RES | Administrative Information Systems, Practice Management Systems and Electronic Health Record
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Health Record
Collection of a patient’s health data or information
Healthcare Providers
need to keep accurate record systems to store information about patients and the use of these records can help them make certain diagnosis, recommendations, and plan of care
Electronic Health Record
digital repository or a form or storage of the health status of the patient
Healthcare Information Systems
use of modern technology in compiling healthcare and information between medical practitioners for a more holistical approach in healing
Healthcare Information Systems
generating network of different systems that can connect or share information within certified and authorized clinicians
Types of Healthcare Organization Information Systems
Case Management Information Systems
Communication Systems
Core Business Systems
Order Entry Systems
Patient Care Support Systems
Case Management Information Systems
process that connects the patients with the healthcare providers, resources, and different services
Case Management Information Systems
directed towards ensuring that patient’s receive the best possible care
Case Management Information Systems
includes numerous assessments, planning, implementation, follow-up, and evaluating outcomes
Case Management Information Systems
the general benefit of this system is to reduce risk, decrease cost, and ensure quality service
Communication Systems
a good communication is critical
Communication Systems
continue to evolve to improve the delivery of healthcare and enhance productivity
Communication Systems
Provider to Provider
Provider to Patient
Internal Messaging Systems
Provider to Provider
giving instructions as to patient transfers, external clinical procedures, insurance transactions
Provider to Patient
telemedicine, any form of consultations
Internal Messaging Systems
emergency notifications and interactions
Communication Systems
promote interaction among healthcare providers and patients
Core Business Systems
5 Common Core Business Systems:
Admissions
Discharge and Transfers
Financial Systems
Acuity Systems
Scheduling Systems
3 Main Goals of Core Business Systems
improve communication across healthcare providers
improve chronic care patient management
reduce unnecessary hospital utilization
Core Business Systems
the trust of the system is the maximization of resources and minimization of waste without of reduction in quality of patient care
Order Entry Systems
request, instructions, intentions to perform specific tasks
Order Entry Systems
can be clinical tasks such as interaction with the patient
Order Entry Systems
may benefit clinicians and patients from faulty, incorrect, and misinterpreted data
Patient Care Support Systems
patient-centered which contains the observations, interventions, and outcomes noted by the care team
Patient Care Support Systems
meaningful interaction between patients and physicians
Electronic Health Record
the transition from the paper-based health records to the EHR is a complex endeavor
Electronic Health Record
many healthcare facilities are currently operating in a hybrid environment
some health record are paper-based while some component are electronic based
some of these electronic systems communicate with each other while some do not
Computer-Based Patient Record (CPR)
used in 1980s by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) which further described it as a system specifically designed to support users through availability of complete and accurate data, practitioner reminders and alerts, clinical decision support, links to bodies of medical knowledge, and other aids.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
systems that integrated dictation, transcription, scanned documents, and print files.
Electronic Medical Records
an electronic record of health-related information of an individual that can be created, gathered, managed, and consulted by authorized clinicians and staff within one healthcare organization
Electronic Medical Records
within the facility where you work
Electronic Health Records
an electronic record of health-related information on an individual that confirms to nationally recognize interoperability standards and that can be created, managed, and consulted by authorized clinicians and staff across more than one healthcare organization
Electronic Health Records
more accessible through other healthcare organizations
Advantages of Manual
low start-up costs
training of staff is simple
requires less technically trained staff
paper records are available because there is no downtime
Disadvantages of Manual
retrieval of information is not easily customized
handwritten information can be illegible
difficult to abstract information
undocumented services are not usually discovered until discharge analysis of record occurs
Advantages of Automated
improves access to patient information
multiple users can access patient information simultaneously and remotely
eliminates paper record storage improves readability of patient information
timely capture of data
views of patient record can be customized by users
updates of information can easily occur
retrieval of customized information
reduces administrative costs
Disadvantages of Automated
increased start-up costs
selection and development of systems is time-consuming
staff training is time-consuming and can be expensive
technical staff need to maintain system
user resistance can occur
Key Components of EHR
Administrative and Billing Data
Diagnoses
Patient Demographics
Medications
Progress Notes
Immunization Dates
Laboratory and Tests Results
Vital Signs
Allergies
Medical Histories
Radiology Images
Electronic Health Record Implementation
The development of EHR system most often begins in a healthcare organization with acquisition of source systems including administrative and financial systems, and ancillary or departmental systems.
Core EHR applications
specialty systems
medical services
connectivity systems
Source System
Administrative and Financial System
Ancillary or Departmental System
Administrative and Financial System
among the first systems implemented by healthcare organization
Administrative and Financial System
usually managed by a specific department
admitting, patient financial services, and health information management
Administrative and Financial System
not considered departmental systems because they manage patient-specific data
Administrative and Financial System
does not process data that aid in management of the departments as do ancillary, or departmental, systems
Two Parts of the Administrative and Financial System
Registration, Admission, Discharge, and Transfer (R-ADT)
Patient Financial Systems (PFSs)
Registration, Admission, Discharge, and Transfer (R-ADT)
registers patients for admission or outpatient services, capturing demographics and insurance data
Registration, Admission, Discharge, and Transfer (R-ADT)
tracks when patients are admitted and opens an account for them
Registration, Admission, Discharge, and Transfer (R-ADT)
tracks all transfers within the hospital
Registration, Admission, Discharge, and Transfer (R-ADT)
closes the account when a patient is discharged
Ancillary or Departmental System
also called clinical departmental systems
Ancillary or Departmental System
serve primarily to manage the department
Ancillary or Departmental System
providing key clinical data for the EHR
Three Types of Ancillary or Departmental Systems
Laboratory Information System
Radiology Information System
Pharmacy Information System
Laboratory Information System
receives order for a lab test
generates a work list for specimen collection, labelling, and accessioning
retrieve results from an auto-analyzer
perform quality control
maintain an inventory of equipment and supplies needed
Radiology Information System
performs similar functions
receives order, scheduling
notifying hospital personnel or the patient
tracking the performance of the procedure and its output
tracking preparation of the report
performing quality control
maintaining an inventory of equipment and supplies
Pharmacy Information System
receives drug checking for contraindications
compounding any drugs requiring special preparation
dispensing the drug in the appropriate dose and for appropriate route of administrations
maintains inventory
supporting staffing and budgeting
Computerized Physician Order Entries and Clinical Decision Support Systems
Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
The process in which individual data elements are represented in the computer by a special code to be used in making comparisons, trending results, and supplying clinical reminders and alerts
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
a special subcategory of clinical information systems that is designed to help healthcare providers make knowledge-based clinical decisions
Electronic Health and Record Functionals Model
Results Management
Order-Entry/Order Management
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical Decision Support Tools
Results Management
electronic results can be displayed automatically for care providers to improve effectiveness and efficiency of treatment while reducing cost of care by eliminating duplicate testing
Order-Entry/Order Management
Computerized Provider Order-Entry (CPOE)/Computerized Physician Order-Entry/Computerized Provider Order Management (CPOM)
Order-Entry/Order Management
Provides physicians and other providers the ability to place orders via the computer from any number of locations and adds decision support capability to enhance patient safety
Benefits of Order-Entry/Order Management
Reduced errors and improve patient safety
Improve efficiency
Improve reimbursements
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
This provides for effective and efficient patient care through decision making tools that are not currently available in paper-based health record systems
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Health record should not be just a simple repository of patient care data
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Assist healthcare providers in the actual diagnosis and treatment of patients
Clinical Decision Support Tools
Review structured electronic data and alert practitioners to out-of-range laboratory values or dangerous trends before problems become evident
Clinical Decision Support Tools
Can recall relevant diagnostic criteria and treatment options on the basis of the data in the records
Clinical Decision Support Tools
Supports the physician as he or she considers various diagnostic and treatment alternatives
Institute of Medicine Key Capabilities of EHR Systems (Evolution of EHRs in Hospitals)
Health information and data
Results management
Order entry management
Decision support
Electronic communication and connectivity
Patient support
Administrative process
Reporting and population health management
Barriers to Electronic Health Record Adoption
Initial cost of implementing a system is consistently considered a top, major barrier to the implementation of electronic health record systems
Technical support, technical concerns maintenance / ongoing costs and resistance to changing work habits
Training
Insufficient time, privacy concerns and workflow challenges
Financial incentives and productivity loss
Barriers to Electronic Health Record Adoption
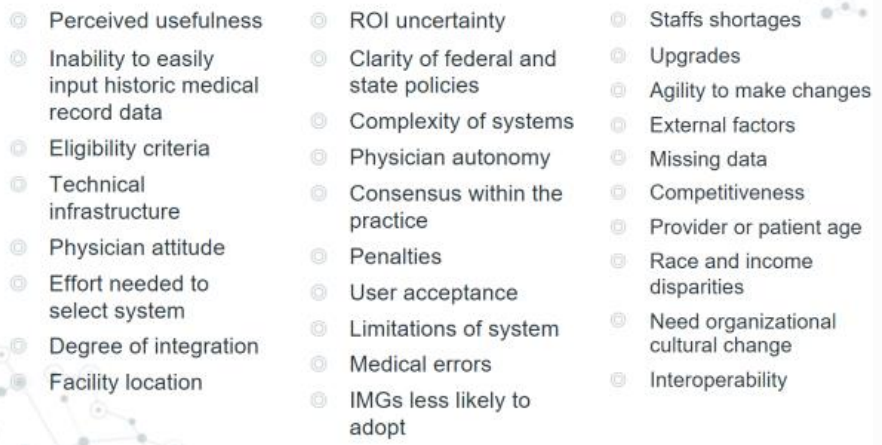
Lack of Interoperability
Providers have voiced out the lack of interoperability because it greatly limits the progression of specialties such as pain management
Lack of Interoperability
Stymies efforts of information governance and information sharing between organizations
Lack of Interoperability
It must be improved to create standardization for data that can or will be staged for a data warehouse
Use of Electronic Health Record
Reduce medical errors
Use of Electronic Health Record
Provide more effective methods of communicating and sharing information among clinicians
Use of Electronic Health Record
Lower national health care costs, better management patient medical records
Use of Electronic Health Record
Improve coordination of care and health care quality
2 Types of Data in Health Record
Clinical Data
Administrative Data
Clinical Data
Documents the patient’s medical condition, diagnosis, and procedures performed as well as the healthcare treatment provided
Administrative Data
Include demographic and financial information as well as various consents and authorizations related to the provision of care and the handling of confidential patient information
Four Main Sources of Standards for Documentation
Facility-Specific Standards
Licensure Requirements
Certification Standards
Accreditation Standards
Facility-Specific Standards
Standards might be found in facility policies and procedures and, when a facility has an organized medical staff in the medical staff bylaws, rules, and regulations
Facility-Specific Standards
Facility-specific guidelines govern the practice of physicians and others within a specific organization
Licensure Requirements
Before they can provide services, most healthcare organizations must be licensed by government entities such as the state or country in which they are located and must maintain a licenses as long as care is provided
Certification Standards
Government reimbursement program standards are applied to facilities that choose to participate in federal programs such as Medicare and Medicaid
Certification Standards
These standards are titled conditions of participation or conditions for coverage. Facilities are said to be certified if the standards are met
Accreditation Standards
end result of an intensive external review process that indicates a facility has voluntarily met the standards of the independent accrediting organization
Description of Alternatives
State regulating agencies
Medicare and Medicaid programs
Accreditation organizations
The joint commission
Patient Record Documentation Guidelines
Authentication
Change in Patient’s Condition
Completeness
Consistency
Objective Documentation
Referencing Other Patients
Permanency
Physical Characteristics
Specificity
Authentication
Entries should be documented and signed (authenticated by the author)
Change in Patient’s Condition
If the patient’s condition changes or significant patient care issue develops, documentation must reflect this as well as indicate follow-through
Completeness
Significant information related to patient’s care and treatment should be documented (e.g. patient condition, response to care, treatment course, and any deviation from standard treatment/reason)
Consistency
Document current observations, outcomes and progress
Consistency
Entries should be consistent with documentation in the record (e.g. flow charts)
Consistency
If the documentation is contradictory, an explanation should be included
Objective Documentation
State the facts about patient care and treatment and avoid documenting opinions:
Incorrect: patient is peculiar
Correct: patient exhibits odd behavior