Bio Ch 7
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
3 types of gene products
Protein
rRNA
tRNA
Mice Experiment that lead to determining DNA carried the genetic code
There were 2 strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae used in this experiment, a deadly smooth coat (S) strain and a nondeadly rough coat strain (R)
When mice were injected with live “S” they died
When mice were injected with live “R” they survived
When mice were injected with heat-killed “S” they survived
When heat-killed “S” was mixed with live “R” and then mice were injected with the mixture, they died
This meant that some component in the dead “S” could be transferred to the “R” to make it deadly
Scientists removed each type of molecule from the dead “S” in that last aforementioned step one at a time
When anything except DNA was removed, the “R” strain still acquired the “S” traits and was deadly and live bacteria exhibiting “S” traits could be recovered from the sample
When the DNA from the heat-killed “S” was removed, the mice survived
This lead to the discovery that the DNA in the “S” strain encoded the ability for the strain to be deadly and was the molecule that could be passed between organisms and generations
Virus Experiment that lead to determining DNA carried the genetic code
Hershey and Chase incubated 2 viral cultures, one with P32 and one with S35
P32 is in DNA phosphates
S35 is in proteins in Met and Cys
Allowed these viruses to infect separate bacteria
Grew the bacteria that were infected through a lysogenic cycle
Introduced unlabeled viruses to the newly grown already infected bacteria to perform a lytic cycle
New viruses that came out of the P32 samples had P32 DNA but viruses that came out of the S35 samples didn’t have S35 protein
Thus DNA carries genetic info not protein
Synapsis
The alignment of homologous chromosomes on top of each other during synapsis
Name of two homologous chromosomes in prophase 1
They become a bivalent or tetrad when they undergo synapsis
Crossing over / recombination
A tetrad is cut allowing the homologous chromosomes to mix and match pieces and exchange alleles
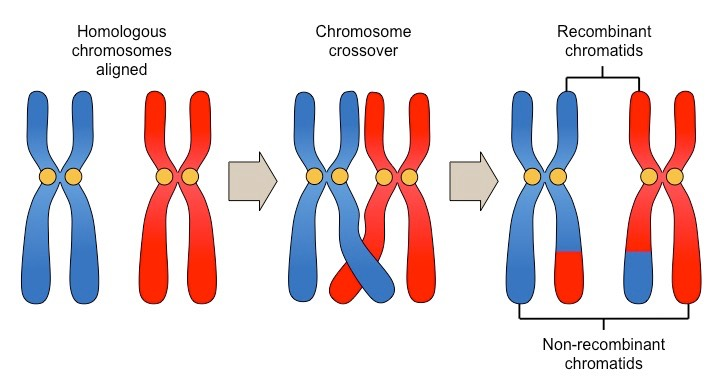
Synaptonemal Complex (SC) and how it works
Mediates synapsis to ensure tetrads are formed correctly
SYCP2 and SYCP3 each attach to the edge of a homologous chromosome and are connected by SYCP1 and other proteins which connects the two chromosomes like a zipper between SYCP2 and SYCP3
Meiosis Phases
Prophase I:
Homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis and form a tetrad which then crosses over using the synaptonemal complex
Metaphase I:
Tetrads line up on the metaphase plate
Anaphase I:
and homologous chromosomes separate now with exchanged alleles with sister chromatids staying together
Telophase I:
Cells separate now each with only one chromosome —- they are haploid. They still have sister chromatids on each chromosome
Prophase II:
Chromosomes re-condense
Metaphase II:
Singular chromosomes line up along metaphase plate
Anaphase II:
Sister chromatids are pulled apart
Telophase II: Cells divide leaving each of the four daughters with one sister chromatid (chromosome) of each type
Nondisjunction
Failure of either homologous chromosomes in Metaphase I or sister chromatids in Metaphase II to separate
This results in gametes with either 2 copies of a chromosome or no copies of a chromosome
If this nondisjunction gametes fuse to form a zygote the zygote will have a trisomy or monosomy
Trisomies and monosomies usually result in death
Trisomy 21
Down syndrome
Intellectual disability
Abnormal growth
Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes
usually nonlethal — can survive as long as you have one X
Usually results in sterility and intellectual disability
If you have a Y you will have male characteristics — SRY gene
No Y = no male characteristics
Turner Syndrome
Only one X sex chromosome and no Y
Results in:
Female appearance
Sterility
Underdeveloped ovaries
Law of segregation
two alleles of an individual are separated and only one is passed onto offspring
Law of independent assortment
Which gamete an allele of one gene goes into has no impact on the gamete that receives an allele from another gene
Mendel’s Two Laws
Law of segregation
Law of independent assortment
Pure breeding strain
Homozygous — always produce same phenotype
F1 generation
the progeny of a testcross
Testcross
breeding a dominant phenotype with a homozygous recessive genotype to figure out if the dominant is homozygous or heterozygous.
If any of the F1 generation (offspring) are phenotypically indicative of the recessive, the dominant parent has to be heterozygous
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete dominance — seen in human height
Given:
R = Red flower
and
r = white flower
RR = Red
Rr = Pink (a blend of red and white)
rr = White
Codominance
Codominance — seen in blood typing
Given:
R = Red flower
and
r = white flower
RR = Red
Rr = Red and White together (maybe red with white spots)
rr = white
Pleiotropic Inheritance
one genotype affects many phenotypes
Polygenic trait
a trait influenced by a combination of many genes
Penetrance
The odds that an individual with a given genotype will express the phenotype for that genotype
Epistasis
Expression of alleles for one gene is dependent on another
Ex. the gene for curly hair cannot be phenotypically displayed if the gene for baldness is activated
Recessive lethal alleles
homozygous genotype that results in the death of the organism
Linkage
the failure of genes to display independent assortment relative to one another when close together on the same chromosome
Mitochondrial Inheritance
Inheritance of traits contained within mitochondrial DNA which is only passed down through the mother
Usually given the prefix “mt”
Ex. mt-Atp6 — encodes an ATP synthase subunit
hemizygous
when a diploid organism only has one copy of a gene
Ex. all mitochondrial genes
X Linked traits common example
Hemophilia
Much more common in males than females
X Chromosome Recombination
X-linked allele combinations may be different in offspring than they are in the female parent because the two female X chromosomes can recombine altering their genotypes during meiosis
Population
members of a species that mate and reproduce with one another
Hardy-Weinberg Law
states that the frequencies of alleles in the gene pool of a population will not change over time
Hardy-Weinberg Assumptions (5)
No mutation
No migration
No natural selection
Random mating
Large population
Hardy Weinberg Equations
p2 + q2 = 1
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
p = dominant allele freq
q = recessive allele freq
p2 = homozygous dominant genotype freq
2pq = heterozygous genotype freq
q2 = homozygous recessive genotype freq
Fitness
how successful an organism is at reproducing and passing its alleles on to future generations
HAS NOTHING TO DO WITH THE INDIVIDUAL’S ABILITY TO BE PHYSICALLY FIT OR COMPETE FOR FOOD — JUST REPRODUCTIVE SUCCESS
Directional Selection
Selecting for one extreme of a trait over the other
Ex. giraffes having longest necks possible
Divergent Selection
Selects for both extremes of a trait leaving the average phenotypes out
Ex. Small deer being selected for because they can hide and large deer being selected for because they can fight but mid-size deer being selected against because they can do neither
Stabilizing Selection
Selecting for the average phenotype and against the extremes
Ex. human birth weight being most successful at a medium weight because too small or large of babies have complications that can impact fitness
Artificial Selection
Humans using controlled mating to select for certain traits in some animals and crops
Sexual Selection
Selecting for traits that attract a mate regardless of how they impact the individual’s survivability
Ex. the bright feathers of a peacock are selected for as they attract more mates
Kin Selection
Describes an individual sacrificing themselves to save their kin
Species
a group of organisms capable of reproducing with each other sexually and producing successful, fertile offspring
Horses and donkeys can mate to make a mule but the mule is sterile. Therefore horses and donkeys aren’t the same species
Two types of reproductive isolation
Prezygotic — prevent the formation of the zygote
Postzygotic — prevent the development, survival to maturity, or reproduction of the offspring
Types of prezygotic reproductive isolation (5)
Ecological — the organisms live in different habitats with an uncrossable barrier
Temporal — the organisms mate at different times of day, seasons, or times of year
Behavioral — the organisms don’t use the same mating rituals
Mechanical — reproductive organs are incompatible
Gametic — gametes cannot fuse to form a zygote
Types of postzygotic reproductive isolation (3)
Hybrid Inviability — hybrid offspring do not develop normally and usually die in the embryonic stage
Hybrid Sterility — hybrid develops normally but is unable to reproduce
Hybrid Breakdown — the second generation of hybrids is biologically defective
Speciation
creation of a new species
Homologous Structures
Physical features shared by two different species as a result of a common ancestor
Analogous Structures
Structures that serve the same function in two different species but cannot be drawn to a common ancestor
Convergent Evolution
When two species come to possess many analogous structures due to similar selective pressures
Divergent Evolution
When two species become phenotypically different due to differing selective pressures
Parallel Evolution
When two species undergo similar simultaneous evolutionary changes
Ex. all animals evolving cold resistance through the ice age
Taxonomy
science of biological classification
binomial classification
Gives every organism a two word classification consisting of genus and species
Invented by Carolus Linnaeus
Ex. Homo sapiens
Descending order of taxonomic categories
Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
Anterior
Front Facing
Posterior
Back Facing
Dorsal
On top or spinal side
Ventral
On bottom or opposite spinal side
Superior
Closer to the head
Inferior
Further from the head, closer to the feet
Cephalad
Towards the head
Caudad
Towards the tail
Two important characteristics of early earth atmosphere
It was anaerobic (No O2)
It was a reducing environment with plentiful electron donors
Abiotic synthesis
the process by which polymers were made on the early earth using metals and clays at catalysts and lightning, radioactive decay, volcanic activity, or sunlight as energy
Proteinoids
polypeptides made through abiotic synthesis
Microspheres
droplets of proteinoids in water
liposomes
lipids covering a microsphere of proteinoids
Coacervate
Molecules that include polypeptides, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides formed using enzymes
Protobionts
Classification that includes Microspheres, Liposomes, and Coacervates
Resemble a cell in that they:
Have a protected inner environment
Can perform chemical reactions
Split into two when they get too big
They lack heredity
Ribozymes
RNA enzymes that splice mRNA
RNA self-replication
one small RNA strand can line up with another and spontaneously polymerize by base pairing with a fairly low error rate