Neurobiology of Brain Development: Stages, Cells, and Environmental Influences
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are the major steps in the neurobiology of development?
1. Cell Birth (neurogenesis; gliogenesis) 2. Cell Migration 3. Cell Differentiation 4. Cell Maturation 5. Synaptogenesis 6. Cell Death 7. Synaptic Pruning 8. Myelogenesis
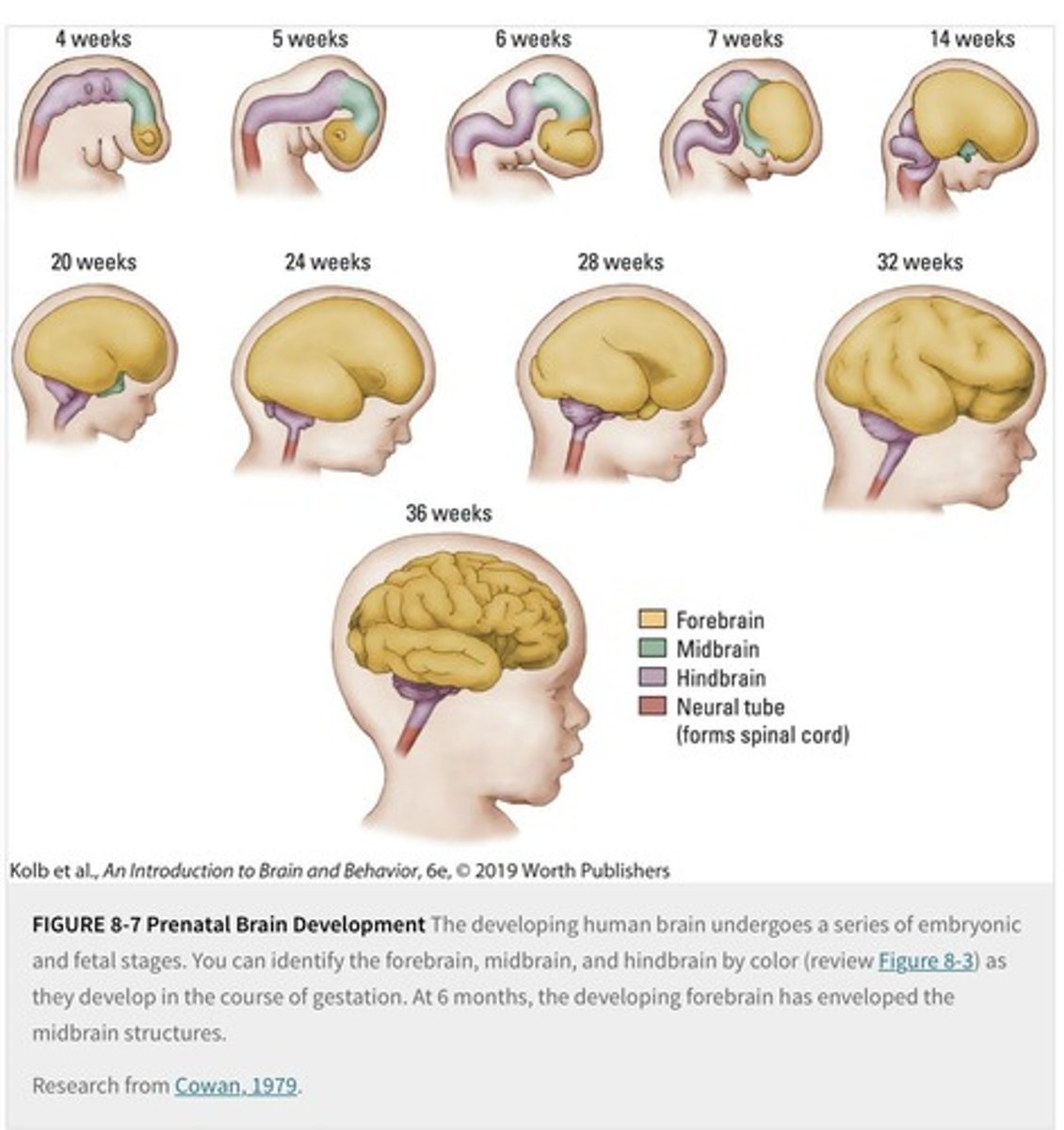
What is the role of neural stem cells?
Neural stem cells are self-renewing multipotential cells that give rise to neurons and glia.
What is a progenitor cell?
A progenitor cell is a precursor cell derived from a stem cell that can produce either a neuron or glial cell.
What is a neurotrophic factor?
A chemical compound that supports growth and differentiation in developing neurons and may help keep certain neurons alive in adulthood.
What is the significance of radial glial cells?
Radial glial cells serve as path-making cells that migrating neurons follow to their appropriate destinations.

What are the two major factors determining cell differentiation?
Intrinsic factors (specific genes turned on or off) and extrinsic factors (chemicals released by neighboring cells).
What is axonal growth?
Axonal growth involves extending axons to appropriate targets to initiate synapse formation.
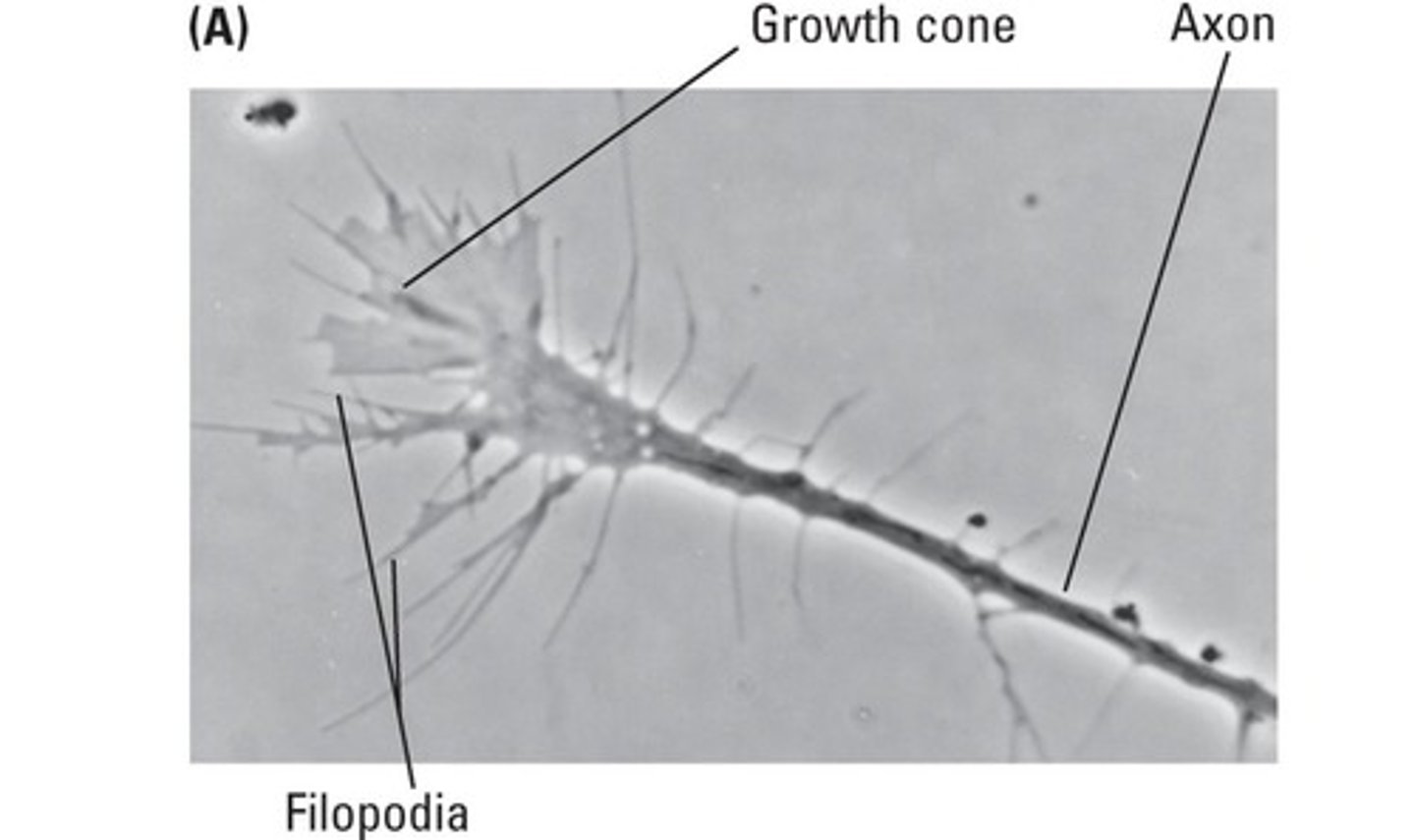
What is synaptic pruning?
Synaptic pruning is the process of eliminating synaptic connections that are not part of a functional network, occurring in an experience-dependent manner.
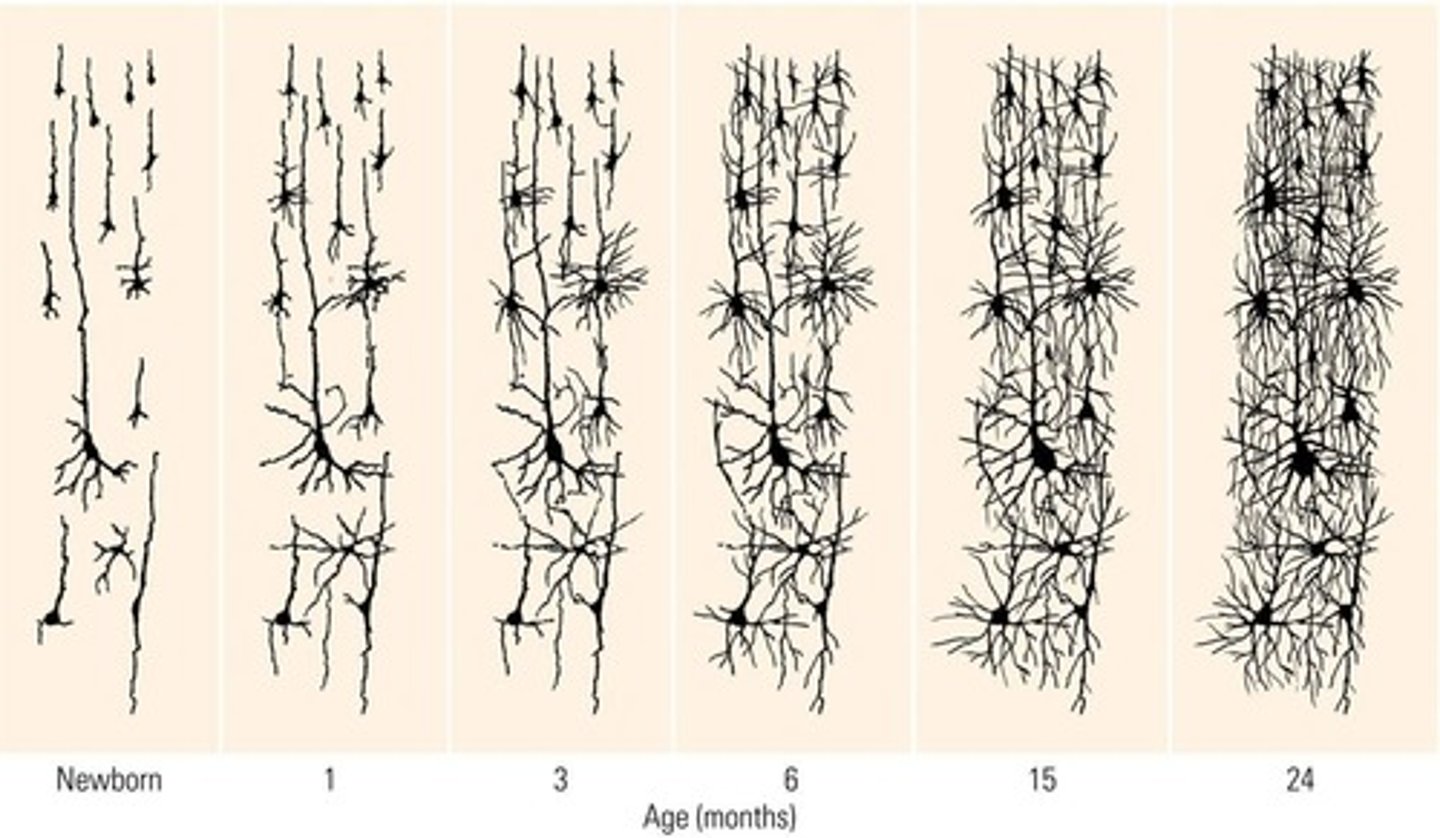
What is neural Darwinism?
The hypothesis that cell death results from competition among neurons for connections and resources.
What is apoptosis?
Apoptosis is genetically programmed cell death.
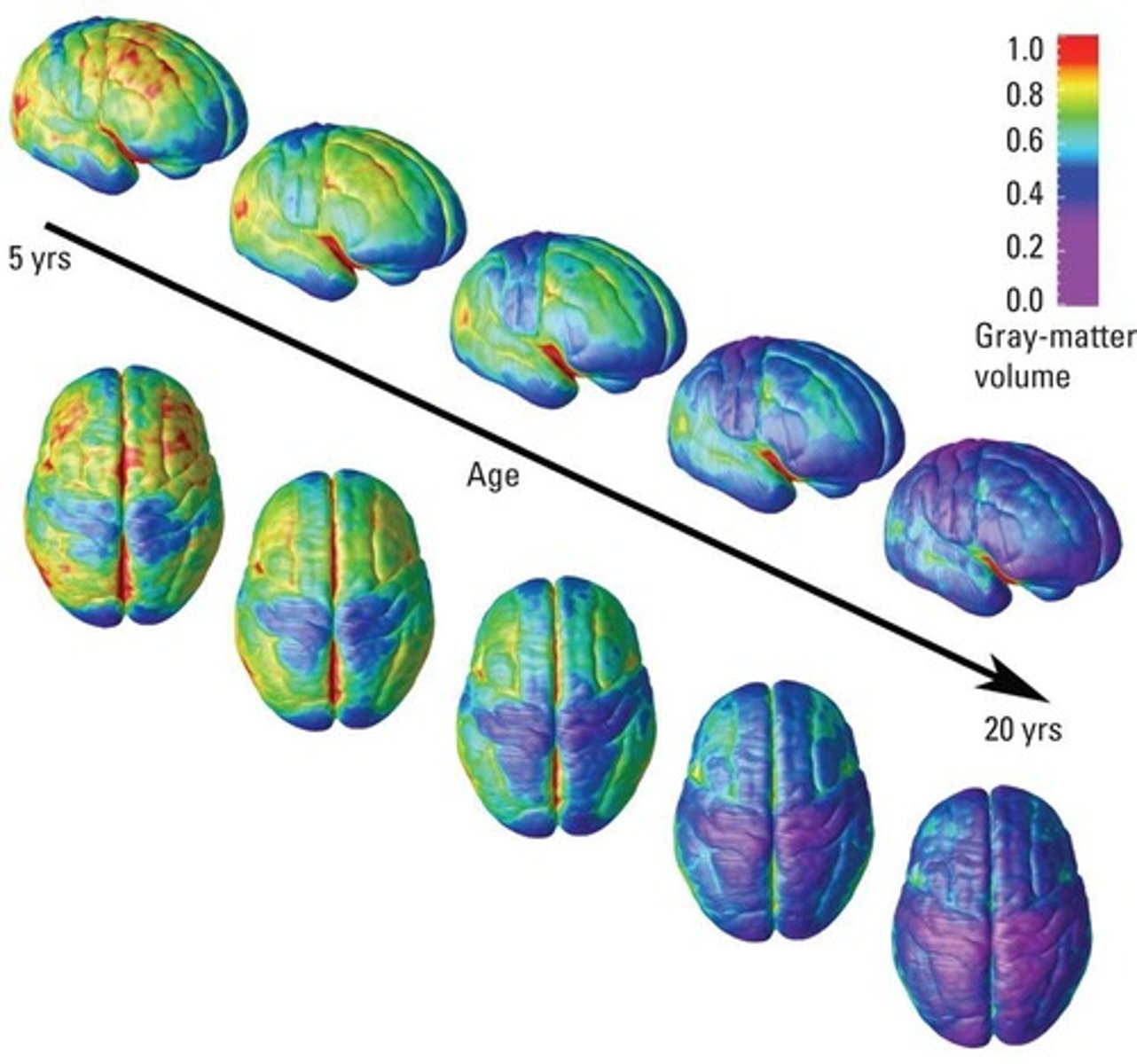
What unique aspect characterizes frontal-lobe development?
The frontal lobe is the last brain region to mature, with maturation extending beyond age 20.
When does language onset typically occur?
Language onset usually occurs between 1 and 2 years of age.
What is the relationship between myelogenesis and motor behaviors?
Myelination correlates with increased motor dexterity and is associated with the development of handedness.

What did Hebb (1947) suggest about cognitive environments?
Hebb suggested that cognitively stimulating environments help maximize intellectual development.
What are critical periods in brain development?
Critical periods are developmental windows during which certain events have a long-lasting influence on the brain.
What is the effect of early deprivation of sensory experience?
Early deprivation of sensory experience leads to atrophy of dendrites.
What happens to synaptic development after birth?
Synaptic development increases rapidly during the first year of life, peaking between 2-3 years of age.
What is the growth cone?
The growth cone is the growing tip of an axon that guides axonal growth.
What is the role of cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs)?
CAMs provide a 'tread' for growth cones to adhere to and can attract or repel them.
What is the impact of enriched environments on brain development in rats?
Rats raised in enriched environments have larger and more synapses and increased support cells compared to those in standard lab cages.
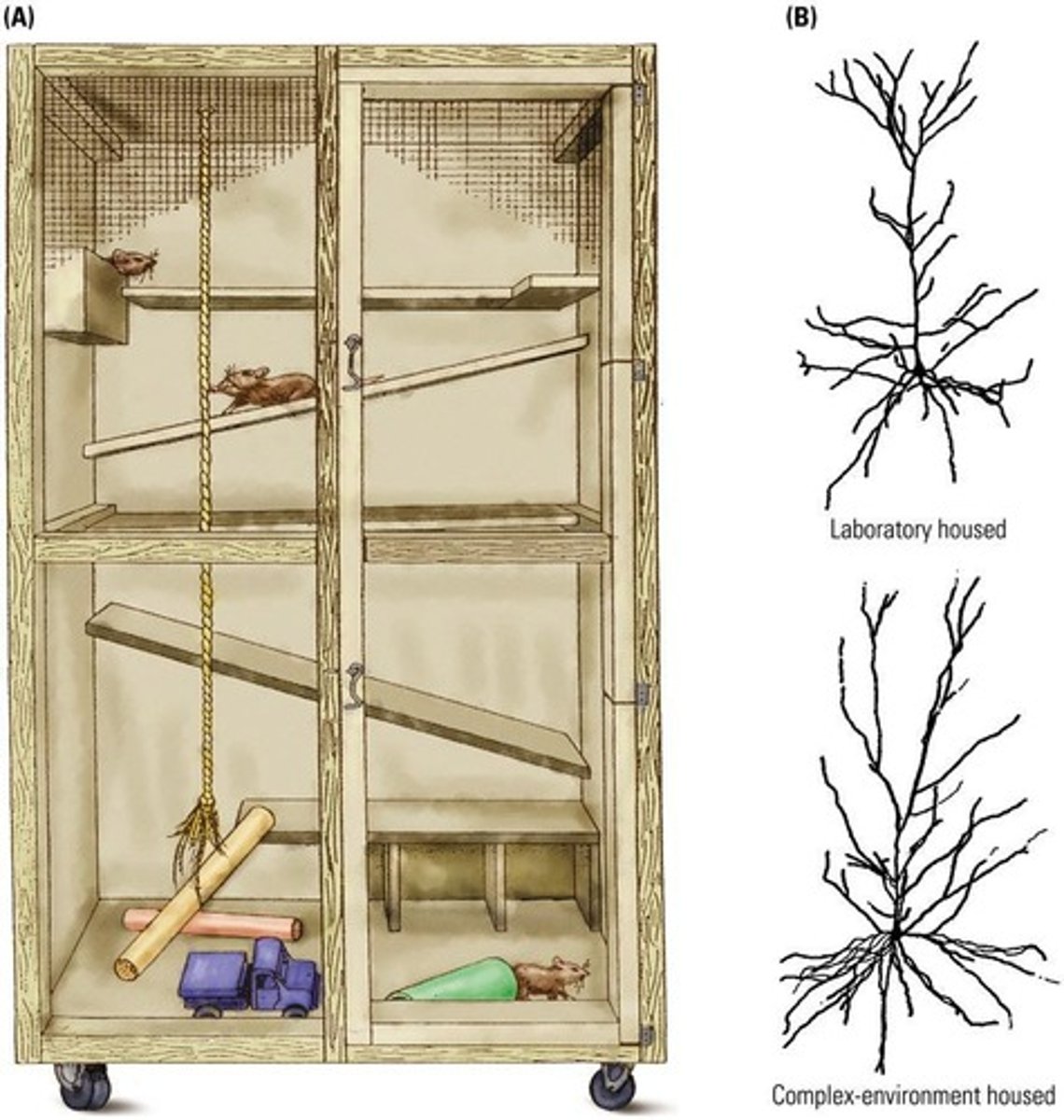
What is the significance of synaptic development during the 5th gestational month?
By the 5th gestational month, simple synaptic contacts begin forming functional networks.
What is the relationship between experience and neural connectivity postnatally?
Postnatally, fine-tuning of connections proceeds in an activity-dependent manner, driven by environmental exposure.
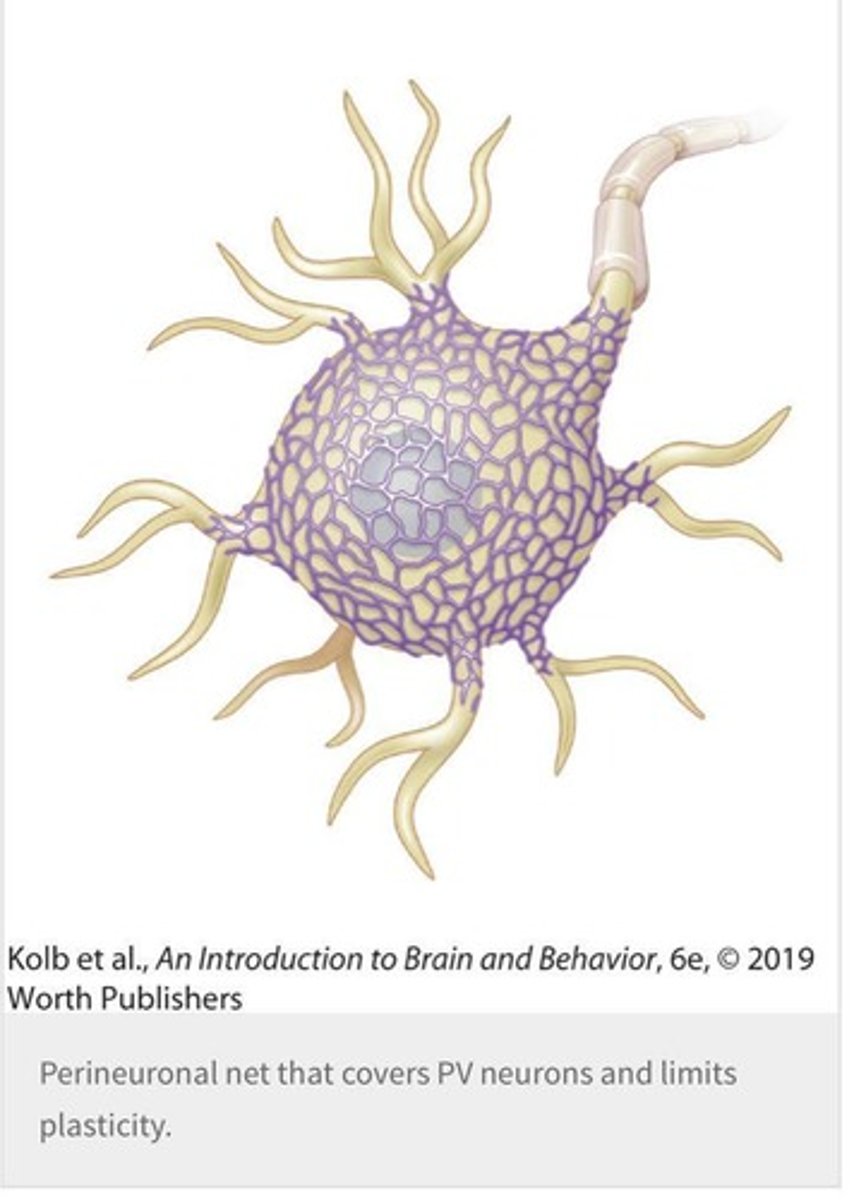
What is the role of perineuronal nets in brain development?
Perineuronal nets are one mechanism that regulates critical periods in brain development.
What happens to gray matter thickness in major language regions of the cortex?
Major language regions show an increase in gray matter thickness during development.