ECHO 3 : Infective Endocarditis
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what is infective endocarditis?
secondary invasion by bacteria, parasites, and fungi that causes infection of endocardium
(or other implanted intra cardiac materials like conduits, prosthetic implants, chamber walls)
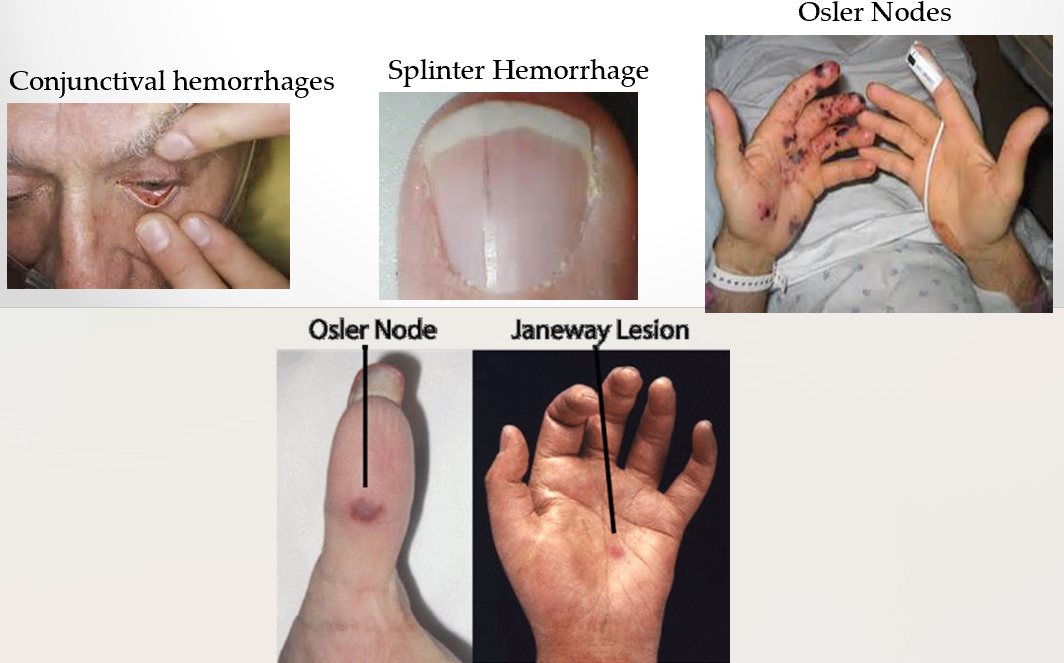
what are common signs and symptoms of IE?
FROM JANE
fever
roths spots
osler’s nodes
murmur
janeway lesions
anemia
nail hemorrhage
emboli
what is the dukes major criteria?
B : blood culture positive for IEA
E : imaging positive for IEA
vegetation
abscess
pseudoanyeurysm
what is duke’s minor criteria?
predisposing heart conditions or IV drug use
fever
vascular phenomena
immunologic phenomena
microbiologic evidence
IV drug use affects
right side of heart (tricuspid valve)
what are janeway lesions?
lesions on palms or soles caused by septic emboli which deposity bacteria forming microabscesses
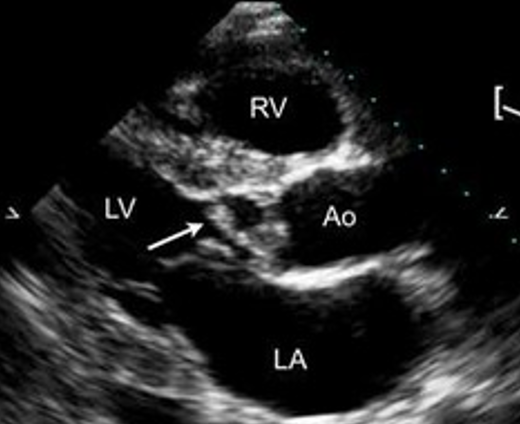
how can echo distinguish between bacterial, viral and parasitic endocarditis?
echo can not
what is the most common bacterial cause of IE?
staphylococcus aureus
how often can an echo be ordered for someone with suspected endocarditis?
if there are positive blood cultures then it can be ordered as many times as needed
which modality is used to detect IE?
TTE first because it is non invasive (negative or inconclusive in 30% of cases)
then TEE is performed because of better image quality and higher sensitivity
how does IE present?
mobile vegetation
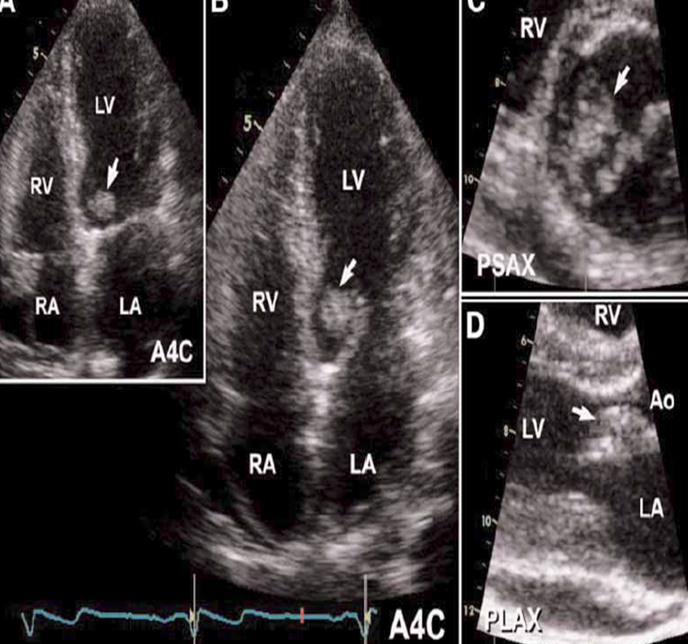
mobile vegetations of size - increases the risk of
>10mm
embolism
which sided vegetations are more common?
left sided vegetations are more common than right
vegetations are more common on sides where
valves are exposed to high velocity regurgitant jets
LV side of AV
LA side of MV
(mv vegetation on LV side which is not usual )
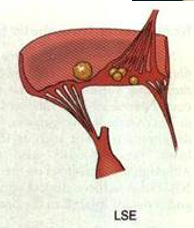
what is the upstream side of the valve?
the sides of the valves that are exposed to high regurg jets
how are IE vegetations formed?
from endothelial disruption caused by high velocity jets that accompany congenital defects, prosthetic valves, intracrdiac shunts, and valv dysfunction
what is libman sacks endocarditis?
form of nonbacterial endocarditis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
what is the most common heart related manifestations of lupus?
pericarditis
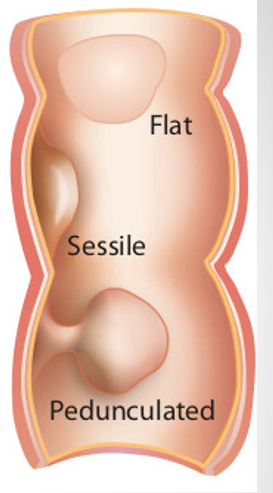
what do IE vegetations look like?
irregularly shaped, low reflective structures that may be sessile (attached at base) or pedunculated
color flow doppler is used to assess what in IE vegetations?
hemodynamic effect
does valvular endocarditis cause stenosis?
rarely
how do vegetations appear on MV
shaggy
partial obliteration of interleaflet separation
abnormal opening and closure times
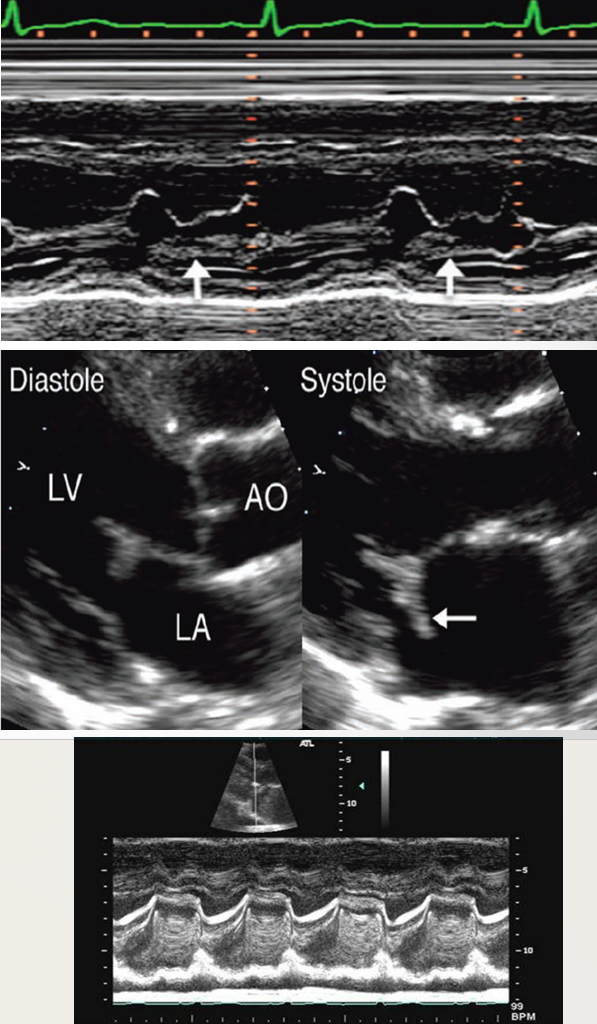
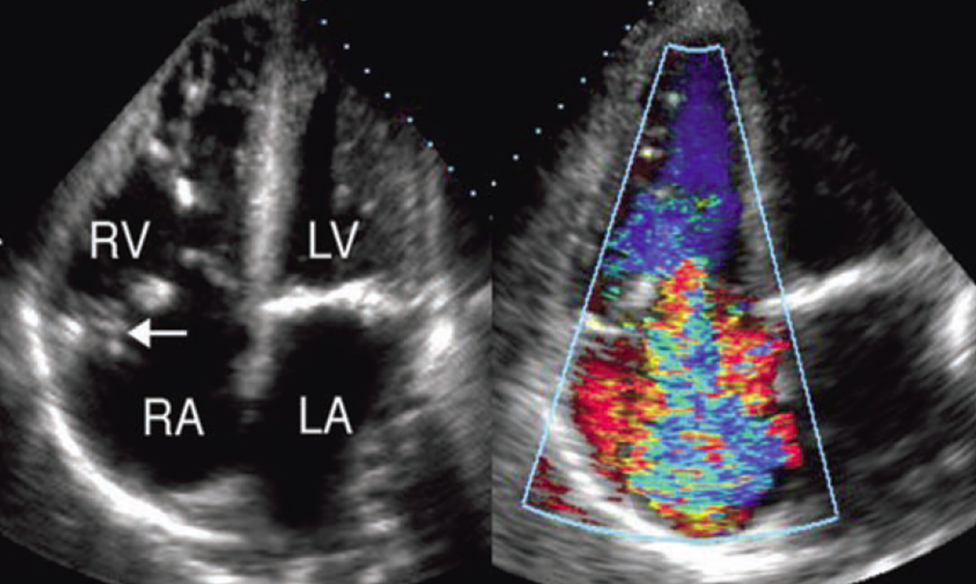
what is seen here?
tricuspid valve vegetation w/ severe regurg
what are other IE findings in the absence of vegetation?
abscesses
fistula
changes in prosthetic valve hemodynamics
valve dehiscence (splitting)
paravalvular leaks
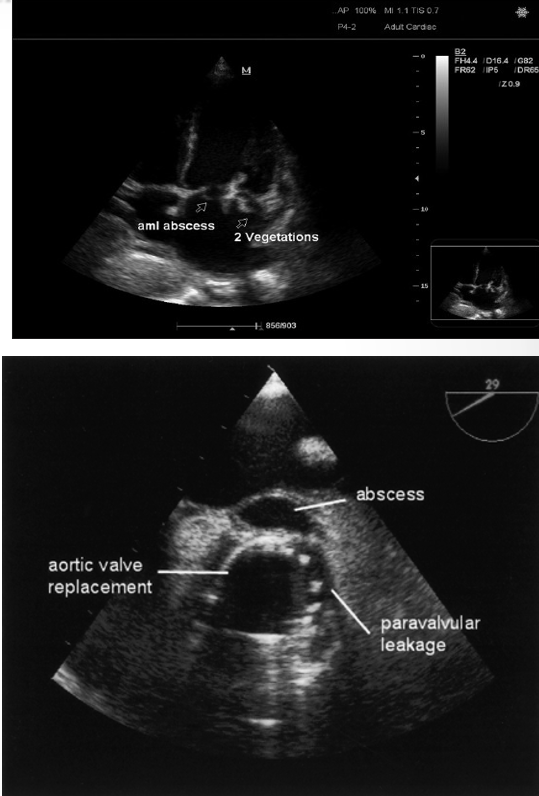
what do IE abscesses look like?
nonhomogenous enclosed area appearing echolucent or echodense
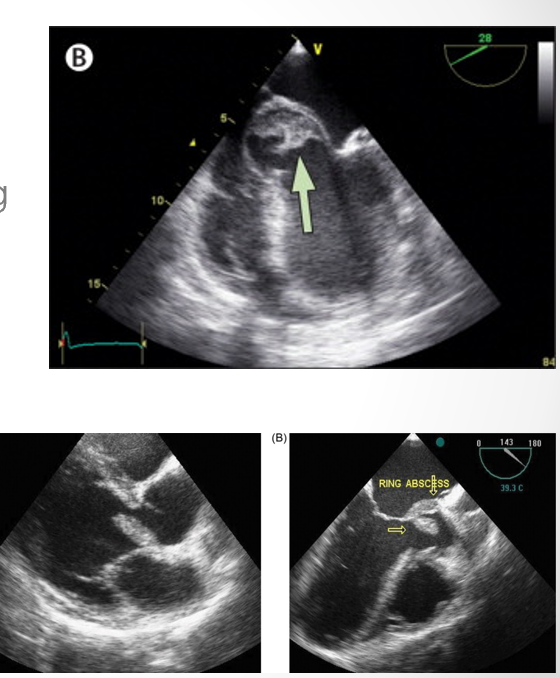
which valve is most affected by endocarditic abscess?
ao valve (then mv)
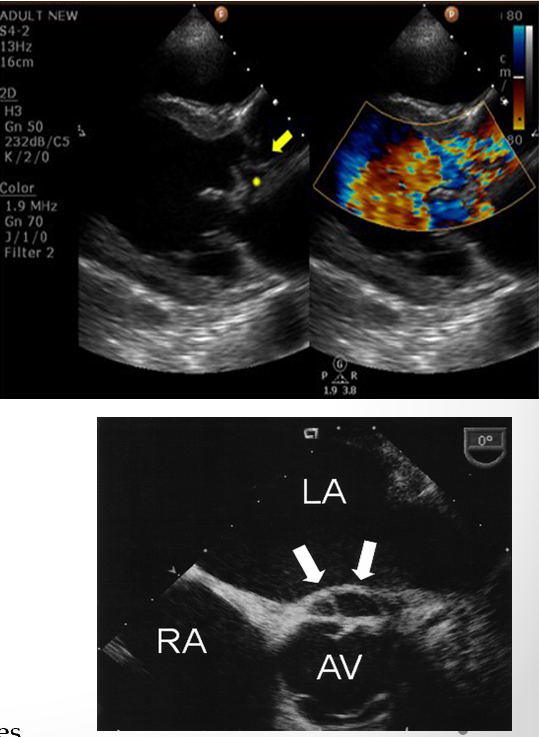
what is this?
abscess
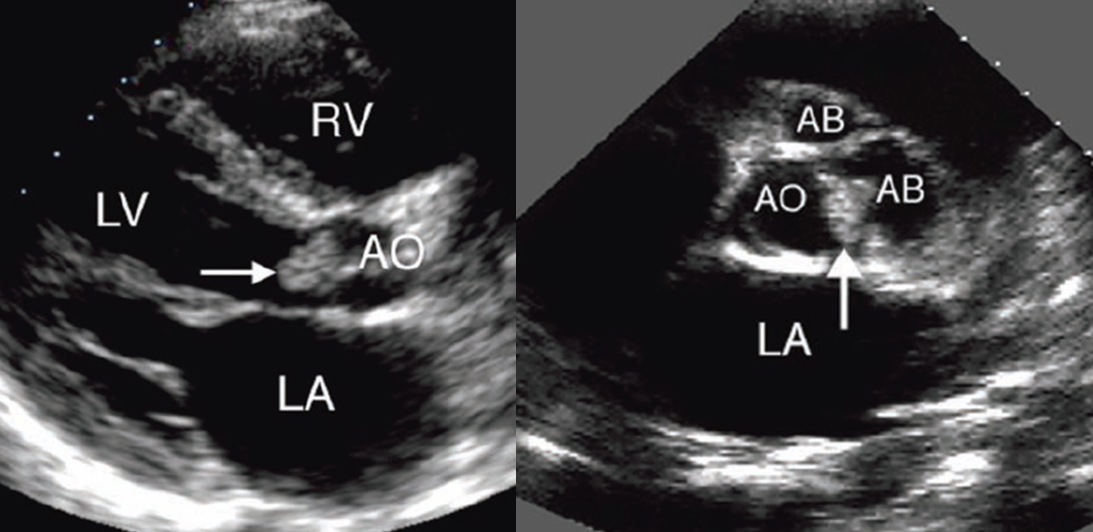
what is shown here?
ao valve vegetation with abscess
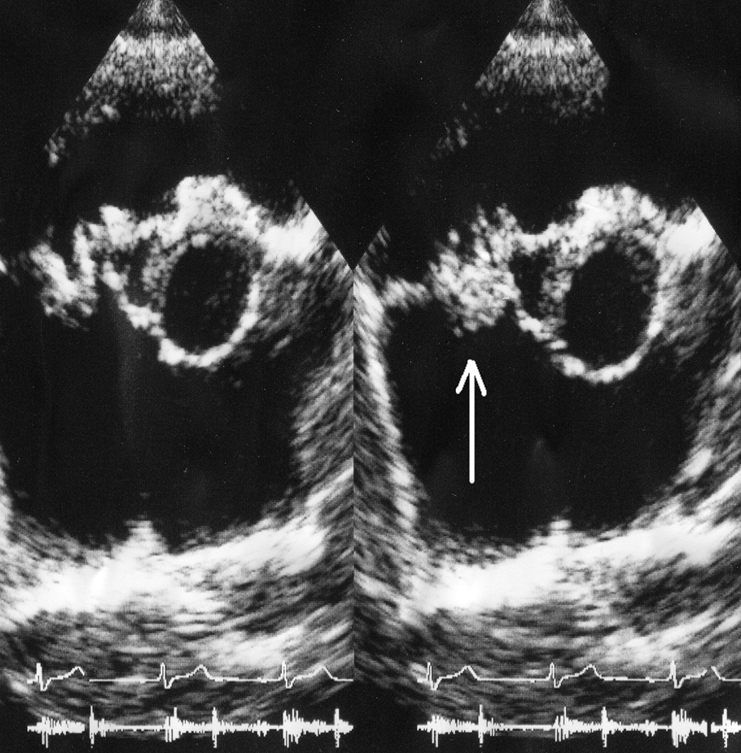
what is seen here?
endocarditis vegetation of tricuspid leaflets and infectious abscess of aortic annulus
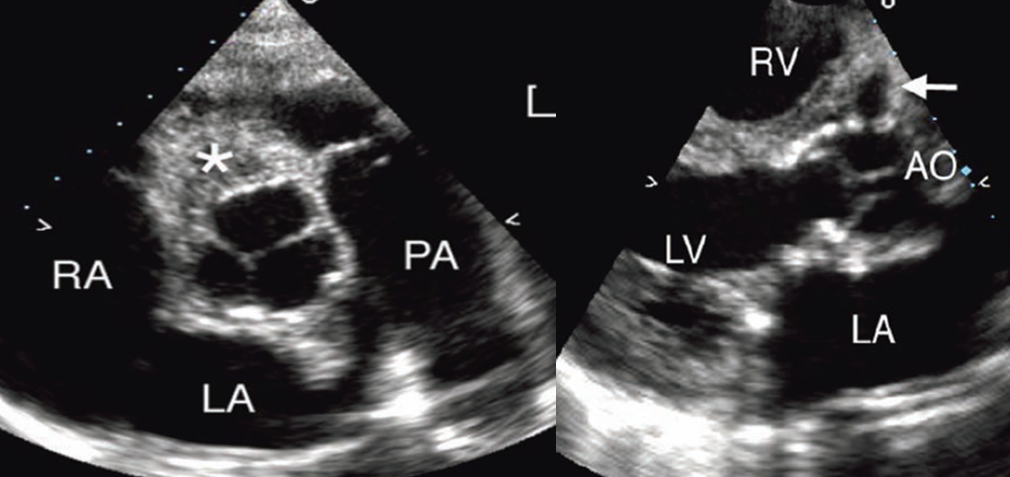
what is seen here?
periannular absces adjacent to sewing ring
what are the differential diagnosis for IE?
severe MAC
wonder if patient has fever or other signs of infection
fibroelastoma
lambl’s excrescences
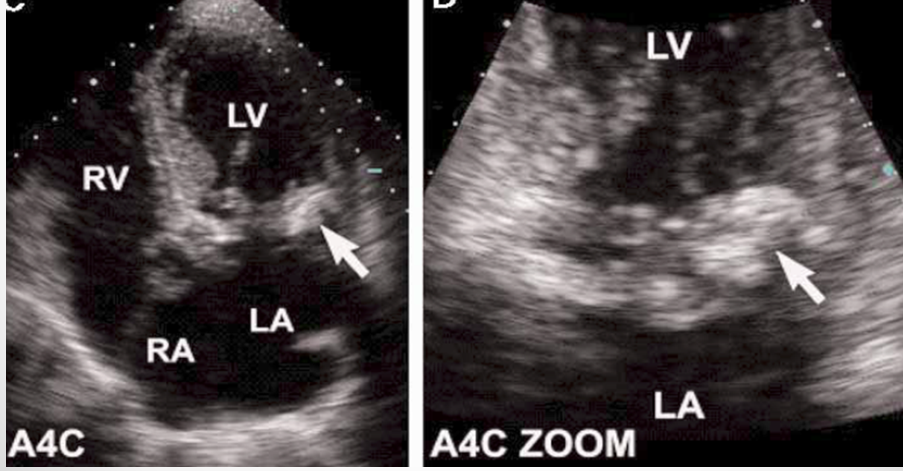
what is the most common benign neoplasm of cardiac valvular structures?
fibroelastoma
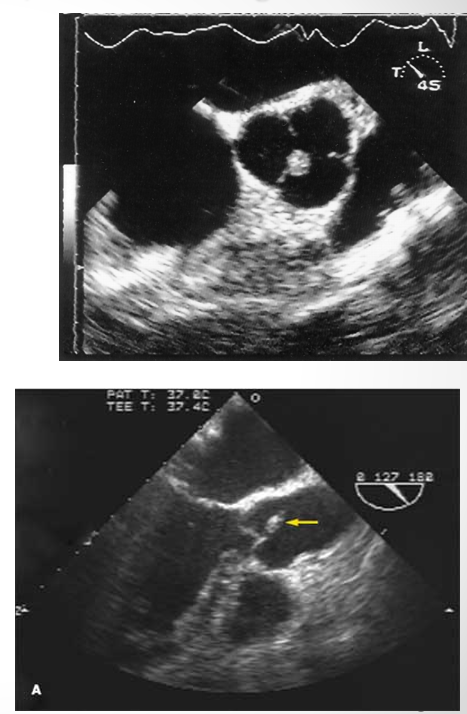
fibroelastoma makes up - % of tumors in the heart
10
what is lambls excrescences
rare thin mobile and filiform cardiac growths that develop at heart valve closure sites
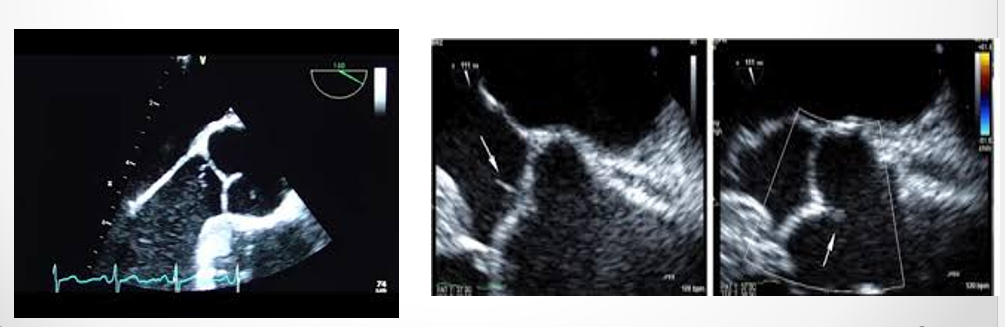
regurg secondary to valvular perforation often have
very steep deceleration slopes
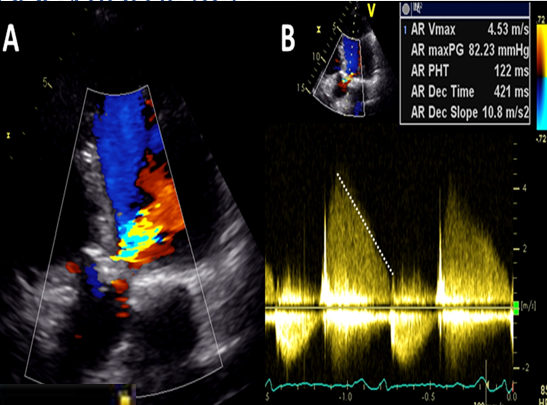
review qs
vegetations are typically caused by
endocarditis
bacterial (staph)
review qs
what are some differential diagnoses of a vegetation caused by infective endocarditis and how can one determine the diagnosis?
MAC, fibroelastoma, lambls excrensces
look for signs of fever or other symptoms
review q
vegetation on the right side of the heart would typically be caused by
IV Drug use
review qs
which side of the heart are vegetations more likely to occur?
left