Thermal Physics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is the definition of 1 mole?
The amount of substance that contains the same amount that is in 12g of Carbon 12.
Difference between perfect and ideal gases?
Ideal follow Boyles law exactly
Perfect gases follow Boyles law nearly exactly.
What is the equation involving moles, molecules and Na?
N = n Na where N = number of molecules, n = number of moles, Na = 6.02 × 10²3

What is work done from A to B (Don’t need calculator)
Work done = Area under graph (W= Pv - pressure x volume!) (20J)
What are the 8 Assumptions in kinetic theory?
All particles identical or have same mass
Collisions of gas molecules are elastic
Inter molecular forces are negligible (except during collisions)
Volume of molecules is negligible (compared to volume of container)
Time of collisions of molecules on container or each other is negligible
Motion of molecules is random
Large number / many of molecules present
Newtonian mechanics applies
Molecules move in straight lines between collisions
The force that acts during collisions lasts for a much shorter time than between collisions.
Can you calculate the kinetic energy of gas molecules without knowing its mass?
Yes:
K.E = 3/2kT = 3RT/2Na
What are the 2 gas law equations?
For moles:
pV = nRT
For molecules:
pV = NkT
What are the values of both k and R?
k = 1.38 × 10^-23
R = 8.31
What must you do if you are given a value in degrees Celsius and want to use it in an equation?
Convert it to Kelvin!
K = C +273(.15)
What should the average kinetic energy of a gas molecule be around?
10^-21J (VERY SMALL SINCE JUST A MOLECULE NOT SOMETHING BIG)
Why can 2 different gases at the same temperature have molecules with different mean square speeds?
Since K.E = ½ m c² , where c is root mean square speed (squared) and K.E = 3/2kT, for the same temperature, the K.E of the 2 molecules must be the same, however they can have different masses, and therefore the mean square speeds will also be different.
What happens to the pressure of a gas if the temperature of an ideal gas falls? (3 marks)
Decreases, since number of collisions per second on container decreases (as temperature is lower, mean square speed lower, so less frequent)
This reduces the rate of change of momentum
P= F/A, where A is constant so if P decreases, F must also decreases, showing that the number of collisions must decrease
What are 3 things that increases as temperature increases, given constant volume?
Pressure
rms speed
Average kinetic energy
What word is a lot better to use than particles?
Molecules
2 things about the movement of air molecules in a smoke chamber?
Their movement is random
They are moving fast
What equation links K, R and Na?
K = R/Na
Is W = P x V valid?
NO! Its W = P x change in Volume
If volume is fixed, the the change in volume is 0!
Give an expression for the total kinetic energy of the molecules in one mole of an ideal gas at kelvin temperature T.
Equation for 1 MOLECULE = 3/2kT
So for 1 mole (which is 6.02×10²3 molecules, just multiply by Na)
K.E of 1 mole = 3/2 Na KT OR 3/2 RT/Na
Why is total energy = kinetic energy for an ideal gas?
Molecules are assumed to have no potential energy, since there are no attractive forces that occur between them. The intermolecular forces are negligible.
What are intermolecular forces?
The forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules.
Use the kinetic theory of gases to explain why the pressure exerted by an ideal gas increases when it is heated at constant volume.
When an ideal gas is heated at constant volume, the molecules gain more kinetic energy, causing them to move faster. As a result, the molecules collide more frequently and with greater force against the container walls. This increase in the frequency and intensity of collisions leads to a rise in pressure, according to the kinetic theory of gases. It also increases the momentum change per collision.
Why does the volume increase when pressure is constant as temperature increases?
Molecules are travelling faster so there are more collisions per second (greater momentum change per collision)
To keep pressure constant, the volume must increase, so that fewer collisions occur, keeping F the same (P = F/A)
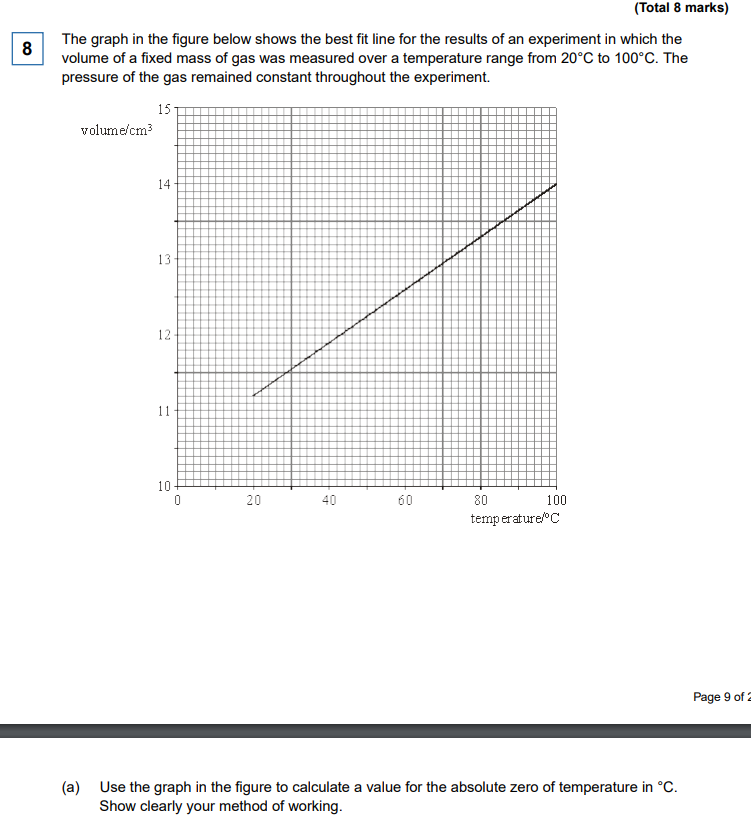
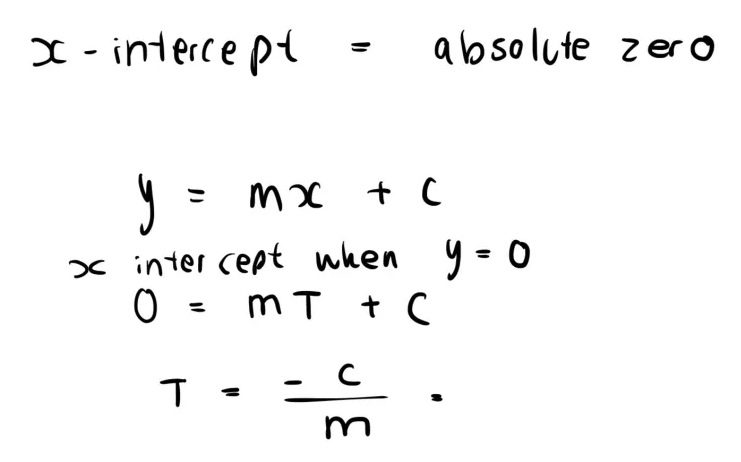
What is molar mass?
The mass of 1 mole of a particular substance
Molar Mass = Mass of substance / Number of moles


The root mean square speed of the gas particles depends on the temperature of the gas but not on its volume. Therefore the speed doesn’t change so its just u (B)
What is internal energy of gas? (2 marks)
The sum of the randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies of all its molecules.
Explain absolute zero in terms of ideal gas laws AND kinetic energy (they are separate things) (2 marks)
Ideal Gas: The temperature at which the volume of a gas extrapolates to 0. (x = -273, y = 0)
Kinetic Energy: The temperature at which the random motion stops (kinetic energy is 0)
What is the equation involving molar mass, mass and moles?
Moles = Mass (of all atoms) /Molar Mass
Mass of 1 particle = Molar Mass/Na
Molar mass is the mass that makes up 1 mole of the specific substance
If 2 different gases are at the same temperature, what is different about their mean kinetic energies?
Nothing, they both have the same mean/average kinetic energy.
Mass and K.E in kinetic theory are not related at all, K.E = 3/2kT - so at a constant temperature, they have the same K.E)
Explain using kinetic theory model why pressure exerted on a containers wall? (3 marks)
Gas molecules move randomly and collide with the container walls, changing their momentum with each collision.
According to Newton's second law, this change in momentum generates a force on the wall (F = mv/t)
Since pressure is defined as force per unit area P = F/A, the collective forces from many collisions across the surface result in the pressure exerted by the gas.
What can be done with the Volume and Temperature independently to reduce the pressure of a gas and why?
the volume could be increased
which increases the time between collisions and so results in less frequent collisions (with the wall so reducing the rate of change of momentum)
OR which increases the area of the piston/wall (and so reduces the pressure)
the temperature could be reduced
which reduces the momentum (change at the wall) since they have less kinetic energy, so less velocity.
If on a Pressure-Temperature graph, with temperature in degrees Celsius, what must you do to find the gradient?
MUST CONVERT IT TO KELVIN since you can’t use Celsius in maths!
What is specific latent heat of vaporisation?
The energy required to change 1kg of material from liquid state to gas state WITHOUT changing its temperature.
What is specific latent heat of fusion?
The energy required to change 1kg of material from solid state to liquid state WITHOUT changing its temperature.
Can you use Celsius in specific heat capacity equation?
Since a change in temperature (ΔT) is the same in degrees Celsius (°C) and kelvin (K), you can directly use Celsius in the equation.
Why does pressure increase when temp increases and volume constant? (3 marks)
Ideas of pressure = F / A and F = rate of change of momentum✓
Mean KE / rms speed / mean speed of air molecules increases✓
More collisions with the inside surface of the football each second✓ Allow reference to ‘Greater change in momentum for each collision’