Population Ecology Study Guide: Key Concepts, Graphs, and Demographics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area.
Demographics
Statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it.
Population size
The total number of individuals in a population.
Population density
The number of individuals per unit area or volume.
Population distribution
The spatial arrangement of individuals within a population, which can be categorized into three types.
Ecology
The branch of biology that deals with the relationships of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings.
Mark-recapture method
A technique used to estimate the size of wildlife populations.
Plot sampling
A method of estimating population size by counting individuals in a specific area.
Immigration vs emigration
Immigration is the arrival of individuals into a population, while emigration is the departure of individuals from a population.
Exponential growth
A growth pattern where the population size increases rapidly in proportion to the current size, typically represented by a J-shaped curve.
Logistic growth
A growth pattern that starts exponentially but levels off as the population reaches carrying capacity, typically represented by an S-shaped curve.
Growth rate per capita
The increase in population size per individual, often expressed as a percentage.
Growth rate
The rate at which a population increases in size, typically expressed as a percentage.
Intraspecific competition
Competition between individuals of the same species for limited resources.
Interspecific competition
Competition between individuals of different species for limited resources.
Carrying capacity (K)
The maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely.
Density-dependent limiting factors
Factors that affect population size in relation to the population density.
Density-independent limiting factors
Factors that affect population size regardless of the population density.
Cohort
A group of individuals of the same age within a population.
Survivorship curve
A graph that represents the number of individuals surviving at each age for a given species.
Ecological footprint
A measure of human demand on the Earth's ecosystems, representing the amount of natural capital used.
Demographic transition model
A model that describes the transition of a country from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as it develops economically.
Biotic potential
The maximum rate of increase per individual under ideal environmental conditions.
Carrying capacity
The maximum number of individuals sustainable by the resources in a given environment.
Limiting factors
Essential resources that restrict population growth when scarce.
Density-independent factor
A factor that influences population growth regardless of the population density, such as harsh weather.
R-selection
A reproductive strategy characterized by high growth rates and the production of many offspring.
K-selection
A reproductive strategy characterized by lower growth rates and the production of fewer offspring with higher parental investment.
Total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime.
Replacement fertility rate
The level of fertility at which a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next.
Age structure diagrams
Graphs that show the distribution of various age groups in a population.
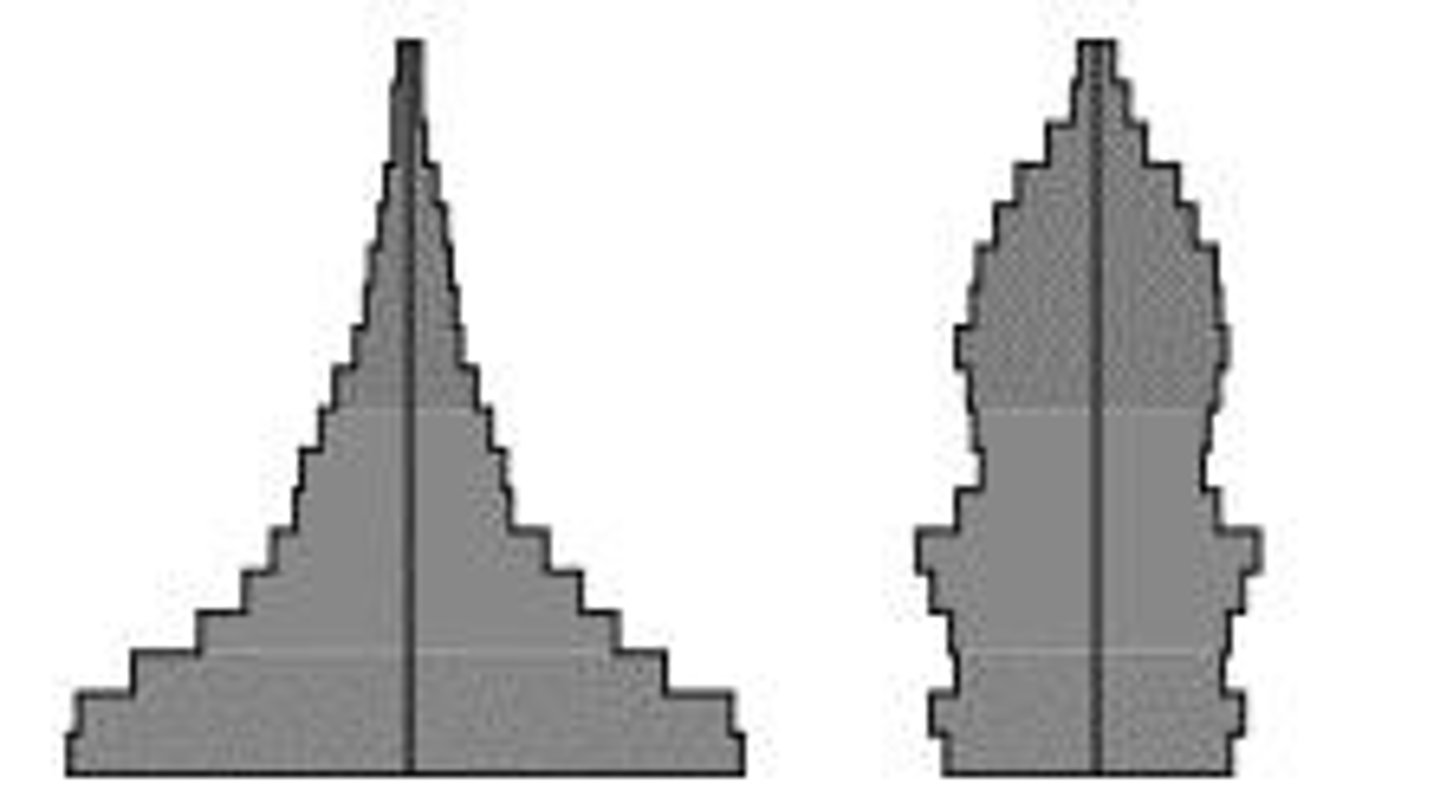
Population growth rate
The rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases or decreases.
Resource consumption rate
The rate at which resources are used by a population.
Infant mortality
The death of infants before their first birthday, often used as an indicator of the health of a population.
Clumped distribution
A pattern where individuals are grouped together in certain areas.
Near uniform distribution
A pattern where individuals are evenly spaced throughout their habitat.
Random distribution
A pattern where individuals are spread out in an unpredictable manner.