Female Reproductive Anatomy
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:46 AM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
1
New cards
What is included in the Cranial region of the reproductive system?
* Hypothalamus
* Pituitary Gland
* anterior
* posterior
* Pituitary Gland
* anterior
* posterior
2
New cards
What is included in the Pelvic region of the reproductive system?
* Gonads
* Tube system
* Tube system
3
New cards
How is the posterior pituitary connected to the hypothalamus?
Direct link, by nerurons
4
New cards
How is the anterior pituitary connected to the hypothalamus?
Indirect link, through the primary portal plexus
5
New cards
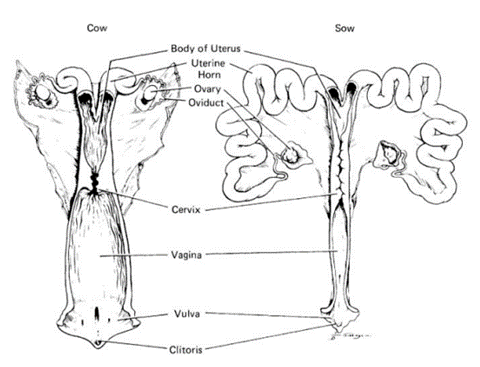
What are the structures included within the female reproductive tract?
* Uterine body
* Uterine horns
* Ovary
* Oviduct
* Cervix
* Vagina
* Vulva
* Clitoris
* Uterine horns
* Ovary
* Oviduct
* Cervix
* Vagina
* Vulva
* Clitoris
6
New cards
What are the main functions of the female reproductive tract?
* Hormone Production
* Gamete production
* Gamete transport
* fertilization
* Growth and development of offspring
* Parturition
* Gamete production
* Gamete transport
* fertilization
* Growth and development of offspring
* Parturition
7
New cards
The main hormones that the female reproductive tract produces include…
* Steroids
* Proteins
* estrogen
* progesterone
* Proteins
* estrogen
* progesterone
8
New cards
what the are cells involved in gamete production?
Oogonia, which develop into Oocytes
9
New cards
Gamete transport of oocytes includes…
* Ovum is what is ovulated from the ovary
* The tube system transports the oocyte and transporting the sperm cells
* The tube system transports the oocyte and transporting the sperm cells
10
New cards
gamete transports of spermatozoa includes…
Spermatozoa are draw into the uterine horns where fertilization occurs (in most animals)
11
New cards
Growth and Development of offspring in the female reproductive system includes both…
* Preimplantation
* Postimplantation
* Formation of the placenta
* Direct line from fetus to maternal blood
* Postimplantation
* Formation of the placenta
* Direct line from fetus to maternal blood
12
New cards
What is the primary reproductive organ of the female reproductive system?
The Ovary
13
New cards
The ovary is responsible for producing the ___
Gametes
14
New cards
The ovary is the only tissue that can produce the ___
oocyte
15
New cards
The ovary produces hormones through what function?
Endocrine Function
16
New cards
ovaries are ___ in mammals
Paired
17
New cards
What are the the two main functions of the ovary?
* Cytogenic
* production of gametes
* oocytes
* Endocrine
* secretes hormones
* steroid (estrogen, progesterone)
* protein peptides
* prostaglandins (derived from fatty acids)
* production of gametes
* oocytes
* Endocrine
* secretes hormones
* steroid (estrogen, progesterone)
* protein peptides
* prostaglandins (derived from fatty acids)
18
New cards
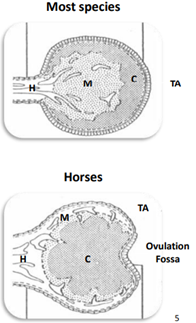
What is the configuration of the ovary going from the outermost layer to the innermost?
* Tunica Albuginia (TA)
* Cortex (C)- outer zone
* Medulla (M)- inner zone
* Hilus (H)
* Cortex (C)- outer zone
* Medulla (M)- inner zone
* Hilus (H)
19
New cards
Characteristics of the Tunica Albuginea (TA)
* Covered by germinal epithelium.
* White layer that covers the ovary (outermost covering)
* Single cell layer
* White layer that covers the ovary (outermost covering)
* Single cell layer
20
New cards
Characteristics of the Cortex (C)
* Where the oocytes are
* Where activity occurs
* Follicles growing
* Corpus luteum developing
* Where activity occurs
* Follicles growing
* Corpus luteum developing
21
New cards
Characteristics of the Medulla (M)
* Center of the ovary in most mammalian species
* Oxygen and nutrients must come into contact with blood and lymphatic system
* Loose connective tissue
* Stroma
* Oxygen and nutrients must come into contact with blood and lymphatic system
* Loose connective tissue
* Stroma
22
New cards
Characteristics of the Hilus (H)
* The neck
* Brings in the blood vessels, and lymphatic system.
* Supplies nutrients to the oocyte in order to develop
* Brings in the blood vessels, and lymphatic system.
* Supplies nutrients to the oocyte in order to develop
23
New cards
How to horse ovaries differ from other domesticated species?
* Horses ovary flips the medulla and the cortex, it is essentially inverse
* Presence of the Ovulation Fossa
* Presence of the Ovulation Fossa
24
New cards
Where are the blood vessels present on a horses ovary?
blood vessels surround the outside of the ovary
25
New cards
the follicles are located on the ___of the ovary in equine species
Cortex
26
New cards
what is one of the biggest challenges in the mare reproduction system due to the configuration of the ovary?
One of the challenges with mares is that you cannot artificially stimulate ovulation, because the would all stimulate ovulation in one central ovulation fossa
27
New cards
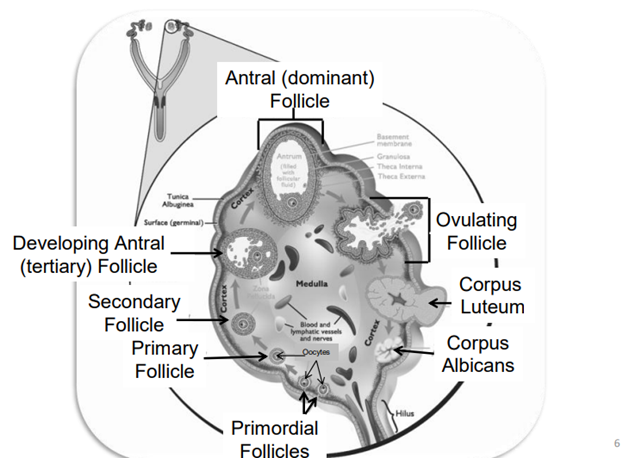
What are the types of ovarian Follicles?
* Primordial Follicle
* Primary Follicle
* secondary Follicle
* Tertiary Follicle (antral follicle)
* Primary Follicle
* secondary Follicle
* Tertiary Follicle (antral follicle)
28
New cards
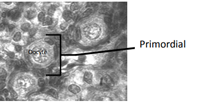
Characteristics of the Primordial Follicles
* 1 layer of cell surrounding oocyte
* Flattened layer of follicular cells surround oocyte.
* Primordial germ cells (PGC)
* Will grow and develop into what is called clusters/nest
* Flattened layer of follicular cells surround oocyte.
* Primordial germ cells (PGC)
* Will grow and develop into what is called clusters/nest
29
New cards
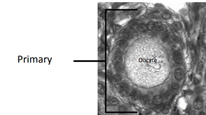
Characteristics of the Primary Follicles
* 1 layer of cells surrounding oocyte (much thicker than in primordial cells, cuboidal cells)
* Increase in size of oocyte and height of follicular cells
* Increase in size of oocyte and height of follicular cells
30
New cards
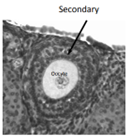
Characteristics of Secondary Follicles
* Surrounded by several layers of follicular cells
* 2 or more layers of cells
* Formation of thecal (outermost) and granulosal cells (innermost)
* No antrum
* 2 or more layers of cells
* Formation of thecal (outermost) and granulosal cells (innermost)
* No antrum
31
New cards
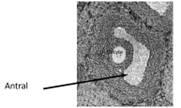
Characteristics of the Tertiary Follicles (Antral Follicles)
* Surrounded by several layers of follicular cells.
* Differentiation in cell layers
* Granulosal cells- inner most cells, surround oocyte.
* Thecal cells surround granulosal cells.
* Follicle forms a fluid filled cavity- antrum.
* Has the potential to rupture and ovulate
* Differentiation in cell layers
* Granulosal cells- inner most cells, surround oocyte.
* Thecal cells surround granulosal cells.
* Follicle forms a fluid filled cavity- antrum.
* Has the potential to rupture and ovulate
32
New cards
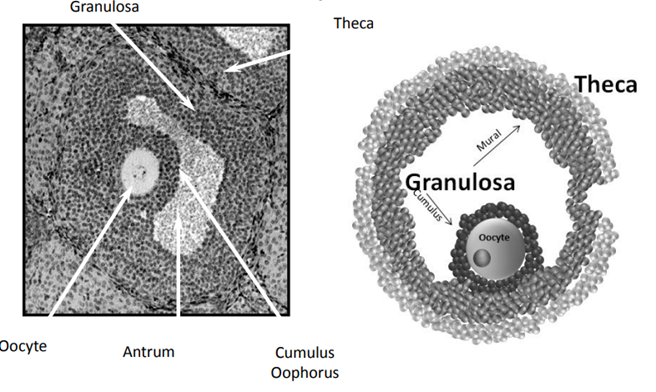
What is the configuration of the two layers of the Tertiary follicle ( Antral Follicle)?
* Granulosal cells- inner most cells, surround oocyte.
* Cumulus GC are sticky and stay wth the oocyte during ovulation, innermost layer around the ovary
* Mural GC are the second most inner layer containing the antrum
* Thecal cells surround granulosal cells.
* Produce testosterone
* 2 layers
* Cumulus GC are sticky and stay wth the oocyte during ovulation, innermost layer around the ovary
* Mural GC are the second most inner layer containing the antrum
* Thecal cells surround granulosal cells.
* Produce testosterone
* 2 layers
33
New cards
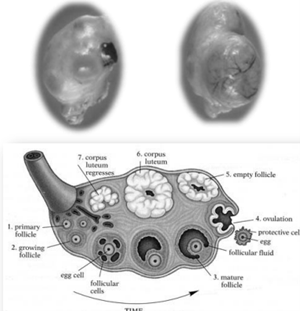
What happens after a Tertiary Follicle (Antral Follicle) ruptures and ovulates?
* It will then be caught by the tube system
* After a follicle ruptures and releases and oocyte they then become a corpus luteum and allow for gestation
* If the animal does not become pregnant the corpus luteum regresses and becomes a scar called the corpus albicans
* After a follicle ruptures and releases and oocyte they then become a corpus luteum and allow for gestation
* If the animal does not become pregnant the corpus luteum regresses and becomes a scar called the corpus albicans
34
New cards
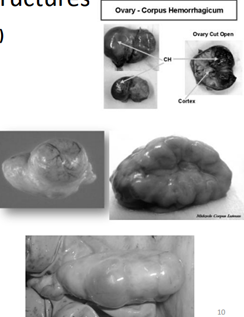
What are the other main ovarian structures other than the Follicles?
· Corpus hemorrhagicum (CH)
· Corpus luteum (CL)
· Corpus albicans (CA)
· Corpus luteum (CL)
· Corpus albicans (CA)
35
New cards
Define Corpus hemorrhagicum (CH)
* Newly ruptures follicle
* Essentially a blood clot
* Traumatic even, rupturing of blood vessels, called the red body
* Essentially a blood clot
* Traumatic even, rupturing of blood vessels, called the red body
36
New cards
Define Corpus luteum (CL)
* “yellow body”
* Produces progesterone
* Produces progesterone
37
New cards
Define Corpus albicans (CA)
* “white body”
* Scar tissue
* Remains after CL regresses
* Scar tissue
* Remains after CL regresses
38
New cards
List all of the Ovarian Structures:
* Primordial Follicle
* Primary Follicle
* Secondary Follicle
* Tertiary Follicle
* Corpus hemorrhagicum (CH)
* Corpus luteum (CL)
* Corpus albicans (CA)
* Primary Follicle
* Secondary Follicle
* Tertiary Follicle
* Corpus hemorrhagicum (CH)
* Corpus luteum (CL)
* Corpus albicans (CA)
39
New cards
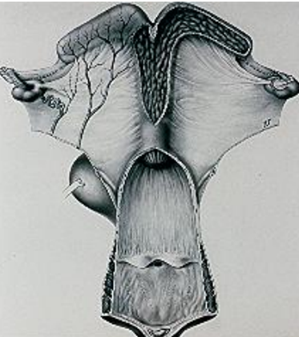
What are the secondary organs of the female reproductive system?
o Oviduct
o Uterine horns
o Uterine body
o Cervix
o Vagina
o Vestibule
o Vulva
o Uterine horns
o Uterine body
o Cervix
o Vagina
o Vestibule
o Vulva
40
New cards
Where does fertilization occur in the female reproductive system?
The Oviduct
41
New cards
Define Vestibule
Where the Urethra comes into the female reproductive tract
42
New cards
The Vulva is located on the ___ of the body
Outside
43
New cards
All of the secondary organs of the female reproductive system are collectively referred to as the ___
TUBE System
44
New cards
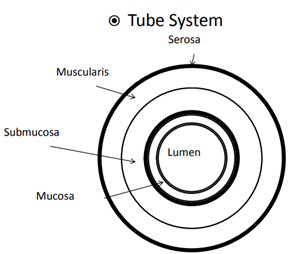
What the the layers of the Tube system going from the outermost to the innermost?
* Serosa
* Muscularis
* Submucosa
* Mucosa
* Muscularis
* Submucosa
* Mucosa
45
New cards
What is the Mucosa?
The innermost layer of the tube system that produces nutrients to support gametes
46
New cards
What is the Submucosa?
The layer of the Tube system that has blood vessels and helps provide nutrients to mucosa and lumen.
47
New cards
What is the Muscularis?
The muscle layer, longitudinal to shorten or lengthen, and circular, allows constriction of the tube to help move fluid and gametes, and during parturition it will contract around a fetus in order to expel it
48
New cards
What is the Serosa?
The outermost protective layer that covers the tube system
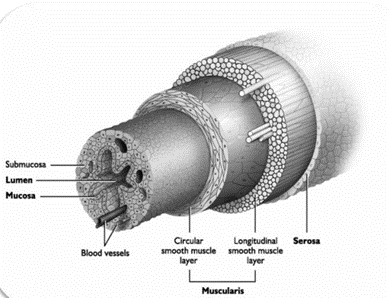
49
New cards
What are the 3 sections of the Broad Ligament?
* Mesovarium = Ovary
* Mesosalpinx = Oviduct
* Mesometrium = Uterus
* Mesosalpinx = Oviduct
* Mesometrium = Uterus
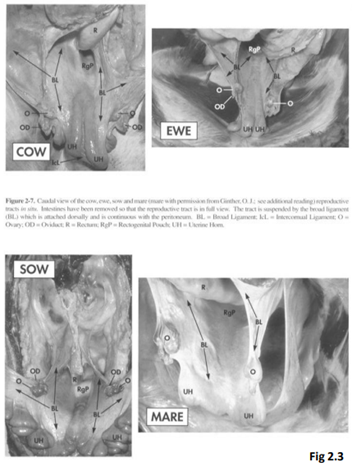
50
New cards
What is the Broad Ligaments main function?
* Support the reproductive tract
* Respond with the sex steroids
* Respond with the sex steroids
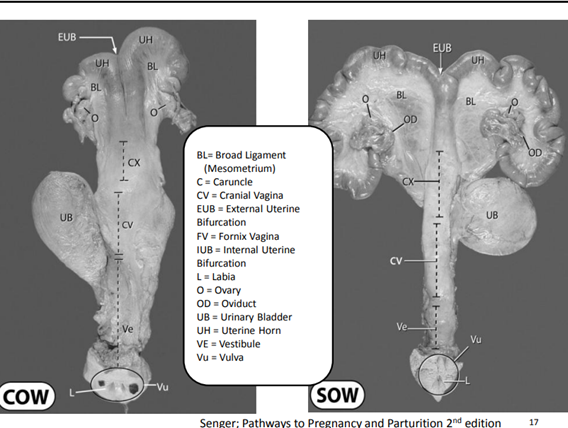
51
New cards
Characteristics of the Mesovarium section of the Broad Ligament?
* Hilus
* Where the broad ligament attaches to the ovary
* Where the broad ligament attaches to the ovary
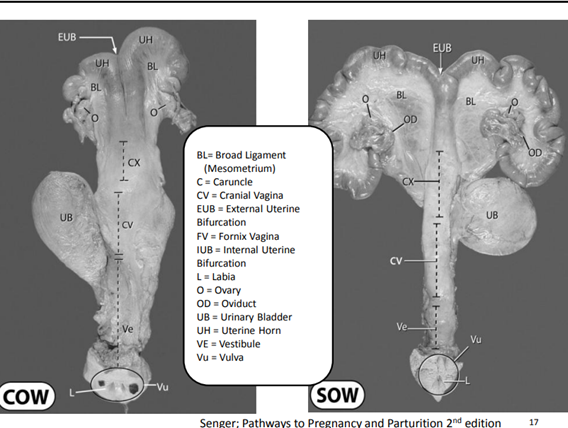
52
New cards
Characteristics of the Mesosalpinx section of the Broad Ligament?
Broad ligament attaches to the Oviduct
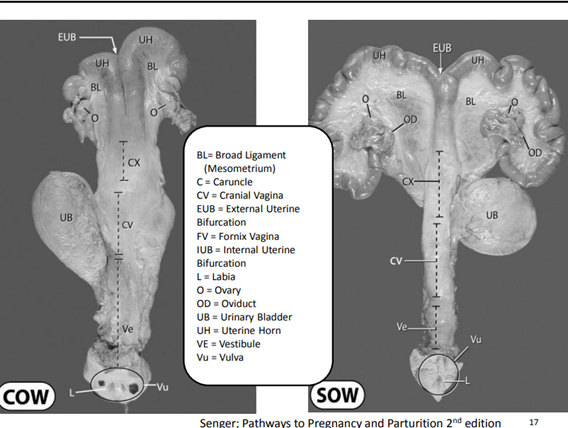
53
New cards
Characteristics of the Mesometrium section of the Broad Ligament?
* Larges part of broad ligament attaches to the uterine body and uterine horns.
* Able to expand and contract to hold fetus in place
* Able to expand and contract to hold fetus in place
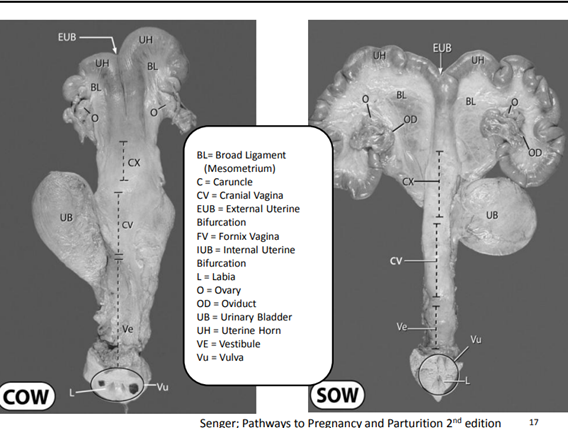
54
New cards
What are the main structures of the Oviduct?
* Infundibulum
* Ampulla
* Isthmus
* Ampulla
* Isthmus
55
New cards
Characteristics of the Infundibulum
* Surrounds ovary
* Fimbriae
* Like a catchers mitt, lefts catch the product of ovulation and guide it down into the oviduct
* Look very thin
* Fimbriae
* Like a catchers mitt, lefts catch the product of ovulation and guide it down into the oviduct
* Look very thin
56
New cards
Characteristics of the Ampulla
* Ampulla is thicker than the isthmus
* Fertilization occurs at the ampulla isthmus junction
* Cilia goes toward th uterine horn and junction
* Fertilization occurs at the ampulla isthmus junction
* Cilia goes toward th uterine horn and junction
57
New cards
Characteristics of the Isthmus
* Keeps sperm cells alive by the mucosa and submucosal laver
* Closest part of the oviduct to the uterine horn
* Cilia moves sperm toward the ampulla
* When progesterone levels are high the cilia changes direction to move gamete toward the uterine horn and way from the ampulla, so if fertilization takes place and embryo can form and implant into the uterus
* Closest part of the oviduct to the uterine horn
* Cilia moves sperm toward the ampulla
* When progesterone levels are high the cilia changes direction to move gamete toward the uterine horn and way from the ampulla, so if fertilization takes place and embryo can form and implant into the uterus
58
New cards
Function of the Oviduct
* Secretory
* pH, has to be around neutral for cells to survive.
* Nourish
* At the time of ovulation there are high estrogen concentrations
* After ovulation progesterone levels are high
* ciliated columnar on the mucosal lining to help move the gamete in the proper direction
* transport
* pH, has to be around neutral for cells to survive.
* Nourish
* At the time of ovulation there are high estrogen concentrations
* After ovulation progesterone levels are high
* ciliated columnar on the mucosal lining to help move the gamete in the proper direction
* transport
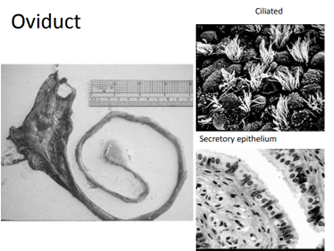
59
New cards
What are the main structures of the Uterus (metiram)?
* Body
* Cornua (horns)
* Much smaller in animals that have one offspring (non-litter bearing species)
* Cornua (horns)
* Much smaller in animals that have one offspring (non-litter bearing species)
60
New cards
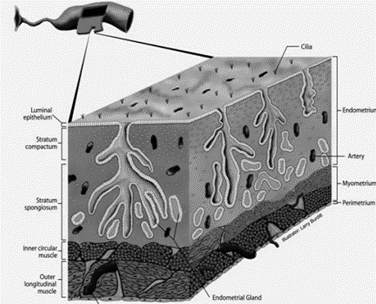
What are the 3 layers of the Uterus (Metiram)?
* Perimetrium (Serosa)
* Myometrium (muscularis)
* Endometrium (submucosa and mucosa)
* Myometrium (muscularis)
* Endometrium (submucosa and mucosa)
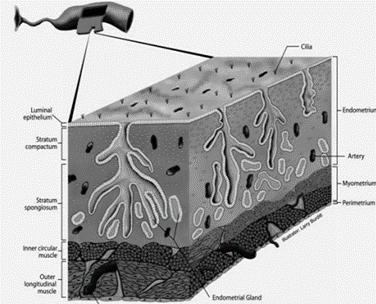
61
New cards
What is the main functions of the Uterus?
* Development of offspring
* Preimplantation
* Post implantation
* Sperm survival
* pH
* nutrients
* regulation of the cycle
* parturition
* Preimplantation
* Post implantation
* Sperm survival
* pH
* nutrients
* regulation of the cycle
* parturition
62
New cards
What is the difference between a fetus and an Embryo?
Fetus has distinct defining features and an Embryo does not
63
New cards
Perimetrium=___
Outer layer
64
New cards
Myometrium=___
Muscle layer
65
New cards
Endometrium=___
Secretory lining
66
New cards
What are the Classifications of Uteri?
* Bicornuate
* highly developed uterine horns
* poorly developed uterine horns
* Duplex (2 cervixes)
* Simplex (no uterine horns)
* highly developed uterine horns
* poorly developed uterine horns
* Duplex (2 cervixes)
* Simplex (no uterine horns)
67
New cards
What is the Structure of the Cervix?
* Constricted and thickened.
* Secretory and ciliated cells lining the cervix
* In order to allow for the survival of gametes, in the cervix this is sperm cells
* Secretory and ciliated cells lining the cervix
* In order to allow for the survival of gametes, in the cervix this is sperm cells
68
New cards
What is the Function of the Cervix?
* Physical barrier
* Chemical barrier
* There are immune cells in there, if there were an infection it could fight it off
* Sperm function and storage ( in some species, such as bats and birds)
* Chemical barrier
* There are immune cells in there, if there were an infection it could fight it off
* Sperm function and storage ( in some species, such as bats and birds)
69
New cards
What are the differences across species pertaining the cervix?
* Annular Rings
* Cow (3-4), Ewe (8-9)
* Interdigitated pads
* Sow
* Longitudinal folds
* Mare
* Cow (3-4), Ewe (8-9)
* Interdigitated pads
* Sow
* Longitudinal folds
* Mare
70
New cards
What is the Purpose of interdigitated pads in Sows?
* To stimulate ejaculation
* Boar penis has a lefthand corkscrew.
* Boar penis has a lefthand corkscrew.
71
New cards
What is the purpose of longitudinal folds in Mares?
* Helps filter out debris.
* Insemination occurs in the cervix.
* Insemination occurs in the cervix.
72
New cards
What is the Major structure of the Vagina?
* Squamous epithelial cells layer surrounded by muscular wall
* More for protection during the process of copulation
* More for protection during the process of copulation
73
New cards
What are the Functions of the Vagina?
* Copulatory organ
* Sperm function
* Semen deposited in the anterior part of the vagina.
* Chemical barrier
* pH gradient, where semen are deposited 7.4, and down toward the vulva it can be as low as 4.0
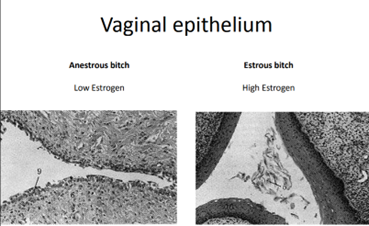
* Responsive to steroids
* Sperm function
* Semen deposited in the anterior part of the vagina.
* Chemical barrier
* pH gradient, where semen are deposited 7.4, and down toward the vulva it can be as low as 4.0
* Responsive to steroids
74
New cards
What are the Major parts of the Female external genitalia?
* Vestibule (portion of the vaginal vault where the urethra comes in) or vulva
* Urethral opening
* Labia majora & labia minora
* Clitoris (organ that has a high number of nerve endings, aids in copulation)
* Urethral opening
* Labia majora & labia minora
* Clitoris (organ that has a high number of nerve endings, aids in copulation)
75
New cards
What are the major functions of the female external genitalia?
* Protection
* Stimulation
* Sexual attractant
* Winking of vulva
* Swelling of vulva, in order to be a visual aid to the males to show reproductive receptiveness
* Stimulation
* Sexual attractant
* Winking of vulva
* Swelling of vulva, in order to be a visual aid to the males to show reproductive receptiveness
76
New cards
Overview of the Ovary
* ==Primary Organ==
* Functions:
* Production of Gametes
* Secretes Hormones
* Estrogen
* progesterone
* Functions:
* Production of Gametes
* Secretes Hormones
* Estrogen
* progesterone
77
New cards
Overview of the secondary female reproductive organs?
* Oviduct
* Uterus (uterine horns)
* Cervix
* Vagina
* External Genitalia
**Functions:**
* Copulation
* Gamete Transport
* Fertilization
* Growth and Development of Offspring
* Secretes Hormones
* Parturition
* Uterus (uterine horns)
* Cervix
* Vagina
* External Genitalia
**Functions:**
* Copulation
* Gamete Transport
* Fertilization
* Growth and Development of Offspring
* Secretes Hormones
* Parturition