Biochemistry - Module16A 2026 Ratio
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
D. An unstable molecule with an unpaired electron in its outer shell.
Which of the following best defines a free radical?
A. A molecule that has gained an extra electron.
B. A molecule that lacks a nucleus.
C. A stable molecule with paired electrons in its outer shell.
D. An unstable molecule with an unpaired electron in its outer shell.
B. Consumption of antioxidant-rich foods.
Which of the following is NOT a potential source of free radicals in the body?
A. Environmental pollutants.
B. Consumption of antioxidant-rich foods.
C. Exposure to ionizing radiation.
D. Normal cellular metabolism.
C. Antioxidants and pro-oxidants.
Oxidative stress is primarily caused by an imbalance between:
A. Vitamins and minerals.
B. Proteins and lipids.
C. Antioxidants and pro-oxidants.
D. DNA and RNA.
D. Superoxide dismutase (SOD).
Which of the following enzymes plays a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals?
A. Catalase.
B. Collagenase.
C. Carbonic anhydrase.
D. Superoxide dismutase (SOD).
D. Increased cellular energy production.
Which of the following is NOT an effect of oxidative stress?
A. DNA damage.
B. Protein oxidation.
C. Lipid peroxidation.
D. Increased cellular energy production.
B. Vitamin C
Which vitamin is considered a potent antioxidant?
A. Vitamin D
B. Vitamin C
C. Vitamin K
D. Vitamin B12
B. All of the choices.
Which of the following diseases is associated with oxidative stress?
A. Type 1 diabetes.
B. All of the choices.
C. Rheumatoid arthritis.
D. Parkinson's disease.
C. Glutathione.
Which molecule helps regenerate vitamin E and vitamin C, enhancing their antioxidant effects?
A. Acetylcholine.
B. Serotonin.
C. Glutathione.
D. Nitric oxide.
C. All of the choices
Free radicals can cause damage to cellular components by:
A. Damaging cell membranes.
B. Breaking down proteins.
C. All of the choices
D. Oxidizing DNA.
A. Chronic stress.
Which of the following lifestyle factors can contribute to increased oxidative stress?
A. Chronic stress.
B. Regular exercise.
C. Adequate sleep.
D. Balanced diet.
C. A state of imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals.
Sarah, a 55-year-old woman, presents with symptoms of fatigue, memory impairment, and difficulty concentrating. She has a family history of neurodegenerative diseases. Upon examination, it is found that Sarah follows a sedentary lifestyle, has a diet high in processed foods, and has a BMI in the obese range. Laboratory tests reveal elevated markers of oxidative stress. Based on this information, analyze Sarah's condition and answer the following multiple-choice questions.
Which of the following best defines oxidative stress?
A. The accumulation of toxins in the body.
B. The body's response to infection.
C. A state of imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals.
D. An excess of oxygen in the bloodstream.
C. Normal cellular metabolism.
Sarah, a 55-year-old woman, presents with symptoms of fatigue, memory impairment, and difficulty concentrating. She has a family history of neurodegenerative diseases. Upon examination, it is found that Sarah follows a sedentary lifestyle, has a diet high in processed foods, and has a BMI in the obese range. Laboratory tests reveal elevated markers of oxidative stress. Based on this information, analyze Sarah's condition and answer the following multiple-choice questions.
What is the primary source of free radicals in the body?
A. Consuming antioxidant-rich foods.
B. Exposure to sunlight.
C. Normal cellular metabolism.
D. Bacterial infections.
D. It decreases blood flow and oxygen supply to tissues.
Sarah, a 55-year-old woman, presents with symptoms of fatigue, memory impairment, and difficulty concentrating. She has a family history of neurodegenerative diseases. Upon examination, it is found that Sarah follows a sedentary lifestyle, has a diet high in processed foods, and has a BMI in the obese range. Laboratory tests reveal elevated markers of oxidative stress. Based on this information, analyze Sarah's condition and answer the following multiple-choice questions.
How can Sarah's sedentary lifestyle contribute to oxidative stress?
A. It increases antioxidant production in the body.
B. It promotes efficient removal of free radicals from the body.
C. It has no effect on oxidative stress levels.
D. It decreases blood flow and oxygen supply to tissues.
C. Processed foods lack essential nutrients needed to combat oxidative stress.
Sarah, a 55-year-old woman, presents with symptoms of fatigue, memory impairment, and difficulty concentrating. She has a family history of neurodegenerative diseases. Upon examination, it is found that Sarah follows a sedentary lifestyle, has a diet high in processed foods, and has a BMI in the obese range. Laboratory tests reveal elevated markers of oxidative stress. Based on this information, analyze Sarah's condition and answer the following multiple-choice questions.
How does a diet high in processed foods contribute to oxidative stress?
A. Processed foods contain high levels of free radicals.
B. Processed foods are rich in antioxidants, reducing oxidative stress.
C. Processed foods lack essential nutrients needed to combat oxidative stress.
D. Processed foods have no impact on oxidative stress levels.
B. Oxidative stress can accelerate the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Sarah, a 55-year-old woman, presents with symptoms of fatigue, memory impairment, and difficulty concentrating. She has a family history of neurodegenerative diseases. Upon examination, it is found that Sarah follows a sedentary lifestyle, has a diet high in processed foods, and has a BMI in the obese range. Laboratory tests reveal elevated markers of oxidative stress. Based on this information, analyze Sarah's condition and answer the following multiple-choice questions.
Considering Sarah's family history of neurodegenerative diseases, what role might oxidative stress play in her symptoms?
A. Neurodegenerative diseases have no connection to oxidative stress.
B. Oxidative stress can accelerate the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
C. Oxidative stress is not associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
D. Oxidative stress can cure neurodegenerative diseases.
C. Programmed cell death
Which of the following best defines apoptosis?
A. Uncontrolled cell growth
B. Cell division
C. Programmed cell death
D. DNA replication
B. Inflammation and tissue damage (C. Cell shrinkage and membrane blebbing)
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of apoptosis?
A. Activation of caspase enzymes
B. Inflammation and tissue damage
C. Cell shrinkage and membrane blebbing
D. Nuclear fragmentation
C. Bcl-2 family
Which protein family plays a key role in regulating apoptosis?
A. Tumor suppressor genes
B. Growth factors
C. Bcl-2 family
D. Cyclins
B. All of the choices
In cancer cells, which of the following is often dysregulated?
A. Apoptotic pathways
B. All of the choices
C. Cell proliferation
D. DNA repair mechanisms
C. Resistance to cell death signals
Which of the following is a hallmark of cancer cells related to apoptosis?
A. Normal response to growth factors
B. Strict control of cell cycle checkpoints
C. Resistance to cell death signals
D. Enhanced DNA repair mechanisms
B. They initiate and execute the apoptotic process
What role do caspase enzymes play in apoptosis?
A. They inhibit DNA replication
B. They initiate and execute the apoptotic process
C. They repair damaged DNA
D. They promote cell division
B. Developmental apoptosis
Which type of apoptosis occurs during normal development to shape tissues and organs?
A. Intrinsic apoptosis
B. Developmental apoptosis
C. Chondrial apoptosis
D. Extrinsic apoptosis
A. Fas/Fas ligand pathway
Which of the following is an example of an extrinsic apoptotic pathway?
A. Fas/Fas ligand pathway
B. Bcl-2 pathway
C. Mitochondrial pathway
D. DNA damage-induced apoptosis
D. Bcl-2 family
Which protein family is often overexpressed in cancer cells and inhibits apoptosis?
A. Tumor suppressor genes
B. Fas ligands
C. Caspases
D. Bcl-2 family
A. Cyclins and CDK’s
What are the key players in regulating the cell cycle?
A. Cyclins and CDK’s
B. DNA damage and checkpoints
C. Tumor suppressor genes
D. Growth factors and receptors
A. YAC, BAC, cosmid, phage, plasmid
Which of the following is the proper order for recombinant DNA vectors in terms of decreasing cloning capacity?
A. YAC, BAC, cosmid, phage, plasmid
B. BAC, cosmid, phage, plasmid, YAC
C. plasmid, phage, cosmid, BAC, YAC
D. phage, cosmid, plasmid, BAC, YAC
B. Southern Blotting
Human linkage analysis by Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism takes advantage of which of the following hybridization technique?
A. Northern Blotting
B. Southern Blotting
C. Immunoblotting
D. Western Blotting
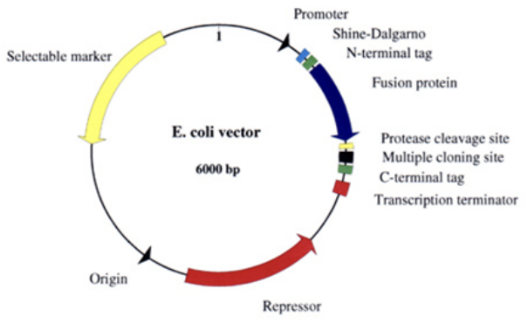
A. functions as ribosome binding site for the expression of gene insert.
What is the function of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence in this expression vector?
A. functions as ribosome binding site for the expression of gene insert.
B. allows insertion of the gene of interest.
C. initiates transcription of the gene insert.
D. acts as a Selectable marker
B. Addition of nucleotides requires free OH group on the 3’ end of the DNA strand
DNA sequencing by Sanger method takes advantage of which property of DNA synthesis to generate a sequencing ladder?
A. Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds
B. Addition of nucleotides requires free OH group on the 3’ end of the DNA strand
C. DNA Polymerase has proofreading capacity
D. DNA has a free 5’ phosphoryl group
D. the disease-causing mutation is at or closely linked to an altered restriction site
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism analysis can only be used to follow the inheritance of a genetic disease if:
A. mutations are outside of the restriction recognition site
B. restriction fragments remain the same in terms of size but their charge changes
C. mRNA probes are used in combination with antibodies
D. the disease-causing mutation is at or closely linked to an altered restriction site
C. TTCGAA
Which of the following could be the recognition site of the restriction enzyme A?
A. ATGCGG
B. GGTATA
C. TTCGAA
D. ATATAC
C. reverse transcriptase
Which enzyme that converts mRNA into cDNA?
A. sigma rho
B. RNA Polymerase
C. reverse transcriptase
D. DNA Polymerase
C. 3
A DNA fragment has 2 restriction sites for MstII endonuclease. How many fragments will be produced if that DNA is cut by such enzyme?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 3
D. 4
A. Antibody
What type of blot can be used for Western Blotting?
A. Antibody
B. mRNA
C. cDNA
D. ssDNA
C. denaturation, annealing, extension
Polymerase chain reaction involves 3 basic steps in which of the following orders?
A. annealing, extension, denaturation
B. denaturation, extension, annealing
C. denaturation, annealing, extension
D. annealing, denaturation, extension
C. Isolation from blood leukocytes followed by PCR amplification and allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) hybridization
Mutation in Sickle cell anemia is best detected by which of the following?
A. Western blot analysis of red blood extracts.
B. DNA isolation from red blood cells followed by PCR and restriction enzyme digestion
C. Isolation from blood leukocytes followed by PCR amplification and allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) hybridization
D. DNA isolation from blood leukocytes followed by DNA sequencing
A. 5’ GAC CT3’
Which of the following primers would allow the copying of the single stranded DNA 5’ ATC AAT AGG TC 3’
A. 5’ GAC CT3’
B. 5’ CTG GA 3’
C. 5’ ATC CC 3’
D. 5’ TAG TT 3’
B. restriction endonuclease and ligase
Which of the following enzymes are necessary for constructing chimeric DNA?
A. DNA polymerase and restriction enzymes
B. restriction endonuclease and ligase
C. helicase and restriction endonuclease
D. ligase and DNA polymerase