Actions of Soaps + Detergent
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Soap Structure
Formed from base hydrolysis of fats and oils
Have a polar hydrophilic head, and a hydrophobic tail
Soap Benefits
Made from natural fats and is hence biodegradable
Effective for human hygiene
Soap Negatives
Able to form soap scum in hard water, which is water with high Ca2+ and Mg2+, and hence form insoluable salts, this is because a soap molecule contains a carboxylic ion, which is able to form an ionic force of attraction
Anionic Detergent Structure
Anionic, negatively charged
Still has hydrophobic tail
Head etc Benzene Sulfonate,
Anionic Detergent Benifets
Do not precipitate in hard water
Availability of materials, such as petrochemicals
Suitable for cleaning of textiles
Anionic Detergent Negatives
Non biodegradable
Excessive foaming
Not suitable for use in personal hygiene, strips away to much oil from body
Cationic Detergennt
Has a hydrophobic tail
Cationic Benefits
Don’t precipate in hard water
Cleans plastics better
Used as fabric softener, reduce friction and static electricity
Cationic Detergent Negatives
Can kill living things (biocidal)
Non Ionic Detergent Structure
Have a non ionic hydrophilic head, containing an oxygen atom in the chain and a terminal alkanol group
Hydrophobic taill
Non Ionic Detergent Benifets
Do not precipate in hard water
Low foaming detergent useful in low-sudsing applications
Such as dishwashers
Polymer Average MM
Related to number of monomer units
Longer the chain, higher the weight, hence higher strength dispersion force
Polymer Chain Branching
High Density:
Forms crystalline polymer (tightly ordered and packed)
Hard and dense material
Low Density:
Non crystalline
Low melting point, hence more flexible and soft
Polymer Chain Stiffening
If a monomer, has a side chain it leads to polymers with reduced flexibility
The larger the side chain, the less it is able to move around
Polymer Cross Linking
When two polymers are joined together in 2d network
Increases strength
Cross linking agent, such as sulfur is required
Polymer Solubility in Water
Polymer consist of long chains of carbon, hence dispersion forces are the most common
This is unless there are polar hydroxyl or carboxyl groups
Polymer Stabiltiy
Most polymers contain C-C, C-H bonds which are very stable
Some polymers, such as PVC contain C-Cl bonds, which are weaker than C-H and break down in the presence of UV light
Addition Polymer
A polymer formed by adding together without loss of atoms
Polymer Initiation
Initiator molecule breaks the double bond, (must have double bond)
etc Hydrogen Peroxide, when is reacted forms a free radical, which want to react
Polymer Elongation/Propagation
Once a free radical starts the reaction, a new monomer forms, forming another free radical
Propogation process
Polymer Termination
sf
Polyethene
Monomer Name: Ethene
Low Density Polyethene
Has branched chain
Amorphous (disordered)
Weak bonding due to disperson forces
Soft plastic
High Density Polyethene
Crystaline (ordered chains)
Stronger dispersion forces
Denser, tougher and rigid
Polychlorethene
Monomer is chloroethene
Polar C-Cl produces string dipole-dipole forces
C-Cl bond vulnerable to U.V light however
Adding plasticiser, will soften it by weakening the IMF
Polyphenylethene
Monomer Name, phenylethen
Looks like an ethene, but with a benzene ring swapped out with a hydrogen
Bulky side group hinders rotation and prevents chain flexibility
Use for takeaway containers
Polytetrafluoroethane
Monomer Name: 1,1,2,2 - tetrafluoroethane
Creates a highly polar, symmetrical polymer
Has weak disperson forces, so is non stick, non-polar, hard to interact
Condensation Polymerisation
Formed by condensation reaction, elimination of a small molecule, such as water when monomers join together
Polyamides
Formed by the reaction between dicarboxylic acid and diamine
There is an amide linkage
Water molecule is released each time
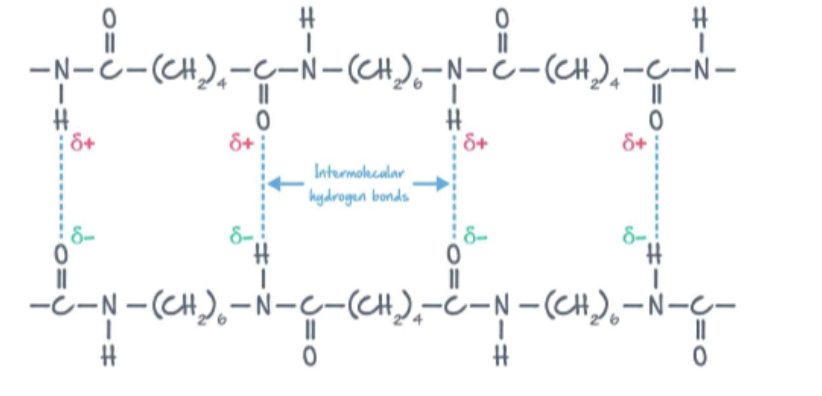
Nylon-6,6
Formed between Hexanedioic Acid and Hexane-1,6-diamine
An amide link is formed
Alternate between 4 CH2 and 6 CH2
Water is produced
High tensile strength (due to H bonding)
Lightweight material, stretch
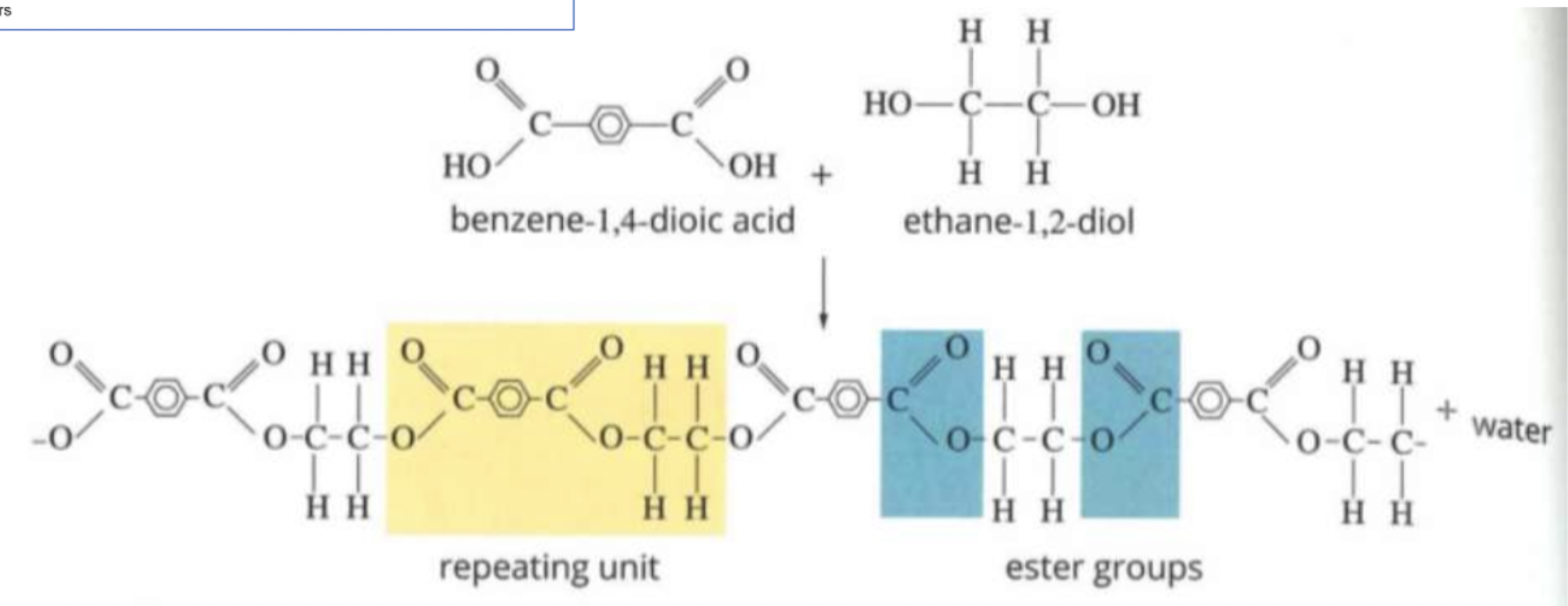
PET - Polyethene Terepthalate
Formed from Benzene-1,4-dioic acid and ethane-1,2-diol
High mechanical strength due to polar ester group
Large benzene ring gives strength and stiffness
Chemically inert
Used for packaging
Polyester
Formed by reaction between carboxylic acid, and alcohol