5007PM- cardiovascular system
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
what does it contain?
heart, blood vessels, veins, arteries, blood etc.
true or false: IS IT A CLOSED SYSTEM?
TRUE
WHAT IS IT ROLE?
TRANSPORT O2 AND NUTRIENTS
REMOVE GASEOUS WASTE
REGULATE BODY TEMP
ASSOCIATED WITH LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
WHAT ARE THE DIVISIONS
PULMONARY
SYSTEMATIC
CEREBRAL
CORONARY
PORTAL
SEE 400PM FOR MORE NOTES
CARDIO CONDITIONS WE MAY SEE AS A PARAMEDIC
Angina (stable & unstable)
Myocardial infarction
Heart failure (CCF, LVF)
Atrial fibrillation
WHERE WOULD YOU SEE AN INFERIOR INFARCT?
V2 AND V1
WHERE WOULD U SEE A ANTERIOR INFARCT
V3 AND V4
WHERE WOULD YOU SEE A LATERAL INFART
V5 AND V6
WHAT IS ANGINA
CHEST PAIN WHEN BLOOD SUPPY TO HEART IS STOPPED
ARTERIES HARDEN AND NARROW
TRIGGERED BY STRESS AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
WHAT IS STABLE ANGINA
Brought on by obvious trigger e.g exercise
Isn't life threatening
Increased risk of MI or stroke
WHAT IS UNSTABLE ANGINA
Unpredictable
No obvious trigger
Happen whilst resting
Medical emergency
Sudden and rapid deterioration - increase risk of MI/stroke
how does myocardial ischemia develop?
coronary blood flow don’t meet myocardial oxygen demand
what is angina a result from?
Reduction of coronary blood flow caused by fixed or dynamic epicardial coronary arterey
Abnormal constriction or relaxation of coronary microcultion
Reduced oxygen IN blood
what causes angina?
chemical and mechanical stimulation of sensory afferent nerve
WHAT DO THE SENSORY AFFERENT NERVE THAT ARE AFFECTED IN AGINA END IN?
coronary vessels and myocardium
what does angina cause?
Myocardial cells to switch from aerobic to anaerobic
metabolism progressive impairment of metabolic, mechnical and electrical functions
HOW DOES ANGINA AFFECT METABOLISM
metabolism progressive impairment of metabolic, mechnical and electrical functions
TRUE OR FALSE - arteriosclerosis is a common cause of epicardial coronary artery stenosis (angina pectorosis)
TRUE
HOW IS ARTERIOCLEROSIS CAUSED?
Cant increase their coronary blood flow during stress to manage myocardial metabolic demand
WHAT IS PRINZMETAL ANGINA?
defined as resting angina associated with ST-segment elevation
WHAT IS PRINSMETAL ANGINA CAUSED BY
focal coronary artery spasm.
WHAT IS ANGINA A DSYFUNCTION OF?
of small coronary arteries and arterioles is called microvascular angina
WHAT DOES CORONARY SPASMS REDUCE
Coronary spasm can also reduce CFR significantly
WHAT DOES CORONARY SPASMS CAUSE
dynamic stenosis of coronary arteries.
WHAT ARE THE POSSIBLE CAUSES OF ST SEGMENT DEPRESSION?
D- drooping valve (MV prolapse)
E- enlargement of the left ventricle
P - potassium loss
R - reciprocal ST depression (inferior MI)
E- encephalon haemorrhage
S - Subendocardial infarct
S - subendocardial ischemia
E- embolism (pulmonary)
D - dilated cardiopathy ( S- shock T- Toxicity)
WHAT IS A SUBENDOCARDIAL INFARCT
(MI that involves the inner most layer and part of middle layer of myocardium but no extend to epicardium)
WHAT ARE THE S&S OF SEGMENT DEPESSION?
Pain or discomfort in chest
Tight, dull heavy pain
Spread to arm, chest, neck etc.
Breathlessness
Nausea
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT FOR ST ELEVATION?
GTN
Aspirin
Oxygen
ECG monitoring
WHAT DOES GTN STAND FOR?
glyceryltrinitrate
WHAT IS GTN
Group of medications called nitrates
Relax and widen the blood vessels - increased bloody supply to heart
Available in tablet form or spray
Experience headaches, dizziness, flushing
Eases pain within 2-3 minas
Second dose taken after 5 mins
WHAT IS A COMPLICATION OF GTN
Heart attack and strokes
Stress of living with a LT condition can impact emotional health
WHAT IS MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION?
Reduced blood flow to coronary arteries
Causes myocardial ischemia. Injury and necrosis's
Fails to deliver enough blood to the heart
WHAT ARE THE CORONARY ARTERIES?
LEFT CORONARY ARTERY
CIRCUMFLEX ARTEREY
RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY
LEFT ANTERIOR DESCENDING ARTERY
AORTA
WHAT DOES THE LEFT CORONARY ARTERY DO?
Supplies- septum & anterior wall of the left ventricle
Occlusion = anterior MI
WHAT DOES THE CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY DO?
Left circumflex
Supplies - lateral wall of left ventricle
Occlusion= lateral MI
WHAT DOES THE RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY DO?
Supplies- right atrium, right ventricle and the septum
Left side of the heart
Occlusion inferior MI
WHAT IS AN MI?
OCCLUSION OF ONE OR MORE ARTERY
WHAT CAN AN MI STEM FROM?
Atherosclerosis
Thrombosis
Platelet aggregation
Coronary artery stenosis or spasm
WH- WHAT DOES UNJURY OF THE ENDOTHELIAL LINING CAUSE?
White cell attraction and early inflammatory response
WHAT IS ATHEROGENESIS?
Early sub-endothelial lipid deposition
WHAT HAPPENS DURING EARLY LIPID DEPOSITION IN ATHEROGENSIS
Cholesterol migrates underneath the intimal layer of the artery wall
Recognises as a foreign substance and cause activation of white blood cells (macrophages)
WHAT DOES ATHROGENSIS ACTIAVATE
WHITE BLOOD CELLS (MACROPHAGES)
WHAT DO WHITE CELLS DO?
DIGEST LIPIDS AND EXPAND TO BECOME FOAM CELLS
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN SITE OF INJURY IS WEAKENED (MI)?
Platelet adhesion causes platelet plugs to form surface of fibrous [plaques
Causes further transient occlusion of the affected coronary artery
WHAT HAPPENS ONCE THE CAPILLARY RUPTURES?
Leads to haemorrhage and thrombosis
Results in a partial or transient reduction of blood flow
WHATS THE FINAL RESULT OF AN MI?
Complete coronary artery occlusion
WHY IS MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMPORTANT?
CELLS CAN EXTRACT AS MUCH O2 AS IT NEEDS IRRESPECTIVE TO WHAT IT DELIVERS
TRUE OR FALSE- CELLS CONSUME 45% OXYGEN DELIVERED TO IT
FALSE- 25% OF OXYGEN CINSUMPTION
WHAT DIES AEROBIC METABOLISM PRODUCE?
PRODUCE ATP
CELLULAR ENERGY PRODUCTION
WHAT DOES ATP STAND FOR?
adenosine triphosphate
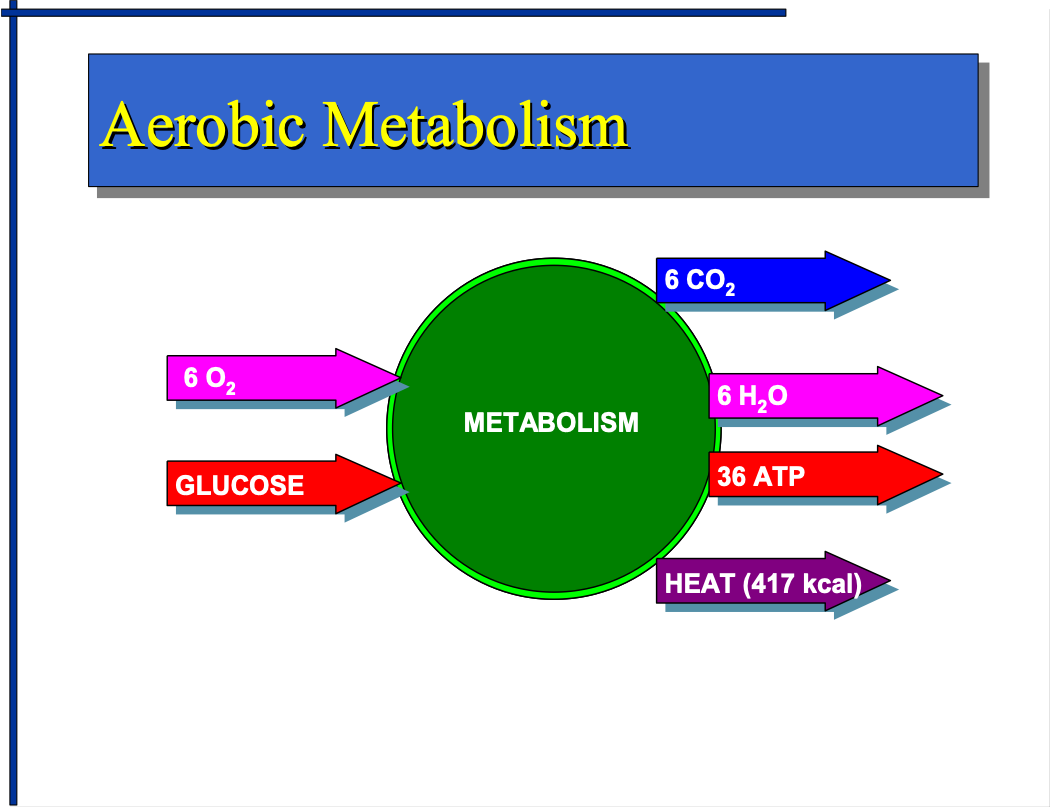
WHAT IS AEROBIC METABOLISM?
602+ GLUCOSE = 6C02+6H2O+32 ATP+ HEAT (417 KCAL)
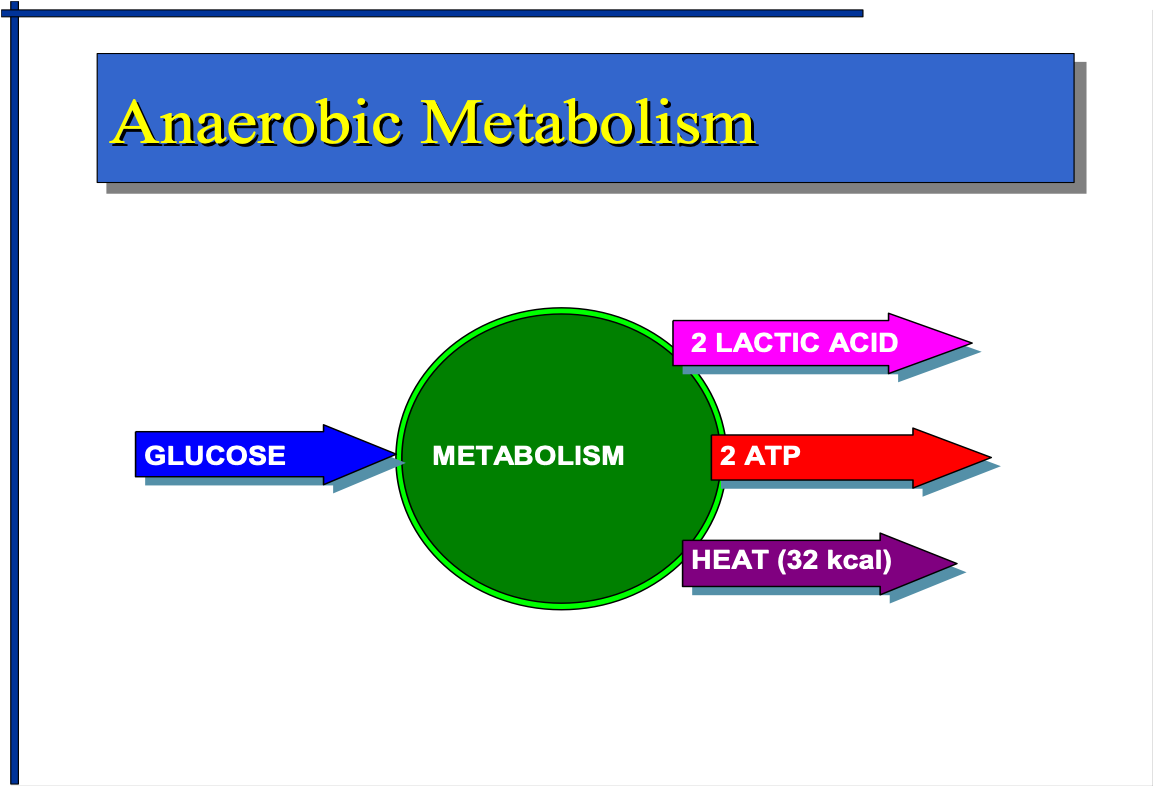
WHAT IS ANAEROBIC METABOLISM?
GLUCOSE= 2 LACTIC ACID+ 2ATP+ HEAT (32KCAL)
WHAT DOES LACTIC ACID CAUSE?
Vasoconstriction - systemic vascular resistance
Myocardial cell death
WHAT DOES LACTIC ACID DECREASE?
Inotropy
Stroke volume
Cardiac output
Blood pressure
WHAT DOES HYPO-PERFUSION STIMULATE?
Adrenaline glands to release epinephrine, norepinephrine
WHAT DOES EPINEPHRENE AND NOREPINEPHINE CAUSE
INCREASED HR (CHRONOTROPHY) AND PERIPHERAL VASOCONSTRICTION
WHAT DOES PERIPHERAL VASOCONTRICITION CAUSE
INCREASED MYOCARDIAL OXYGEN DEMAND
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS FOR AN MI?
Hypertension
Hyperlipidaemia
Depression
Lupus
Diabetes
Kidney failure
Peripheral vascular disease
Previous heart attack
Stroke/TIA
Sleep apnoea
WHAT LIFESTYLE CHOICES INCREASE RISK OF CAD?
Smoking
Obesity - high fat diet
Stress
Lack of exercise
Cocaine use
WHAT ARE THE S&S OF CAD/MI?
Persistent crushing substernal pain that radiates to left arm, jaw, neck, shoulder blades
Described as a heavy squeezing, crushing
Persist more than 12 hours
Feeling of impending doom
Sweaty, clammy
Increased RR (SOB)
Nausea/vomiting
Fatigue
Indigestion
Cool extremities - delayed cap refill in fingers
Anxiety
Restlessness
Confusion - due to hypoxia
HOW TO TREAT MI/CAD?
Cannulation
Aspirin
Oxygen - below 94
GTN - only if BP above 90
Pain relief - morphine (BP above 90), Entonox
Take them to PCI (if fits criteria)
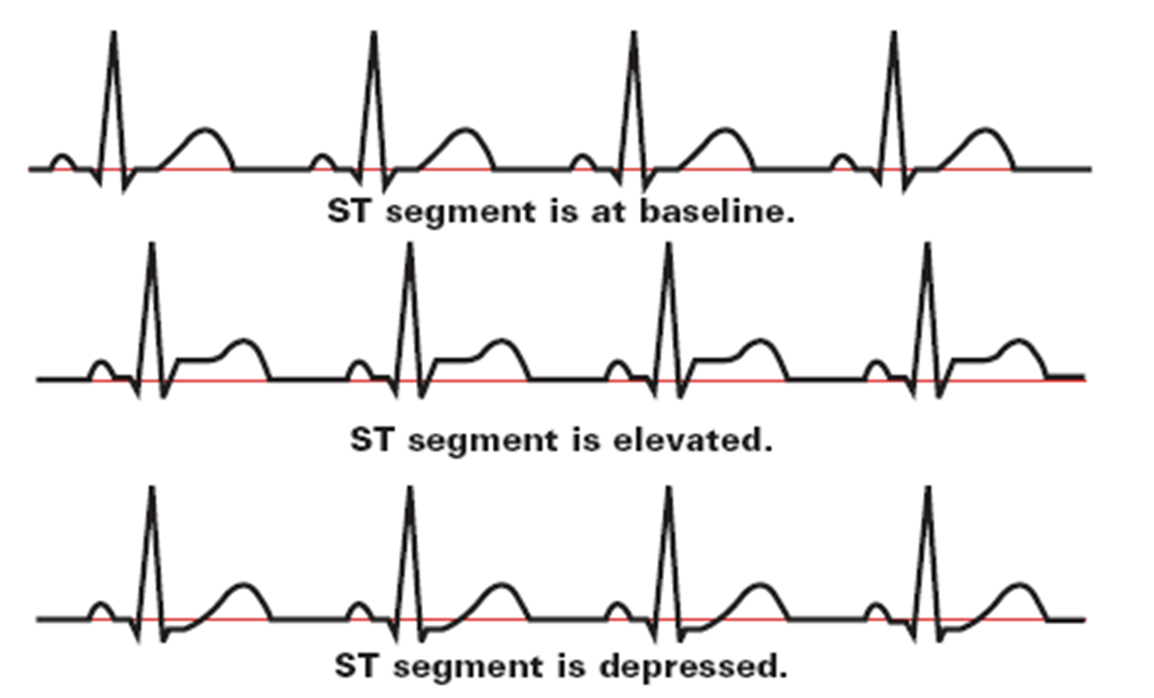
WHAT MIGHT THE ECG SHOW?
ST segment is at baseline - NORMAL!
ST segment is elevated - STEMI
ST segment is depressed
WHAT DOES II, III AND AVF LEAD SHOW?
Inferior wall Vt ventricle
WHAT DO I & AVL LEAD SHOW?
High lateral wall Lt ventricle
WHAT DOES V1 AND V2 LEAD SHOW?
Rt ventricle, septum wall
WHAT DOES V3 AND V4 LEAD SHOW?
Anterior wall Lt ventricle
WHAT DOES V6 AND V5 SHOW?
Lateral wall Lt ventricle
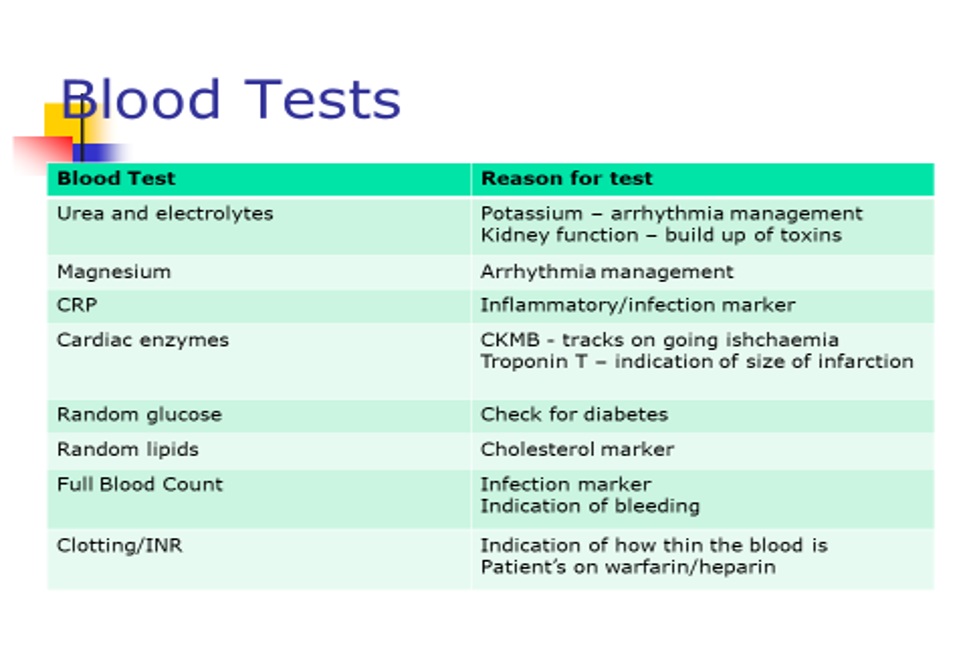
WHAT DO BLOOD TESTS SHOW?
WHAT ARE MI TREATMENT GOALS?
Relieve chest pain
Stabilise heart rhythm
Reduce cardiac workload
Take to PCI- stent etc.
WHAT ARE BETA BLOCKERS?
Slow heart rate and reduce workload
Used to control abnormal heart rhythms and symptoms of heart failure
WHO SHOULD YOU BE CAUTION OF WHEN PRESCRIBING ASPRIN
people with resp problems
WHAT IS BETA 1 RECEPTOR?
IT….
Increased inotropy
Increased chronotropy
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN BETA 1 RECEPTOR IS STIMULATED
increased membrane permeability
WHERE BETA 1 RECEPTORS FOUND
Found in SA node, AV node and myocardium
WHAT IS A BETA 2 RECEPTORS?
Decreased systematic vascular resistance
WHERE IS BETA 2 RECEPTORS FOUND
Found in smooth muscle, blood vessels, bronchi and skeletal muscles
WHAT IS A ACE INHIBITOR?
angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
TRUE OR FALSE- ACE INHIBITORS END IN “PRIL”
FALSE
E.G
Captopril
Enalapril
Lisinopril
Perindopril
Ramipril
WHAT HAPPENS IN ACE?
Medulla identifies a low BP
Afferent arteriole in nephron release enzyme renin into blood
Liver produces plasma protein- angiotensinogen
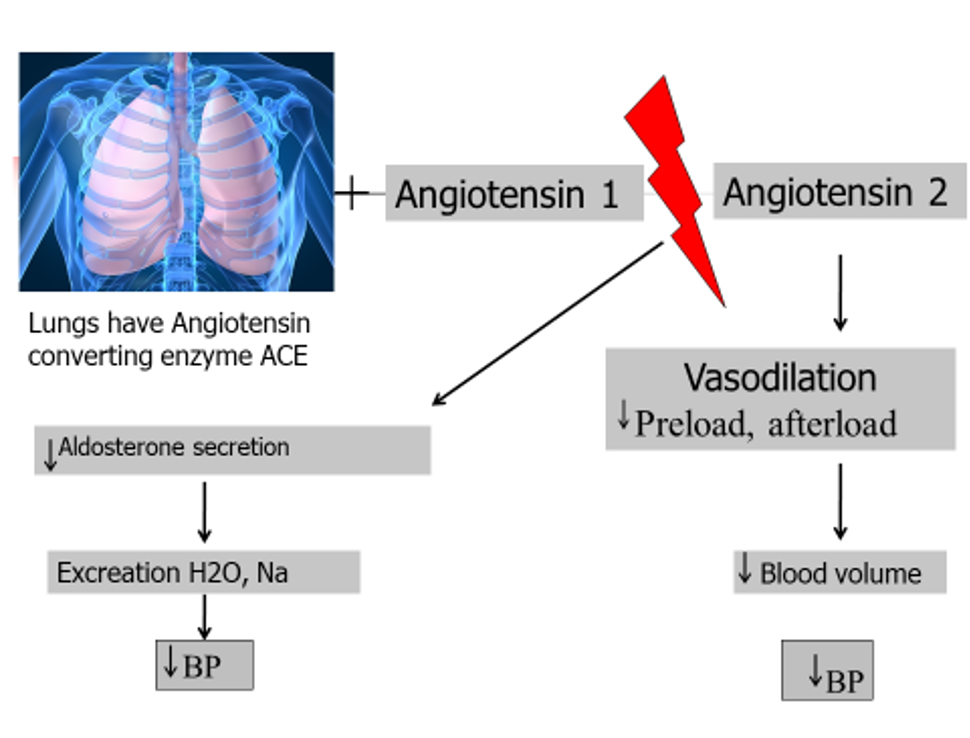
WHAT IS ANTOTENSINOGEN
PLASMA PROTEIN
WHAT DO ASPRINS DO?
Thins the blood
Lowers risk of blood clots in coronary arteries
WHAT DO CLOPIDOGREL DO?
Post MI patients
Minimum of 14 days
12 months for post PCI, stent
LT therapy for most
WHAT DO NITRATES DO?
Relaxes muscles in walls of blood vessels - cause them to dilate
Improve amount of oxygen rich blood to heart
WHEN ARE NITRATES EFFECTIVE
Good for preventing angina in LT
May become less effective when using LT
WHAT ARE SOME OTHER MEDICATIONS TO TREAT CAD?
DIRETICS
STATINS
WHAT ARE DIRETICS
acts on the kidneys to increase output of salt in urine and water
WHAT ARE STATINS
reduces level hypertriglyceridemia produced by the liver (bad cholesterol)
WHAT IS CARDIAC REHAB
Secondary prevention
Helps heart recover in controlled and supervised manner
Restoring exercise capacity and endurance
WHAT ARE CARDIAC REHAB AIMS
Limit effects that HD has on body
Limits psychological impact
Lowers risk of heart attack and death
Can help slow/stop CAD
WHAT IS ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
Abnormal fast irregular heartbeat
Abnormal heartbeat rhythm - arrhythmia
Normal resting HR 60-100
Fast HR - 140-180
WHAT IS FAST AF HR
140-180
WHAT MAY BE A RISK OF AF
Take medication to thin blood to stop a blood clot
Clot may travel in blood vessels and cause a stroke
WHAT HAPPENS IN AF?
Normal controlling timer is overridden by random electrical impulses that fire off from heart muscle in the atria
Atria quiver randomly (fibrillate)
Only some impulses pass through ventricles - random and haphazard
WHAT HAPPENS IN A NON AF HEART
Contractions controlled by electrical system keeps four chambers contract normally, in correct order
HOW MANY TIMES DO VENTRICLES CONTRACT
Ventricles contract 50-180 times (usually 140-180)
Ventricles contract in a vary of force
HOW MANY CHAMBERS ARE THERE AND WHAT IS IT MADE OF?
4 CHAMBERS MADE OF SPECIAL HEART MUSCLE
WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF AF
Paroxysmal AF
Persistent AF
Permeant AF
WHAT IS PAROXYSMAL AF
Have episodes that come and go
Come on suddenly
Stop suddenly without treatment within 7 days (usually 2 days)
Heart beat goes back to normal
Period of time between episodes can vary greatly
It stops on its own- can take treatment to make it stop quicker!