Pulmonary embolism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the different types of pulmonary embolism?
Blood clot (thrombus) → >90%
Fat globule (fat embolism)
Bubble of air/gas (gas embolism)
Foreign material (tumour cells or bacteria)
virchows triad
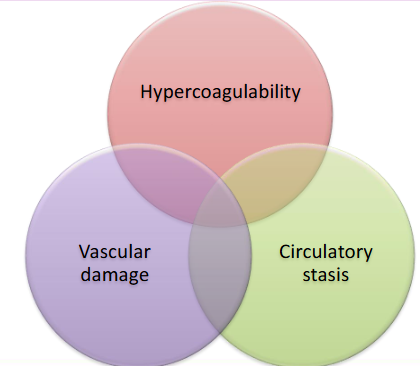
What can cause hypercoagulability?
Thrombophilia
Pregnancy (post-partum)
Infection/sepsis
Autoimmune disease
Dehydration
Post surgery/trauma
What can cause vascular damage?
Injury/trauma
Catheter
Venepuncture
Atherosclerosis
What can cause circulatory problems?
Immobility
Venous obstruction
Varicose veins
Low heart rate
Atrial fibrillation
Congenital conditions
Risk factors for Pulmonary embolism
THROMBOSIS
Trauma or history of travel
Hospitalization and hormones
Relatives, family history
Old age
Malignancy
long Bone fractures
Obesity and obstetrics
Sand Smoking
Immobilization
other Sickness (nephrotic syndrome)
What does pulmonary embolism mechanical obstruction lead to?
Reduced perfusion V/Q>1 (in the affected area) → Blood get re-directed V/Q<1 (in other areas of lungs) → Results in low pO2 (hypoxaemia)→ hyperventilation→ hypocapnia→ respiratory alkalosis
What does pulmonary embolism inflammatory response lead to?
Endothelial injury → endothelin→ pulmonary oedema→ Pleural effusion→crackles/rales
How does pleural effusion affect the heart?
mechanical obstruction + inflammatory response → pulmonary A hypertension →
Increase RV afterload will cause:
Increased venous pressure→ Jugular vein distension
Septum gets pushed→ septal dyskinesia→ affecting LV
Eventually reduce LV preload→ Reduced CO→ Reduced BP→ Syncope
Increased HR to correct reduced Bp
Low LV preload→ reduced coronary circulation→ Ischemia → MI
Signs of pulmonary embolism
tachypnoea
rales/crackles
tachycardia
change in heart sounds
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism
dyspnoea
pleuratic chest pain
cough
haemoptosis
What are the different classifications of pulmonary embolism?
Time:
Acute: Immediately after obstruction
Subacute: within days or weeks after obstruction
Chronic: Over many years, development of pulmonary hypertension (chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, CTEPH)
hemodynamic stability:
Hemodynamically unstable PE: present with hypotension → high risk
Hemodynamically stable PE: may be associated right ventricular strain → risk if RV strain
How can you diagnose a pulmonary embolism?
Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiogram (CTPA)
D-Dimer test: if presence of D-Dimer in blood = there is a clot but don’t know where
Ventilation perfusion scan
→ Air circulation: breathe in radioactive gas and the machine scan the air flow
→ Blood circulation: Radioactive albumin injected into a vein and the machine scans the lungs as blood flows through them
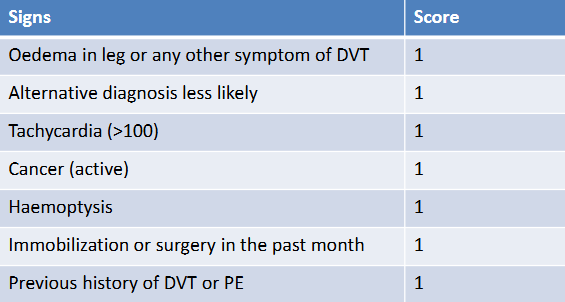
Wells criteria to diagnose pulmonary embolism (using signs)
If score >1, PE likely
If score<1, PE unlikely
General/ immediate treatment of pulmonary embolism
Oxygen supplementation
IV Fluids (restoring perfusion if unstable)
Vasopressor support (if unstable
Stabilise airway with intubation and mechanical ventilation (if necessary)
How does fibrinolysis happen?
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is released from endothelial cells (stimulated by thrombin)
tPA cleaves plasminogen → plasmin
plasmin cleaves fibrin → releases D-dimer + fibrinogen
How does a clot form?
vWF activates platelets → release ADP, seratonin, thromboxane A2
activate GPIIb/IIIa receptor →platelet can bind to fibrinogen
→ platelet plug → activate clotting factors (extrinsic + intrinsic): prothrombin → thrombin → cleaves fibrinogen → fibrin
** requires Ca2+ and K+
How do we prevent coagulation?
endothelial cells secrete:
NO + prostaglandins → inhibit platalets
heparin sulphate → activate anti thrombin III → inhibit clotting factors
thrombomodulin → modulates thrombin → activates protein C → binds to protein S → inhibit clotting factors
What anticoagulant drugs can we use to prevent clot formation?
Warafin + heparin
Vitamin K antagonist → inhibit vit k
inhibits factor II, VII, IX, X
also inhibits Protein C so we need more heparin (natural anticoagulant)
Direct oral anticoagulants
inhibit thrombin/prothrombin
Some inhibit factor Xa
what pathway does INR test?
extrinsic pathway
time taken for blood to clot compared to normal time
what test tests for intrinsic pathway?
aPTT test
How do you treat blood clots?
Thrombolytic agents: tPA activator, Streptokinase/urokinase → lyse existing blood clot
Inferior vena cava filters: prevent clots entering the heart and Pulmonary A
Percutaneous pulmonary embolus mechanical thrombectomy: surgical removal of the emboli