SCH4U - Unit Four Structures & Properties
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
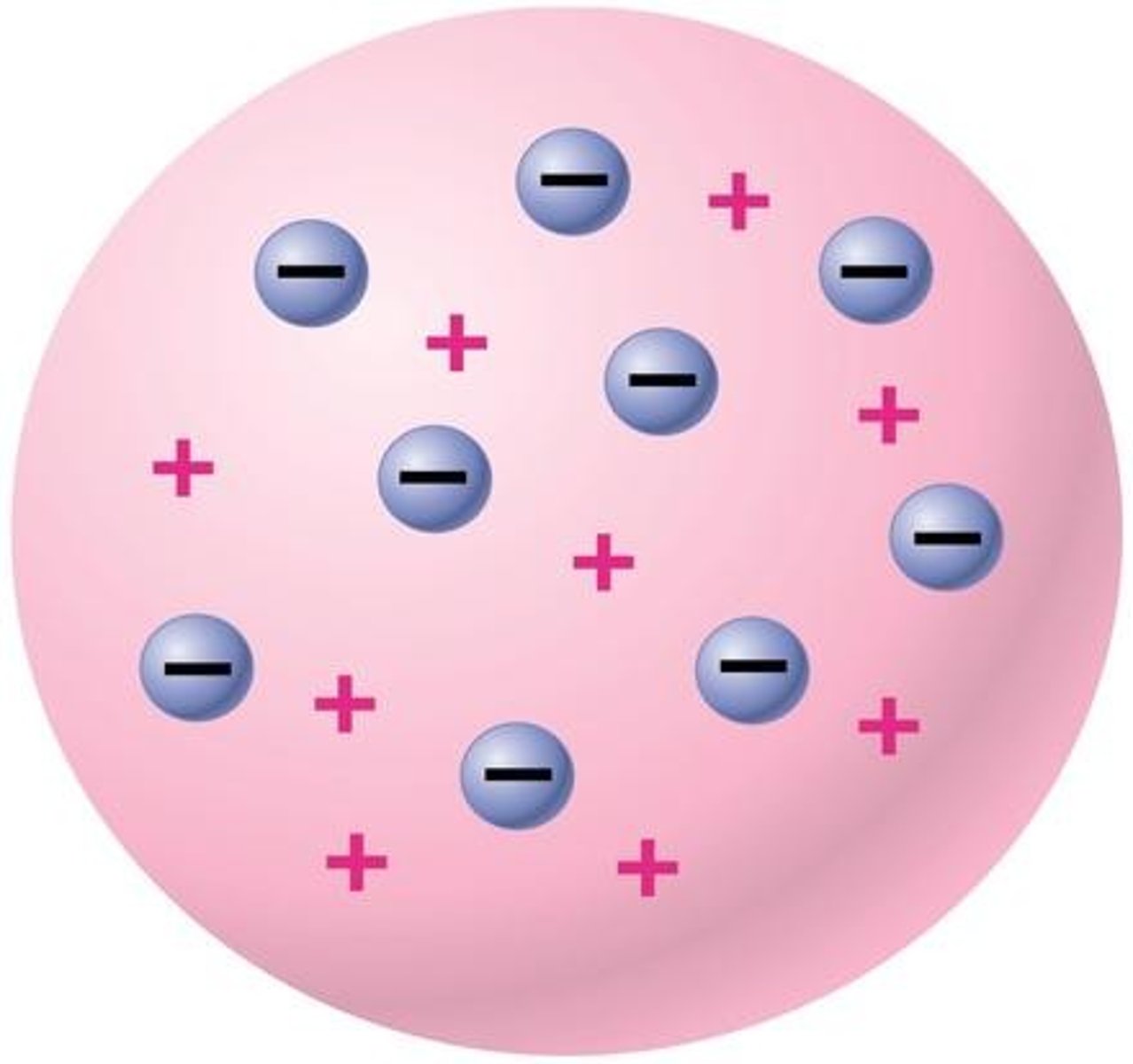
JJ Thomson
used the cathode ray tube to discover electrons
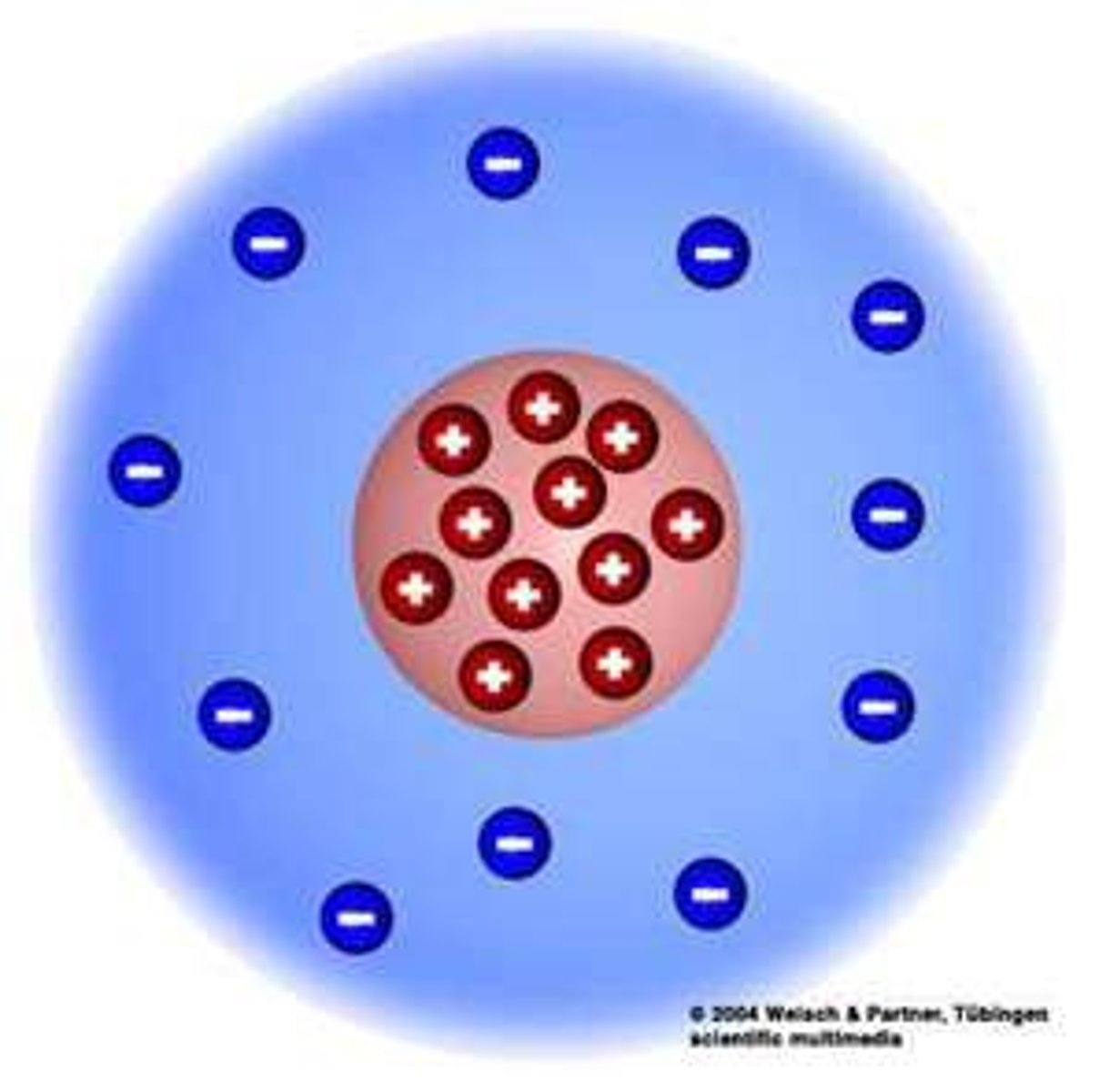
Ernest Rutherford
used the gold foil experiment to discover the positively charged nucleus
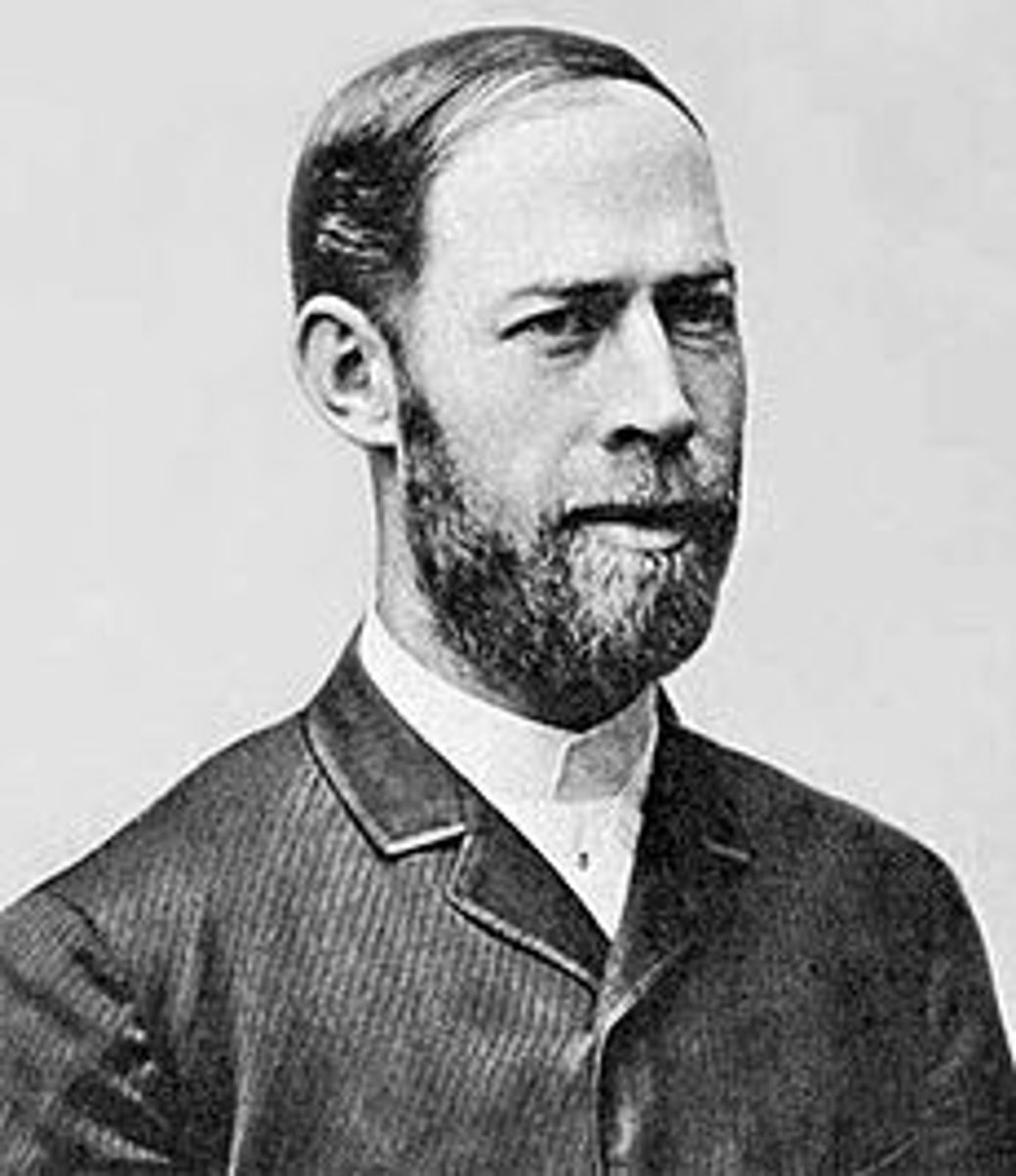
Who developed the photoelectric effect?
Heinrich Hertz

photoelectric effect
objects will release e if struck by light
minimum threshold (energy) is needed
frequency (colour) determines the energy of the emitted e
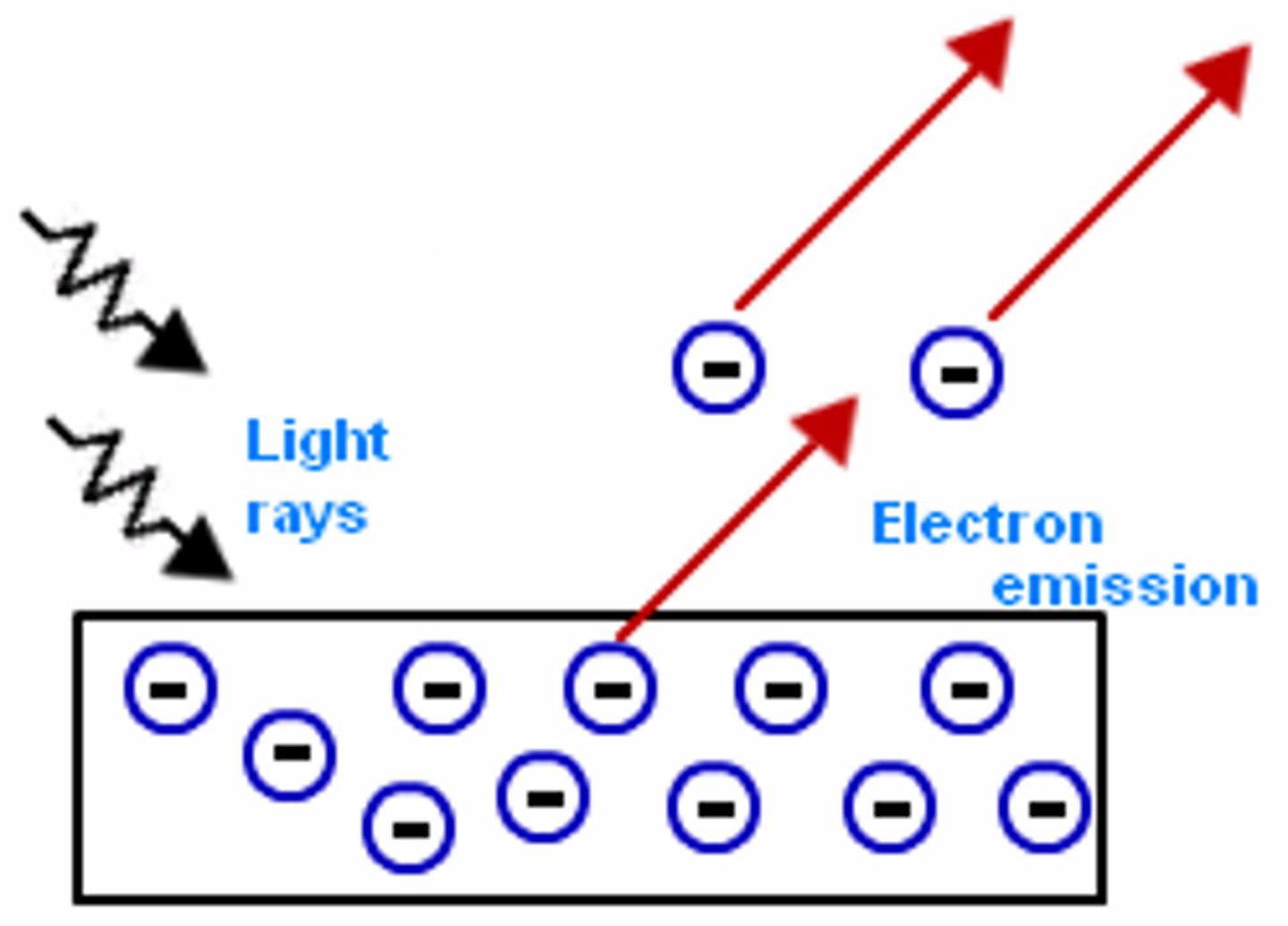
Heinrich Hertz
the strength of emitted electrons depend on the frequency/colour of the light, not the brightness

Who developed quantum theory?
Max Planck

what did Max Planck study to develop quantum theory?
blackbody radiation
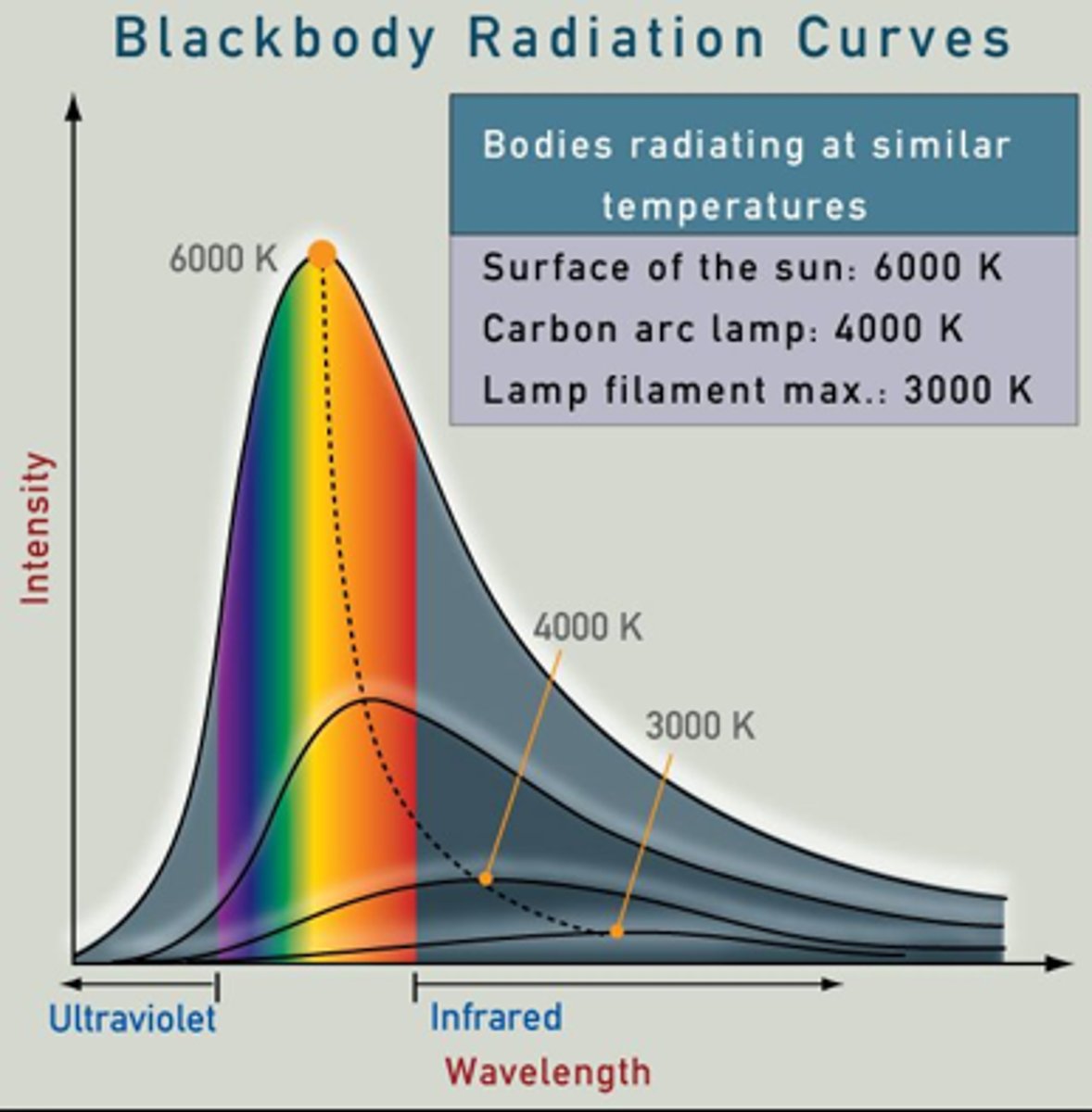
blackbody radiation
Energy (light/heat) given off by an object because of its temperature.
Hotter objects emit more energy and at shorter wavelengths (bluer)
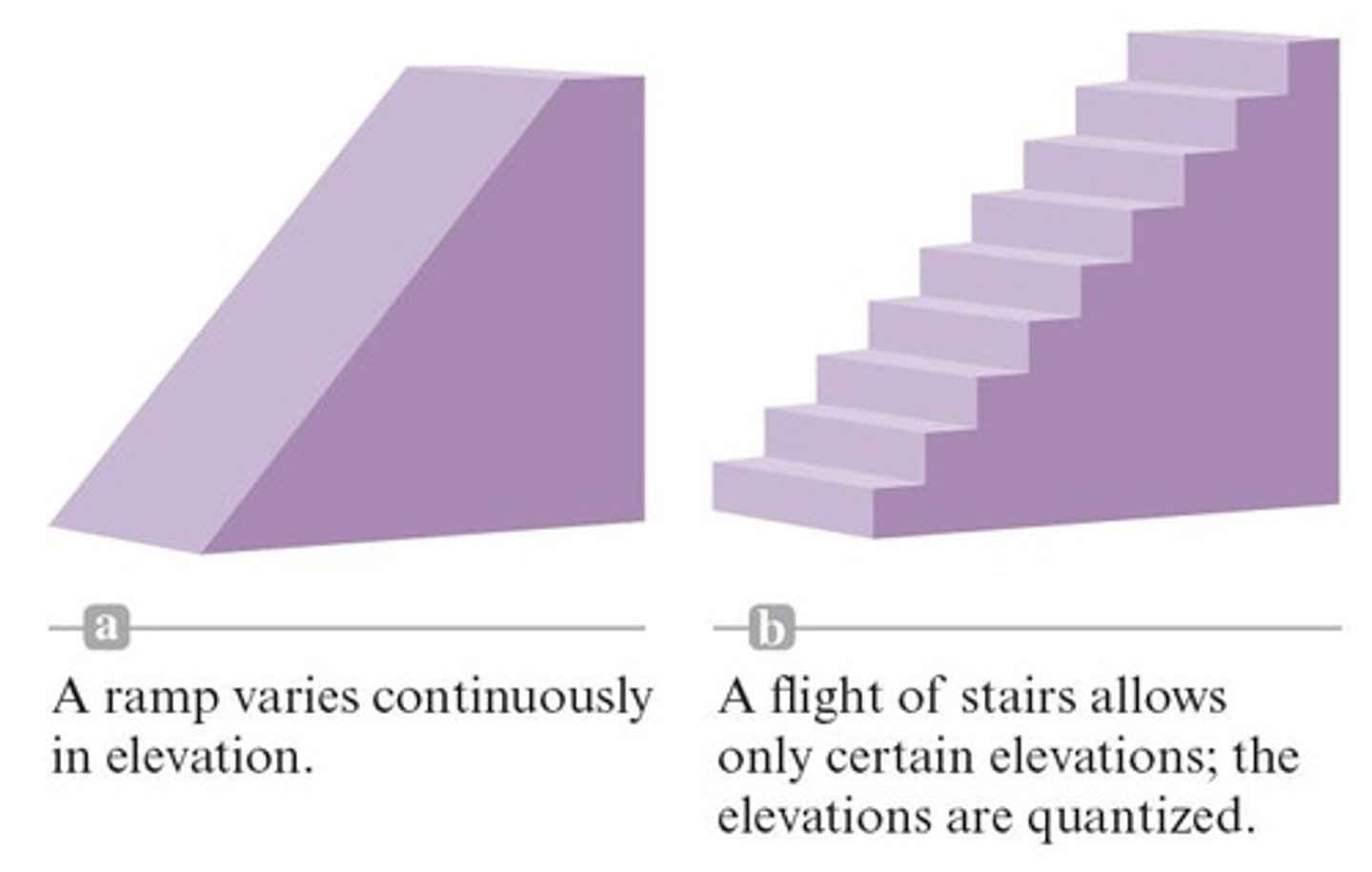
quantization of energy
energy is not continuous, packaged in small amounts of quanta
Albert Einstein
light is both a wave AND particle
Albert Einstein's proposition
electrons were emitted from the surface of the metal because a photon collided with the electron
Why would an electron emit when colliding?
transferred energy to the electron would cause it to break away
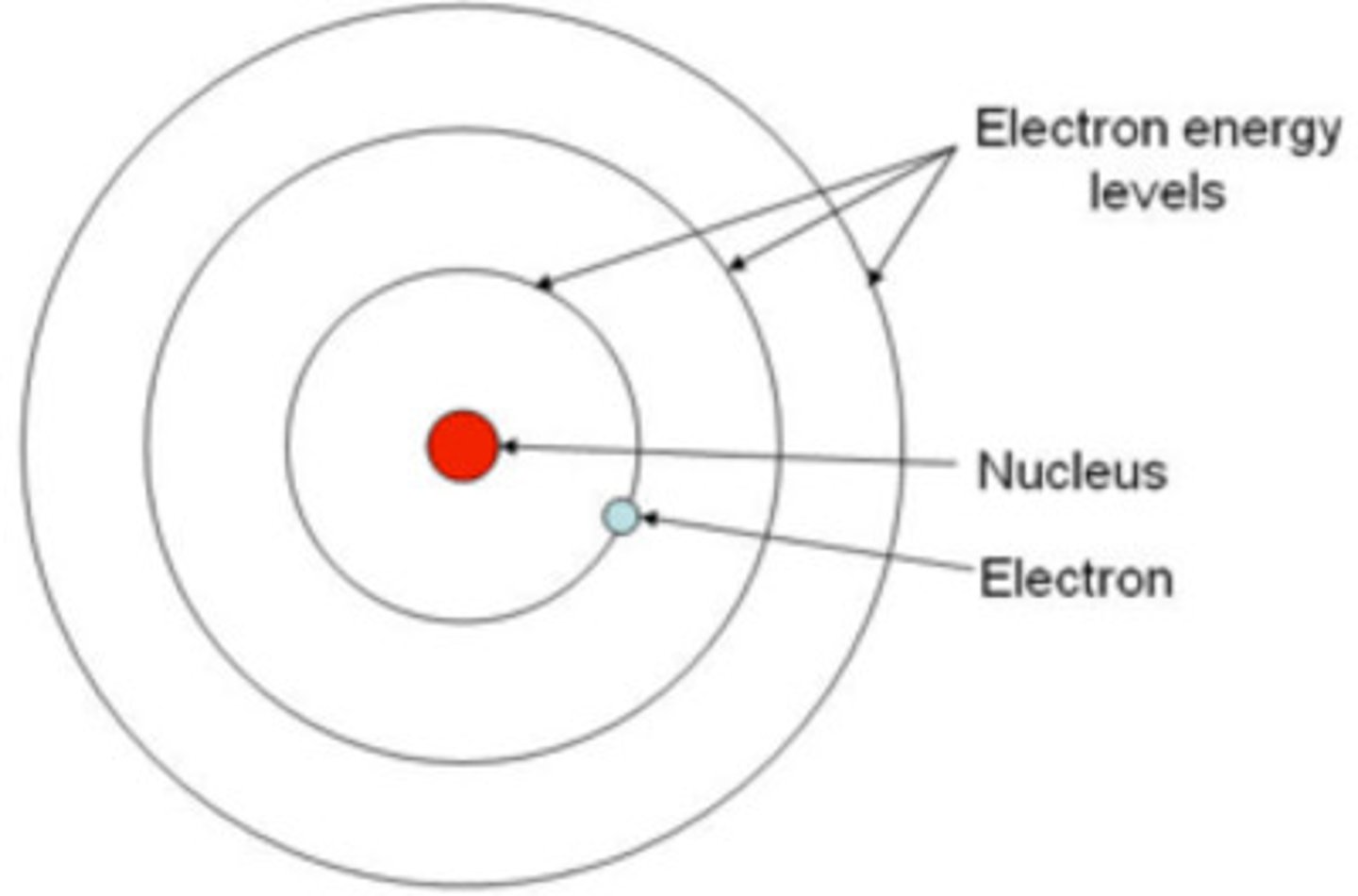
Niels Bohr
determined electrons have certain energies

Bohr's discovery
the energy of electrons are quantized, existing in special energy states, ground and transition
transition/excited state
an electron can absorb energy and jump to a higher energy level (shell)
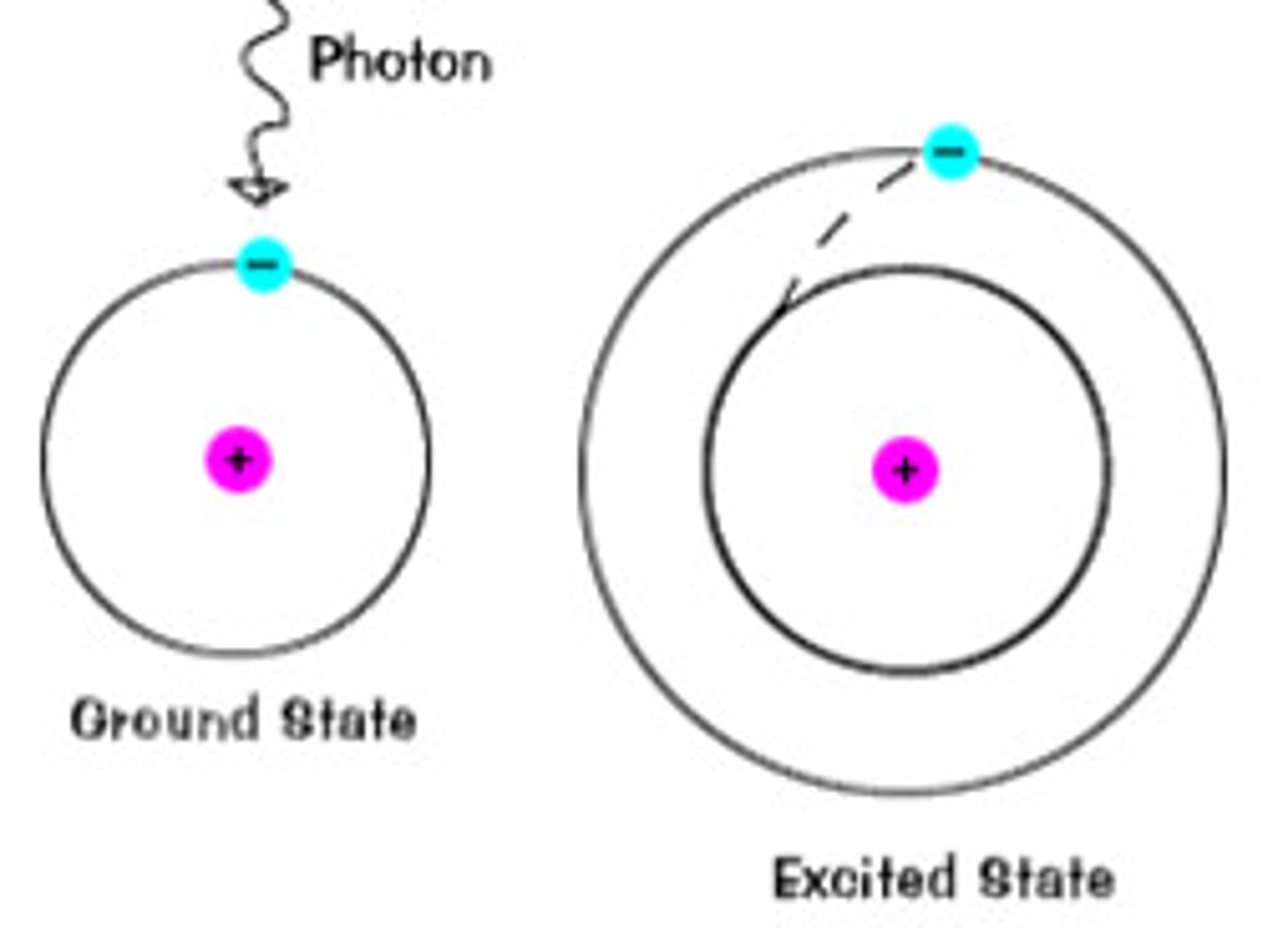
electron returns to its ground state
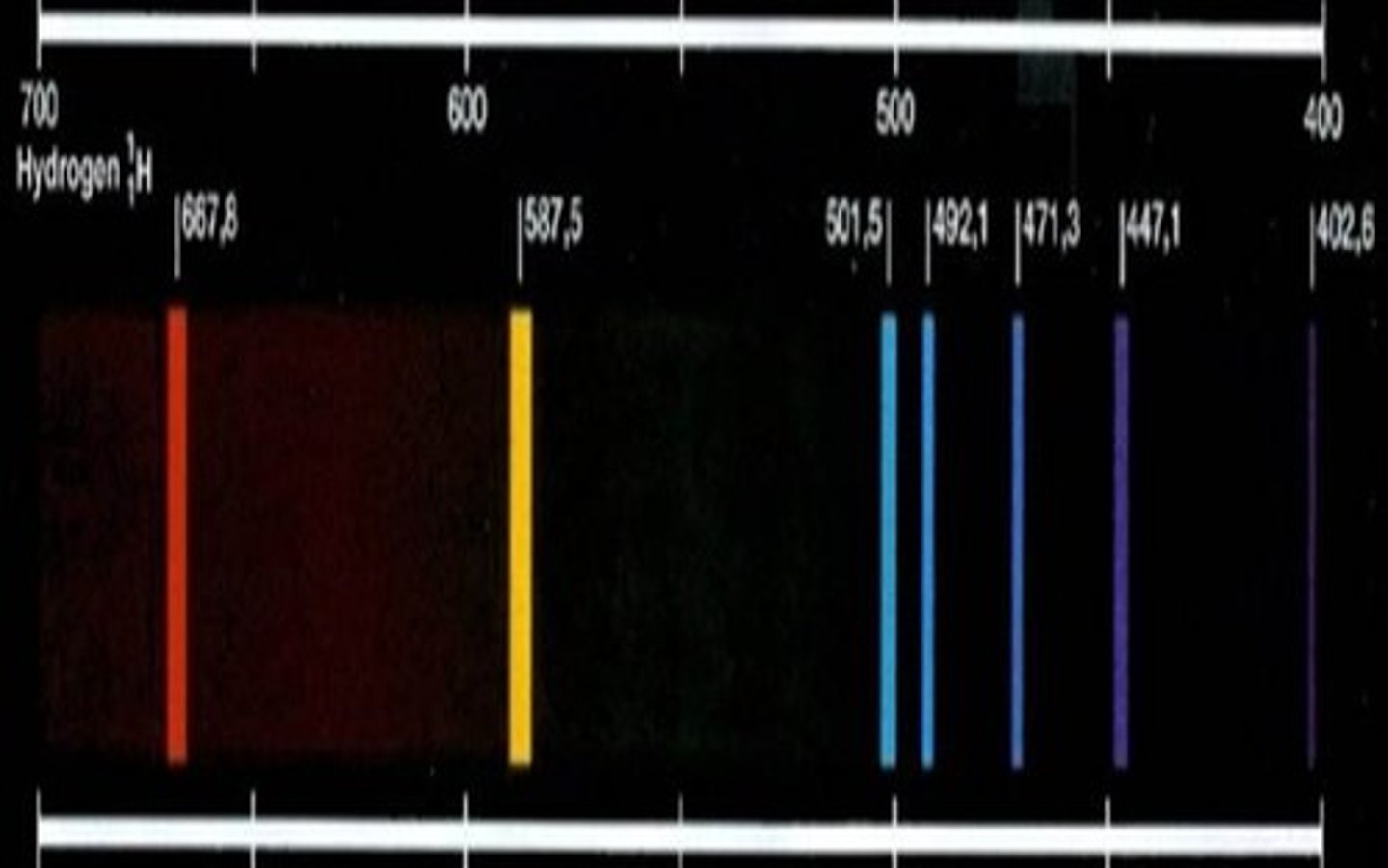
excess energy is emitted as photons
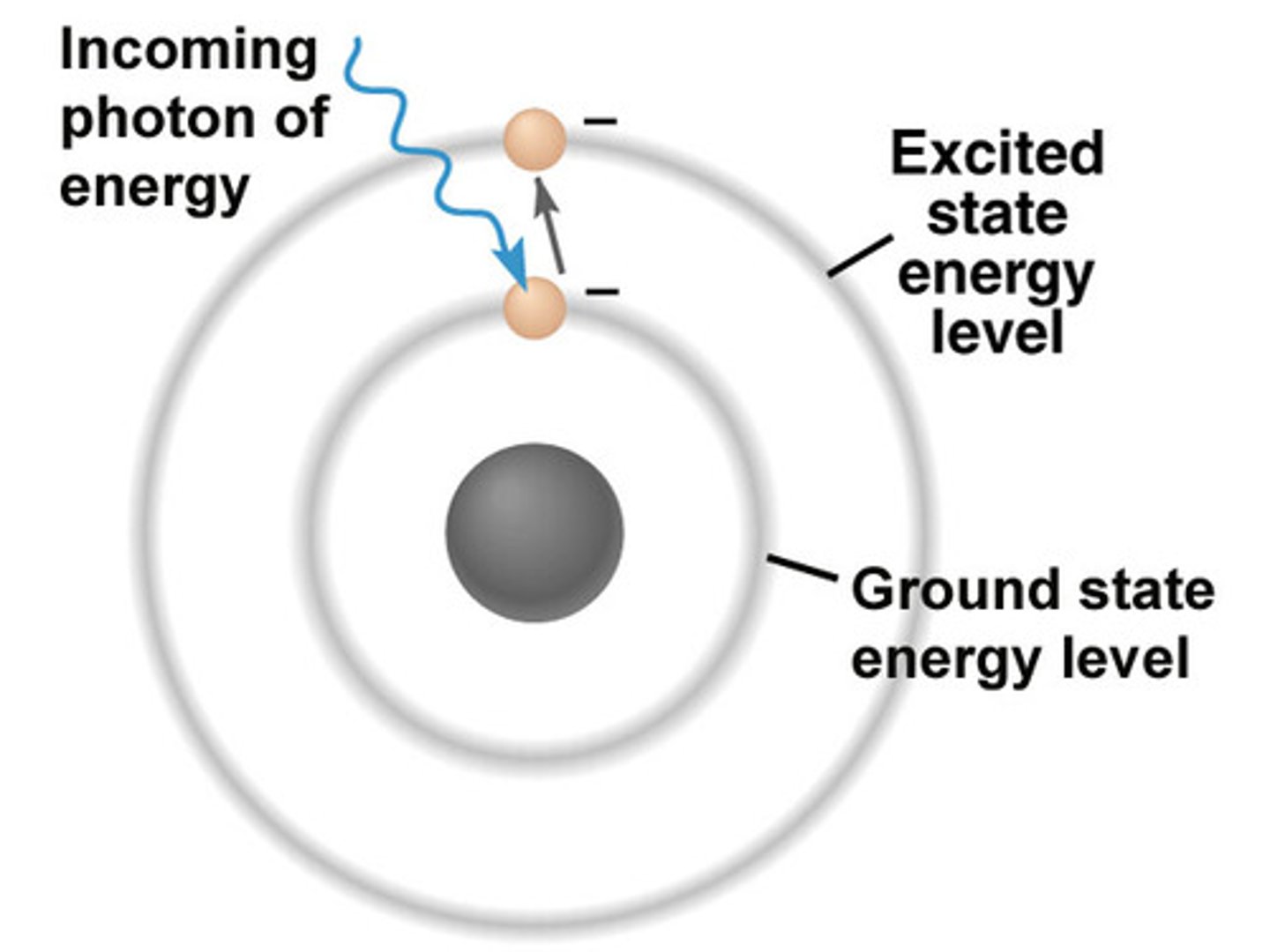
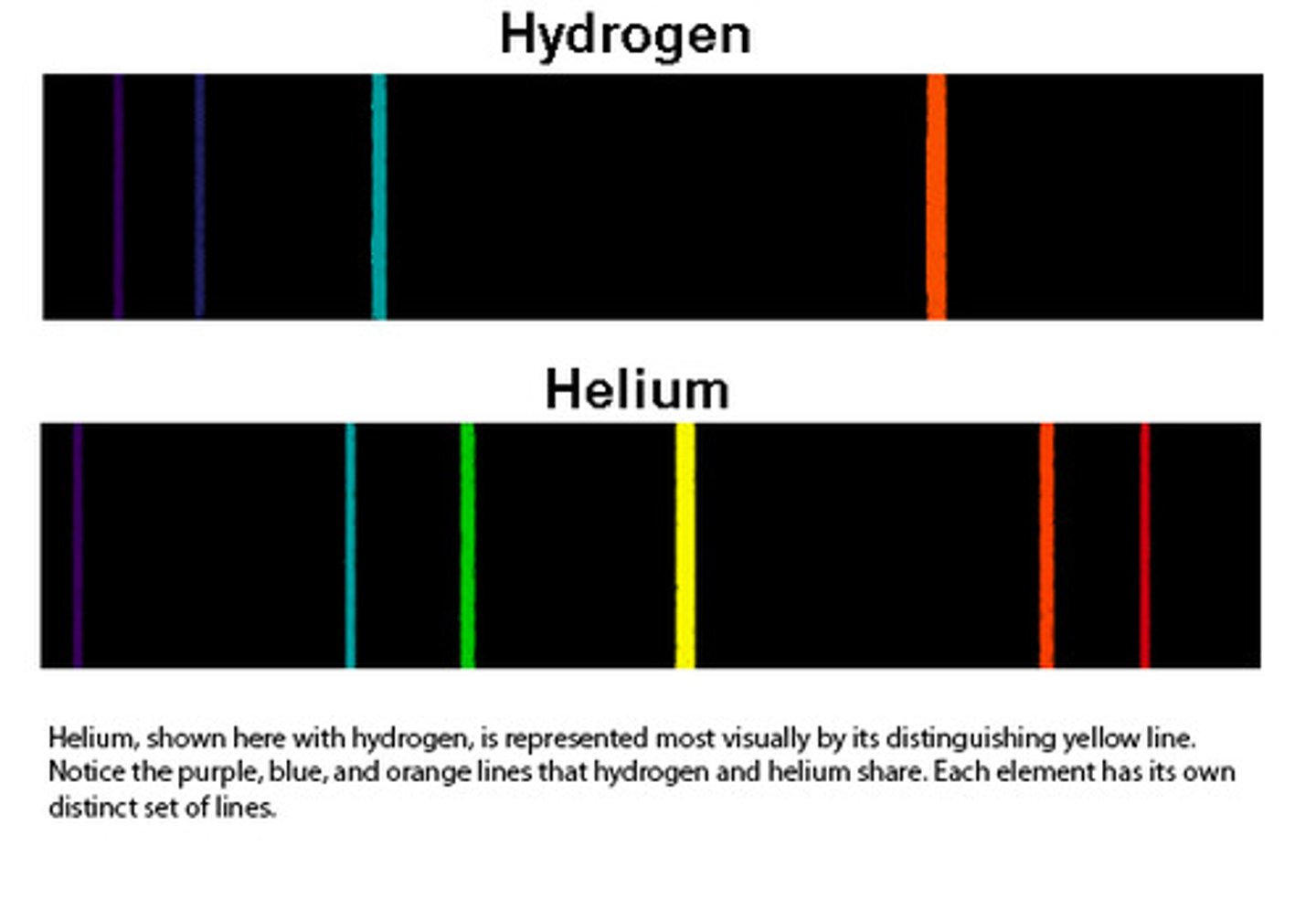
excess of energy emitted
different elements will produce different frequencies/colours of electromagnetic radiation
de Broglie
matter, specifically electrons, has particle-wave duality

Schrodinger studied
focused on the wave properties of electrons

Werner Heisenberg
uncertainty principle
uncertainty principle
wave and particle nature of electrons are complementary, being inversely related, the more we know about one, the less we know
uncertainty principle and electrons
since we cannot know both of these at a specific time, we state the probability of finding electrons
quantum model
electrons can be in different orbitals by absorbing or emitting energy, and the location of electrons is given by probability
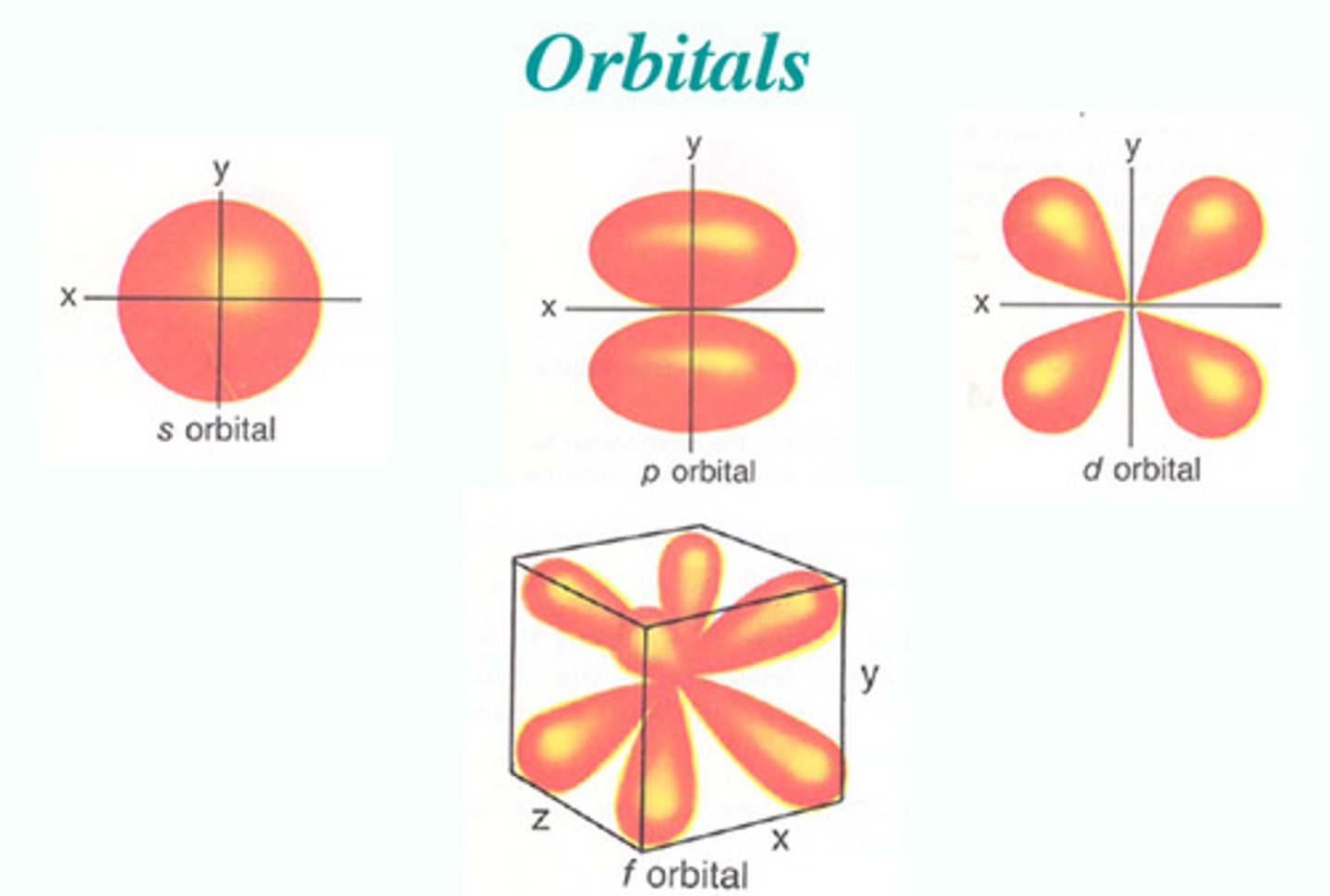
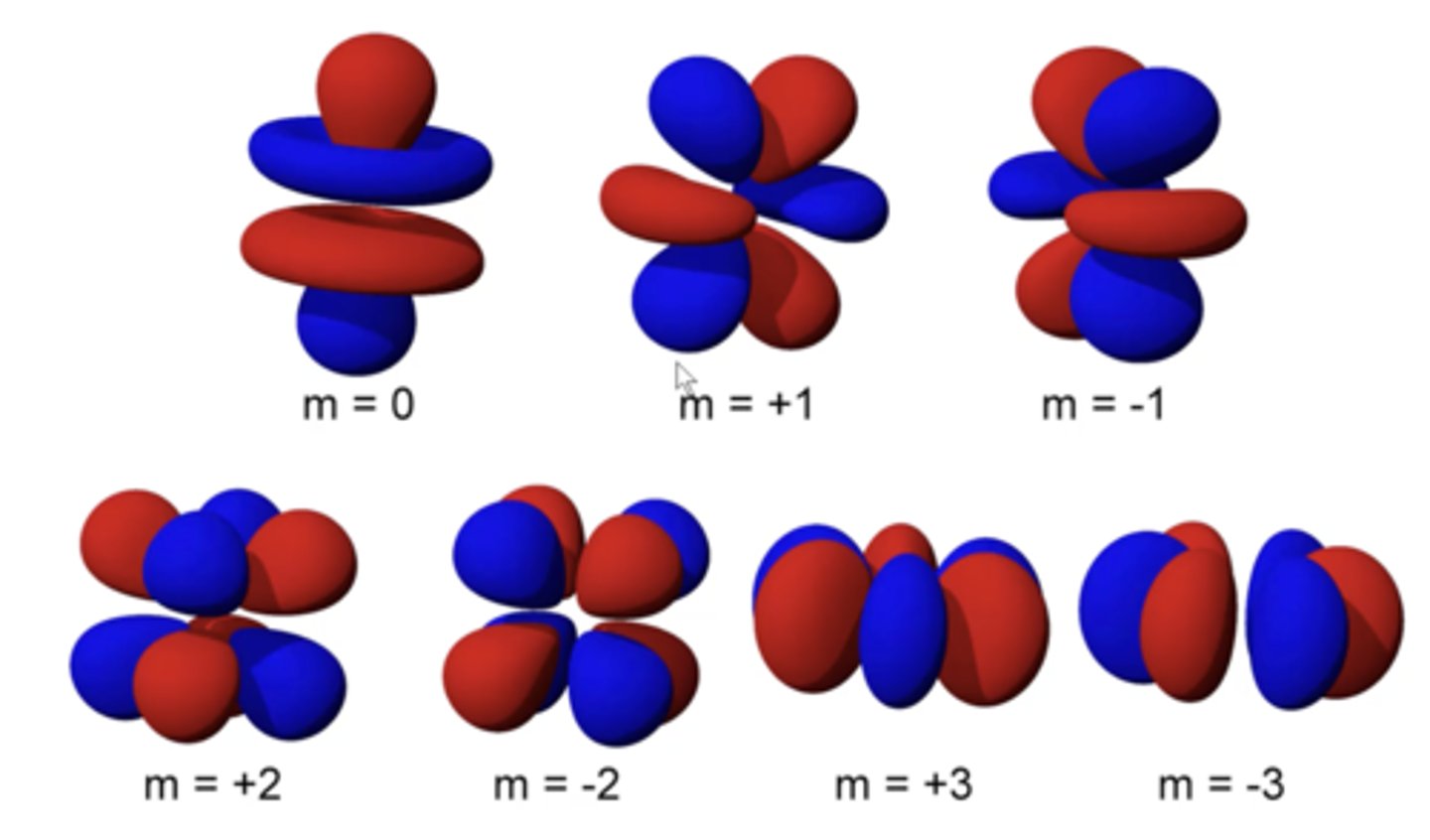
orbitals
space where only two electrons can be found, based on probabilities
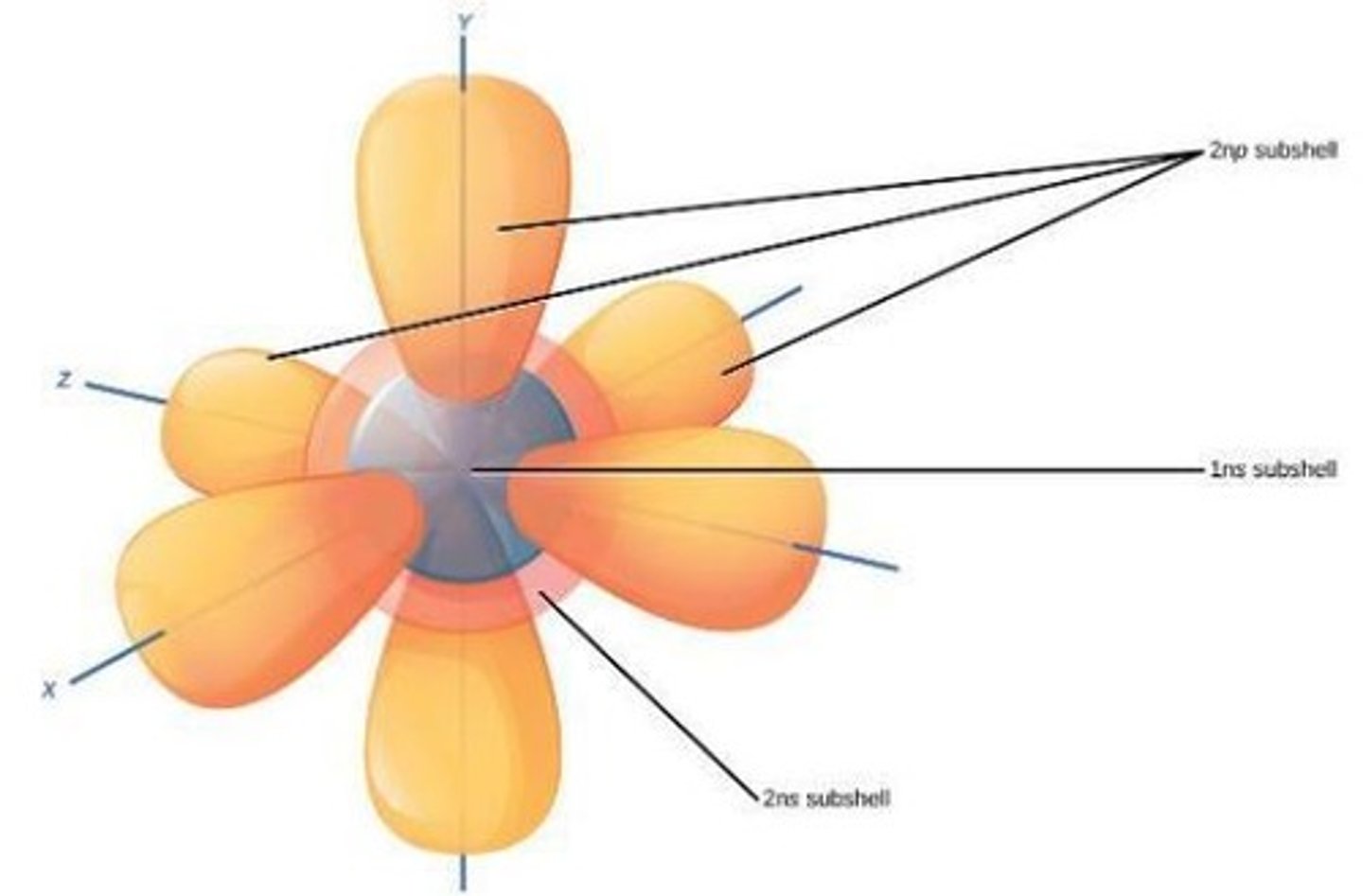
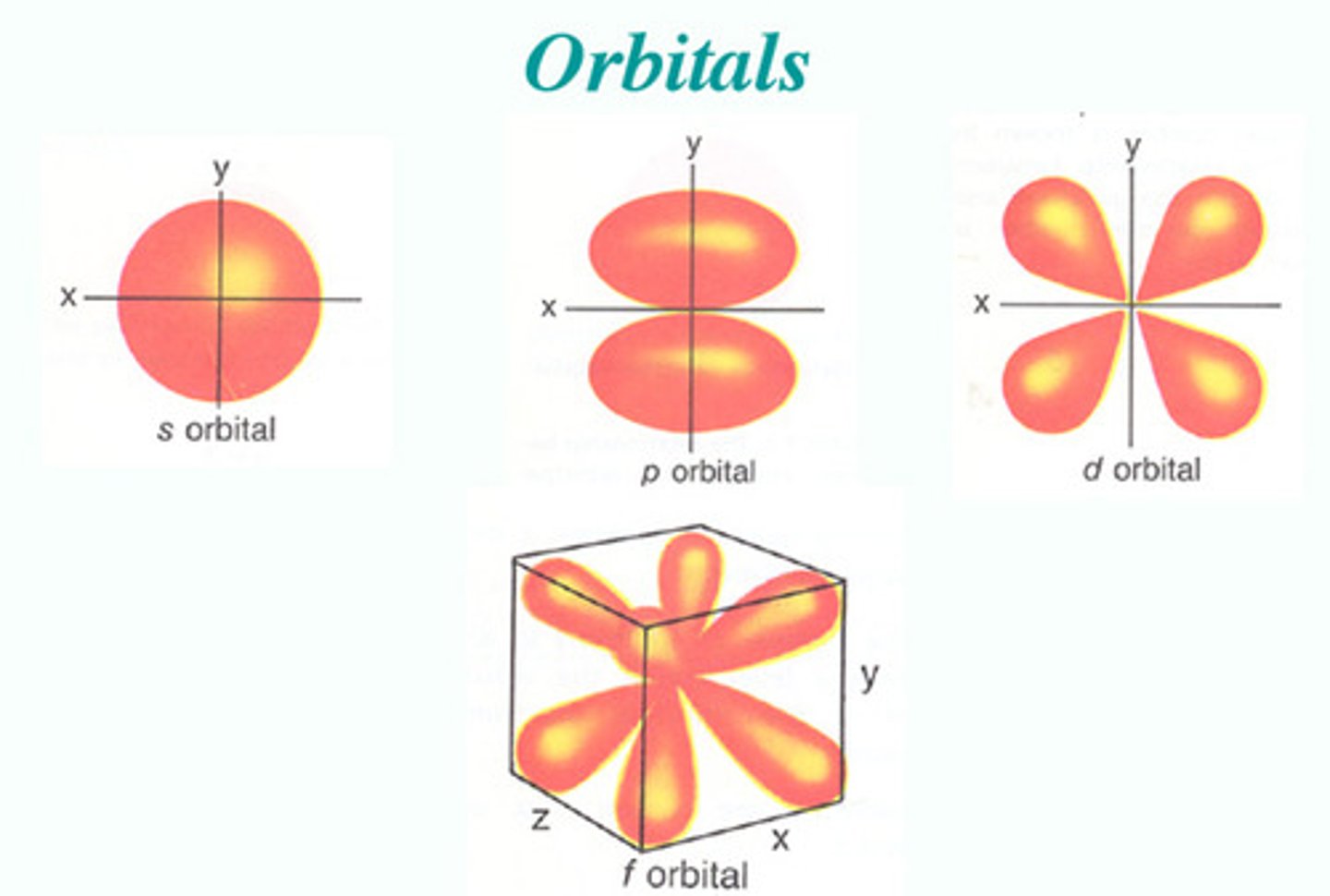
types of orbitals
S, P, D, F
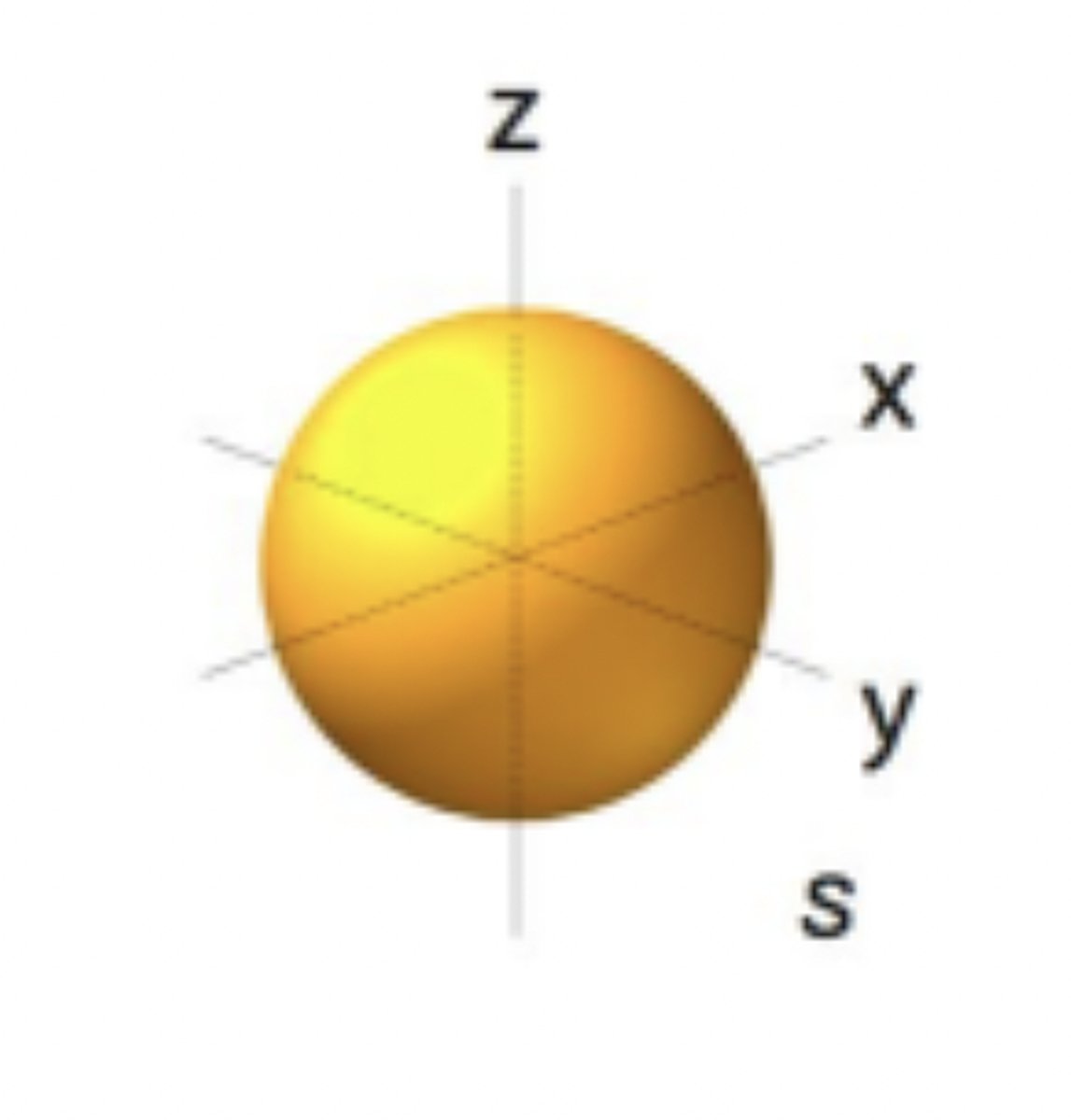
S orbitals
spherical-shaped orbitals, n=1/L=0
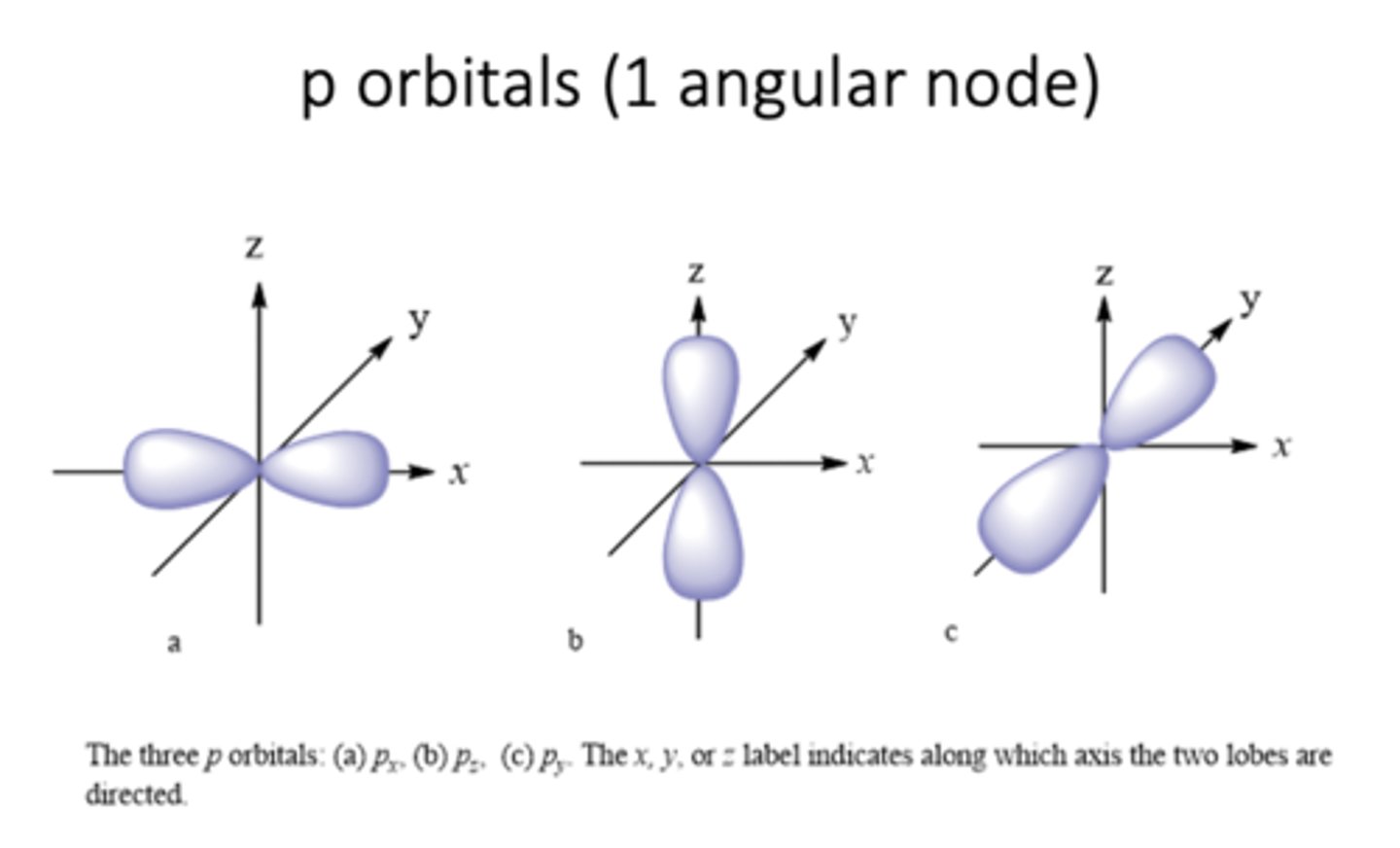
P orbitals
Px, Py, Pz
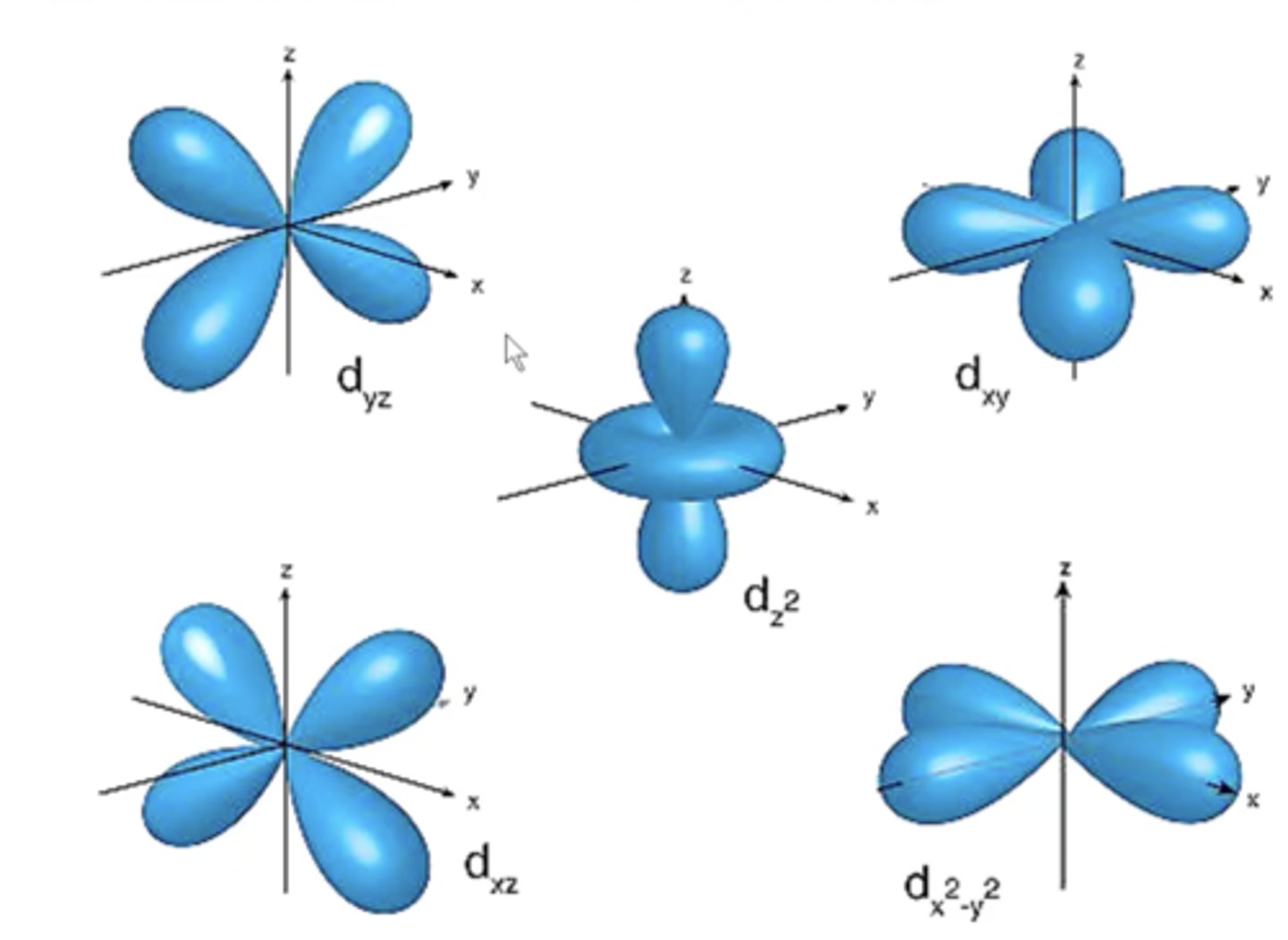
number of D orbitals
five orbitals
number of F orbitals
seven orbitals
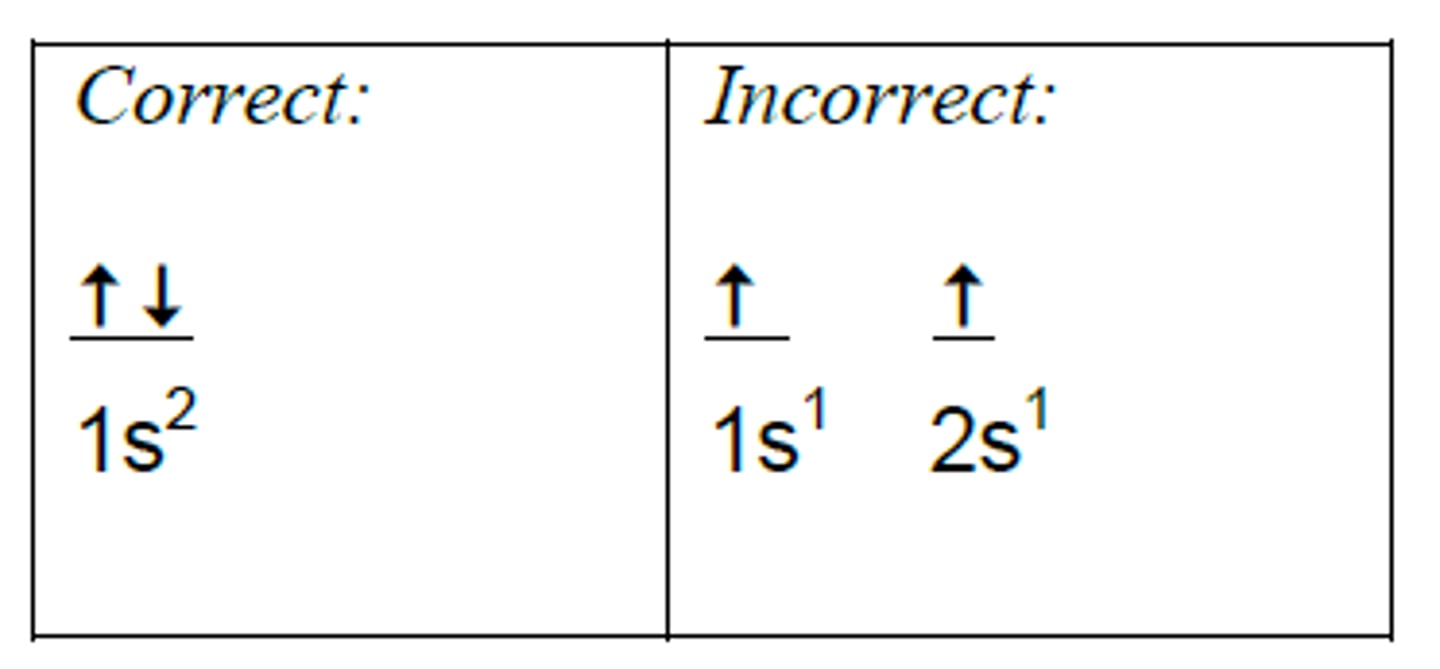
pauli exclusion principle
no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers

principal quantum number
describes size and energy level or orbitals, whole number value n = 1, 2, 3...
orbital shapes affected by principal quantum numbers
since they can exist at different energy levels, they increase in size with their energy
secondary quantum numbers
refers to the subshell and shape of orbitals, with whole number values from zero to n - 1
l = 0 (s)
l = 1 (p)
aufbau principle
lowest energy orbitals are filled first
Hund's rule
one electron is added to each level before electrons can be paired
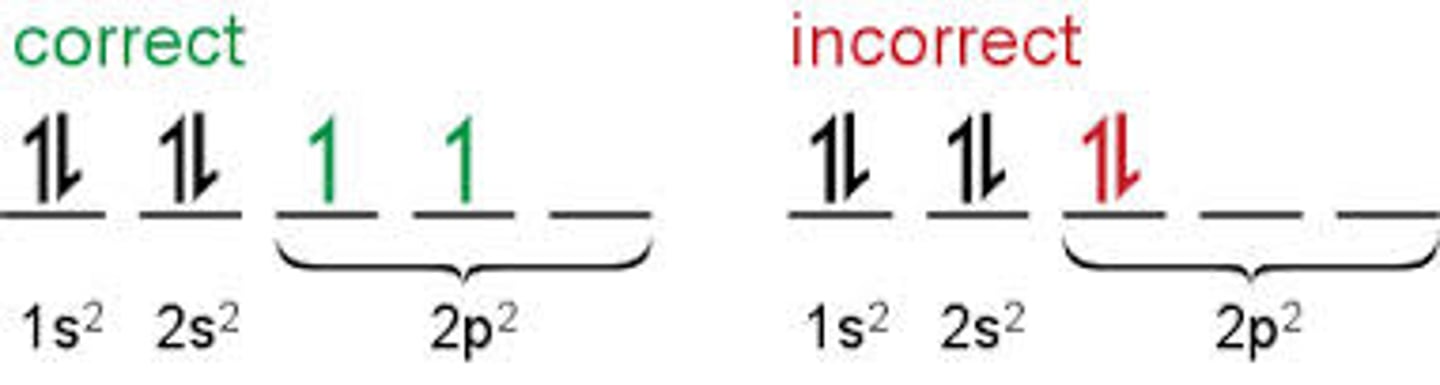
electron configurations
summary of energy level diagram
principal number, orbital subshell, number of electrons
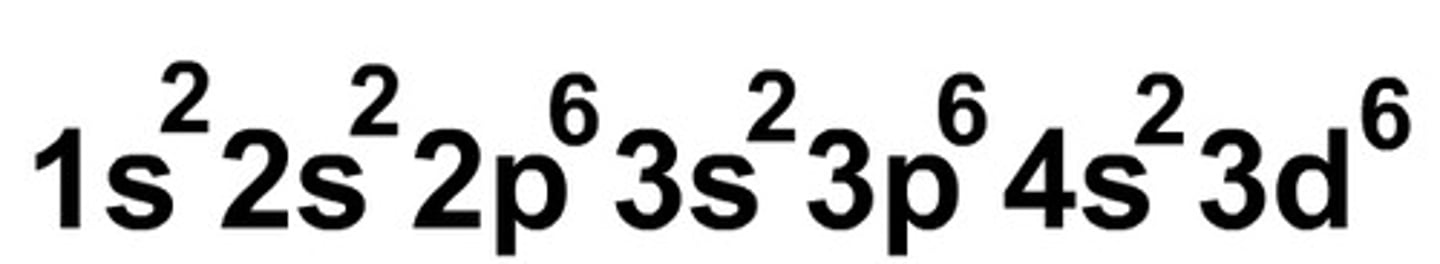
condense full electron configurations
by using noble gas placeholders
e.g, [Xe] ...
![<p>by using noble gas placeholders </p><p>e.g, [Xe] ...</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d59514b5-86a2-45dc-af2a-8967032cbbab.jpg)
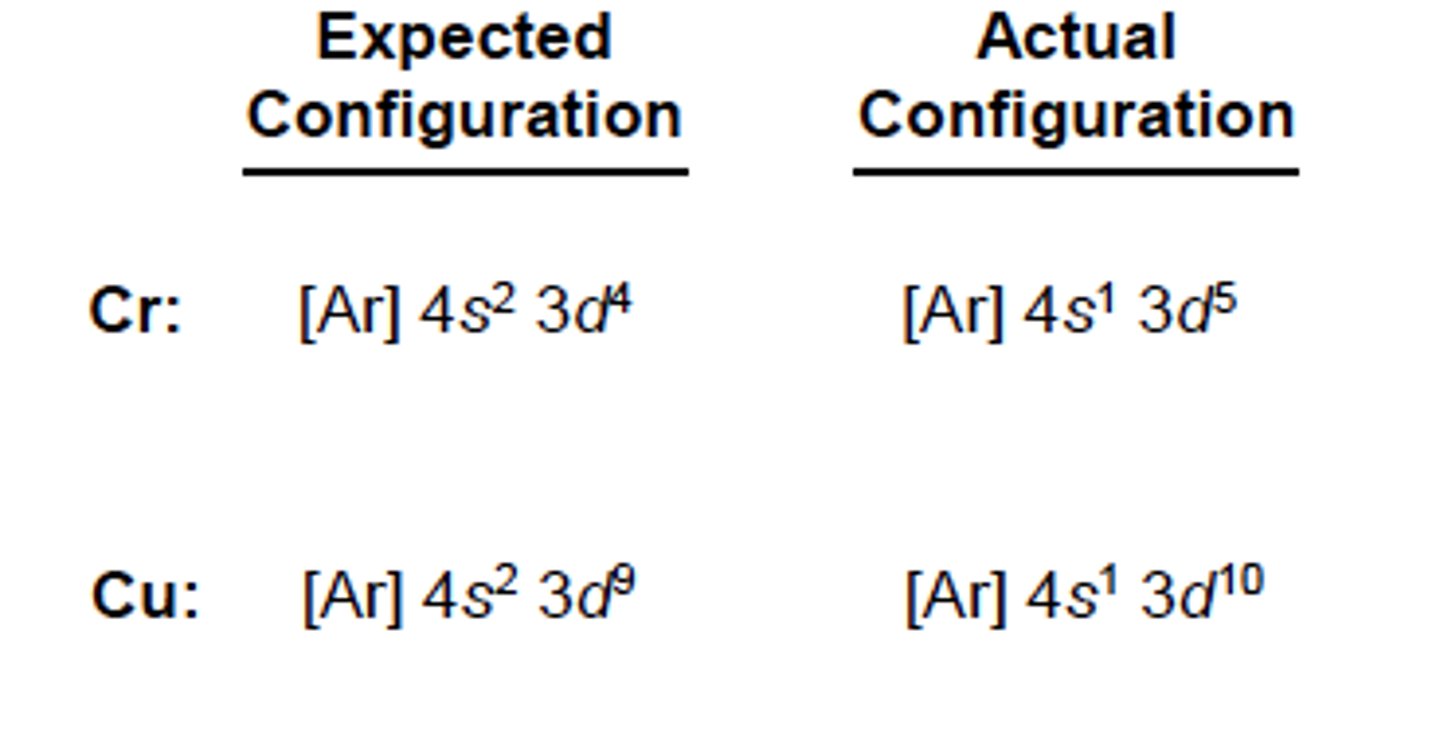
electron anormalies
half-filled subshells are more stabe than partially filled subshells
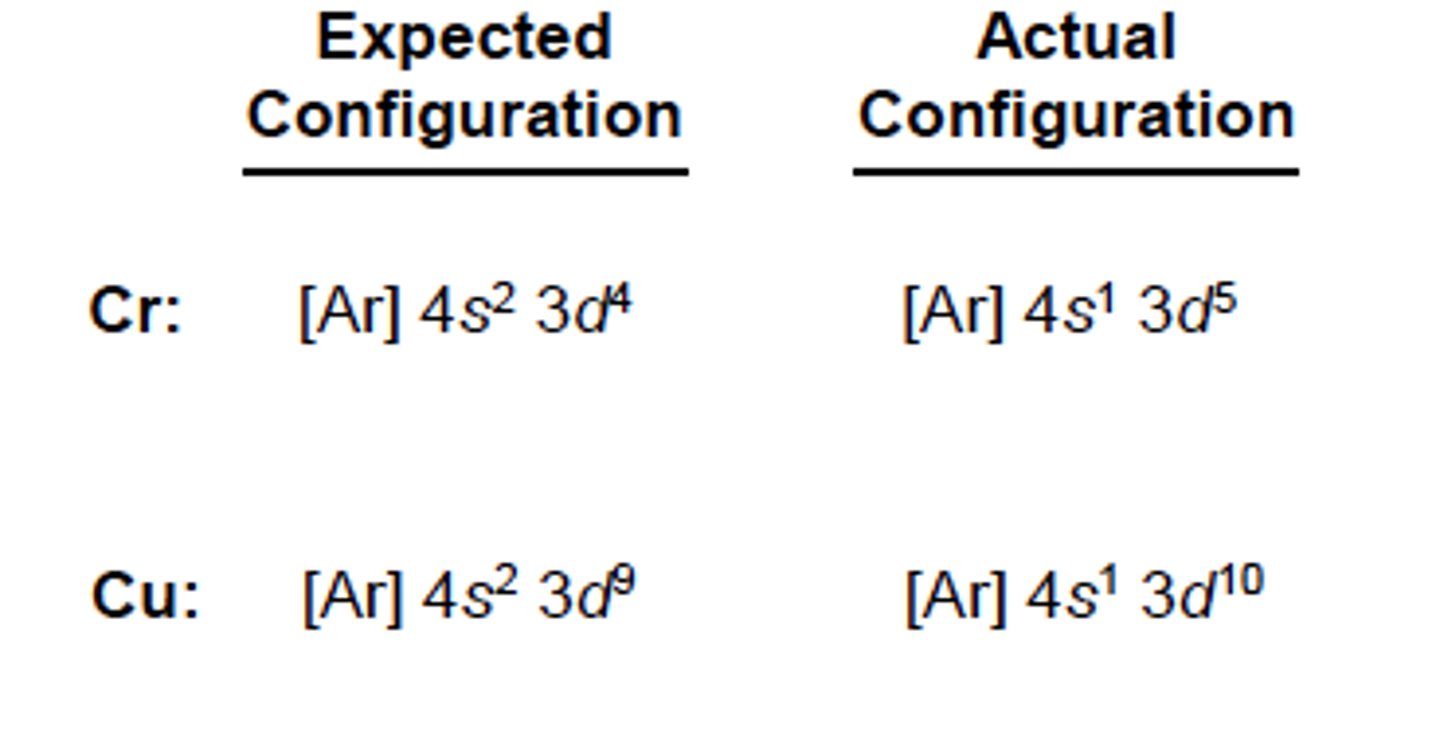
electron configurations differs
electrons can jump energy levels to go from partially filled, to half-filled subshell to become stable
charge affect configuration
add electrons to the lowest energy orbital (anion)
remove electrons from the highest principal number (cation)
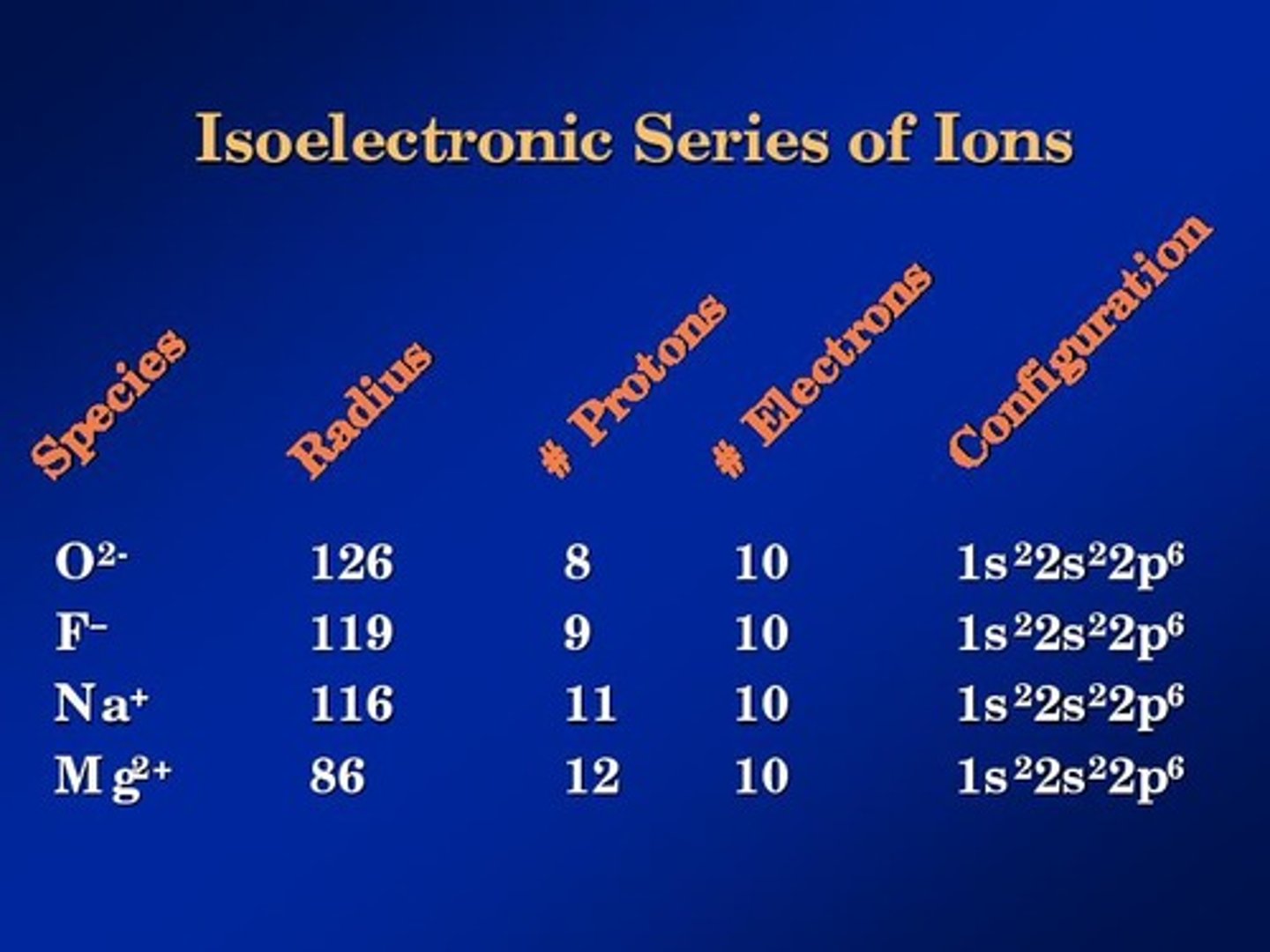
isoelectronic
having the same electron configuration between to elements
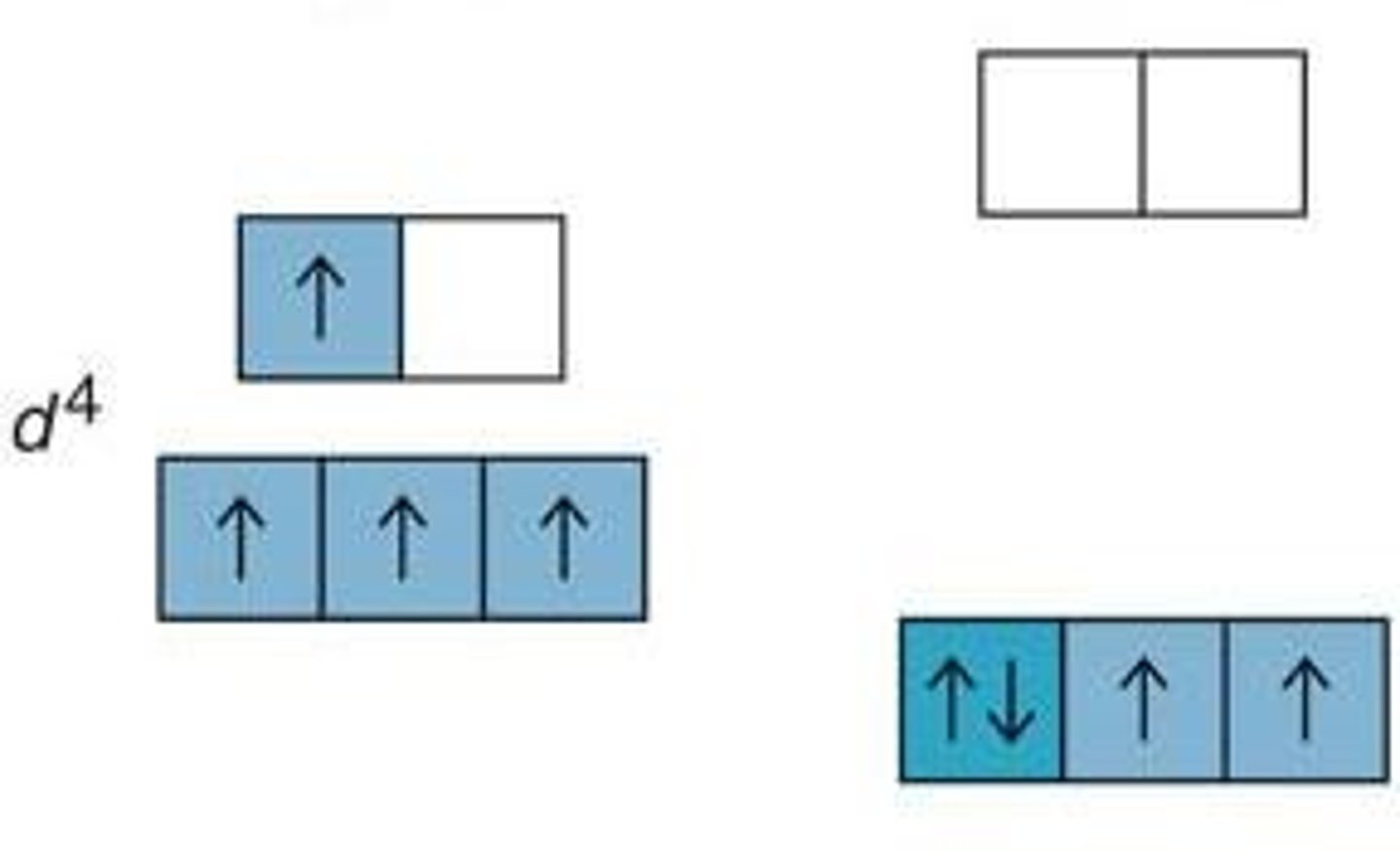
paramagnetism
the weak attraction of a substance to a magnet, caused by unpaired electrons having the same spin
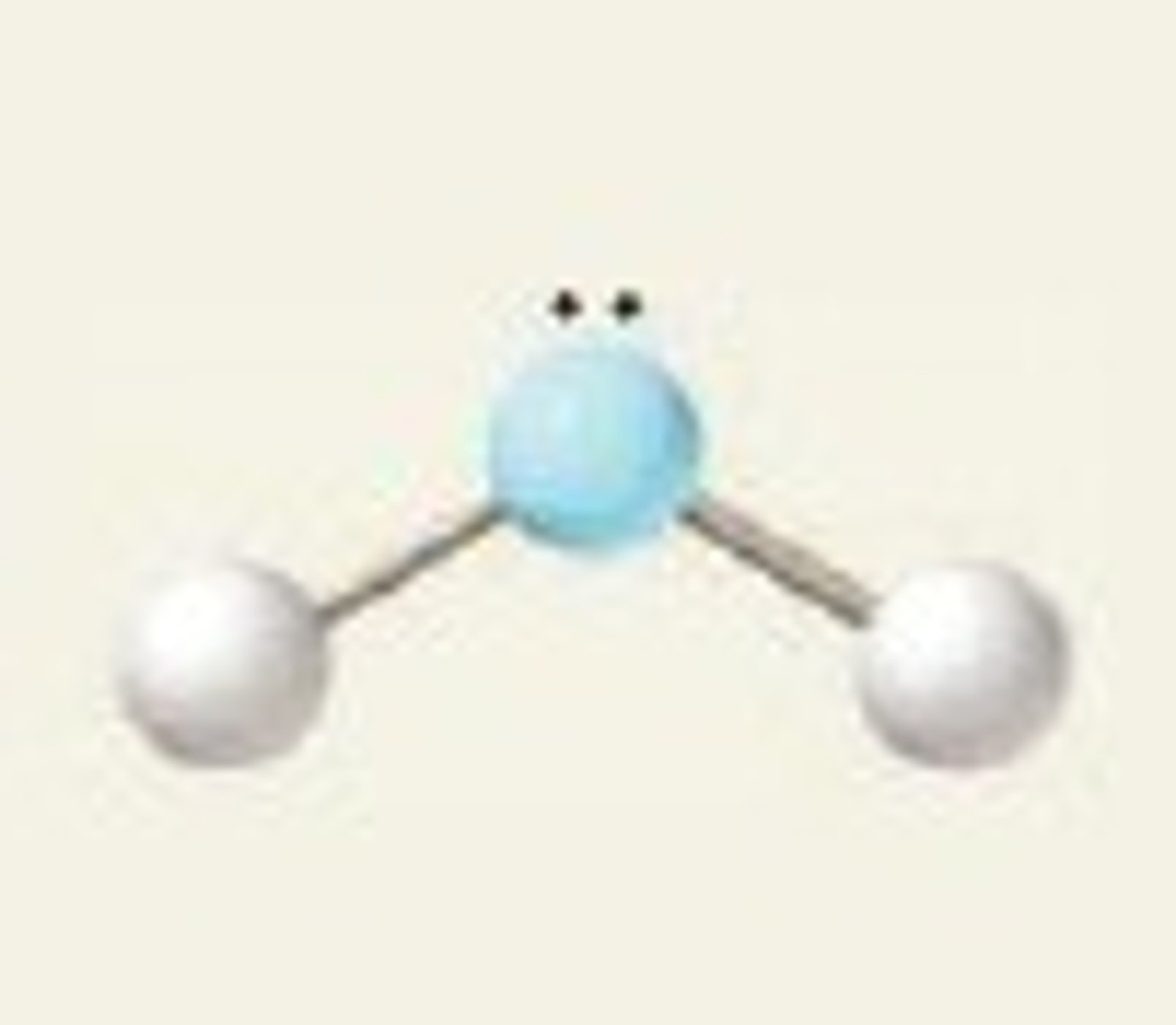
VSPER theory
method to determine geometry of molecules, based on how electron pairs will want to repel one another
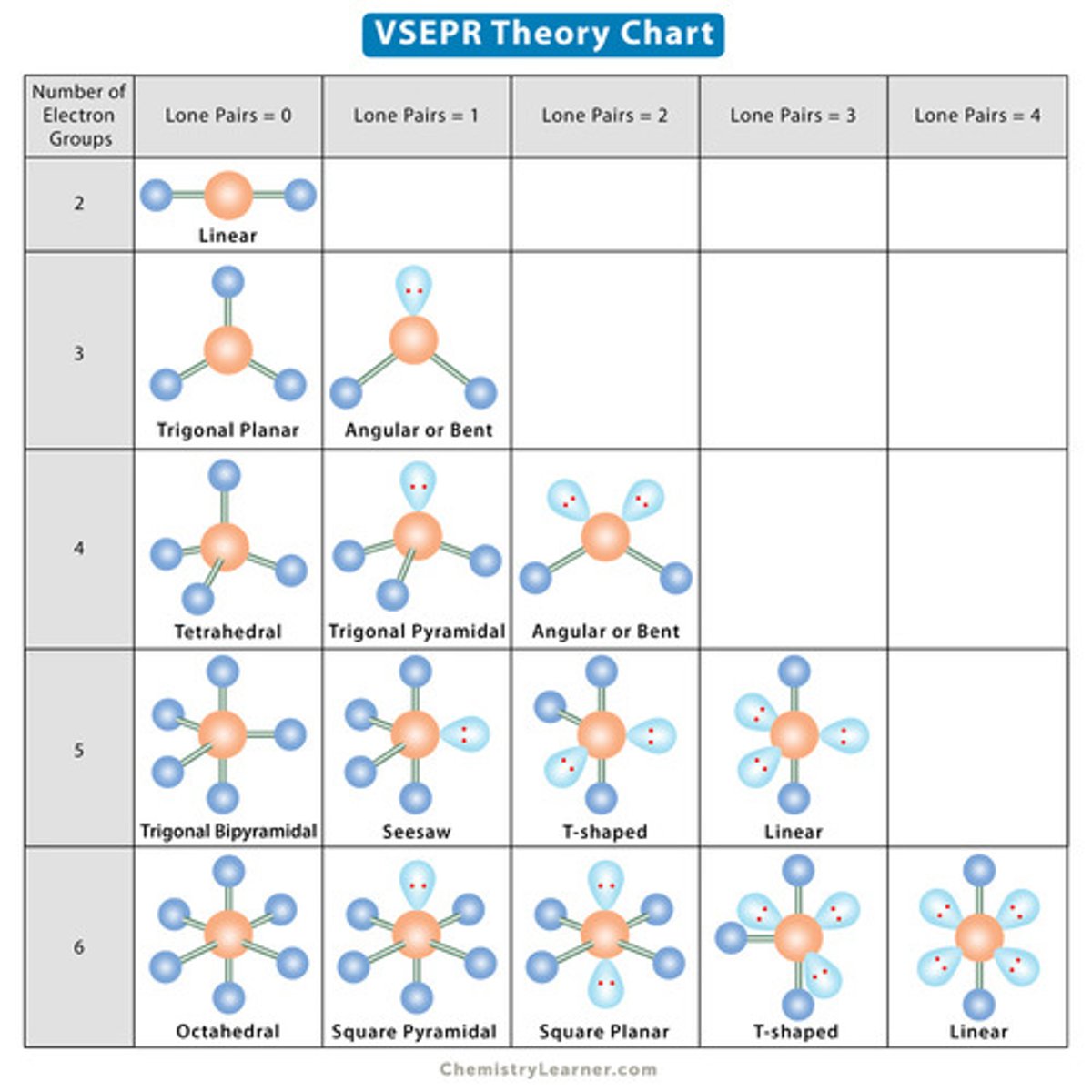
electron groups on a central atom
groups of electrons will either be a lone pair, or other atoms connected to a central atom
triple bonds affect how many groups are considered
No...
single, double, and triple bonds are all considered as one group
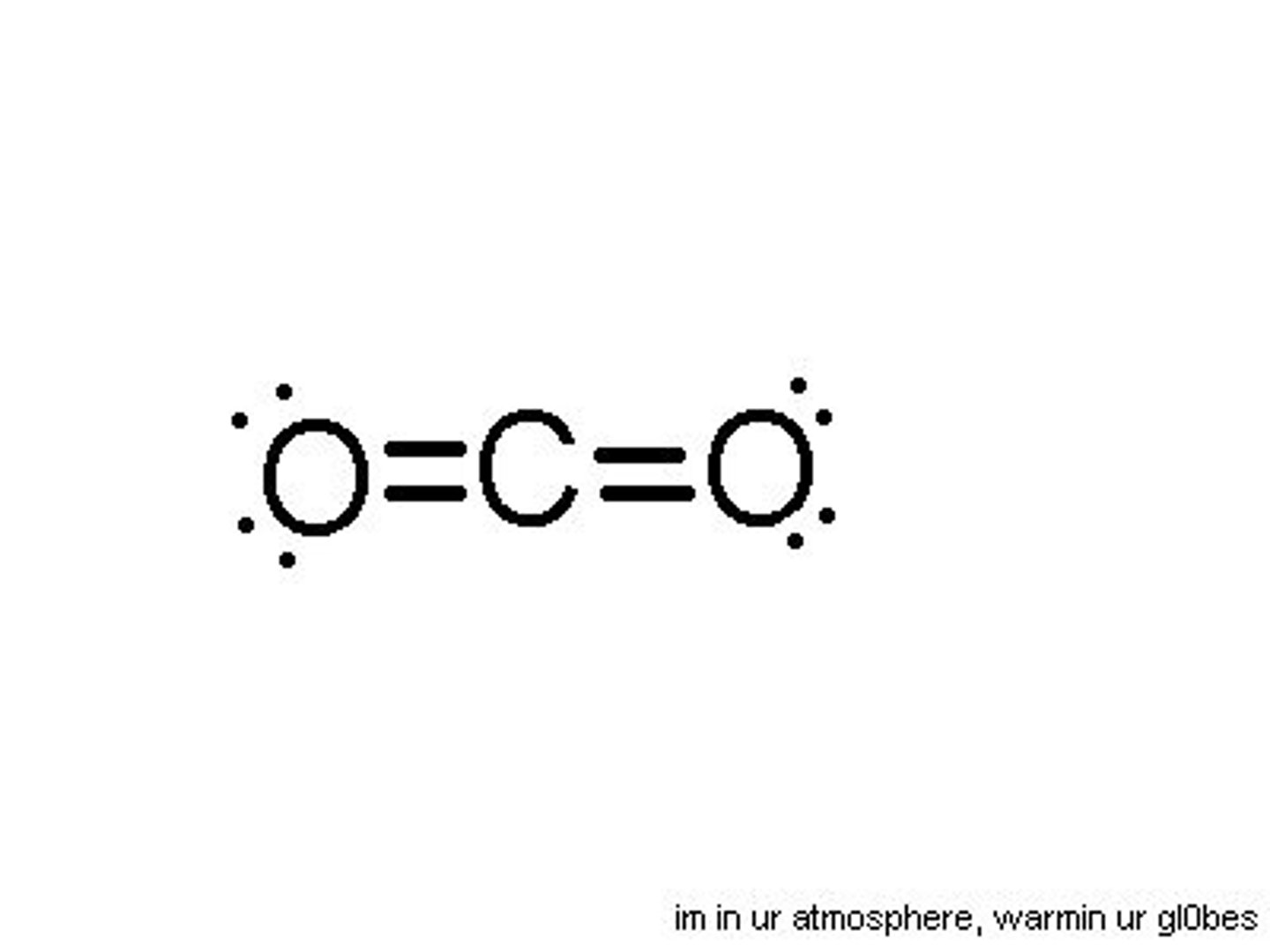
AZE method
determine # of central atom: A
determine # of bonded atoms: Z
determine # of lone pairs: E
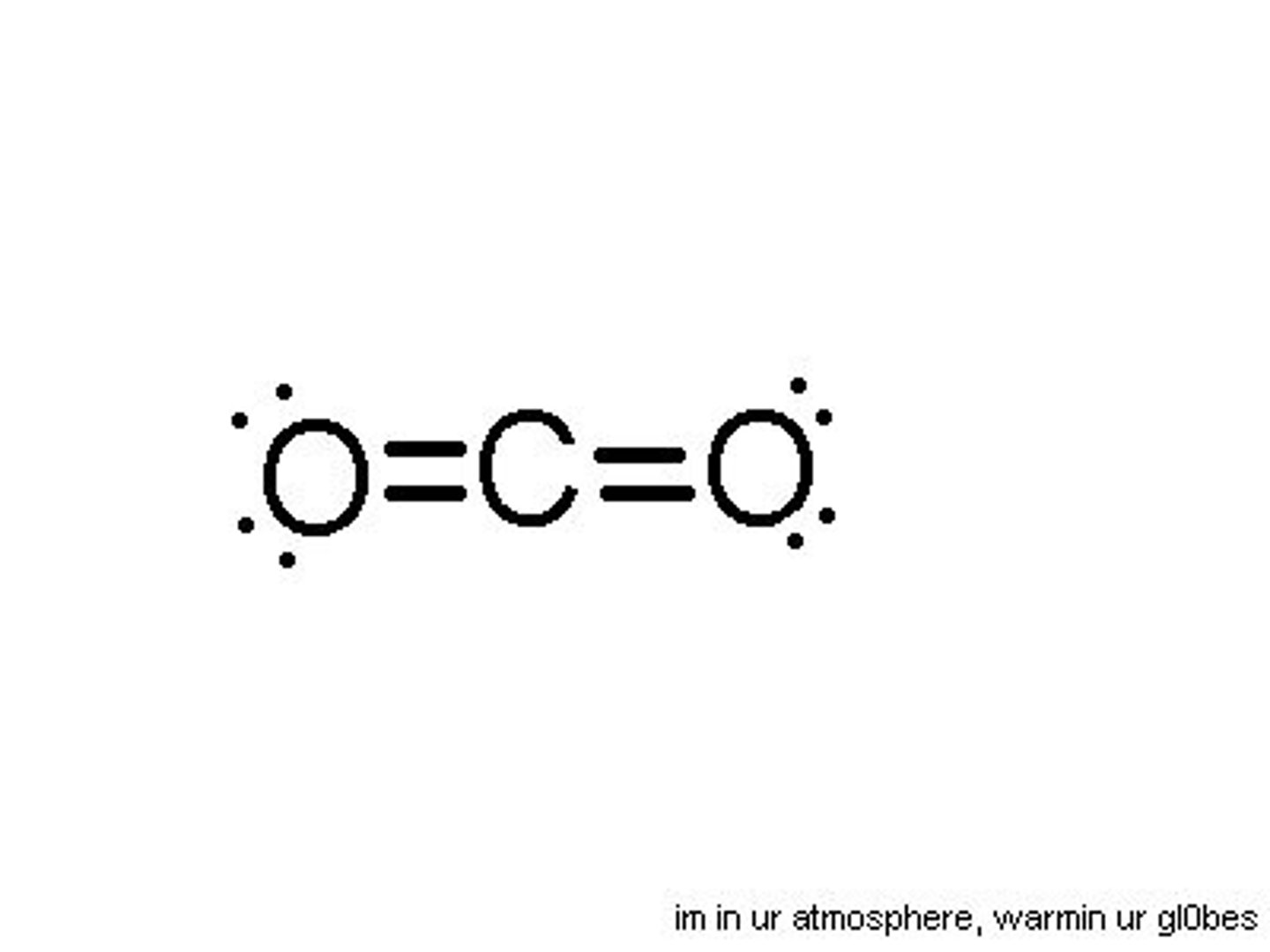
lone pairs
lone pairs take up more space, lessening the angles between atoms
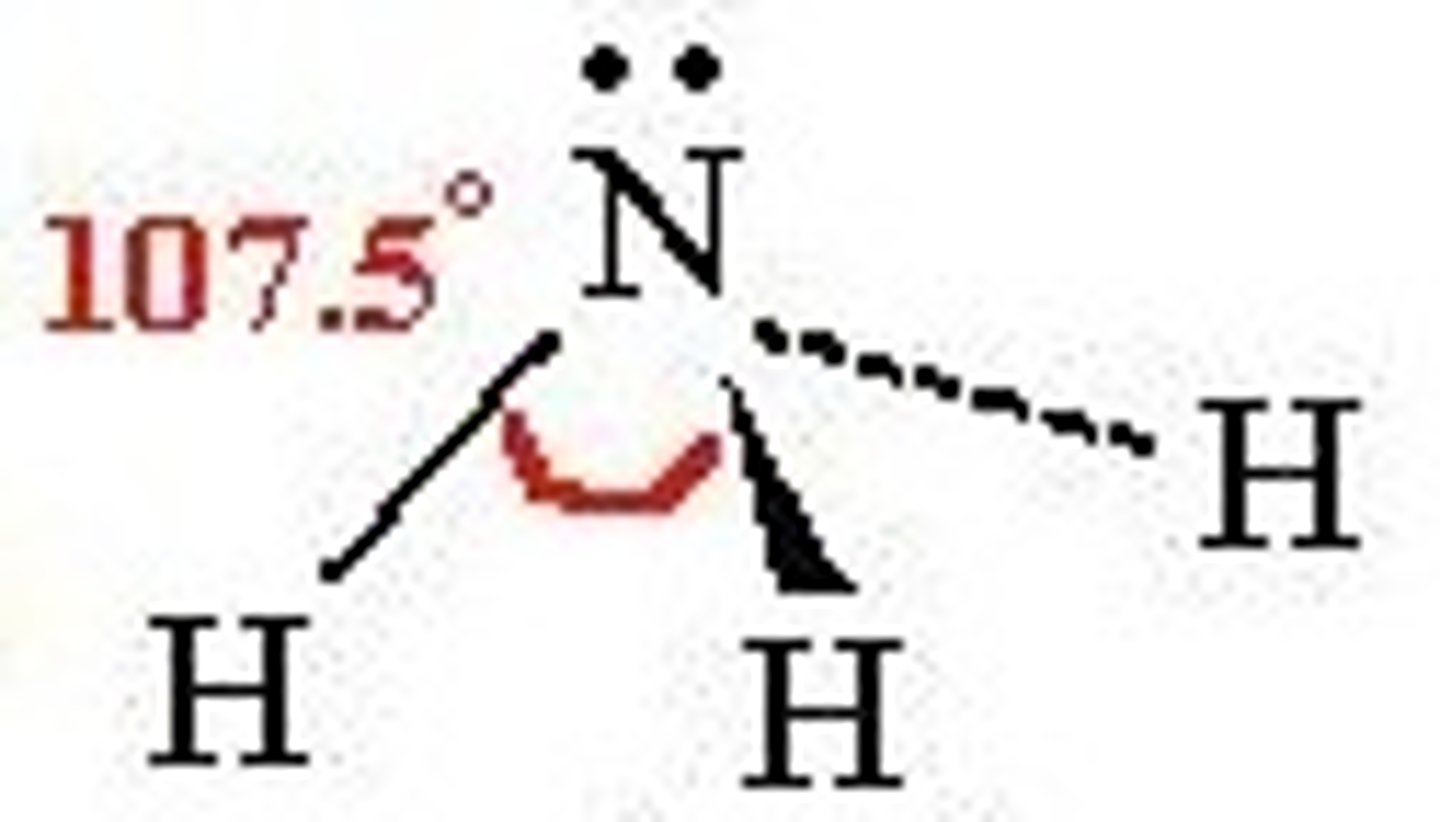
Do you show angles between lone pairs and atoms?
No...
technically the lone pairs are invisible, only angles between atoms are considered
