Topic 3 - Genetics
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
How many parents does sexual reproduction require?
2 parents.
How many parents does asexual reproduction require?
1 parent.
Does sexual reproduction require the fusion of gametes?
Yes.
Does asexual reproduction require the fusion of gametes?
No.
Does sexual reproduction create identical or non - identical gametes?
Non - identical.
Does asexual reproduction create identical or non - identical gametes?
Identical.
How many chromosomes does the zygote receive from each parent during sexual reproduction?
23 chromosomes.
In sexual reproduction, does the zygote receive 50% or 100% of DNA from each parent?
50%.
In sexual reproduction, is the zygote genetically different or identical to its parent?
Genetically different.
In asexual reproduction, does the zygote receive 50% or 100% of DNA from each parent?
100%.
In asexual reproduction, is the zygote genetically different or identical to its parent?
Identical.
Does sexual or asexual reproduction mix different DNA from each parent?
Sexual.
Does sexual or asexual create variation within a species?
Sexual.
Explain 1 advantage of sexual reproduction.
Increased genetic variation meaning there is an increased chance of survival when adapting to new environments/foreign disease as natural selection can take place.
Explain 3 disadvantages of sexual reproduction.
Requires more time/energy so takes longer.
Less offspring produced.
2 parents required meaning organisms must find a mate which uses energy + is slower.
Offspring can have features that are less advantageous than the parents.
Explain 3 advantages of asexual reproduction.
Produces lots of offspring very fast (rapid reproductive cycle).
1 parents required meaning there’s no need to find a mate which is fast + uses less energy.
Requires less time/energy.
Organisms with beneficial characteristics of the parent can be produced.
Explain 1 disadvantage of asexual reproduction.
No genetic variation as they are all clones. This means there is less chance of survival if environment changes or a new disease is introduced.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction.
Advantages - Increased genetic variation meaning there is an increased chance of survival when adapting to new environments/foreign disease as natural selection can take place. This is allowing evolution to take place.
Disadvantages - No genetic variation as they are all clones. This means there is less chance of survival if environment changes or a new disease is introduced.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction.
Advantages - Produces lots of offspring very fast (rapid reproductive cycle), 1 parents required meaning there’s no need to find a mate which is fast + uses less energy, requires less time/energy, organisms with beneficial characteristics of the parent can be produced.
Disadvantages - Requires more time/energy so takes longer, less offspring produced, 2 parents required meaning organisms must find a mate which uses energy and takes time, offspring can have features that are less advantageous than the parents.
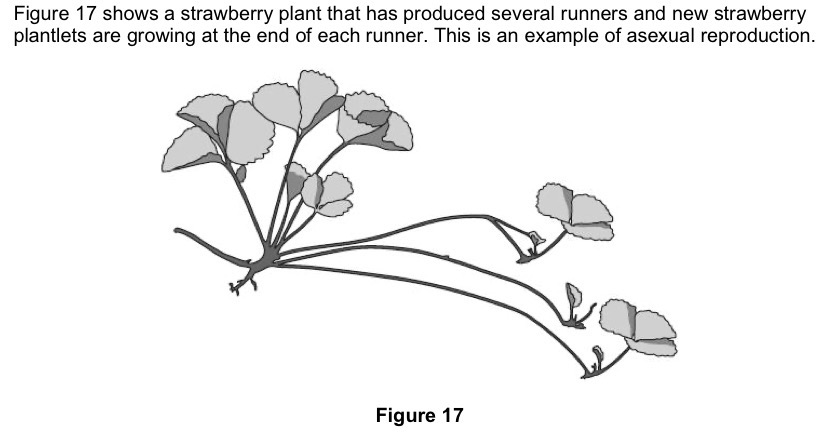
Explain why asexual reproduction in strawberries is beneficial to strawberry farmers.
It produces genetically identical plants, so farmers can reliably grow plants with desirable traits such as good fruit quality, disease resistance, and high yield.
It is fast and efficient, allowing many new plants to be produced in a short time from one parent plant leading to increased profit.
Strawberry fruits containing seeds are produced after a flower is fertilised. Explain why seed production is an advantage to the strawberry plant.
Seeds are produced by sexual reproduction, which mixes genetic material from two parents. This creates variation in the offspring, increasing the chance that some plants will be better adapted to survive changes in the environment, pests, or diseases, allowing natural selection to take place.

Name the type of reproduction involving flowers.
Sexual reproduction.
Is the egg cell haploid or diploid?
Haploid.
Is the sperm cell haploid or diploid?
Haploid.
How many chromosomes does a gamete have?
1 set of chromosomes / 23 chromosomes.
What is a fertilised egg cell?
Zygote.
What is a zygote?
Fertilised egg cell.
Is a zygote diploid or haploid?
Diploid.
How many chromosomes does a zygote have?
2 sets of chromosomes / 46 chromosomes.
How does a zygote form an embryo?
Mitosis.
Describe what happens during fertilisation.
The nucleus of a sperm (male gamete) and egg cell (female gamete) fuse together to form a zygote.
Explain how fertilisation and meiosis lead to the formation of a foetus.
During fertilisation, the nucleus of a haploid sperm (male gamete) and haploid egg cell (female gamete) fuse together to form a diploid zygote.
This gives the zygote 46 chromosomes in total; 23 from each parent.
Mitosis then allows the single cell to multiply and divide and continuously increase the cell number.
Differentiation then produces all of the specialised cells.
What is meiosis?
A type of cell division that produces haploid gametes.
Name the process that forms gametes for sexual reproduction.
Meiosis.
Does meiosis begin with a diploid or haploid cell?
Diploid (4 chromosomes).
What happens first in meiosis?
DNA replicates (4 to 8 chromosomes).
Chromosomes form an x shape, becoming 2 armed chromosomes.
Chromosomes line up along the middle.
How many cell divisions does meiosis include?
2 cell divisions.
Explain the full process of meiosis.
DNA replicates (4 to 8 chromosomes)
Chromosomes form an x shape, becoming 2 armed chromosomes.
Chromosomes line up along the middle.
The cell divides but not fully. The pairs are also pulled apart, leaving 4 chromosomes one each cell.
The cell divided fully and cells become 1 armed, instead of 2 armed.
Cells divide again, leaving 4 genetically different haploid gametes. 2 chromosomes each.
Describe the cells produced at the end of meiosis.
Genetically different to each other and parents.
Haploid gametes.
4 cells produced.
2 chrosmomes.
Explain the difference between meiosis and mitosis.
Mitosis
Genetically identical .
Diploid body cells produced.
2 cells produced.
1 cell division.
Meiosis
Genetically different.
Haploid gametes produced.
4 cells produced.
2 cell divisions.
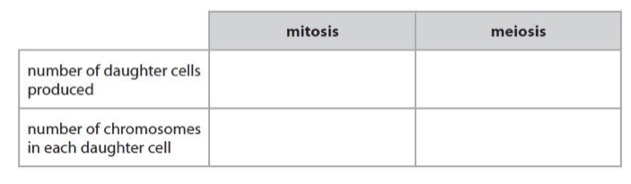
Complete the table.
Mitosis - 2, 46/23 pairs.
Meiosis - 4, 23.
Describe the structure of DNA.
Double helix structure.
DNA backbone made of phosphate and sugar.
Many nucleotide which are made of a phosphate bonded to a sugar bonded to a base.
Bases are cytosine, guanine, thymine and adenine. C pairs with G. A pairs with T.
Bases pair via weak hydrogen bonds.
How is DNA arranged?
Double helix structure.
What shape does DNA have?
Double helix structure.
What do nucleotides consist of?
Sugar, phosphate, base.
Which molecules make up the DNA’s backbone?
Sugar and phosphate.
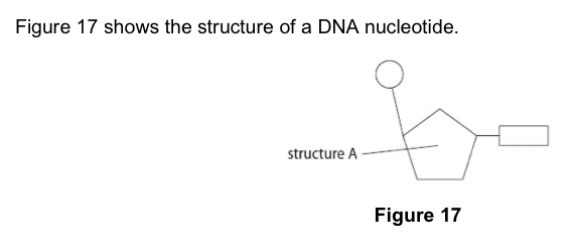
Label structure A.
Sugar.
Name the four DNA bases.
Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine.
How are DNA bases bonded?
Weak hydrogen bonds.
What type of bond bonds DNA bases together?
Weak hydrogen bonds.
Are the hydrogen bonds between bases strong or weak?
Weak.
Which DNA bases complementary base pairs with thymine?
Adenine.
Which DNA bases complementary base pairs with adenine?
Thymine.
Which DNA bases complementary base pairs with cytosine?
Guanine.
Which DNA bases complementary base pairs with guanine?
Cytosine.
If a sample contains 30% adenine, what percentage of cytosine would be in the same sample of DNA?
20%.
If a sample contains 40% guanine, what percentage of thymine would be in the same sample of DNA?
10%.
What does a sequence of the three bases code for?
Amino Acid
Define: Chromosomes
Long, coiled molecules of DNA found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
Where are chromosomes found?
Nucleus
Define: Gene
Section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a protein.
Define: Genome
All of an organisms DNA.

Pick A, B, C or D.
C.
A new project called the Earth BioGenome Project aims to discover the sequence of bases in the DNA of all plants and animals. State two benefits of discovering the sequence of bases for all plants and animals.
Identify useful genes.
Understand diseases.
Discover new medicines/find a cure.
In 2003, the first complete human genome was sequenced. The genomes of different people have small changes in the sequence of the DNA bases.
Describe how these changes in DNA sequence can affect the individuals and how sequencing a person's genome could influence their medical treatments.
DNA sequences - DNA has 4 different bases, changes in the DNA are mutations, results in different alleles for these genes, affects the phenotype / produces variation
Outcome of DNA sequencing for the individual - identify genetic diseases, identify the risk of developing diseases, knowing that a disease could develop allows the individual to modify their lifestyle to reduce risk.
Impact on medical treatment - HGP has determined the location of genes/determined the function of proteins so we have a better understanding of some diseases and can tailor-made medical treatments/personalised medicines.
In 2003 scientists finished sequencing the 3 billion base pairs in the human genome. State to benefit benefits that a HGP could have for medicine.
Genetic screening to located genes associated with diseased.
Personalised medicine.
Treat genetic disorders.
Explain the full method for the DNA Extraction practical.
Crush fruit using pestle and mortar
Add detergent
Add salt
Add protease
Filter mixture
Add ethanol
Why do we crush the fruit during DNA extraction?
To break down the cell wall.
Why do we add detergent during DNA extraction?
Break down the cell membrane/nucleus to release DNA.
Why do we add salt during DNA extraction?
To clump DNA.
Why do we add protease during DNA extraction?
To break down the enzymes that would usually break down DNA.
Why do we filter the mixture during DNA extraction?
To remove large pieces of insoluble fruit.
Why do we add ethanol DNA extraction?
To precipitate DNA.
How does the DNA appear at the end of the DNA extraction practical? How can it be extracted?
Appears as a stringy white precipitate; can be fished using a glass rod.
Define: Allele
A different version of the same gene
What is the difference between a genotype and phenotype?
Genotypes are the alleles someone has whilst the phenotypes are the physical characteristics someone has a result of their alleles.
Define: Heterozygous
Alleles are different e.g. Aa
Define: Homozygous
Alleles are different e.g. AA
Name the 3 genotypes.
Homozygous recessive.
Homozygous dominant.
Heterozygous.
Define: Dominant Allele
Alleles that will always be expressed in the phenotype as only 1 is needed to be expressed. Always overrules the recessive allele.
Define: Recessive Allele
Alleles that will only effect the phenotype if the other allele is the same. Will always be overruled by the dominant allele.
In a recessive linked disease, how many alleles are needed for someone to have the disease?
2.
In a dominant linked disease, how many alleles are needed for someone to have the disease?
1.
How many pairs of chromosomes are there in the human body?
23.
Haw many pairs of body chromosomes and sex chromosomes are there in the human body?
22 Body Chromosomes + 1 Sex Chromosomes
Which chromosomes do males have?
XY
Which chromosomes do females have?
XX
What is the chance of a couple having a baby girl?
50%
What is the chance of a couple having a baby boy?
50%
Does the male or female determine the babies gender? Why?
Males as they can pass on X or Y chromosomes whilst females can only pass on X chromosomes.
Is the Y chromosome smaller or bigger than the X chromosome?
Smaller
Does the Y chromosome carry more or less genes than the X chromosome? Why?
Carries less genes as it’s smaller.

Fill in the punnet square and percentage.
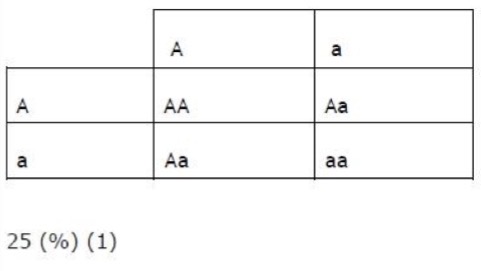
Explain one advantage to pea plants using sexual reproduction to produce offspring.
Increased genetic variation meaning there is an increased chance of survival when adapting to new environments/foreign disease as natural selection can take place.
What does a family pedigree chart show?
The occurrence of different phenotypes in a family tree.
Name the 4 blood groups
A, B, AB and O
Why can different blood groups not be mixed?
It can cause clotting
Which blood type can be given to anyone?
O
Which blood type can receive any blood type?
AB
Which blood group alleles are codominant?
IA and IB