UH Biol 3301 Exam 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio
Expected F2 ratio of dihybrid cross
No gene interaction/absence of epistasis
9:7 ratio
complementary gene action
15:1 ratio
in an examination of progeny from dihybrid crosses, this could indicate a gene duplication event
9:6:1 ratio
dominant gene interaction
A 9:3:4 ratio in the F2 indicates a type of gene interaction known as
recessive epistasis
12:3:1 ratio
dominant epistasis
13:3 ratio
Dominant Supression
1:1:1:1 ratio would be expected for
unlinked genes
result of heterozygous & homozygous recessive parent
Haplosufficient
For a particular gene, one functioning copy is enough for a wildtype phenotype.
haploinsufficient
For a particular gene, one functioning copy is not enough for a wildtype phenotype.
loss of function mutation
Causes the complete or partial absence of normal function.
Mutant alleles are usually RECESSIVE
often lethal in HOMOZYGOUS state.
gain of function mutation
Produces a new trait or causes a trait to appear in inappropriate areas or at inappropriate times in development.
ALMOST ALWAYS DOMINANT; produces dominant phenotype in mutant heterozygous
in the right conditions can be recessive
Lethal in HOMOZYGOUS state
loss of function mutation can be caused by
1.) Deletion of ALL or Part of a gene
2.) Gene product that lacks activity
3.) mutational events ( those that block transcription)
A partial loss-of-function mutation is
hypomorphic means "reduced form" aka a "leaky mutation"
dominant negative mutation
A heterozygote produces a nonfunctional altered protein that also prevents the normal gene product from functioning
Hypermorphic mutation
(GAIN OF FUNCTION) = overdrive
-extremely rare
-usually dominant
pushes process fwd more rapidly
or for too long
or in the wrong place
or @ the wrong time
usually the result of a regulatory gene(not receiving signal to stop) an Increase in gene trasncription.
neomorphic mutation
a mutant expressing a new or novel function not seen in the wild type
usually dominant
homozygote more severe than heterozygote phenotype.
incomplete dominance
A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles, inherited from the parents, are neither dominant nor recessive. The resulting offspring have a phenotype that is different from parent
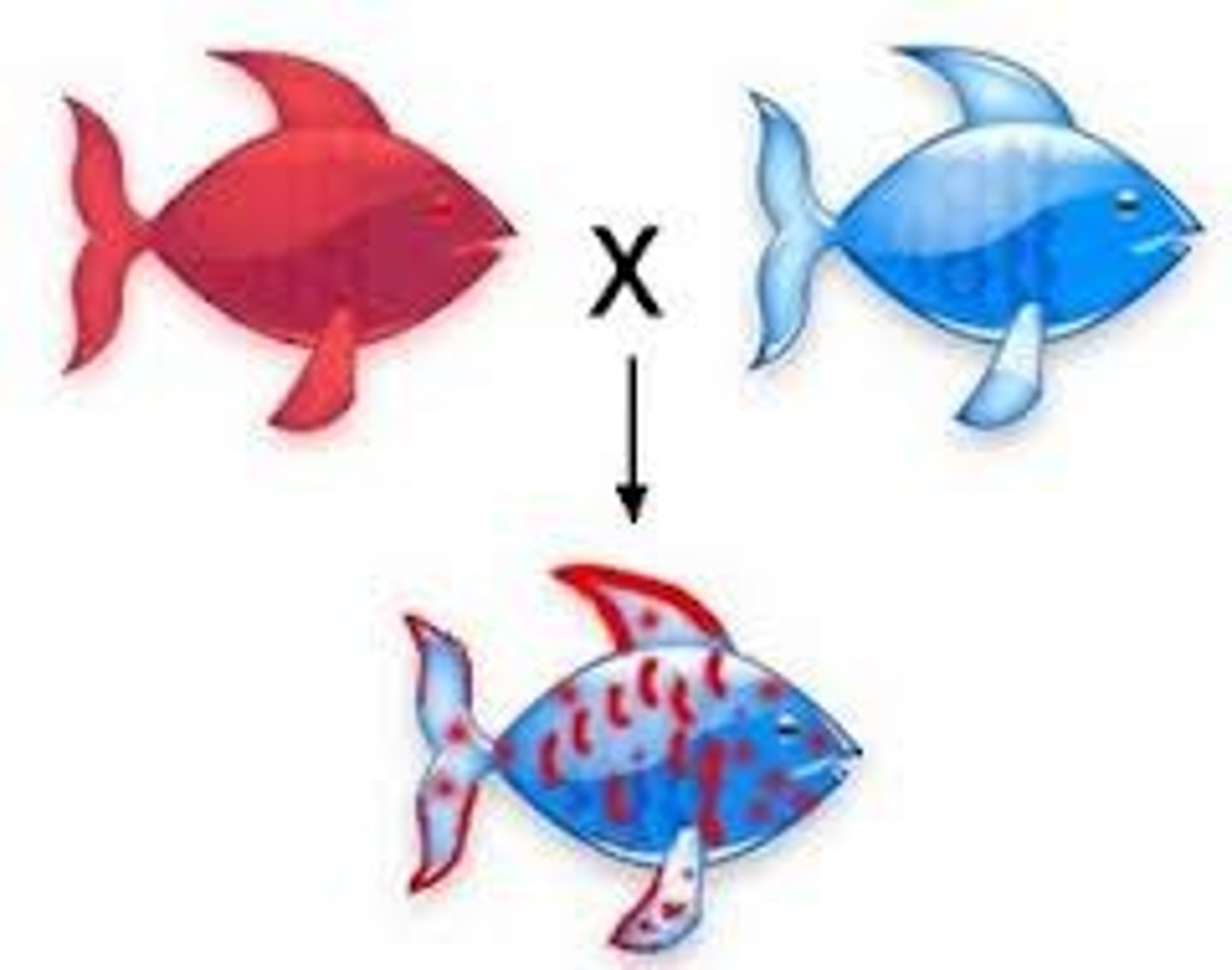
Codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
Penetrance
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that actually displays the phenotype associated with the genotype.
incomplete penetrance
the genotype does not always produce the expected phenotype
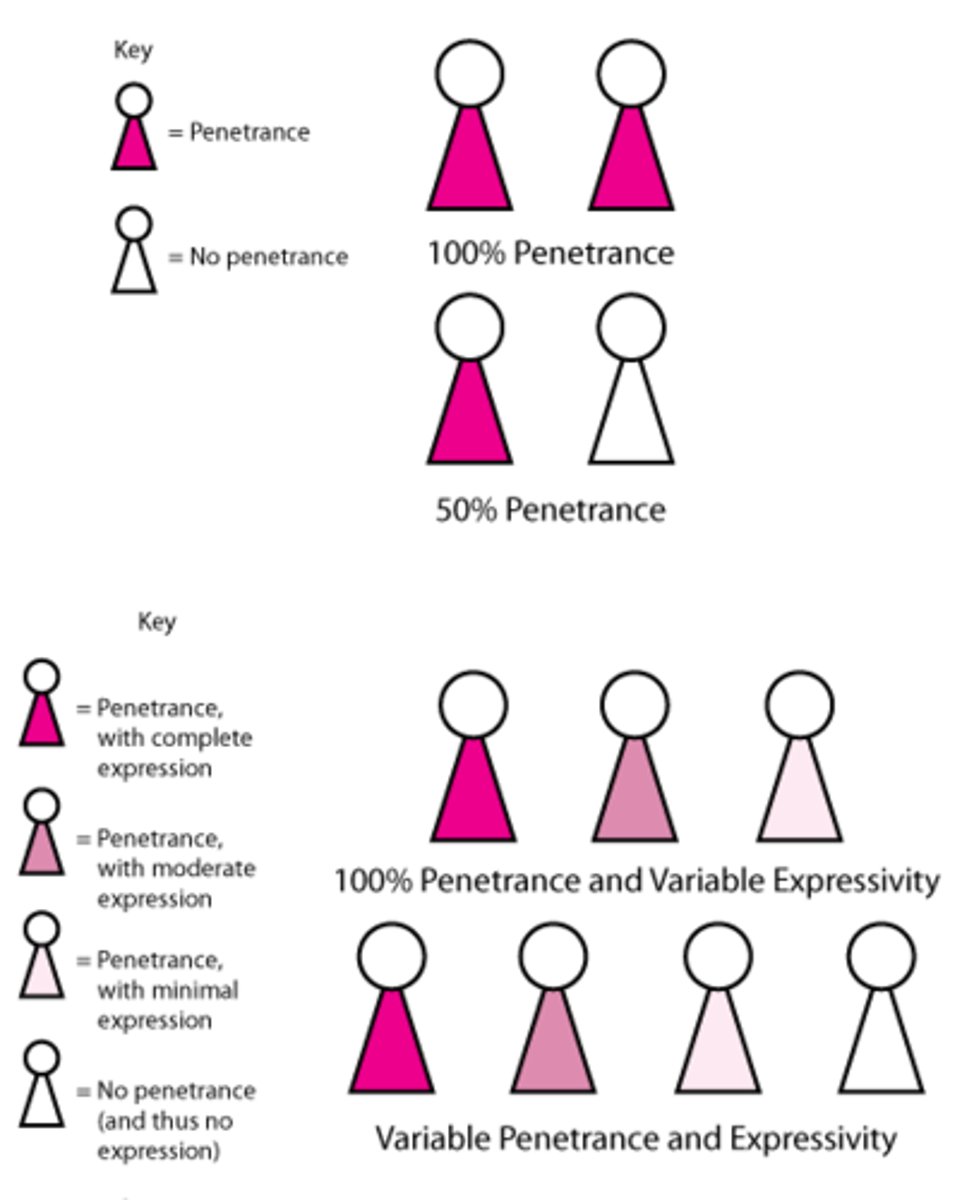
nonpenetrant
when an organism with a particular genotype fails to produce the corresponding phenotype
variable expressivity
individuals with the same genotype have related phenotypes that vary in intensity
interactions between alleles produce
dominant relationship
Hardy-Weinberg equation
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
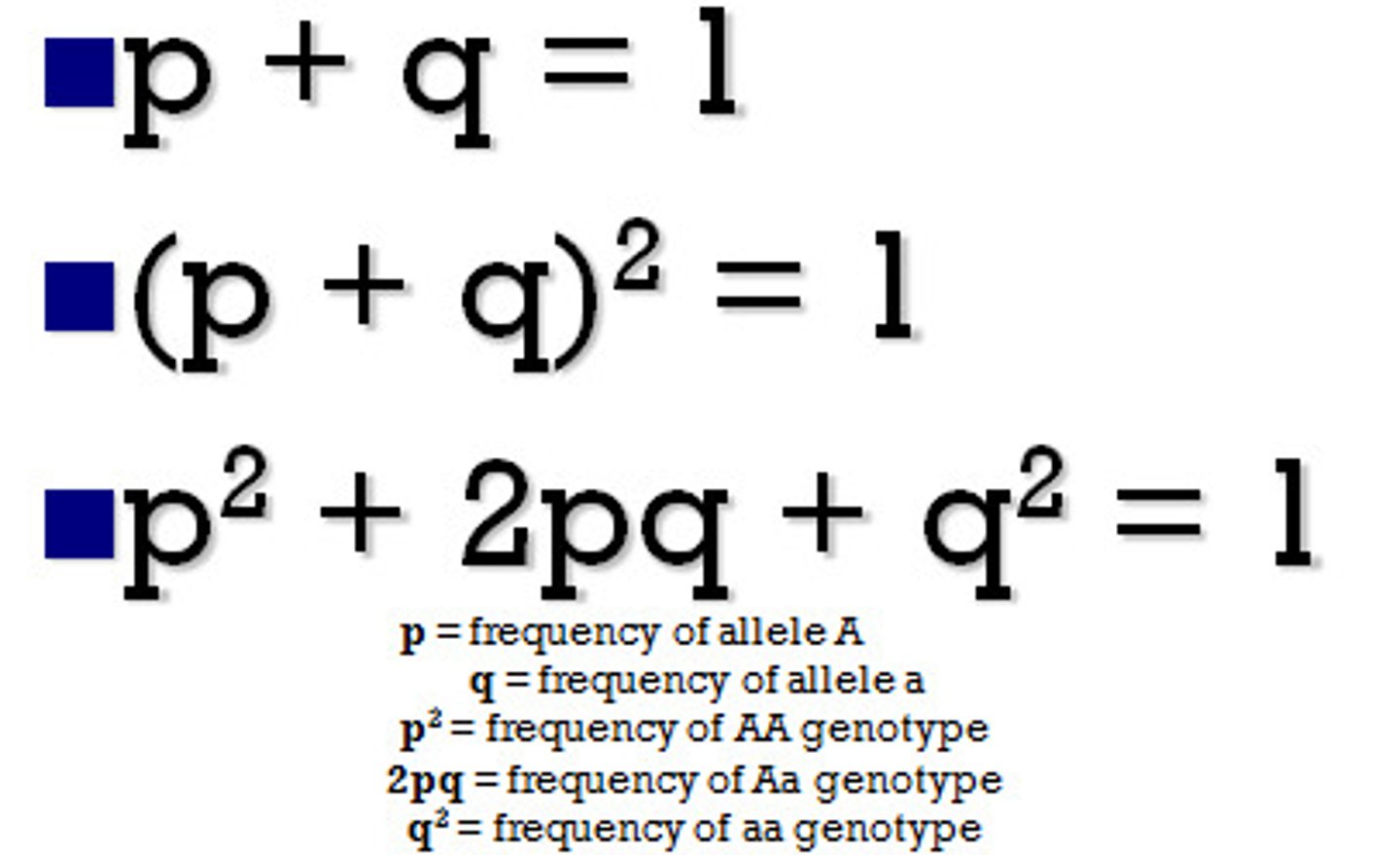
haplosufficient is usually
Dominant
haploinsufficient is usually
recessive
loss of function usually
recessive
gain of function usually
Dominant
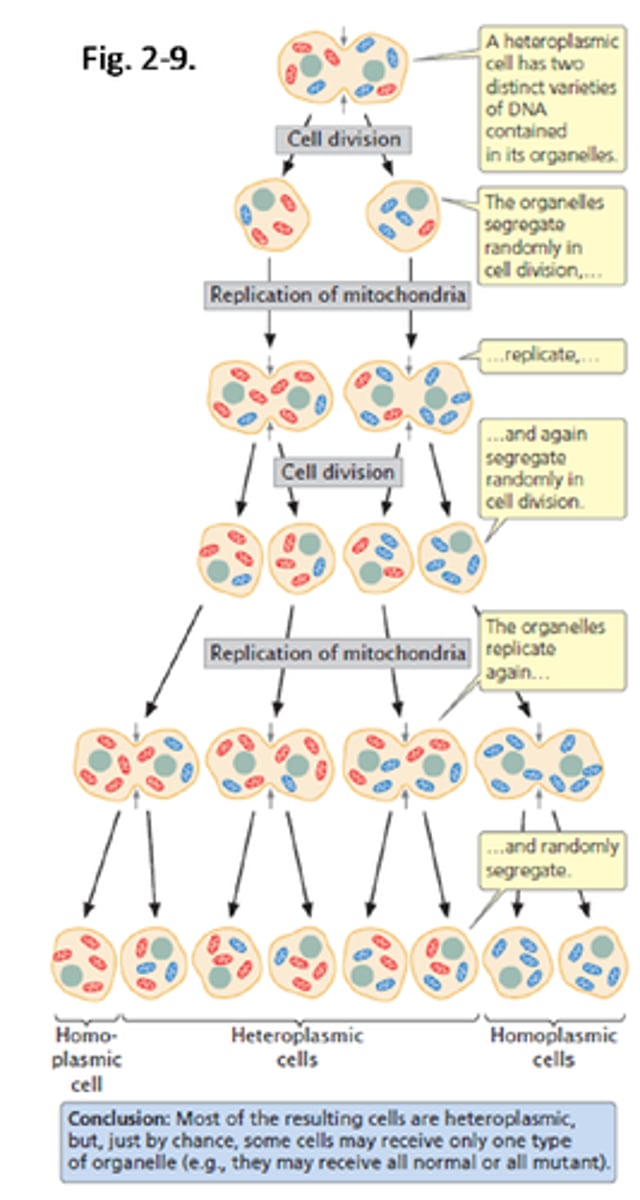
replicative segregation
Random segregation of organelles into progeny cells in cell division. If two or more versions of an organelle are present in the original cell, chance determines the proportion of each type that will segregate into each progeny cell.
Pleiotropy
A single gene having multiple effects on an individuals phenotype
Which of the following would contain genetic material that is 100% identical
Sister Chromatids
Which of the following is NOT one of the principles of linkage that Morgan obtained from his experiments?
Genes that are on the same chromosomes are always transmitted together as a unit
Principles of Linkage from Morgan
Crossing over exchanges pieces of chromosomes and creates new allele combinations.
The likelihood of crossing over occurring between two genes is dependent on the distance of the genes from one another.
Gene that are on the same chromosome may be inherited together
In a mapping experiment with three linked genes, which phenotype should occur most often in the F2offspring
Parental Phenotypes
Visual proof that chromosomes exchange pieces of information during crossing over was provided by
Stern
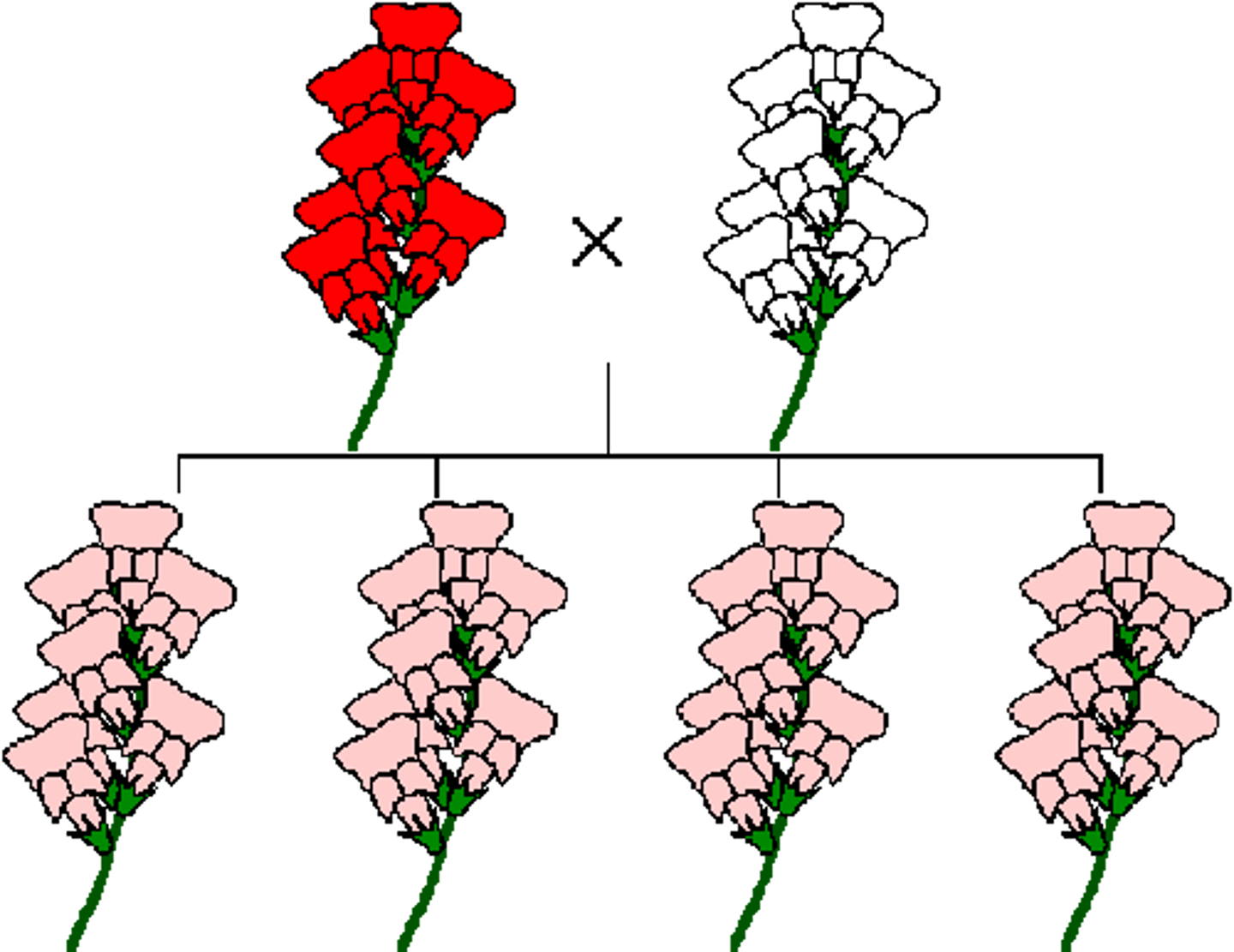
In four-o’clock plants, red flower color is dominant to white flower color. However, heterozygous plants have a pink color
Flower color demonstrates a pattern of incomplete dominance in the four-o'clock plant. The genotypes of the plants in this cross are (pink) × (white).
½ pink, ½ white
In rabbits, full coat color (c) is the dominant trait. A second allele, chinchilla is recessive to full coat color. Himalayan coat color is recessive to chinchilla and full coat colors, and albino (c) is recessive to all coat colors. If two chinchilla rabbits mate, what coat color is NOT possible
Full Coat Color
Chinchilla is recessive to full coat color, so a cross between two rabbits with chinchilla coat color cannot produce offspring with full coat color. If both rabbits were heterozygous with the genotype , then all three of the other phenotypes (chinchilla, himalayan, albino) are possible.
The production of wild-type offspring from a cross between parents that both display the same recessive phenotype illustrates the genetic phenomenon of ________
Complementation
A heterozygote possesses a phenotype that is intermediate between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. This is most likely an example of_________.
incomplete dominance
In a chi-square test to determine if two genes are linked or assorting independently, what is the default (null) hypothesis that is tested?
The genes are assorting independently
Which of the following is NOT correct concerning epistatic interactions?
They always result in a 9:7 ratio of a dihybrid cross.
A bivalent contains how many chromatids?
4
You are studying a diploid organism that has 14 pair of chromsomes, How many chromatids would this cells have in G2phase
56 14×4
>Once chromosome replication during S phase is completed, a cell has twice as many chromatids as it had chromosomes in the G1phase. In this example, a somatic cell from this organism in phase G1 has 28 distinct chromosomes, whereas it has 28 pairs of sister chromatids, for a total of 56 chromatids, in G2
Crossing over after what type of chromosomal aberration leads to a dicentric chromosome and an acentric fragment?
Paracentric Inversion
If the gametes of an organism are different morphologically, they are said to be
Heterogamous
Crossing over is more likely to occur between genes that are on a chromosome
far apart
The multiple effect of a single gene on the phenotype of a organism is called
Pleiotropy
The coat characteristics of Siamese cats, where proteins in the extremities function differently than in other parts of the body, is an example of
temperature-sensitive alleles
A loss of an internal piece of a chromosome is called a
interstitial deletion
While mapping two genes in Drosophila, you observe 30 recombinants among 200 total offspring. What is the distance between these genes?
15 map units
calculated by dividing the number of recombiant offspring (30) by the total number offsrping (200) and mulitply 100
The location of a gene on a chromosome is called its
locus
You are studying a new species of plant similar to Mendel's pea plants. You are specifically interested in two genes that are located on two different chromosomes. In this plant, the gene for height has two alleles, T (tall) and t (short). The gene for leaf color has two alleles P (purple) and p (pink). What meiotic products do you expect from diploid cells that are homozyous for the tall allele and heterozygous for the leaf color alleles?
An equal number of TP and Tp gametes
A true-breeding line of green pod pea plants is crossed with a true-breeding line of yellow pod plants. All of their offspring have green pods. From this information, it can be stated that the green color is
dominant
In a Punnett square diagram, the outside of the box represents the
haploid gametes
A cell that has a diploid number of 6 chromosomes has 3 chromosomes lined up in the center of the cell, each chromosome containing two joined sister chromatids. What phase of the cell cycle is this cell in?
Metaphase II of meiosis
Because the chromosomes are lined up at the center of the cell, we know this cell is in metaphase. A cell with a diploid number of 6 would have 6 chromosomes lined up at the center of the cell in metaphase of mitosis. A cell in metaphase of meiosis I would have pairs of homologous chromosomes lined up at the center of the cell. This cell is in metaphase II of meiosis.
In a dihybrid cross using Mendelian inheritance, if both parents are heterozygous for both traits, what will be the phenotypic ratio of their offspring?
9:3:3:1
There are two chromsomes in a normal cell ( the asterix indicates a centeromere the letters different genes):
Chromosome 1: ABCDEFG*HIJKLMN
Chromosome 2: OPQRST*UVWX
And in an abnormal cell they are now:
Chromosome 1: ABCDEFG*HIWX
Chromosome 2: OPQRST*UVJKLMN
What type of mutation has occurred?
Reciprocal Translocation
Since two non-homologous chromosomes have enchanged pieces it is a reciprocal translocation
In animals, somatic cells are and germ cells are
diploid; haploid
A. allele is the most prevalent allele in a population and usually encodes a protein that is made in the proper amount and functions normally
Wild-type
Which of the following is NOT an example of euploidy?
Aneuploid
A karyotype is a
organized representation of the chromosomes within a cell
In a mapping cross, you determine that the recombination frequency between the Q and P is 12% and between loci Q and L is 15%. If locus Q is in between loci P and L, then the recombination frequency between P and L should be approximately
27%
Gene loci are arranged in a linear order along chromosomes, where map distances between loci are additive.
The common goldfish Carassius auratus has 100 chromosomes and is tetraploid. The goldfish therefore has _________ sets of chromosomes containing _________ chromosomes each
4;25
Tetraploid means that there are four sets of chromosomes. If there are 100 chromosomes, that means there are 25 in each set
Inversion
flip on same chrom
No change in genetic material
Breakpoint effect
Inversion can disrupt a gene
Big
Diploid
Haploid
Triploid
2n
n
3n