history of our planet week 9 B
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Humans in the quaternary – origin of the species - Human dispersal – out of Africa - Homo sapiens dispersal – the first global human - Into the stone age(s). – on ele
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Origin of the species:
1859: on the origin of species by means of natural selection
1871: the ascent of man and selection in relation to sex
“man must be included with other organic beings in any general conclusion respecting his manner of appearance on this earth”
i.e. humans must have evolved in the same way as other species
- but lack of ‘intermediate’ species
1856: homo neanderthalensis remains found in Germany, diseased humans?
The search for the missing link – ape and humans
1891: eugene dubois in java, homo erectus
1920s: further hominin remains found in Africa
‘intermediate’ species found
Terminology:
hominid (family: Hominidae) – the great apes – currently 8 living species
hominin (tribe: hominini) – all members of homo genus (aka. Humans) and ancestors
humans in the quaternary:
homo sapiens last common ancestors
australopithecine, 2-3 million years ago
pan (chimps) – 4-13 million years ago, theory dependent
Sahelanthropus tchadensis:
Chimp/ human features
Brain size comparable to chimp
May have walked upright
Australopithecus anamensis:
Probably walked upright
Teeth adapted to eating tough food
Australopithecus afarensis (lucy):
Walked upright
1.2-1.4m tall
Brain 35% size of homo sapiens
No stone tools
Homo habilis:
First in homo genus
Brin 50% size homo sapiens
Primitive stone tools
Homo ergaster:
Small face and teeth
Brain 60% size of homo sapiens
Advanced stone tools, handaxes
First use of fire?
Important place in homo genus family tree
Homo erectus:
Features and anatomy fairly similar to homo sapiens
Brain 60-70%
Successful, 2. 2million years
First species ‘out of Africa’
Coexisted with homo sapiens
Out of africa:Homo heidelbergensis:
Brains 88% size humans
Used tools like h. erectus
European h. heidelbergensis developed neanderthal-like features
African h. heidelbergensis evolved into homo sapiens?
Out of africa:Homo neanderthalensis:
Stocky and cold adapted
Used advanced tools
Social structure and rudimentary language
Slightly larger brain than homo sapiens?
Dominated in Europe
Out of africa: Homo sapiens:
cultural adaptability:
complex tools
proficiency in practical and social innovation
Hominin evolution, climate, and environment:
East Africa – centre for human evolution, 10-2 million years ago
Tectonics have transformed region: flat, homogenous to varied, heterogeneous deserts to cloud forests
‘rifting’ (great rift valley) led to lake formation
Link with hominin speciation, endephalisation, and dispersal
Particularly at 1.8m – homo erectus

7-4 million years ago |
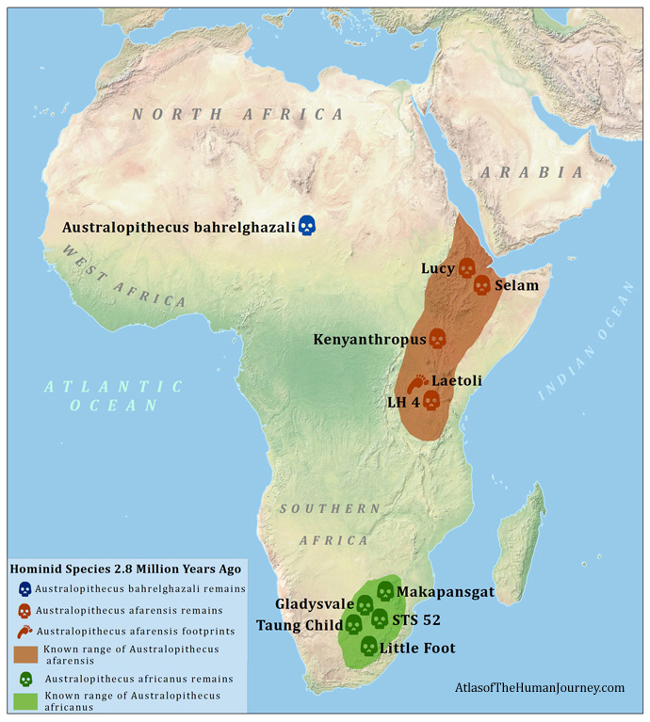
2.8 mil years ago
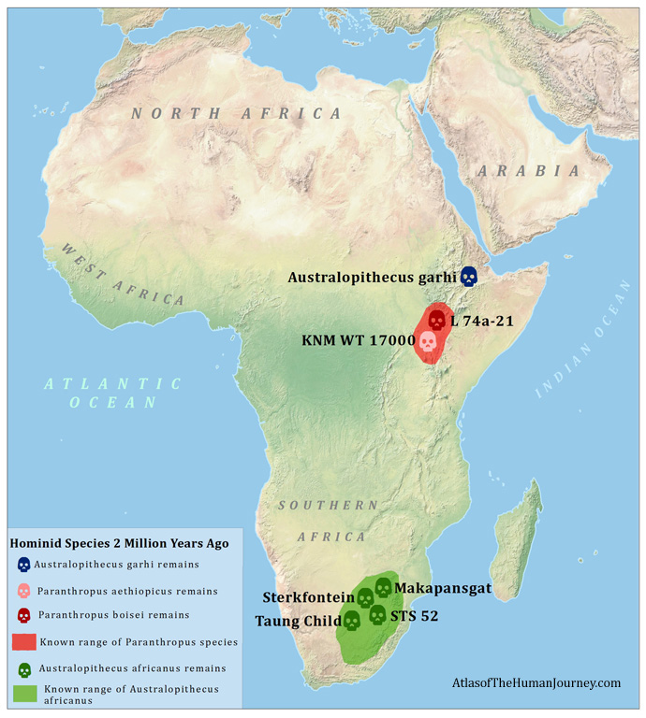
2 mil years ago

1.8 mil years ago
Emergence of first homo, h.habilis
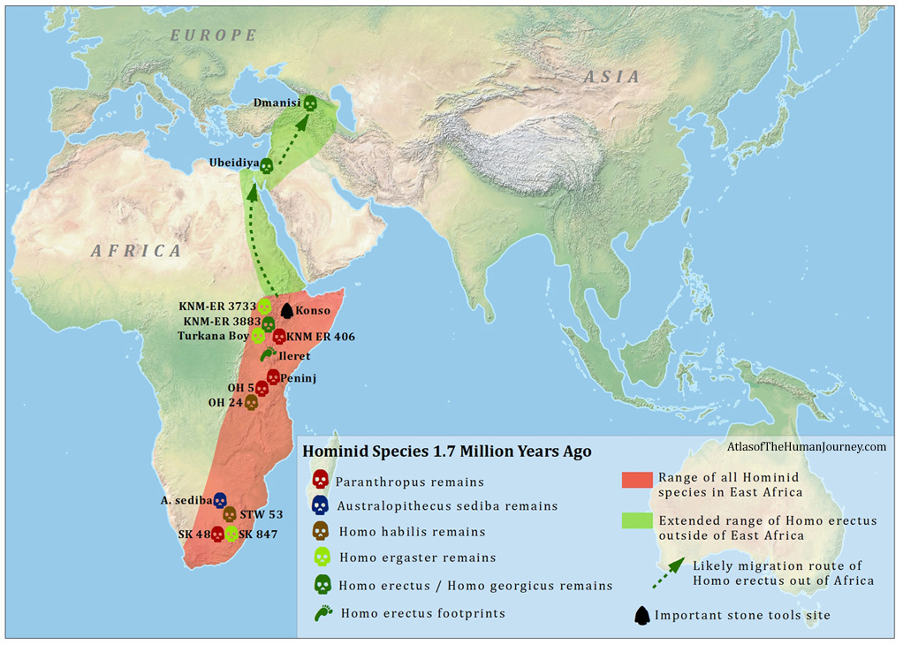
1.7 mil years ago
h. erectus first ‘out of africa’
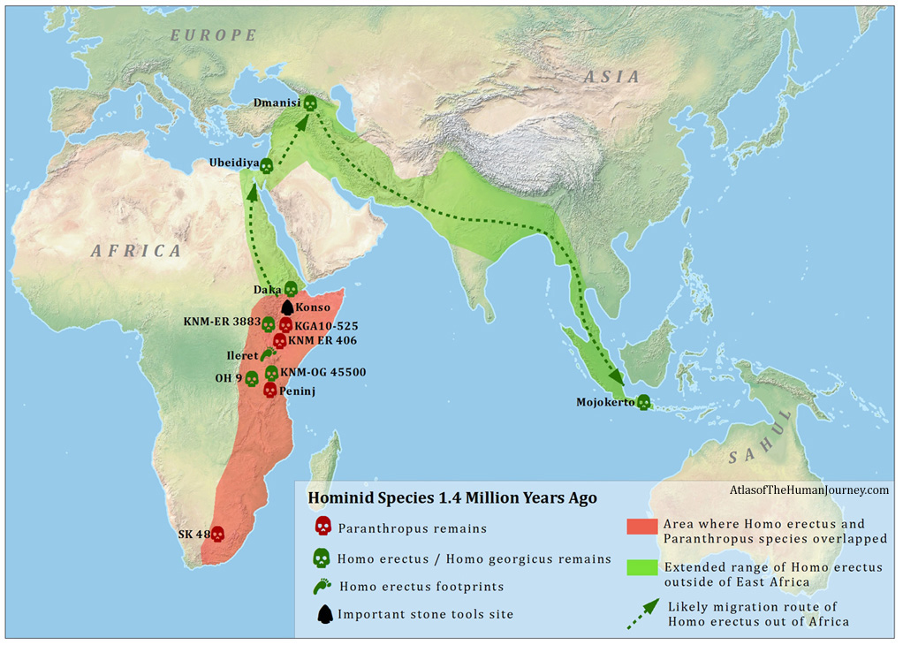
1.4 mil years ago
h. erectus expands into mainland asia and indonesia
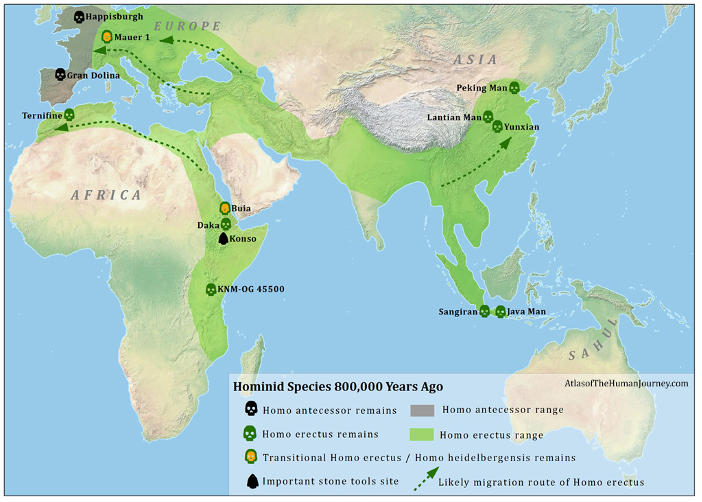
800,000 years ago
h. erecus expands into north africa, china and possibly eastern Europe
h. antecessor in western Europe?
(descended from h. ergaster?)

500,000 years ago
h. heidelbergensis ‘out of africa’ expands into north africa, china and possibly eastern Europe
overlap with h. erectus in asia
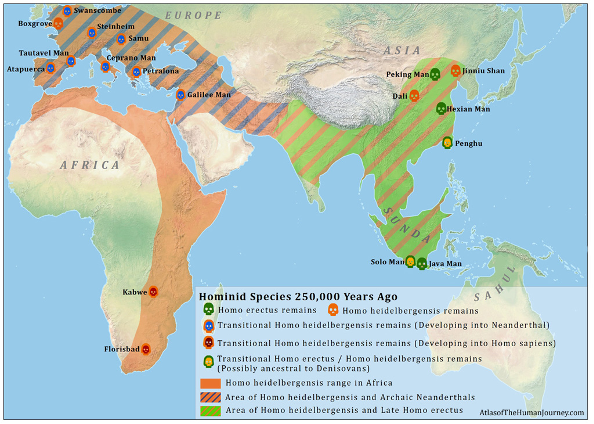
250,000 years ago
Period of transition
Emergence of h. neanderthalensis and h. sapiens from h. heidelbergensis in Europe and africa
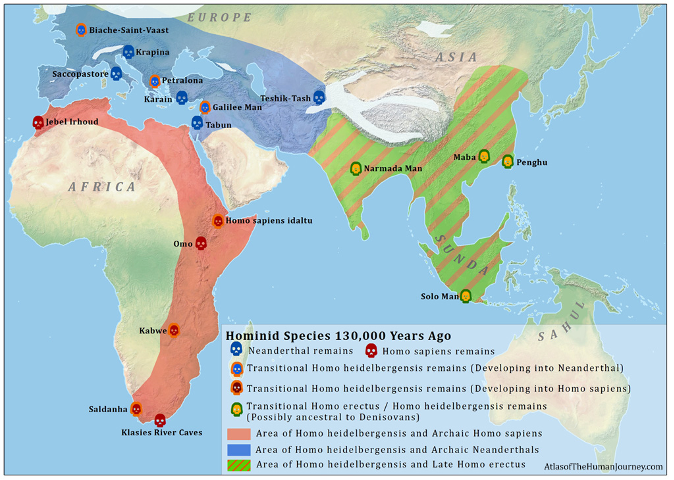
130,000 years ago
Three distinct species:
h. neanderthalensis
h. erectus
e. sapiens
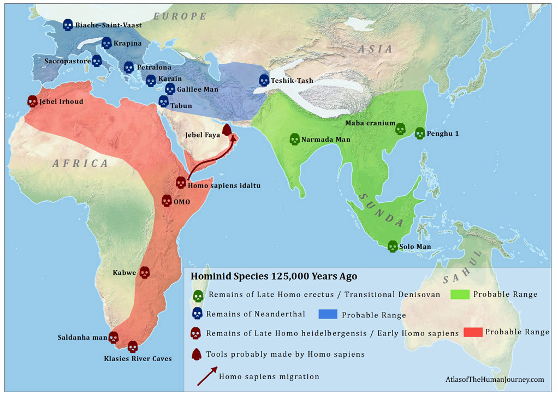
125,000 years ago
First h. sapiens out of africa?
Homo heidelbergensis:
Brains 88% size humans
Used tools like h. erectus
European h. heidelbergensis developed neanderthal-like features
African h. heidelbergensis evolved into homo sapiens?
Homo neanderthalensis:
Stocky and cold adapted
Used advanced tools
Social structure and rudimentary language
Slightly larger brain than homo sapiens?
Dominated in Europe
Homo sapiens:
cultural adaptability:
complex tools
proficiency in practical and social innovation
homo sapiens dispersal:
variety of theories
early (120kyr): middle east, southern asia, Australia
Then (60kyr): Europe, Northern asia, Indonesia
Hominin evolution, climate and environment:
Freshwater fluxes, ice sheet surges in north Atlantic (Heinrich events)
Southerly migration of ITCZ over Africa
Cooler but drier climate
Changes in African vegetation cover, Sahel
North, east and west Africa uninhabitable
Driver for homo sapiens ‘out of Africa’ dispersal?
Carto et al (2009, j human evolution)
30,000 years ago:
Approaching height of last glacial peiod (Devensian, MIS3)
Homo erectus extinct
Homo sapiens and h. neanderthalensis coexisting
20,000 years ago:
Last glacial maximum
H. neanderthalensis gone
H. sapiens – nearly a global species
did h. neanderthalensis and h. sapiens coexist
In Europe, archaeological evidence shows h. neanderthalensis and h. sapiens coexisted for c. 5000 years
coexisting - Competition
Neanderthals were more socially isolated, lived in smaller groups.
Division of labour (between men and women).
Running, warm climate animals
coexist - Climate
H. neanderthalensis disappeared c. 40-24 ka
They and h. sapiens forced out of Europe during last glacial
H. neanderthalensis poorly adapted for warmer climate and fauna
Outcompeted by h. sapiens – social groups, problem solving, division of labour
coexist - conflict
Archaeological evidence for inter-species aggression
coexist - Copulation
Inter-breeding is possible between both species, and DNA evidence suggest that it occurred:
Modern non-Africans possess c. 1-3% neanderthal DNA markers
20% of neanderthal DNA markers still represented in AMH (vernot and akey, 2014, science)
leaving Africa
Several homo species left africa
In Europe, h. neanderthalensis and h. sapiens
In asia, h. erectus until c. 140,000 years ago
H. sapiens only extant species left
Human evolution and race:
What race means in a scientific and social context is an ongoing process
Does race exist:
All homo sapiens (humans) are genetically 99.9% identical (human genome research institute, US)
Scientifically, race doesn’t exist
Race is a social construct which groups people based on skin colour, features (and cultural and religious differences)
Physical differences result from superficial phenotypic differences
Why does the concept of race exist:
Ideas emerged in 16th C to ‘make sense’ of physical differences
Racialisation – categorisation of grops assigned characteristics, given value
White Europeans became privileged through European thought, used to justify European colonialism after the medieval period
Concept of race has been used to reinforce hierarchy, racism ever since
Human evolution and race: Polygenism
Different human races have different taxonomic origins and significantly different genetic histories, has reinforced racial hierarchy, violence
Human evolution and race: monogenism
All humans have almost identical genetic histories and have same taxonomic origins
Human evolution and race:
Physical differences (skin colour) are phenotypic responses to environmental factors (epidermal melanin)
No homogenous African race
More genetic diversity in Africa than all other continents combined
Modern humans originated in Africa and lived there longest
Rich genetic diversity
Aricas linguistic diversity often used as a guide
Homo sapiens dispersal: the first global human:
by the LGM, humans were only ones left
Spread across Africa, Europe, Asia and Australasia
Into the Americas:
Expansion of homo sapiens into north America relatively late, c. 15 ka
Bering land bridge during glacial, low sea level. Now: Alaska-Russia (50 miles)
North Americas first people:
At LGM, Laurentide and cordilleran ice sheets fused resulting in coast-to coast ice
Ice-free corridor route – original hypotheses.
People migrated into central N America as cordilleran ice sheet melted
Radiocarbon dating of first human archaeology in N America: 14,500 – 18,000 years ago
Via pre-LGM ice free corridor – why not more archaeology?
How accurate are the age estimates?
Pacific coast route? Combination?
south Americas first people:
Oldest archaeological remains c. 14,500-14,250 years old. Monte Verde, southern Chile
well before cordilleran ice sheet retreat at end of last ice age
Speed: oldest archaeology comparable with north America
Majority of early archaeology is along west coast
Peopling of the Americas: support pacific coast route hypothesis
Or across pacific ocean?
Peopling of the pacific:
Lower sea level during LGM
Estimates for first autralians arrival between 40,000 – 80,000 years ago
Growing evidence for early arrival
Archaeological evidence, but radiocarbon dated to c. 60,000 years
Other evidence:
-Changing fire regimes (70-1000ka)
Human genome (over 60ka)
Mass megafauna extinction event (c. 46ka)
On through pacific island – to south America?
Was bigfoot real?
Folk stories exist across world about large ape-like creatures (bigfoot, sasquatch, yeti)
Gigantopithicus blacki, 3.5m tall
Went extinct 300,000 years ago
Ponginae tribe (one survivor, orangutan) – the Eurasian apes
Humans in the late quaternary:
Assumption that homo sapiens was only homo species to survive last glacial continues to be challenged
New archaeological finds and DNA analysis also hint at increased complexity in the evolution of our species
Morwood et al (2004, nature) – discovery of a new hominin species
Flores island, southern Indonesia
Liang bua, limestone cave
Remains of 9 individuals and 1 complete skull
Anatomically distinct from h. erectus and h. sapiens
Named homo florensiensis
C. 110cm tall, 3ft 7in
Nicknamed the hobbit
human evidence
Originally radiocarbon (14^C) dated to c. 12,000 years ago
Longest surviving non-h. sapiens hominin?
Revised stratigraphy of the cave and additional dating suggested 50,000 years old more likely
Native folk tale – ebu gogo
Suggestions of dwarfism, downs syndrome
human evidence 2010
Denisovan hominin, currently unclassified
Dates to 41,000 years ago but genetically distinct from AMH, neanderthals
Common ancestor with neanderthals, but interbred with amh?
3-5% of Melanesian and Australian Aboriginal DNA shared with Denisovans
human evidence 2
Progress in our understanding sometimes doesn’t involve archaeology
DNA analysis of human genomes reveals hidden surprises
Some west African populations share up to 20% DNA markers with unknown ancient human
Archaeological remains yet to be discovered
‘absence of evidence is not evidence of absence’
the stone age:
the palaeolithic:
The stone age
Palaeolithic – old stone age
Mesolithic – middle stones age
Neolithic – new stone age
Defined by use of stone tools
Growing levels of societal and technological complexity
lower palaeolithic – pre-h. sapiens, h. habilis onwards
Middle palaeolithic – h. sapiens and others
The first Britons:
2013: earliest evidence of hominins discovered in British isles
Footprint discovered following storm in habbisburgh, norfolk
Dated to 900,000 years ago (990,000 – 780,000 years ago)
Oldest footprints outside africa
Previously stone tools found in cliff deposits nearby, by dog walkers, then thought to be oldest evidence (c. 700,000 years)
No hominin remains but probably homo antecessor
The palaeolithic:
Prior to happisburgh footprints:
2005: earliest evidence of uk hominins, Pakefield , Suffolk
Flint percussion flakes associated with handaxe industries identified from interglacial river terraces
Dated to 700,000 years ago, MIS 17 with cromerian complex
Associated mediterranean species, and old water vole – mimomys Savini
Earliest evidence of humans north of alps
The palaeolithic:- Prior to Pakefield flints:
1982-1996: excavation at sand/ gravel quarry, boxgrove, west Sussex
Hundreds of handaxes, percussion, flints and megafauna
C. 500,000 years ago, MIS 13 (cromerian complex)
Cut marks on bones (e.g. fallow deer) found, indicating butchery
H. heidelbergensis tibia – oldest hominin remains in British isles
Other important finds:
Swanscombe woman, Dartford, Kent
400,000 years old
Homo erectus?
Discovered by Alvin Marston, local dentist, 1935
Kent’s cavern ‘neanderthal’ devon
42,000 years old
Discovered 1927
Possibly h. sapiens? Oldest in N. Europe
A cultural revolution – evidence from Swabian Alb region, Germany
1939: ion man of hohlenstein stadel
First anthropomorphic animal carving, male
32,000 years old, 11 inches high, Carved using flint tools
2008: Venus of Hohle fels – mammoth ivory
First undisputed human depiction
35,000-40,000 years old
2008: hohle fels flute:
Vultures wing, mute swan bone, mammoth ivory
Radiocarbon dated to 41,000-42,000 years old
Pentatonic scale – developed musical tradition existed amongst first AMH in Europe – can still be played
First Britons: Middle palaeolithic:
Kent’s cavern, 42,000 years old
First Britons: Upper palaeolithic:
30,000 – 10,500 years ago
Humans absent in British isles during last glacial maximum
First Britons: Goughs cave, nr. Cheddar gorge, somerset
Evidence of recolonisation of Britain after c. 14,700 years ago (14^C)
Persisted through bolling-allerod interstadial to start of younger dryas
Evidence of hunter-gatherers
Abundant remains elk, aurochs, wild horse
Cheddar gorge, ideal hunting ground
First Britons: Evidence of cannibalism:
Human forearm bone, engraved with zigzags and broken open for marrow extraction
Human bones with human teeth marks
Skulls show evidence of careful preparation to form skull cups
Suggests careful filleting of human bodies, with engraving
Cannibalism went beyond just survival – ritual?
First Britons: Cheddar man – oldest complete AMH skeleton
Found on Goughs cave, but more recent cannibalistic evidence, c. 10,000 years old
Assumption that early british AMH were white proved wrong by recent DNA analysis
Likely dark to black skin, blue eyes
Light skin gene in AMH likely spread in europe much later than previously thought
The palaeolithic:
First evidence of construction and settlement – 12,000 -10,000 years ago
Anatolia/ Mesopotamia/ levant
Future cradle of civilisation
Ritual sites?
Humans in the quaternary – story so far:
Potentially multiple co-existing homo species with AMH
Britain inhabited throughout late quaternary
Earliest evidene c. 900,000 years ago from Happisburgh
Occupation ebb and flow with glacial-interglacial cycle
Palaeolithic dominated by stone tool technology, but art and music
Human evolution over last 10 million years
Emergence of homo genus in quaternary-
Global expansion of homo sapiens
Technological and cultural advances through the palaeolithic in the Mesolithic
The mesolithic:
After end of last ice age
Mesolithic – 10,500 – 6000 years ago – timings of period debated
Characterised by dramatic technological advancement
Significant advances in stone industry
Microlithic flaked tools and blades
The mesolithic:- Other preserved artefacts:
Nets, baskets, creels, boast, paddles, sleds
The Mesolithic subsistence:
Hunting and gathering
Wide diet breadth with seasonal specialisation
Isotopic studies (teeth) demonstrates marine and terrestrial mammal consumption, fishing and shellfish
Still largely nomadic (apart from in the ‘cradle of civilisation’