AP BIO UNIT 5
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the result of meiosis?
4 haploid cells (gametes)
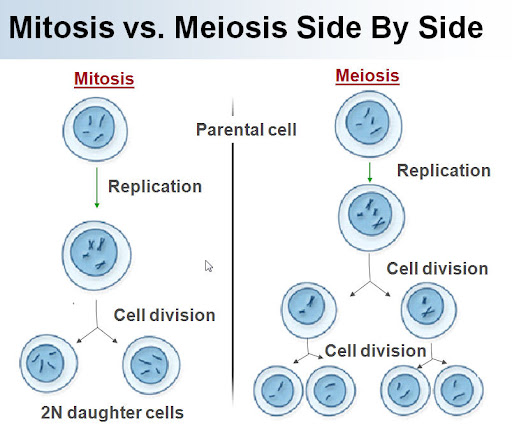
Name some key differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis has 1 division, and meiosis has two. Meiosis produces NEW cells with a novel set of genes, while mitosis produces original copies.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are a pair of a particular type of chromosomes that carry genes controlling the same characteristics
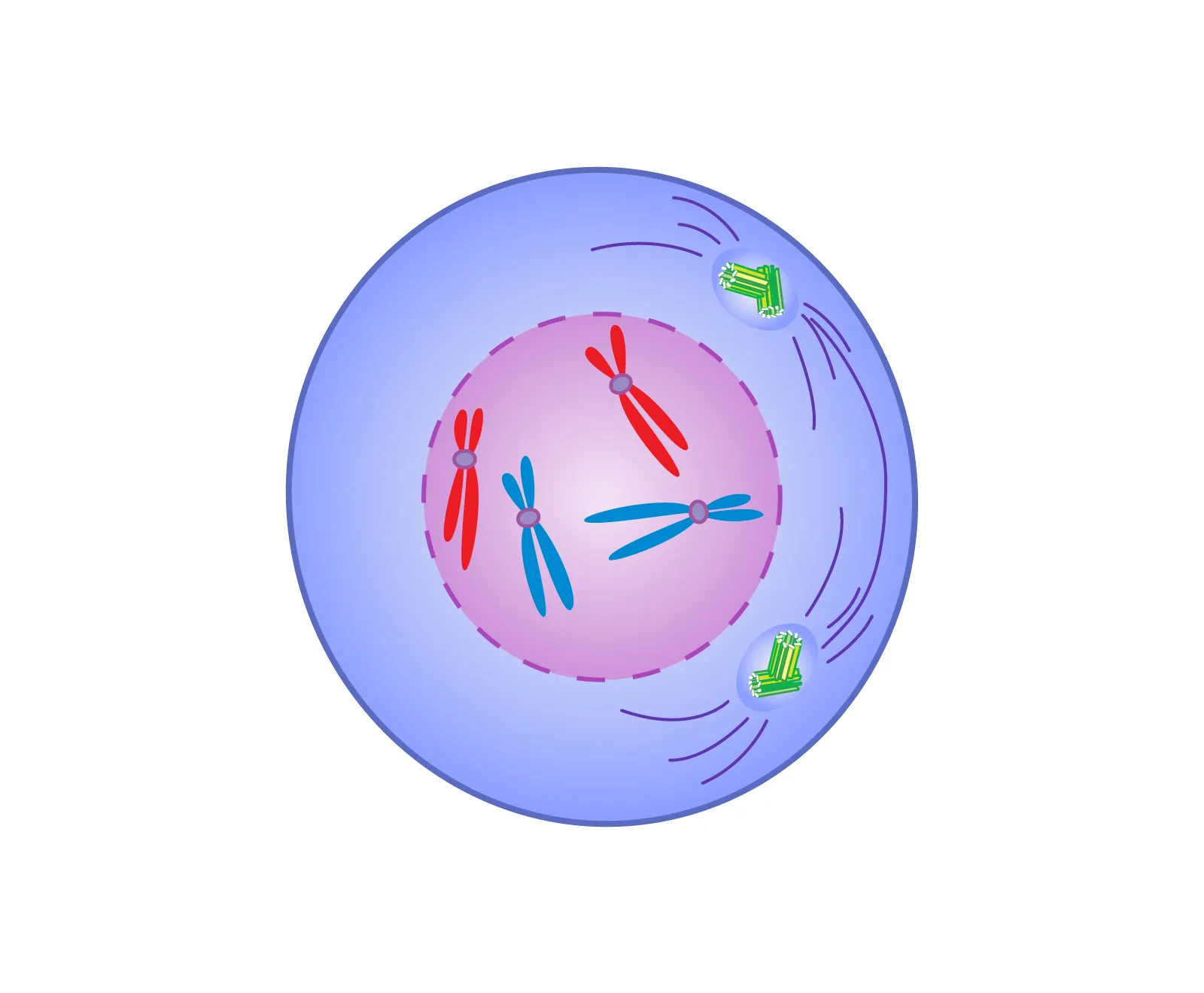
What occurs in prophase 1?
Crossing over occurs, which is when certain proteins break apart the DNA of nonsister chromatids at exactly the same location. This location is refered to as the chiasmata. The spindle forms and the nucleus comes apart.
What are recombinant chromosomes?
Recombinant chromosomes are chromosomes that have undergone genetic recombination, typically through the process of crossing over during meiosis. This results in a mix of genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic diversity among offspring.
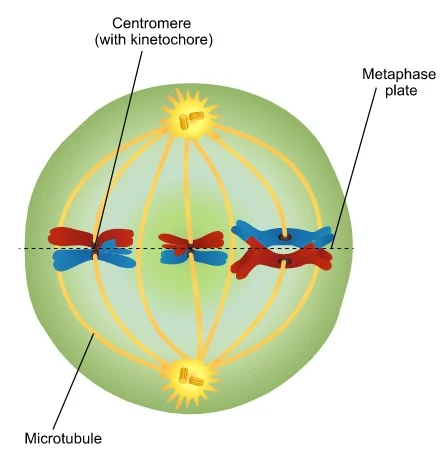
What happens in metaphase 1?
Homologous Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate (the middle of the cell) in a line.
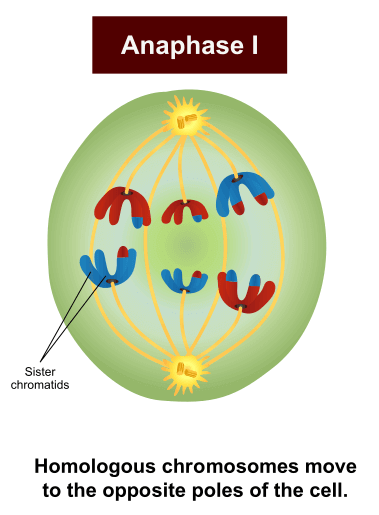
What happens in anaphase 1?
Homologues get pulled apart (each complete with both sister chromatids)

What happens in telophase 1?
The nuclear membrane reforms, cytokinesis occurs, and 2 haploid cells are created
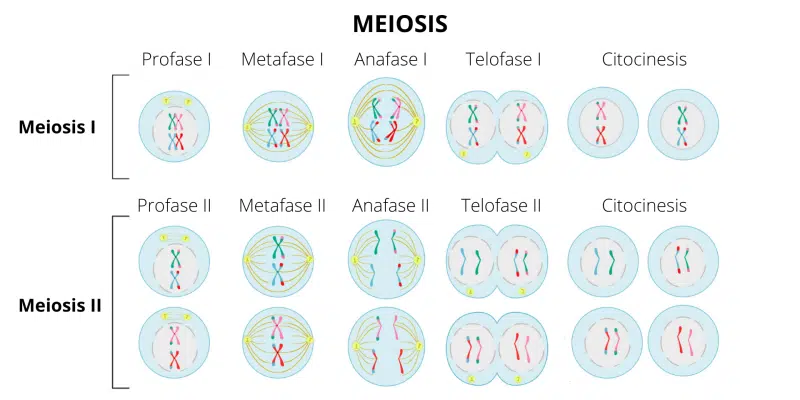
What happens in meiosis II?
It is basically the same as mitosis except for the fact that chromatids are not identical due to crossing over from prophase 1, and the chromatids line up on the metaphase plate instead of the homologous pairs.
What is complete dominance?
Presence of a dominant trait that is always expressed.
What is Codominance?
Both dominant traits are expressed at the same time
What is incomplete dominance?
Hybrid offspring phenotype will be a blend of parental phenotypes (think interracial couples = mix of colors)
What is non disjunction?
The failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis
What times can nondisjunction occur?
When sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis II OR when homologous chromosomes fail to separate in meiosis.
What can nondisjunction cause?
If the homologous chromosomes fail to separate, gametes will have incorrect number of chromosomes. If sister chromatids fail to separate, 2 gametes will have correct number of chromosomes, and 2 will have an incorrect number (missing or more)
What is the law of segregation?
Each gamete must have an allele from each parent
What is the law of independent assortment?
each pair of homologous chromosomes splits independently, alleles of different genes can mix and match
What is sickle cell anemia and tay sachs disease caused by?
Due to a missense mutation, which is a single change in DNA sequence.
What is Huntington disease caused by?
35+ CAG a repeat that overwhelms proteins and causes neurons to degenerate over time
What are homologous chromosomes?
Duplicate versions of each chromosome that contains genes in the same locations
What is an allele?
An allele is a version of a gene that can create different traits, like eye color or hair color
What is the P generation
Parental generation (first gen)
What is the f1 or filial generation?
The offspring of the parental or p generation
What is a mono hybrid cross?
When two individuals are crossed and one gene is being studied
What is a di hybrid cross?
Similar to mono hybrid but studies how two genes are passed down to offspring
What are linked genes?
Genes on the same chromosome that stay together together during assortment and are considered “linked”, meaning they will be inherited together. Cannot segregate independently
What is polygenic inheritance?
In some cases, a trait results from the interaction of many genes. Each gene will have a small effect in a particular trait. He ugh, skin color, and weight are all examples of polygenic traits
What is a gene?
A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the code for producing a specific protein, which ultimately determines a particular trait or characteristic in an organism
What is phenotype plasticity?
Occurs if two individuals with the same genotype have different phenotypes because they are in different environments,
What is synopsis?
When In meiosis, the chromosomes line up side by side with their counterparts (homolog). Synapsids involves two sets of chromosomes that come together to form a tetrad which consists of 4 chromatids. Synapsis is followed by crossing over
What is aneuploidy?
The prescience of an abnormal amount of chromosomes in a cell
What is translocation?
Occurs when a segment of a chromosome moves to another nonhomologous chromosome
What is pleiotropy?
Pleiotropy is the phenomenon where a single gene influences multiple, seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits.
What are some examples of pleiotropy?
- Sickle Cell Anemia: A mutation in the hemoglobin gene affects red blood cell shape, leading to various symptoms including pain, anemia, and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A mutation in the CFTR gene affects the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems, leading to thick mucus production and a range of complications.
- Phenylketonuria (PKU): A mutation in the PAH gene affects amino acid metabolism, resulting in cognitive impairment and a range of other developmental issues if untreated.