Ontario Planning Law: Hierarchy, Legislation, and Official Plans
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
What is the primary legislation governing planning in Ontario?
The Planning Act
What is the constitutional basis for Ontario's planning powers?
The province controls 'property and civil rights' and municipalities have powers granted by the province.
What is the purpose of the Planning Act?
To manage growth, balance private rights with public interest, protect resources, and ensure orderly development and public participation.
What are the key components governed by the Planning Act?
Official plans, zoning, subdivisions, consents, variances, and site plan control.
What is the role of the Provincial Policy Statement (PPS) in Ontario planning?
Municipal decisions must be consistent with the PPS.
What are some examples of provincial plans that municipalities must conform to?
Greenbelt Plan, Niagara Escarpment Plan, Growth Plan for Northern Ontario.
What are zoning by-laws?
Planning instruments that set out detailed regulations on uses, density, height, and setbacks.
What principle ensures that planning decisions align with higher-level policies?
Consistency and conformity.
What is the role of the Ontario Land Tribunal (OLT)?
The OLT serves as the appeal body for most planning-related appeals.
What is the significance of Minister's Zoning Orders (MZOs)?
MZOs allow the Province and municipalities to fast-track growth.
What is the duty to consult in planning law?
It requires notice to be given to Chiefs within 1 kilometer of a development proposal subject to an official plan or zoning by-law amendment.
What does the term 'stare decisis' refer to?
The legal principle of determining points in litigation according to precedent.
What is the federal system in Canada?
A system where law-making power is divided between federal and provincial governments.
What does Section 52(1) of the Constitution Act, 1867 state?
The Constitution is the supreme law of Canada; any inconsistent law is of no force or effect.
What areas does the federal government legislate on according to the Constitution?
Key areas include peace, order, good government, criminal law, and trade.
What are some key areas of provincial powers under the Constitution?
Property and civil rights, administration of justice, municipal institutions, and education.
What is the significance of the Development Charges Act 1997?
It is significant legislation related to funding municipal infrastructure through development charges.
What is the role of committees of adjustment in Ontario planning?
They handle minor variances and land severances.
What does the term 'obiter dicta' refer to?
Comments made by a judge in a legal opinion that are not essential to the decision.
What is the importance of case law in planning law?
Case law helps interpret statutes and establishes legal precedents for future cases.
What is the purpose of regulations such as O. Reg. 543/06?
They provide specific rules for official plans and plan amendments.
What does 'mandatory language' in legislation imply?
It indicates requirements that must be followed, often using terms like 'shall' or 'must'.
What does 'discretionary language' in legislation imply?
It indicates options that may be followed, often using the term 'may'.
What is the role of the Municipal Act, 2001 in Ontario's planning framework?
It outlines the powers and responsibilities of municipalities in Ontario.
What do Sections 91 and 92 of the Constitution describe?
They describe federal and provincial powers as exclusive.
What is meant by 'watertight compartments' in early constitutional cases?
It refers to the idea that federal and provincial powers were seen as completely separate and distinct.
What is concurrent jurisdiction?
It allows both federal and provincial levels to legislate on certain matters, such as old age pensions and supplementary benefits.
In the case of a conflict between federal and provincial laws, which laws prevail?
Federal laws prevail in a conflict.
How is the jurisdiction over the environment determined?
Jurisdiction depends on the specific aspect, as the environment was not explicitly listed in 1867.
What is the role of municipalities under the Constitution?
Municipalities are not a separate level of government; they are 'creatures of the province' and derive their powers from provincial legislation.
What types of matters are municipalities typically limited to?
Municipalities are usually limited to local matters such as zoning, building permits, property taxes, and local services.
What are the three main ways to challenge legislation?
1. Validity 2. Applicability 3. Operability
What does the validity challenge assess?
It assesses whether the law is within the enacting government's power using doctrines like Pith and Substance.
What is the purpose of the Pith and Substance doctrine?
To determine the true nature of a law to see which level of government has authority.
What is the significance of the Double Aspect doctrine?
It reflects co-operative federalism, allowing both levels of government to legislate on the same subject if there are no conflicts.
What does Interjurisdictional Immunity protect?
It protects the core of a jurisdiction's power from intrusion by other levels of government.
What is the effect of federal paramountcy?
When valid federal and provincial laws conflict, federal law prevails, and the provincial law becomes inoperative to the extent of the conflict.
What is the two-step test for Pith and Substance?
1. Characterize the Law 2. Classify the Law's essential character to the correct head of power.
What is meant by 'intra vires' and 'ultra vires'?
'Intra vires' means within jurisdiction, while 'ultra vires' means outside jurisdiction.
What did the case Mississauga (City) v. GTAA establish?
It established that Parliament's exclusive jurisdiction over aeronautics barred Mississauga from imposing municipal requirements on federal undertakings.
What was the outcome of Canada Post Corporation v. Hamilton?
Hamilton's road-permit by-law was inoperative against Canada Post due to federal paramountcy.
What can municipalities do under their 'general welfare' powers?
They can restrict non-essential pesticide use, provided it allows for dual compliance with federal and provincial regimes.
What is the significance of s.35 of the Constitution regarding Indigenous rights?
It enshrines treaty rights and recognizes Indigenous interests in land, creating a duty to consult.
How many levels of court are there in Ontario?
There are four levels of court: Ontario Court of Justice, Superior Court, Ontario Court of Appeal, and the Supreme Court of Canada.
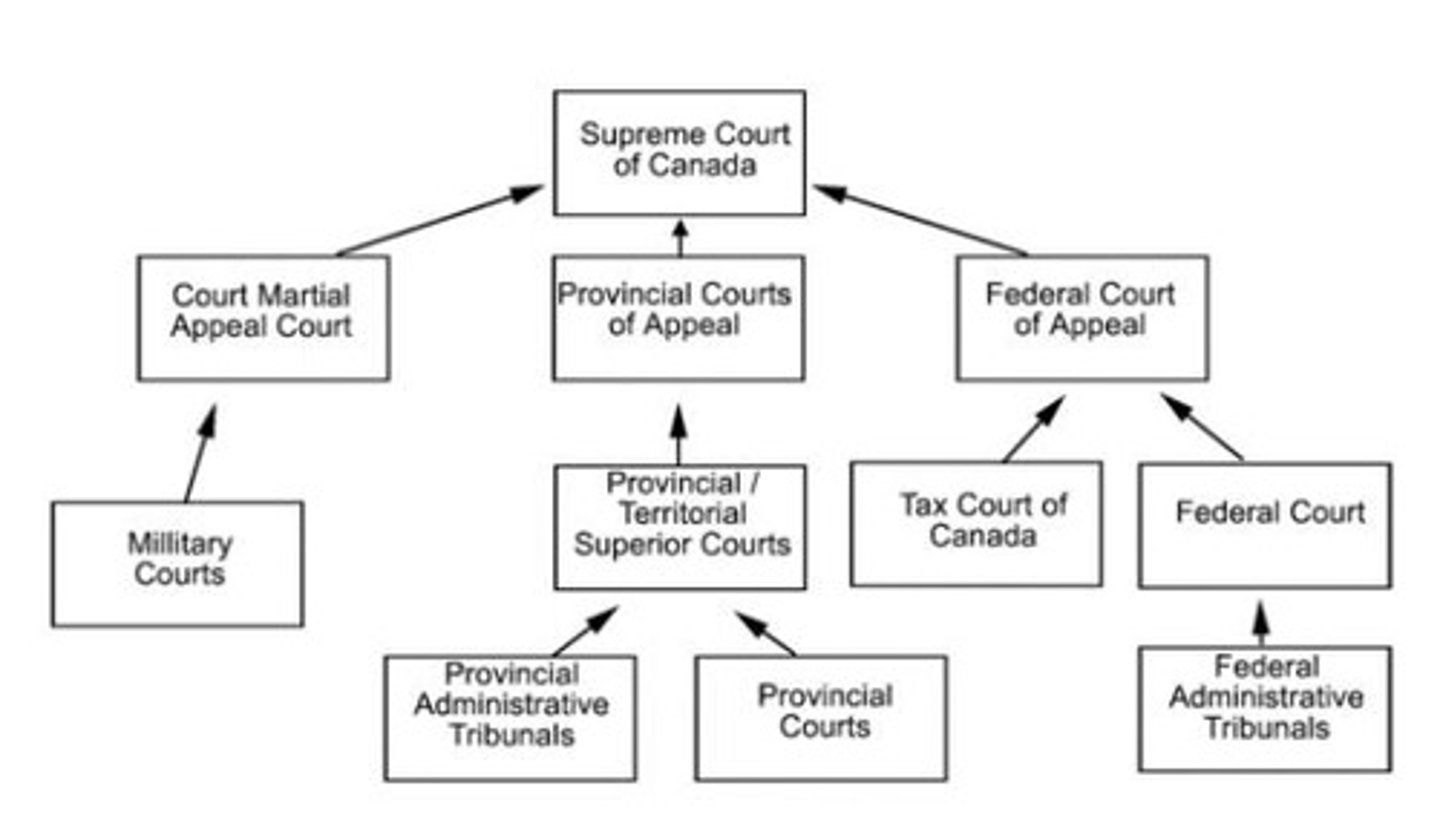
What types of matters does the Ontario Court of Justice handle?
It handles certain criminal, family, and mental health matters.
What is the role of the Superior Court in Ontario?
It hears leave to appeal matters from the Ontario Land Tribunal and judicial reviews of municipal and administrative decisions.
What is the function of the Ontario Court of Appeal?
It hears appeals from lower courts based on the facts of those cases.
What is required to appeal cases to the Supreme Court of Canada?
Leave to appeal is needed, which is difficult to obtain and focuses on cases of national or public interest.
What is the primary legislation governing municipalities in Ontario?
The Municipal Act, 2001.
How did the Municipal Act, 2001 change in 2011?
It became less prescriptive, providing more flexibility for municipalities to govern local matters.
What are some specific municipal powers outlined in the Municipal Act?
Powers include managing highways, bridges, public works, utilities, parks, health and safety.
What is the role of municipal councils in planning decisions?
Councils adopt by-laws and review development applications, with rights of appeal depending on submissions made.
What is the Ontario Land Tribunal (OLT)?
A quasi-judicial tribunal established by the Ontario Land Tribunal Act, 2021, that hears appeals under the Planning Act.
What is the guiding principle of the Ontario Land Tribunal?
To ensure fair, just, and expedited resolutions of appeals.
What does the Planning Act aim to promote?
Sustainable economic development, fair planning processes, and integration of provincial interests in municipal planning.
What are some matters of provincial interest according to the Planning Act?
Protection of ecological systems, agricultural resources, conservation of natural resources, and public health and safety.
What is the significance of 'shall have regard to' in the Planning Act?
It requires serious consideration of matters of provincial interest in planning decisions.
What is the role of the Minister regarding policy statements in the Planning Act?
The Minister may issue policy statements that require approval and must confer with interested parties before issuance.
What is the purpose of the Provincial Planning Statement, 2024?
To outline provincial interests and guide municipal planning decisions.
What is the Greenbelt Plan?
A provincial plan aimed at protecting green spaces and managing urban development in Ontario.
What is required for a planning decision to be made by the Tribunal?
The Tribunal must consider any relevant information and decisions made by municipal councils regarding the same planning matter.
What are the responsibilities of the OLT under sections 8 and 9?
The OLT has exclusive jurisdiction to determine questions of law and fact and can make orders or give directions.
What is the process for consolidating appeals in the OLT?
Section 21 allows for the consolidation of appeals into one hearing.
What is the role of local councillors in the planning process?
They are the first line of review for development applications before consideration by Council.
What is the significance of the Planning Act's section 2?
It outlines the matters of provincial interest that must be considered in planning decisions.
What does the Planning Act say about accessibility?
It emphasizes the need for accessibility for persons with disabilities in all facilities and services related to planning.
What is the importance of public submissions in the planning process?
Public submissions must be made before the adoption or approval of a by-law to have appeal rights under the Planning Act.
What is the role of the OLT in relation to municipal councils?
The OLT sits in place of a municipal council once an appeal is filed.
What does the Planning Act require for the development of communities?
It promotes the orderly development of safe and healthy communities.
What are the requirements for municipalities regarding policy statements?
Municipalities must notify local boards of any policy statements they receive.
What must decisions of municipal councils and planning boards be consistent with?
Policy statements issued under provincial regulations that are in effect on the date of the decision.
What is the central focus of the Provincial Policy Statements 2024?
Housing supply and affordability.
What does the Provincial Policy Statements 2024 replace?
PPS 2020 and the Growth Plan (2019).
What are the core themes of the Provincial Policy Statements 2024?
Housing supply & affordability, growth management, economic development, environment & climate change, infrastructure coordination, and protection of prime agriculture and aggregates.
How should the Provincial Planning Statement be interpreted?
It should be read in its entirety, considering all relevant policies together without implied priority.
What is the importance of specific policy language in the PPS?
It provides direction on implementation and indicates whether policies are directives, limitations, or supportive.
What are the criteria for allowing settlement area expansions according to PPS 2024?
Settlement areas are the focus of growth and must accommodate a range of land uses to meet projected needs.
What is the goal regarding employment areas in the PPS 2024?
To promote employment uses, address land use compatibility, and preserve areas for current and future uses.
What does the term 'area of employment' refer to in the Planning Act?
An area of land designated in an official plan for clusters of business and economic uses.
What are the types of uses included in an area of employment?
Manufacturing, research and development related to manufacturing, warehousing, and associated retail and office uses.
What is the stance of PPS 2024 on natural heritage and agriculture?
It aims to protect natural features and prime agricultural lands for the long term.
What is required for mineral aggregate resources according to PPS 2024?
They must be protected for long-term use and extraction should minimize social, economic, and environmental impacts.
What does PPS 2024 say about cultural heritage?
It emphasizes the conservation of protected heritage properties, including built heritage resources and cultural landscapes.
What is the role of municipalities regarding watershed planning?
Municipalities must undertake watershed planning to restrict development near sensitive water features.
What does the PPS state about residential intensification?
It encourages residential intensification on underdeveloped lands, such as shopping centers.
What does 'complete communities' refer to in the context of PPS 2024?
Communities that improve accessibility and social equity while accommodating a range of land uses.
What is the significance of comments and submissions in planning matters?
They must be consistent with the policy statements and conform to provincial plans in effect at the time they are provided.
What does the PPS 2024 indicate about energy conservation?
It includes provisions for energy conservation and addressing climate change in planning.
What is the approach to agricultural systems in PPS 2024?
Planning authorities are to use an agricultural system approach to protect prime agricultural lands.
What is the importance of balancing policies in the PPS?
Decision-makers must consider how relevant policies work together rather than applying them in isolation.
What does PPS 2024 say about the economic base in rural areas?
It promotes diversification of the economic base and sustainable tourism while protecting agricultural uses.
What is the directive regarding development and site alteration?
Development and site alteration shall not be permitted in certain contexts as specified by the policies.
What is an Official Plan?
A vision document for a municipal policy framework to ensure orderly development in all aspects of development in a municipality.
What does the Greenbelt Act, 2005 authorize?
It authorizes the establishment of growth boundaries and planning frameworks for land use.
What is the primary focus of the Growth Plan?
It prioritizes agriculture as the predominant land use and the environment as the natural system.
What must be considered when developing lands with archaeological resources?
No development is allowed unless heritage attributes will be conserved.
What is the purpose of engaging with indigenous communities in planning?
To ensure their interests are considered in development decisions.
What are the three key sections integrated into the planning framework?
Section 2: Provincial interest in planning, Section 3: Binding provincial policy framework, PPS 2024: Provincial priorities.
What is the significance of the Provincial Policy Statement 2024 (PPS)?
It outlines provincial priorities regarding housing and growth in planning.
What is the hierarchy of Official Plans?
Provincial Policy Statement, Upper-tier Official Plans, Lower-tier Official Plans.