Light an EM spectrum
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
white light
can refracted (bent) through a prism into separate wavelengths
Types of colours in white light (in order)
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet (ROYGBIV)
EM stands for
Electromagnetic
EM spectrum
our eyes can only see a small part of the EM spectrum (visible light)
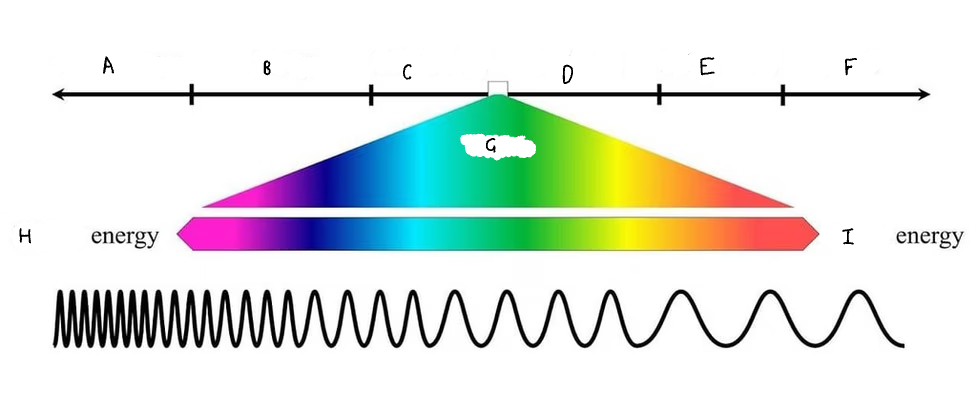

A: Grammar rays
B: X- rays
C: Ultraviolet rays (UV)
D: infrared rays
E: microwave rays
F: radio rays
G: visible light
H: high energy
I:low energy
what is a sound wave
a longitudinal wave
sound waves ability to travel
travel through solids, liquids and gases, but are unable to travel through a vacuum
speed of sound waves in air
330 m/s to 350 m/s, depends on temperature
what is a EM wave
transverse wave
EM waves ability to travel
unable to travel through some substances but can travel through a vacuum
speed of EM waves in air
about 300.000,000 m/s
analogue quantities
can have any value
can change continually over time
digital quantities
can have only particular values
are represented by numbers
FM
frequency modulation - meaning frequency is changing
AM
amplitude modulation - meaning amplitude is changing
digital
has stronger signals and other signals from different sources cannot interfere
analogue
has weaker signals, other signals can interfere with it leading to original signals becoming distorted