IB Biology Year 1 - Transport & Biomolecules
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
When the temperature of an enzyme controlled reaction was increased from 15°C to 30°C the reaction rate also increased. Why?
The enzymes have more kinetic energy so collide with more substrate molecules.
How do R group interactions contribute to protein structure?
I. Determining the sequence of amino acids in the primary structure
II. Stabilizing beta pleated sheets in the secondary structure
III. Stabilizing further foldings of a polypeptide into a tertiary structure
III only
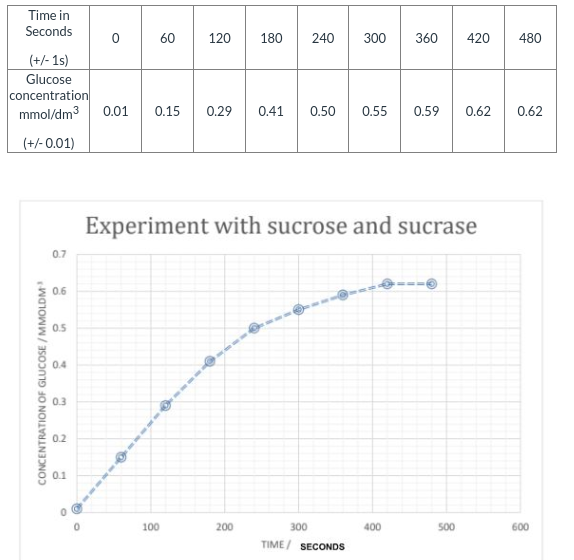
Sucrase is an enzyme which hydrolyses the disaccharide sucrose into the products, glucose and fructose. In an experiment, 10 cm3 of 1% sucrase was added to 10 cm3 of a 1% sucrose solution in a 50 cm3 beaker. Every minute, the concentration of glucose was measured using a glucose meter. The meter gives direct readings of glucose concentrations in mmol/dm³
The raw data is given in the table. The graph below shows the data for these results as a scatter graph.
1. Suggest a more valid title for the graph in this experiment. (1 point)
2. List two variables that should be controlled in this experiment. (2 points)
3. Using the table of results as well as the graph, discuss if the data collected indicate that the rate of reaction is constant during the first three minutes (180 seconds). (1 point)
4. Use the data table to calculate the rate of reaction in the first 3 minutes. (2 points)
5. State why it is not necessary to collect data after the 480 second mark. (1 point)
6. Predict, with reason, the fructose concentration in the reaction mixture at 360 seconds. (2 points)
1. A more valid title would be: the effect of sucrase on sucrose and glucose concentration.
2. The amount and the concentrations of the sucrase and sucrose solutions should be control variables.
3. The results show that the graph is slowly decreasing from the times 0-60, 60-120, and 120-180 seconds; thus, the rate is not constant.
4. The rate of reaction in the first 3 minutes is 0.002 seconds.
5. The rate of reactions plateaus, indicating that there is no significant change afterwords---the rate remains relatively the same.
6. 0.59/0.6 mmol/dm3.
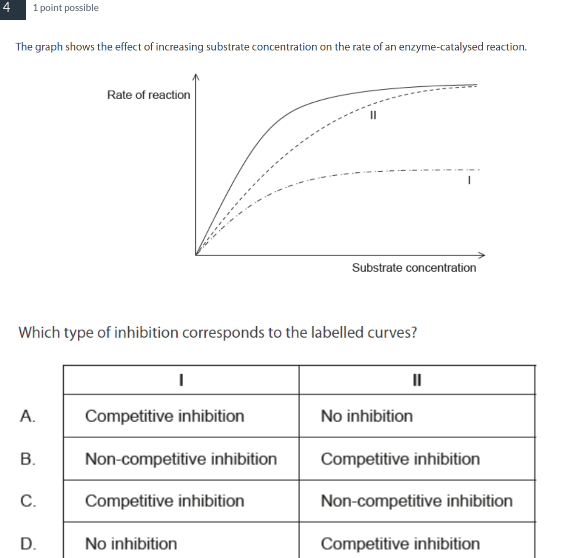
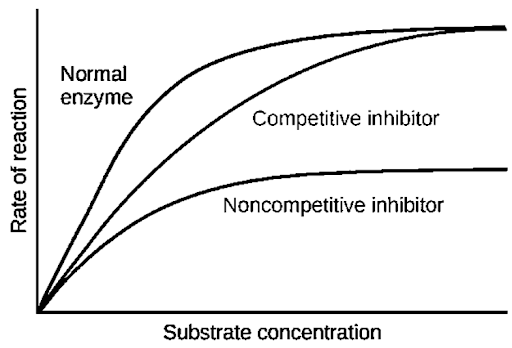
B
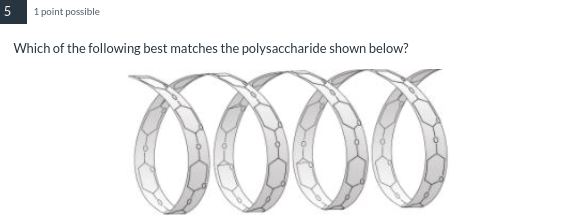
used for energy storage in plants
Explain how high heat and pH extremes affect the structure and function of proteins.
High heat and pH denature the enzyme, irreversibly changing the shape of its active site and making it unable to bind with a substrate; therefore, reaction speeds slow down.
What is/are required for facilitated diffusion?
I. A concentration gradient
II. ATP
III. A channel protein
I and III
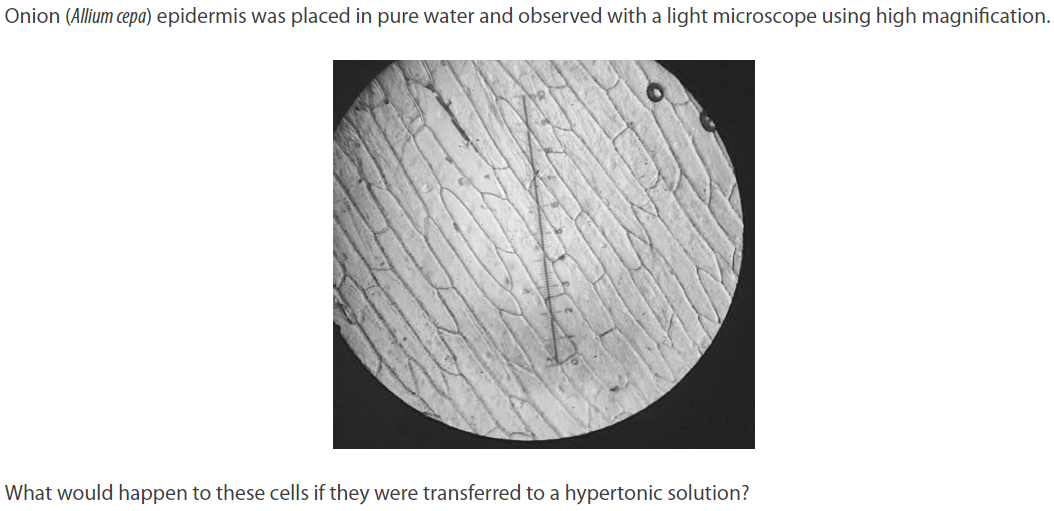
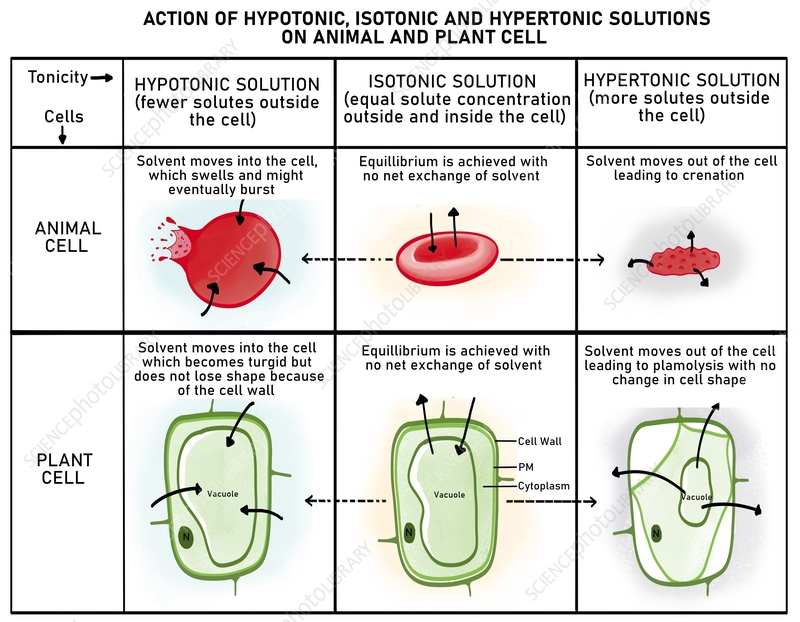
Cell membranes would detach from walls at some points.
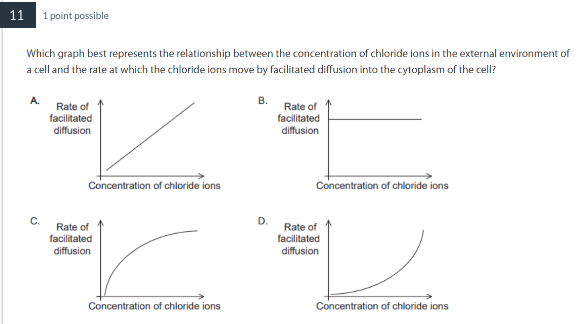
Which statement applies to enzymes?
Enzyme function depends on collisions between substrate and active sites.
C b/c there will be many substrates in the beginning and so enzymes can catalyze with them. However, overtime, all of the enzymes will be occupied with a substrate so the rate of reactions will slow down and level off at one point.
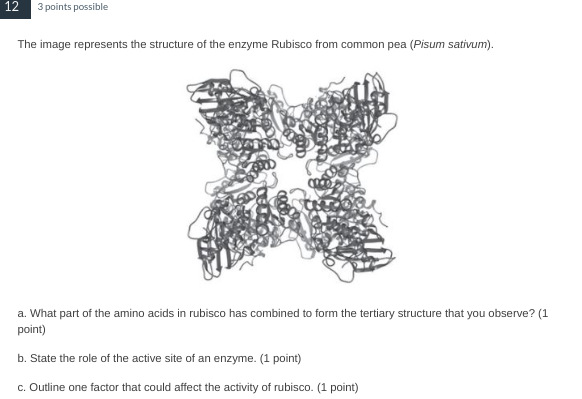
a. The R group of rubisco's amino acids have combined to form the tertiary structure.
b. The role of the active site of an enzyme is to bind with the substrate and break it down/build it up into a usable product.
c. An competitive inhibitor could bind with the active site, prevent substrates from binding with rubisco's active site.
Which process is an example of catabolism?
Hydrolysis of protein
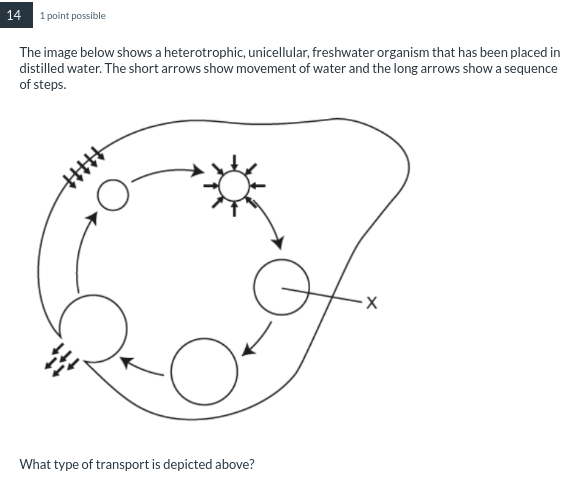
exocytosis
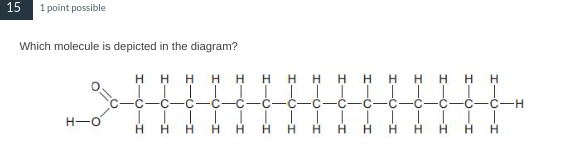
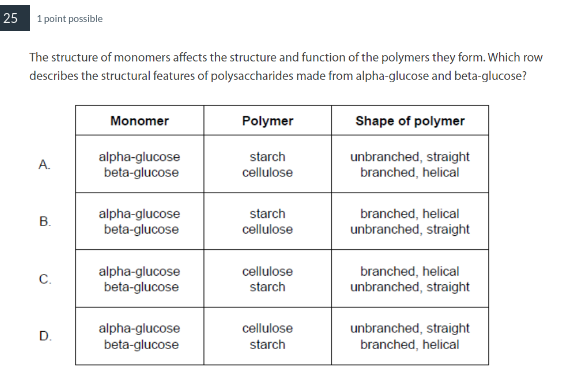
A saturated fatty acid
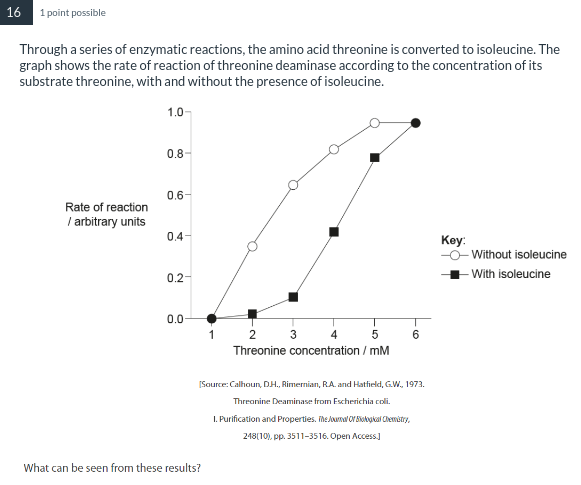
Isoleucine inhibits threonine deaminase at low concentrations of threonine.
Proteins are polymers with a large range of structures and functions because...
They can be folded into unique three dimensional shapes
Carbon is the basis of biological polymers because…
It can form chains by bonding to other carbon atoms
It can form four covalent bonds

It occupies the active site of alcohol dehydrogenase I, preventing ethylene glycol from binding.
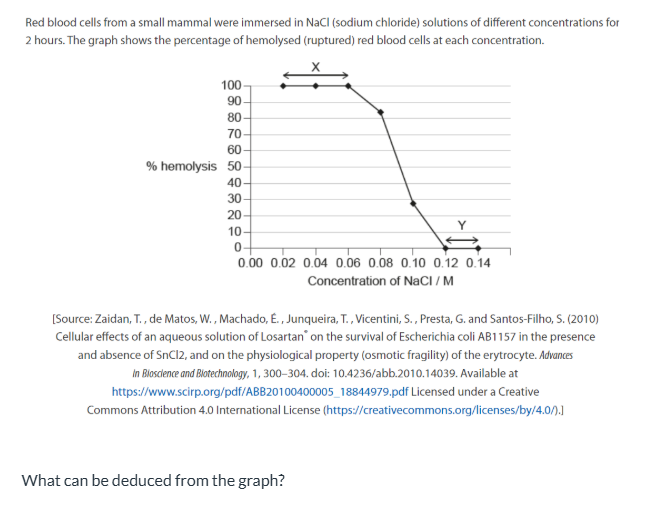
At X, water has moved by osmosis into the red blood cells.
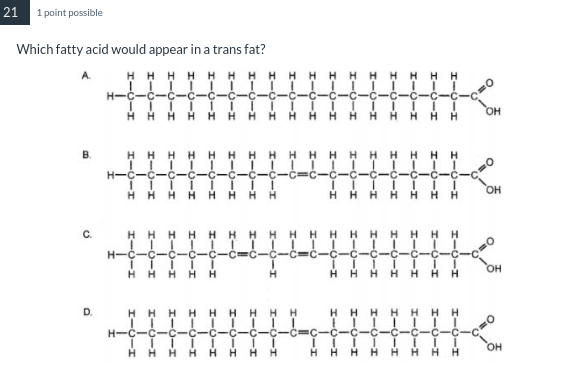
D
A human organ is being prepared for transplant. In what type of solution must it be bathed?
A solution with the same osmolarity as the organ tissue
When a dipeptide is formed from two amino acids which type of reaction takes place?
Condensation (aka dehydration synthesis)
Knowing the water potential and solute potential of pure water (distilled), what must the pressure potential be?
0
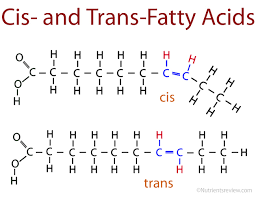
B
Which statement applies to the tertiary structure of enzymes?
A change in the tertiary structure of an enzyme may result in a change in the structure of the active site.
What distinguishes cellulose from glycogen and starch?
Cellulose has a structural role whereas starch and glycogen function in energy storage.
Distinguish the difference between carbohydrates and lipids.
Carbohydrates
Short term energy
C6H12O6
Galactose & fructose
Lipids
C10H20O2
Long term energy
Glycerol and fatty acids
Which molecule contains beta glucose subunits?
Cellulose
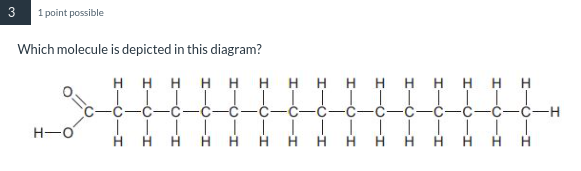
A saturated fat
Which molecule would be most suitable for long-term energy storage in humans?
Lipids!!
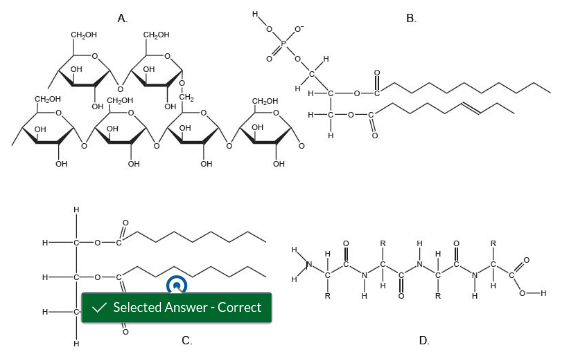
Which reaction would be used to attach a fatty acid to a glycerol backbone?
Condensation (dehydration synthesis)
This molecule is the stored form of glucose in animal cells.
Glycogen
What distinguishes cellulose from glycogen and starch?
Cellulose has a structural role whereas starch and glycogen function in energy storage.
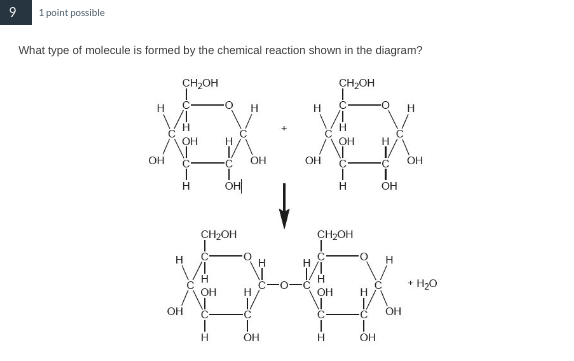
Disaccharide
What is the name of the bond that forms between a glycerol molecule and a fatty acid tail during an anabolic reaction?
The name of the bonds is ester bonds.
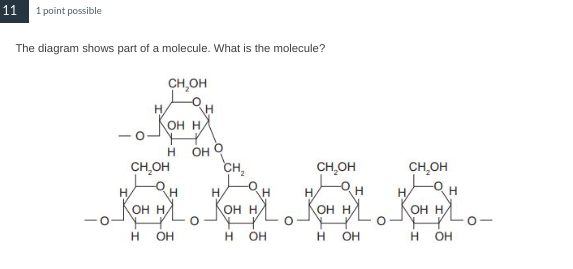
Amylopectin
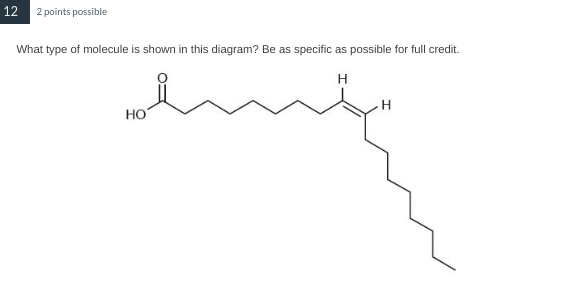
This molecule is a cis-monounsaturated fat.
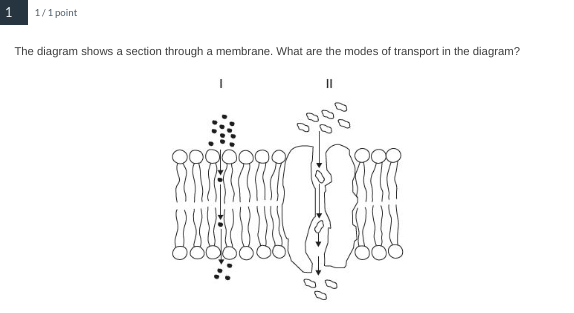
I- diffusion, II- facilitated diffusion
Distinguish between facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Facilitated diffusion
Movement from high to low concentrations
Passive
Protein channels
Active transport
Requires energy
Movement from low to high concentrations
Protein pumps
How is water potential determined?
Sum of solute potential and pressure potential
A human organ is being prepared for transplant. In what type of solution must it be bathed?
A solution with the same osmolarity as the organ tissue
The salt concentration inside an animal cell is 1.8 %. The salt concentration in the surrounding medium becomes 5% due to external factors. What will be the likely response for the animal cell?
Because the concentration of solute in the cell is hypertonic when compared to the concentration of solute in the solution, the animal cell will lose water, shrivel, and die.
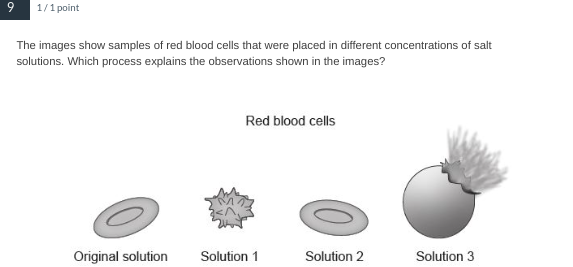
Osmosis
fyi - solution 1 is hypertonic, solution 2 is isotonic, and solution 3 is hypotonic