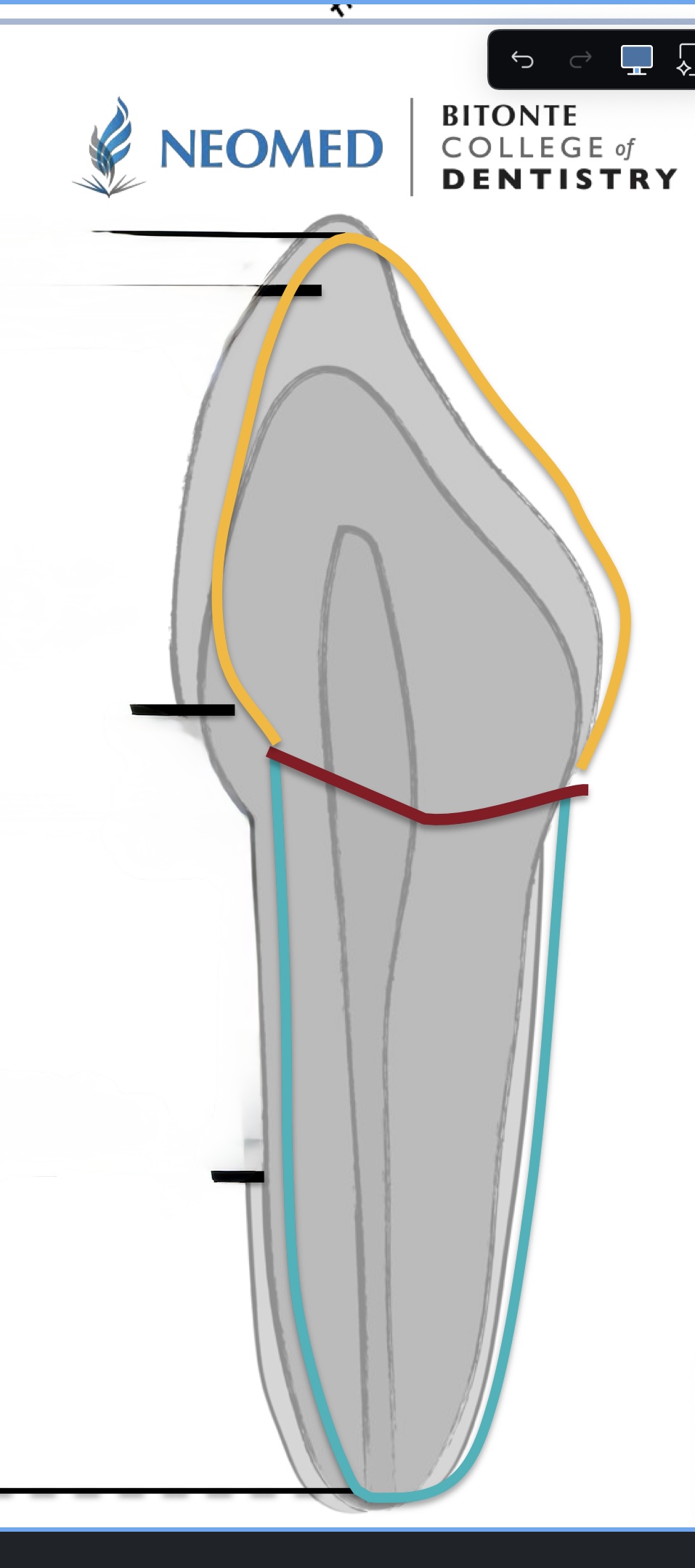
What junction is yellow?
Dentinoenamel
What is pulp?
Soft, mineralized connective tissue
Contains blood vessels and nerves
Normally not visible
What does a normal pulp indicate?
Vitality and nutrition in the tooth
A root canal is needed when a tooth is non-vital
What does the pulp do if a filling becomes too deep?
It protects the tooth!
The pulp is as formative, sensory, nutritive, and protective functions
What is the formative pulp function?
Odontoblasts produce dentin (layers)
What is the sensory function of pulp?
Sense of pain
What is the nutritive function of pulp?
Transports nutrients
What is the protective function of pulp?
Repairs dentin in response to injury (drilling too deep)
Periodontal Structures
Alveolar bone
Gingiva
Periodontal ligament
Alveolar bone
Bone that surrounds the roots
Gingiva
Soft tissue that covers the alveolar bone
Periodontal ligament
Thin ligament that connects tooth and surrounding bone
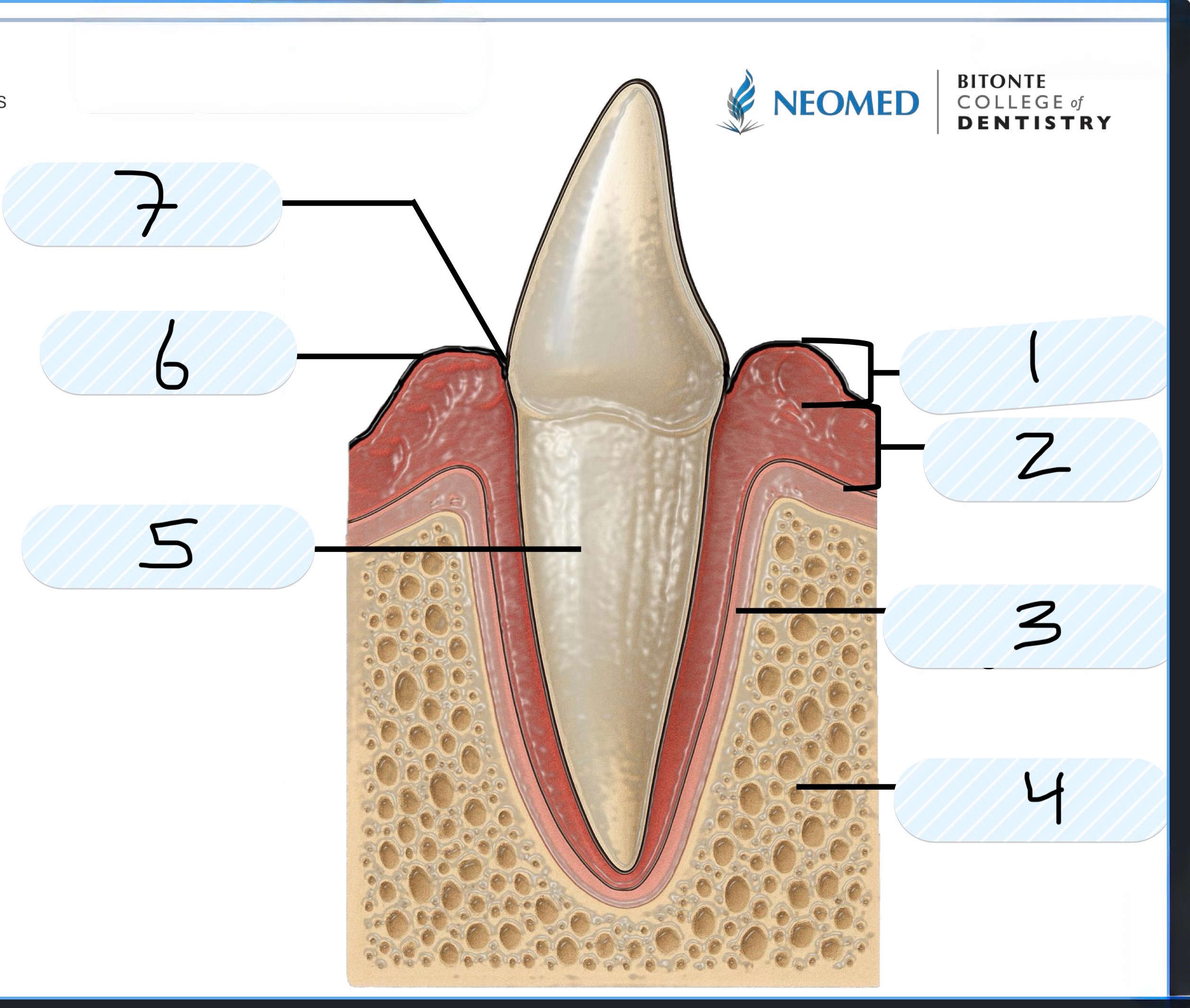
What is number 1?
Free Gingiva
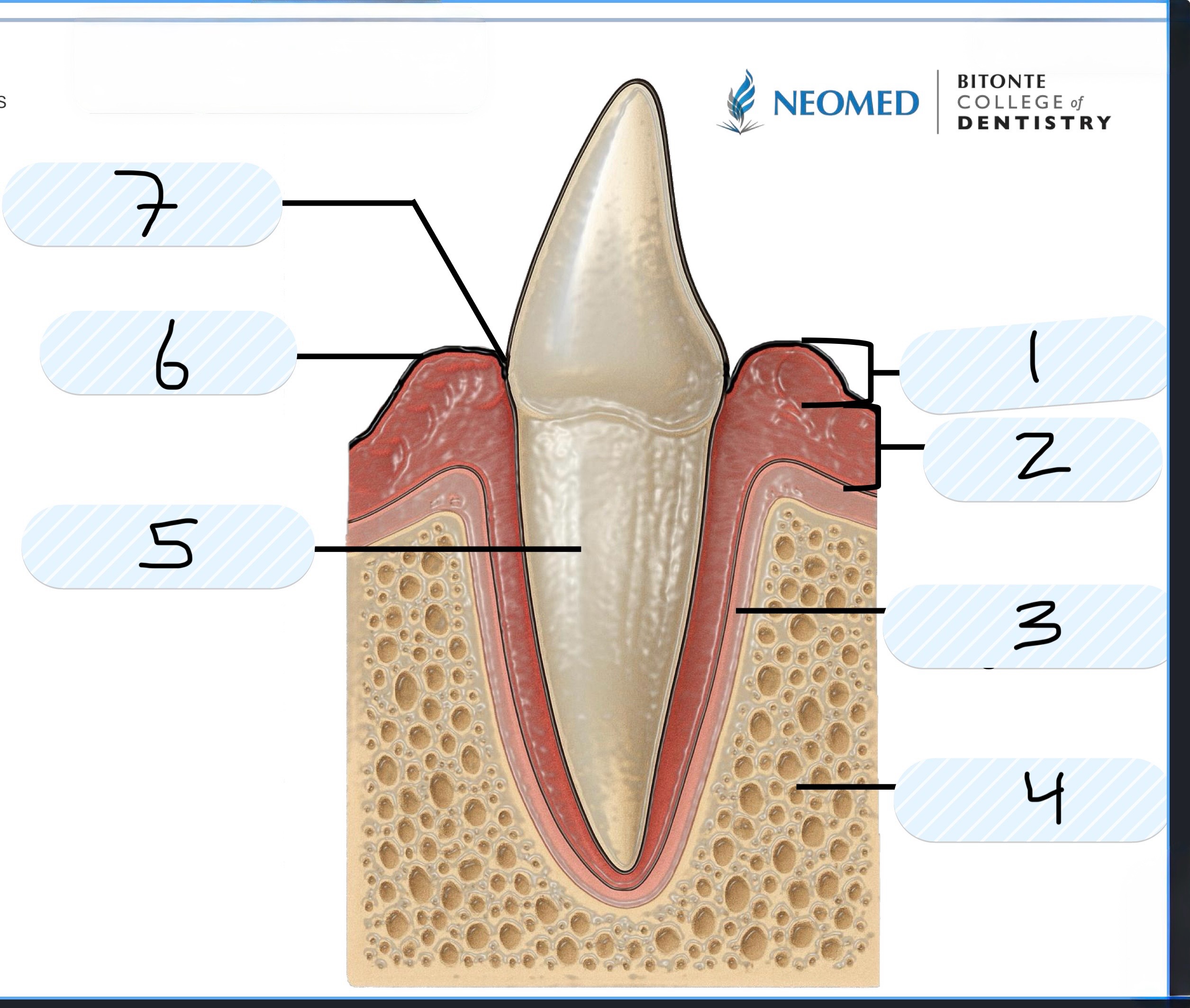
What is number 2?
Attached gingiva
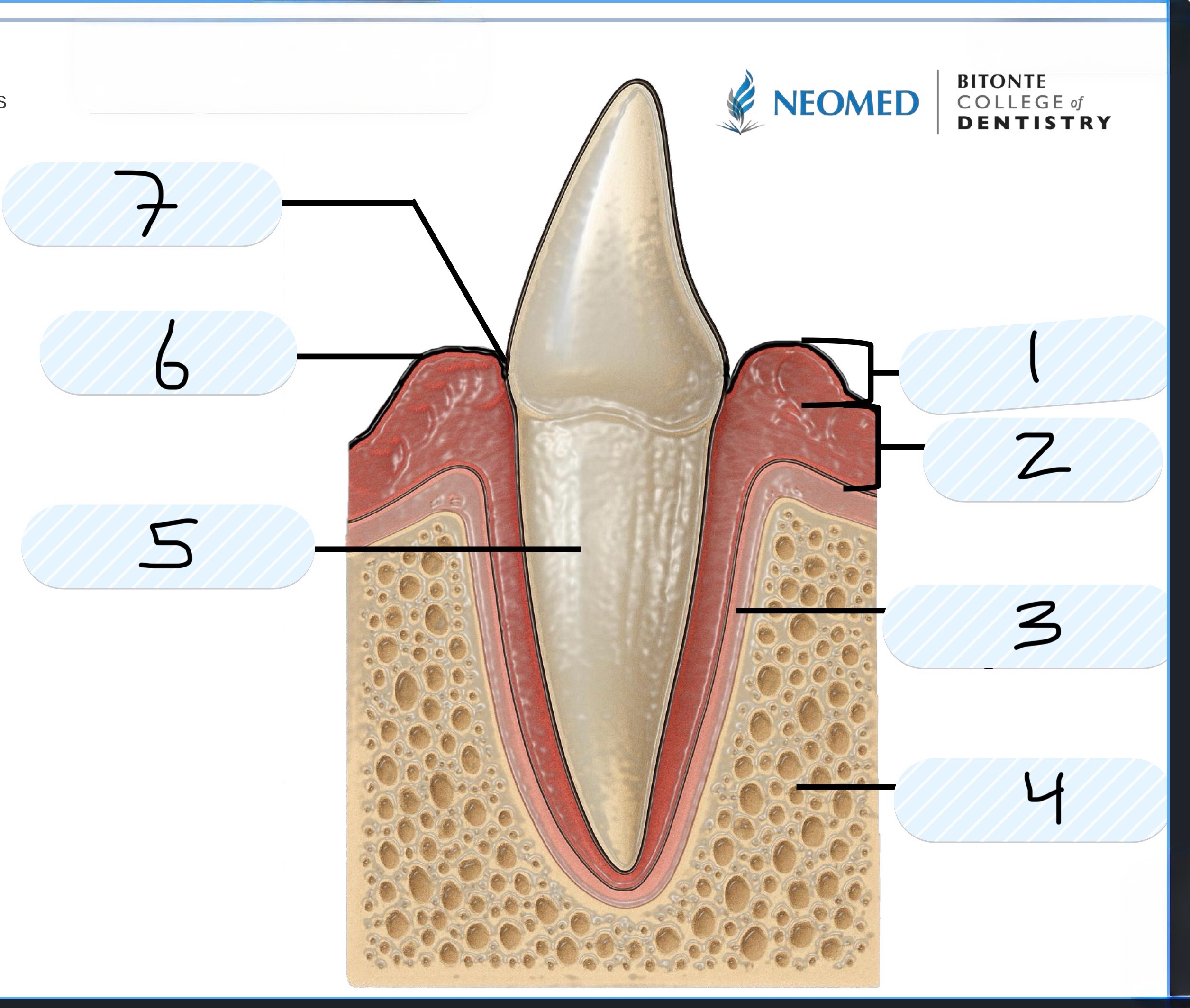
What is number 3?
Periodontal ligament
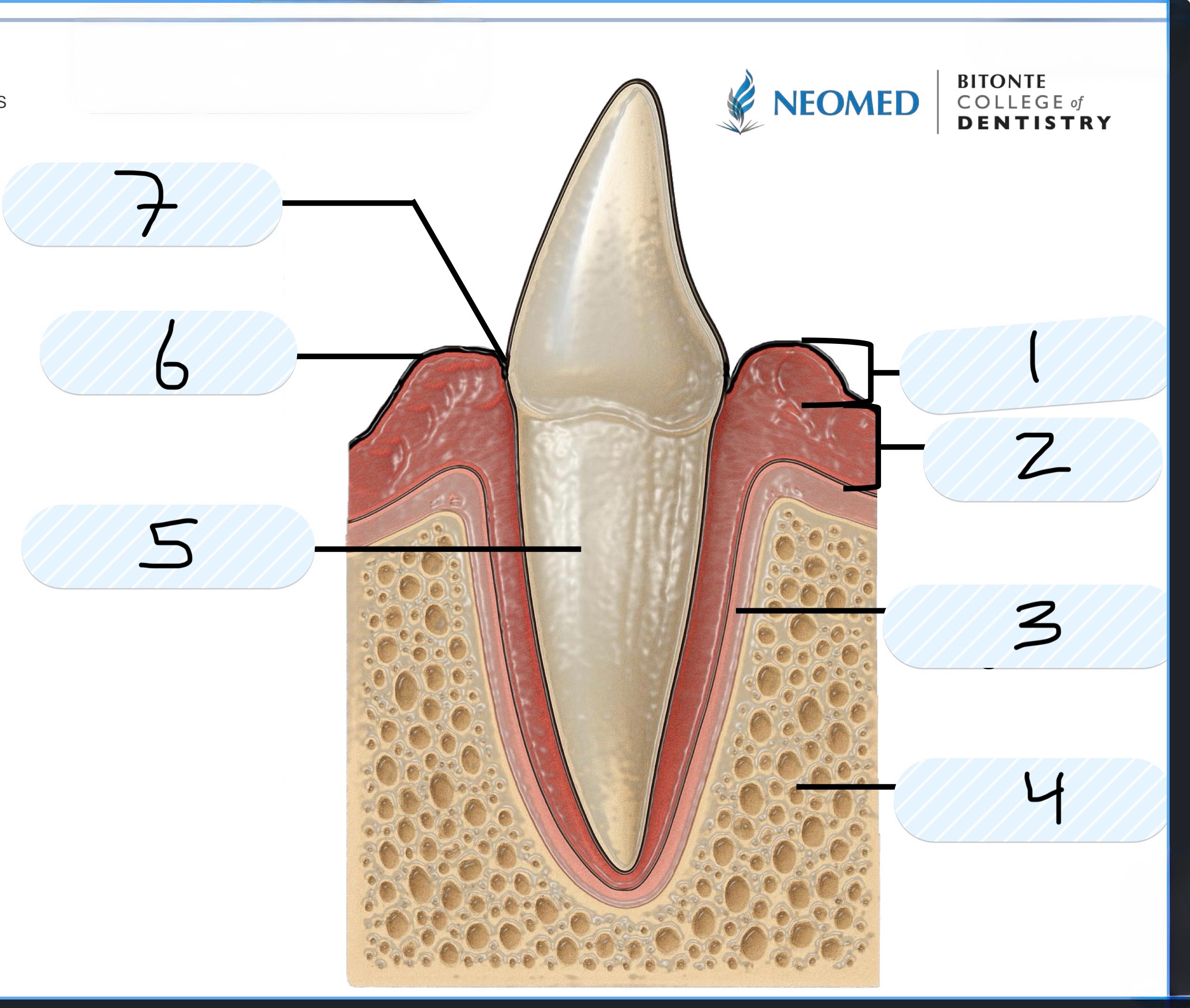
What is number 4?
Alveolar bone
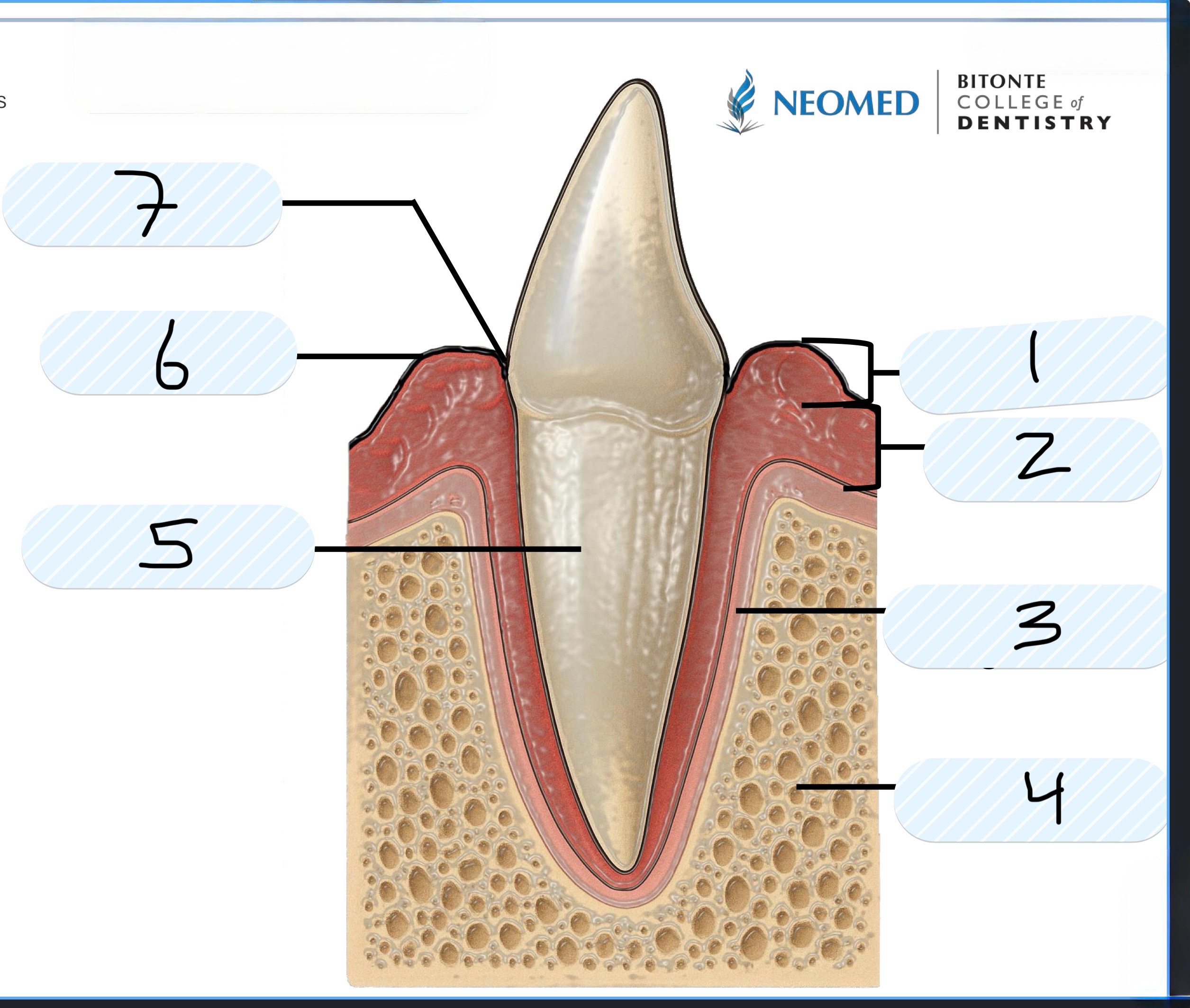
What is number 5?
Cementum of root
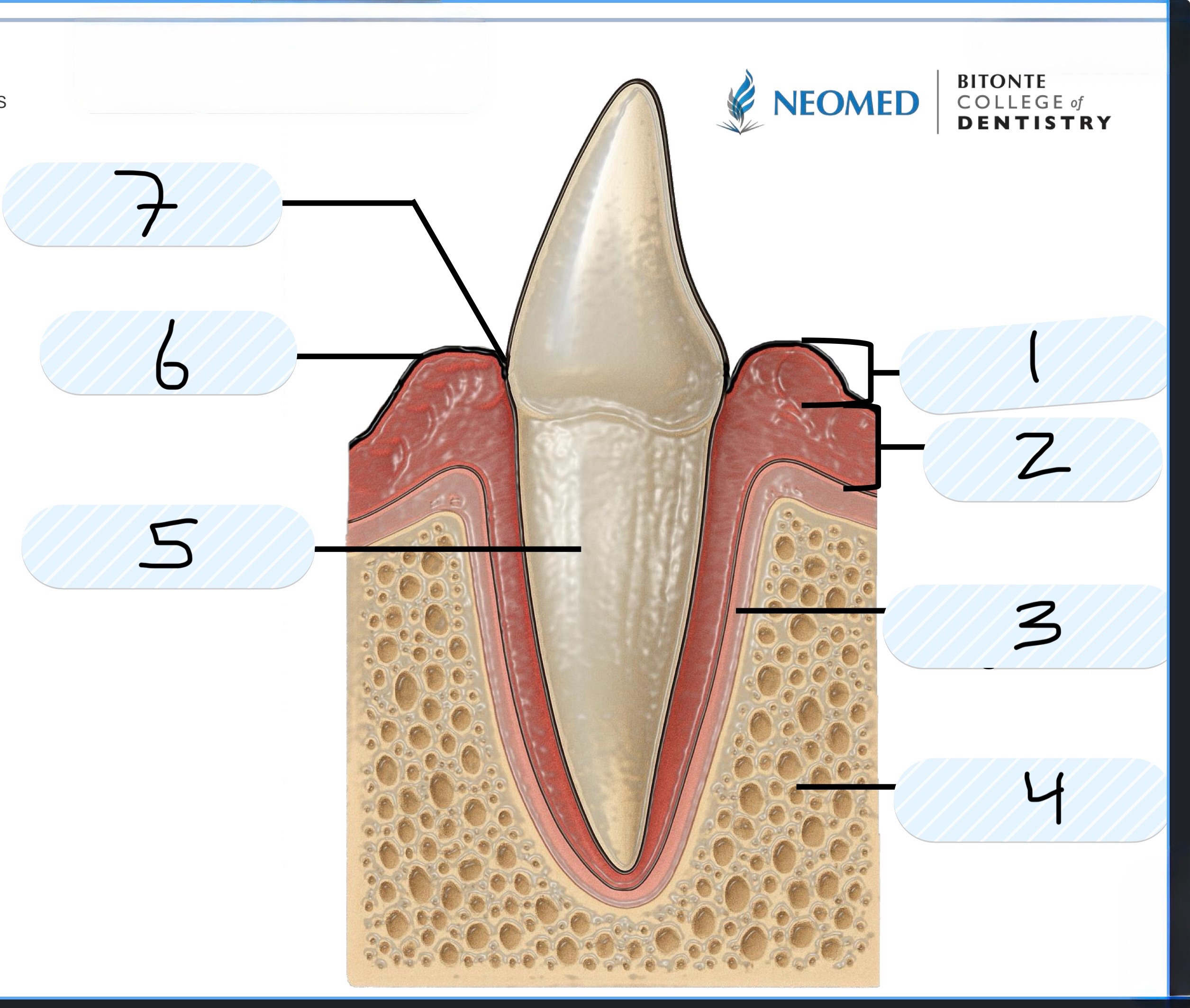
What is number 6?
Gingival margin