Ichthyology at UCM
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
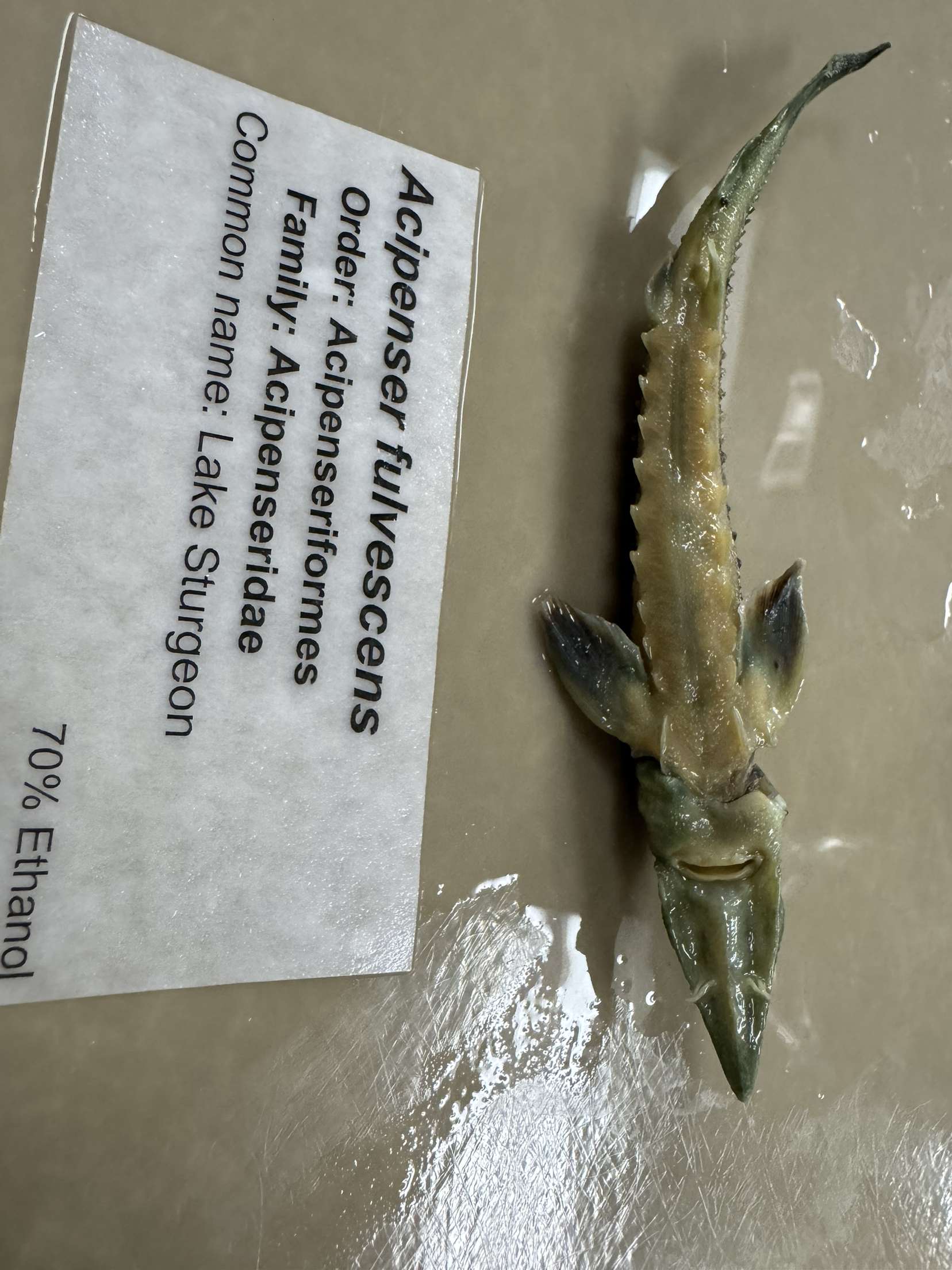

Acipenser fulvescens
Lake sturgeon (unfringed barbels)
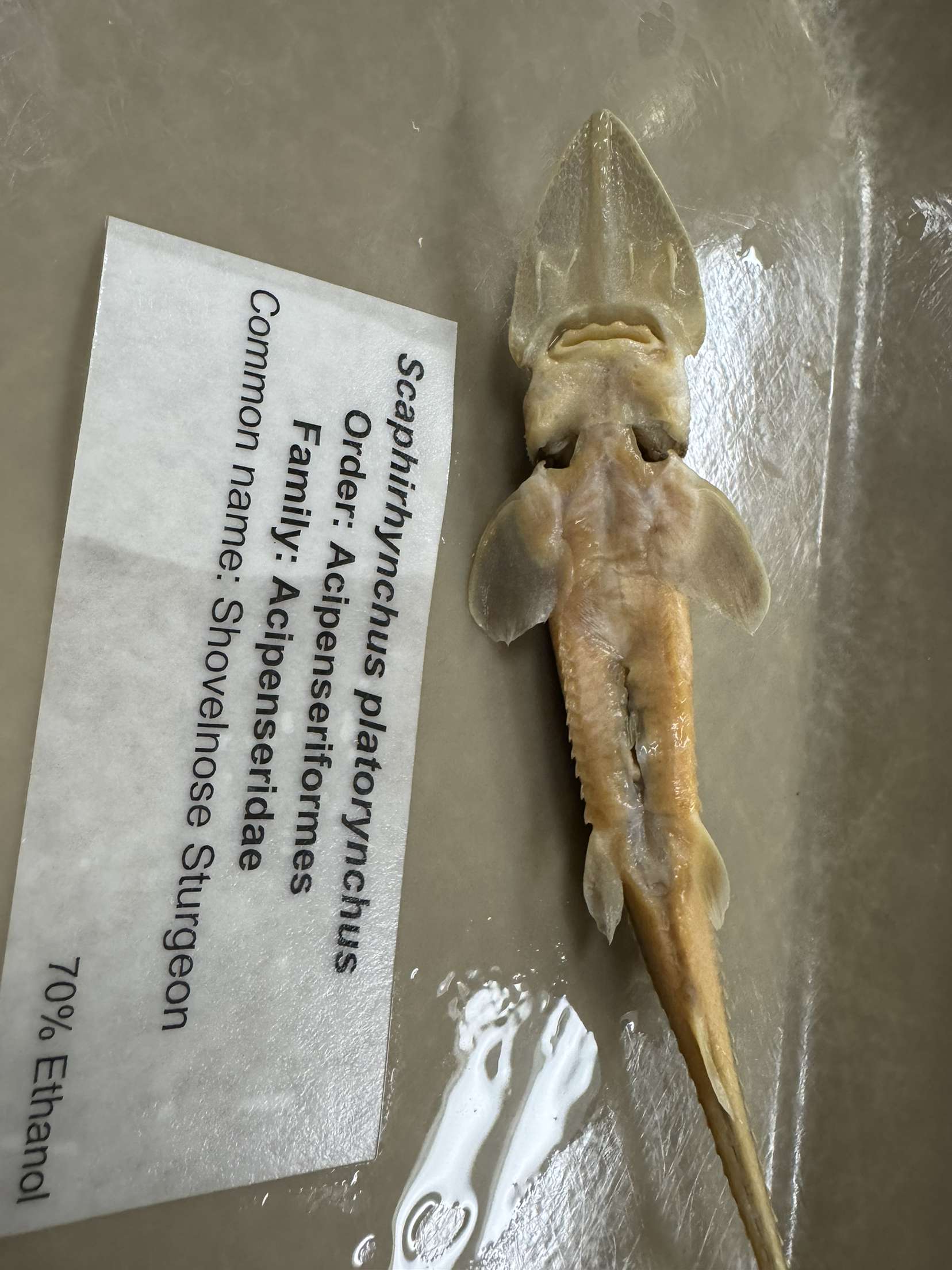

Scaphirhynchus platorynchus
Shovelnose Sturgeon (4 lobed lips curved)

Scaphirhynchus albus
Pallid Sturgeon (4 lobed lips flat)
Cypriniformes
Includes the Carp
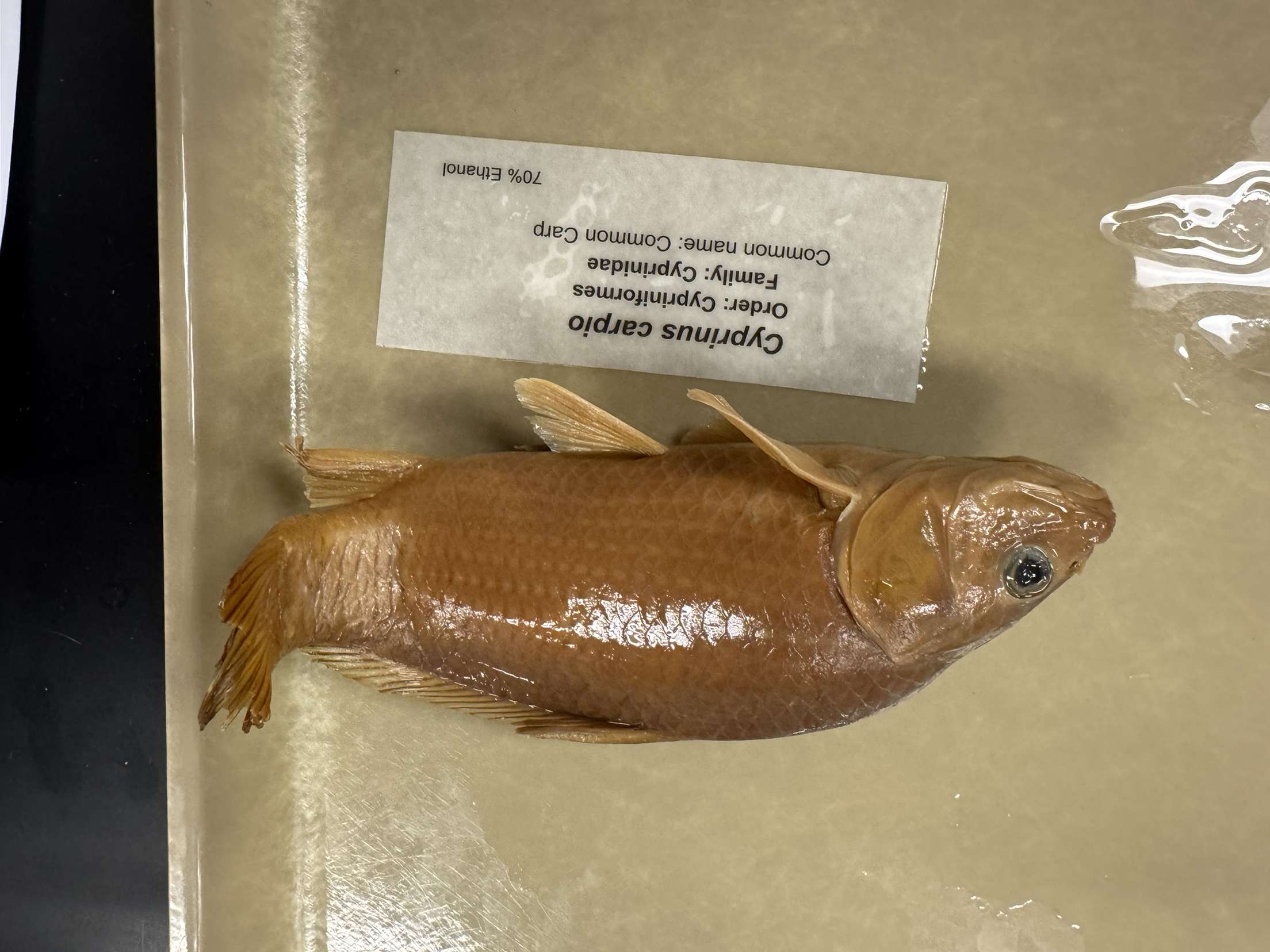

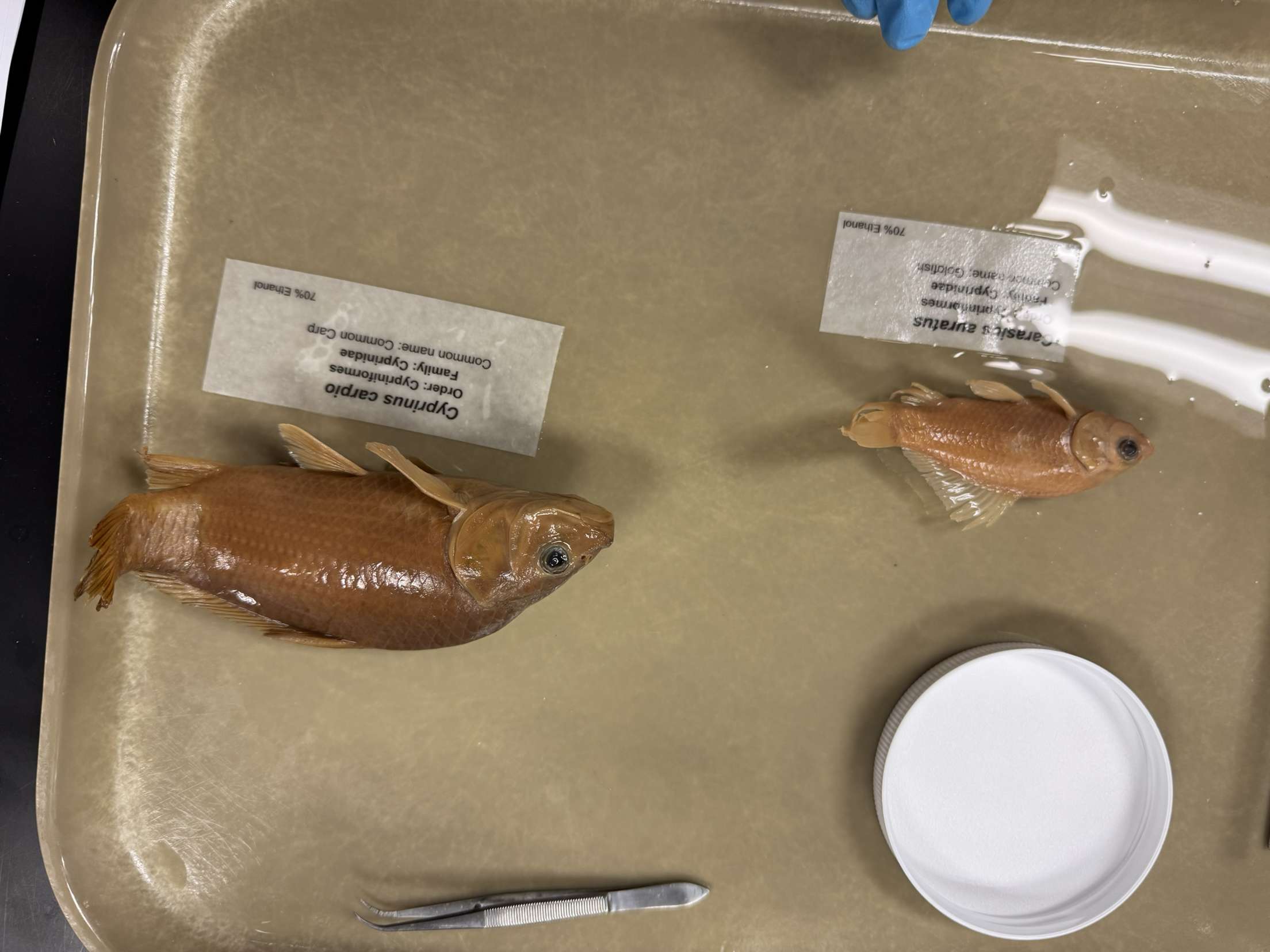
Cyprinus carpio
Common Carp
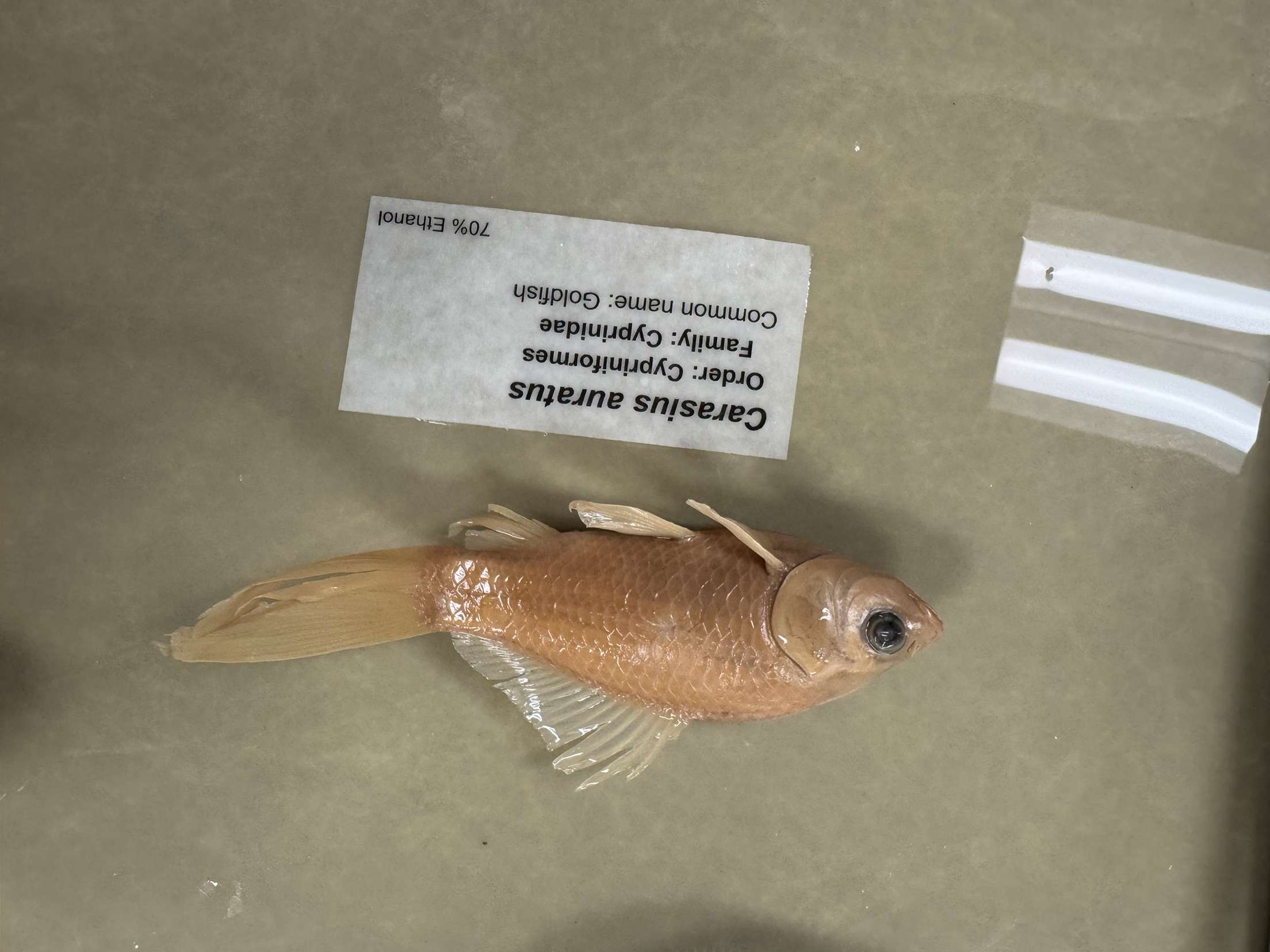

Carassius auratus
Goldfish
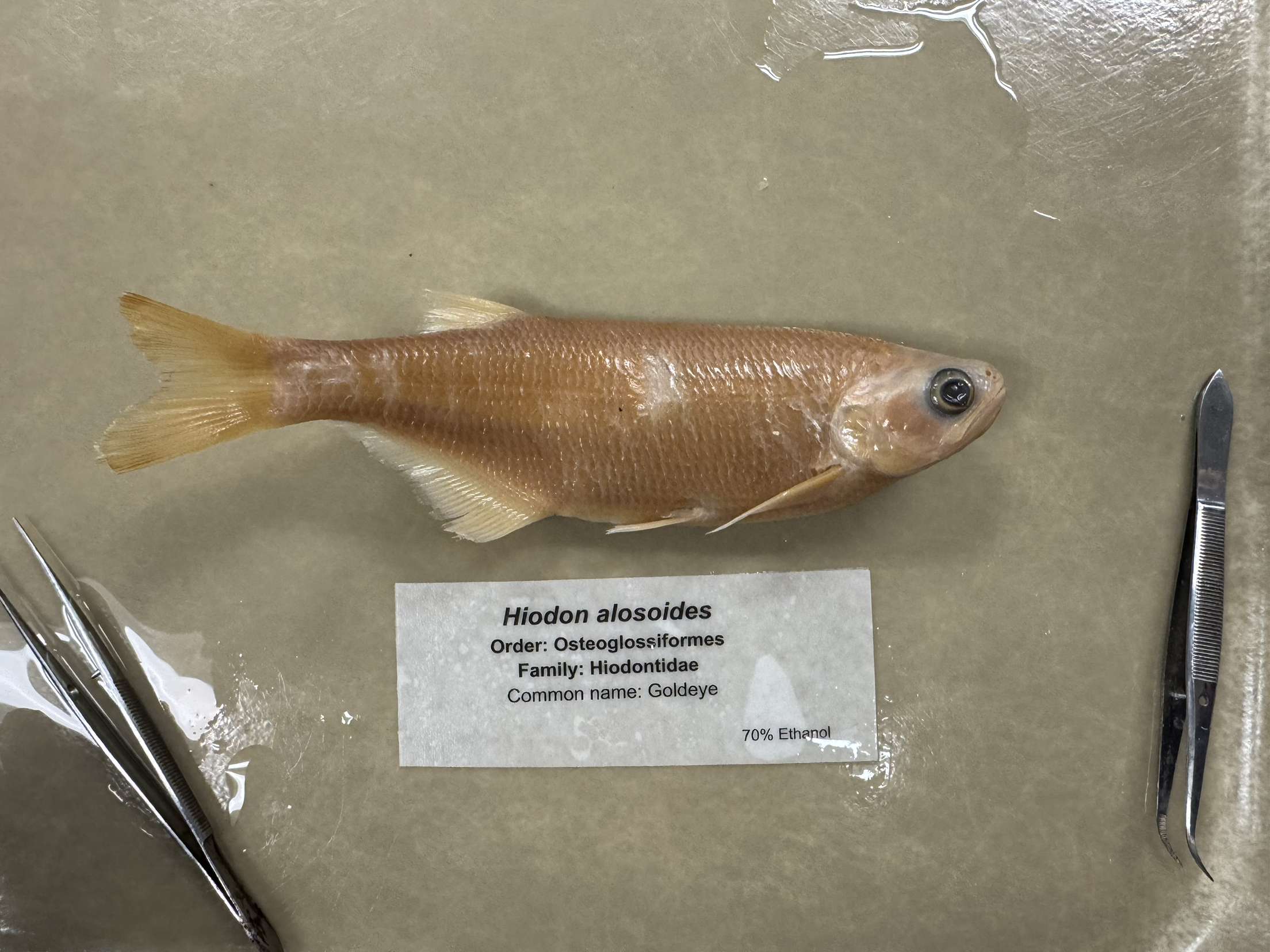

Hiodon alosoides
Goldeye
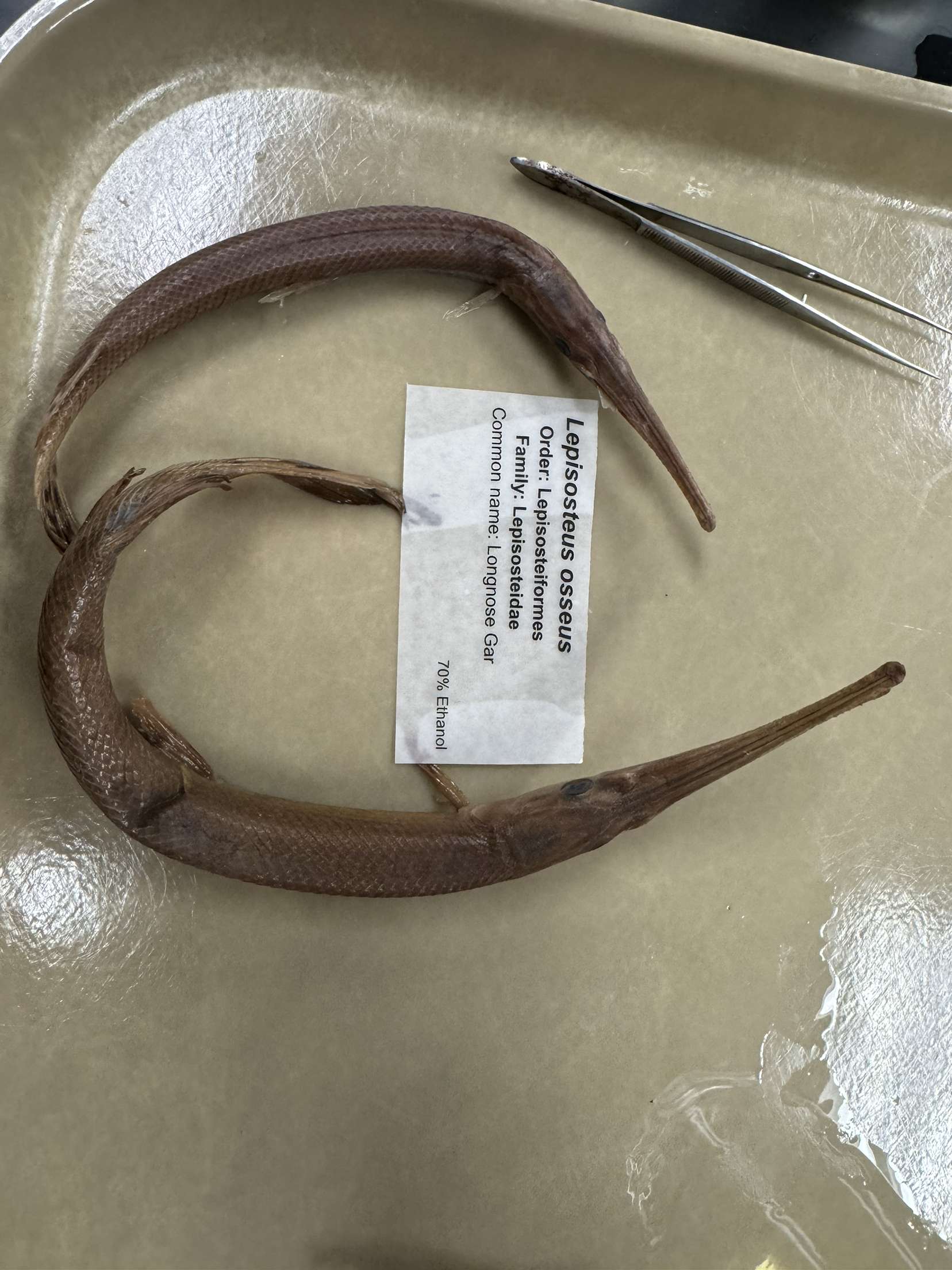

Lepisosteus osseus
Longnose gar

Lepisosteiformes
Includes the Gars
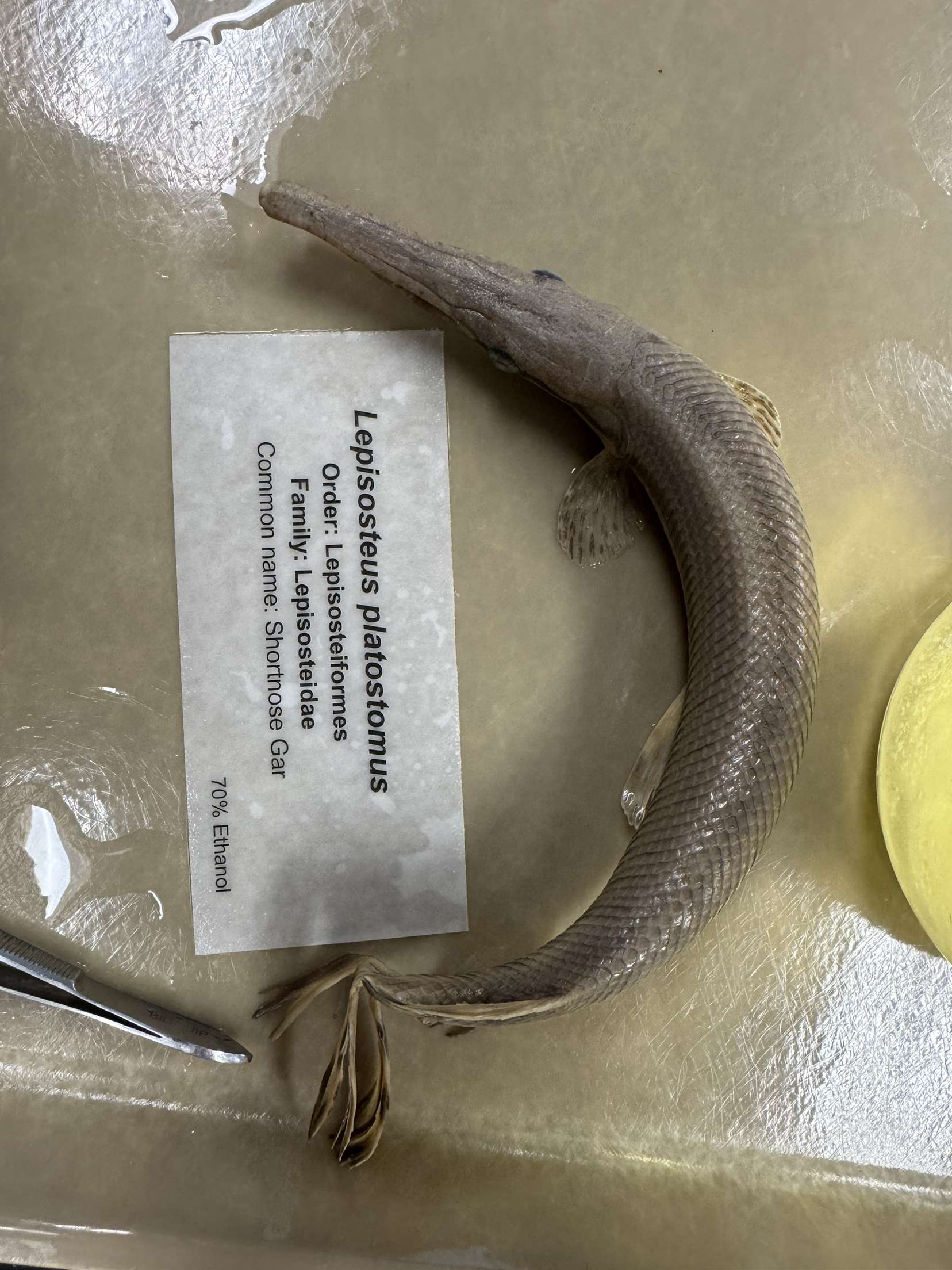

Lepisosteus platostomus
Shortnose Gar
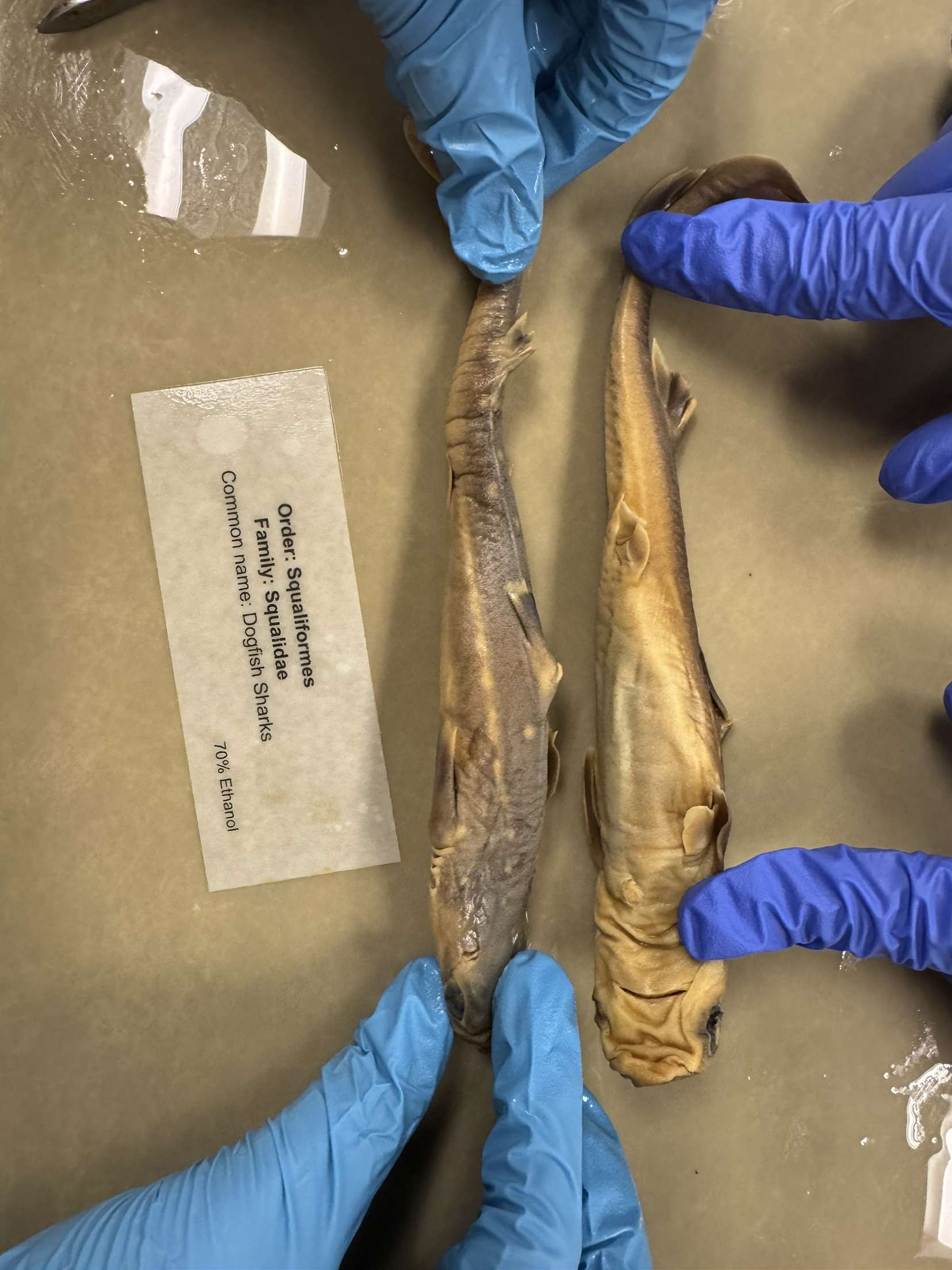
Squalus acanthias
Dogfish

Dorosoma petenense (left) and Dorosoma cepedianum (right)
Threadfin (left) and Gizzard shad (right)
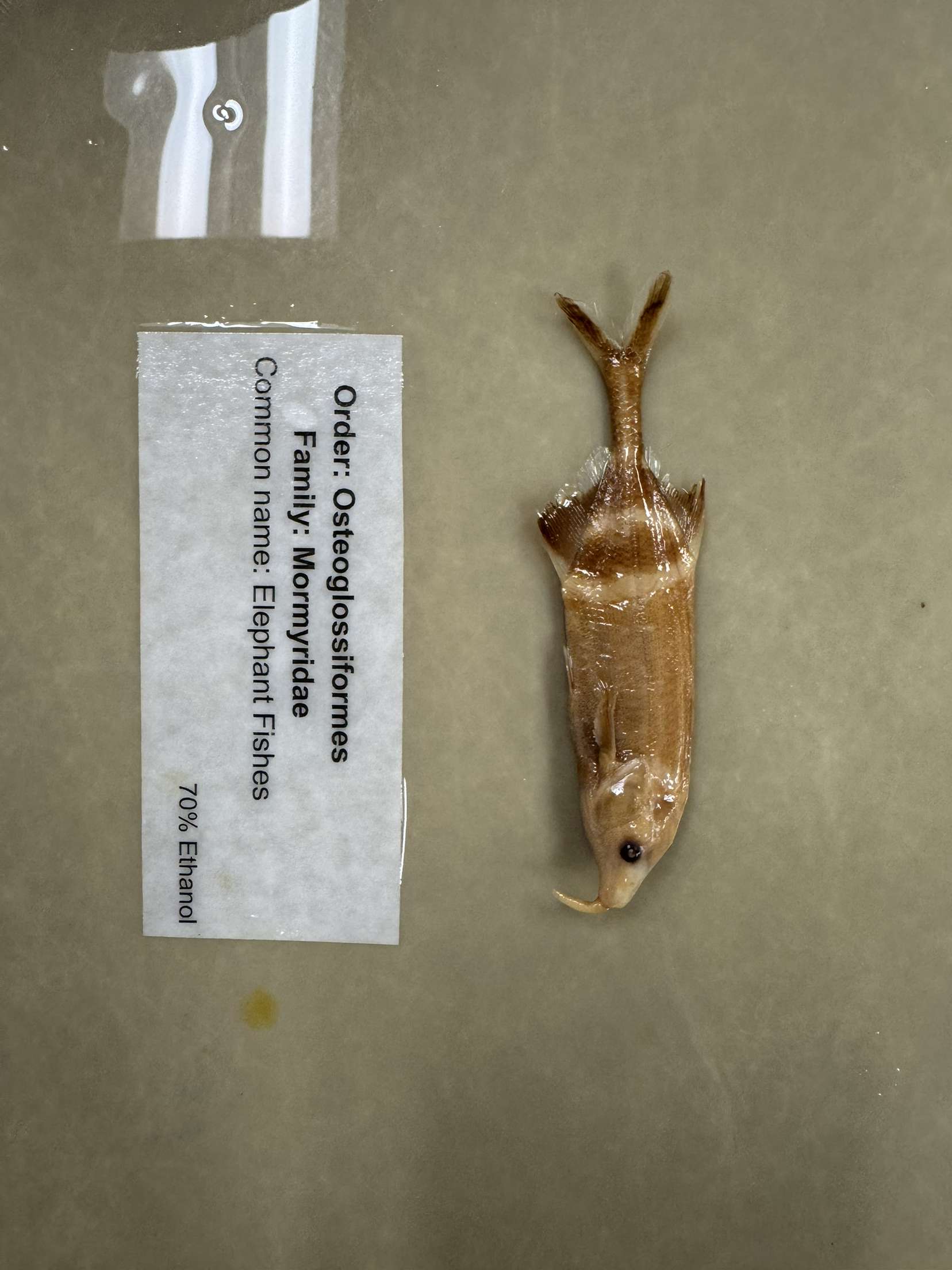

Mormyridae
Elephant fish
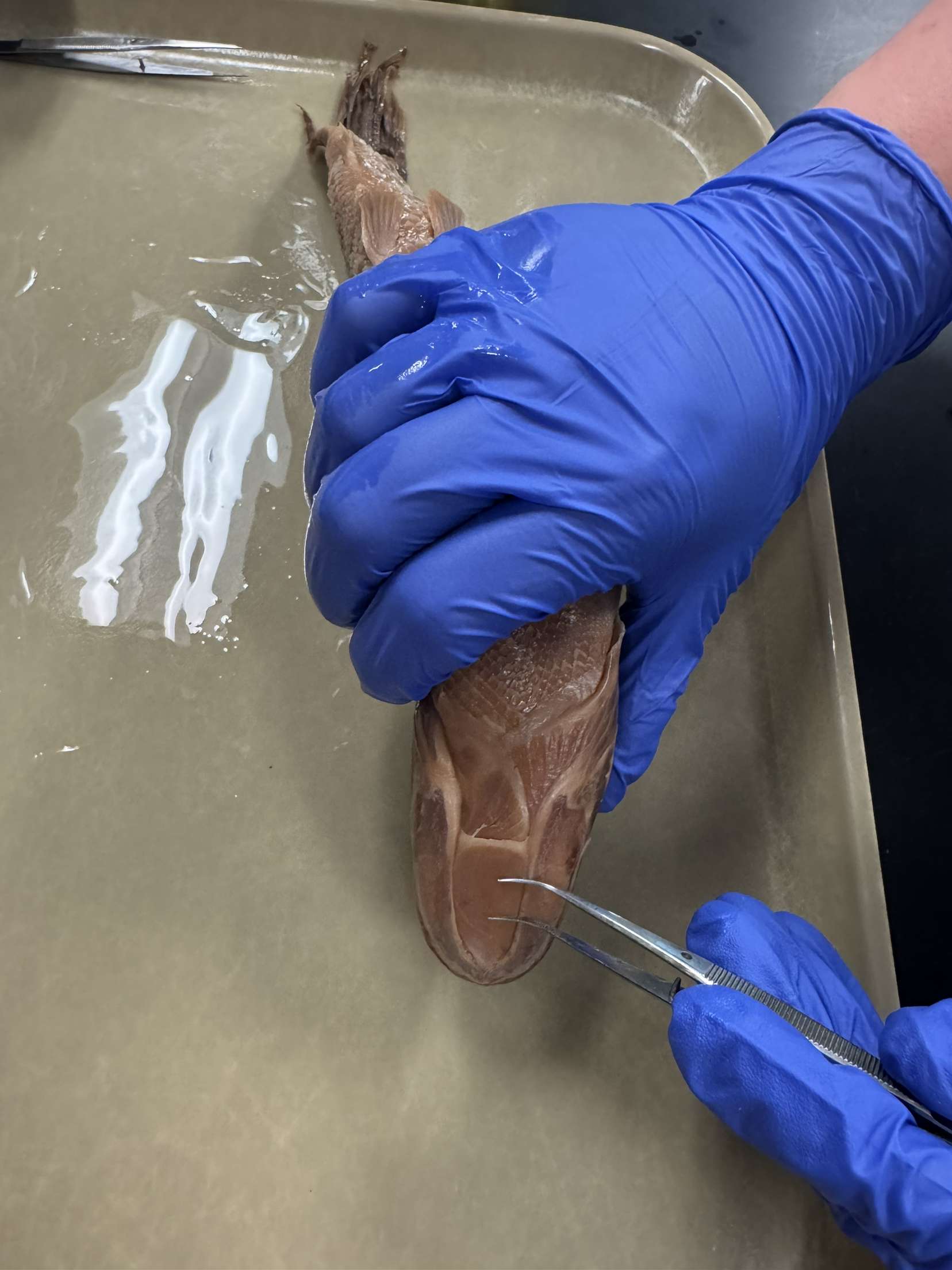

Gular plate
The flap on the bottom jaw of some fish
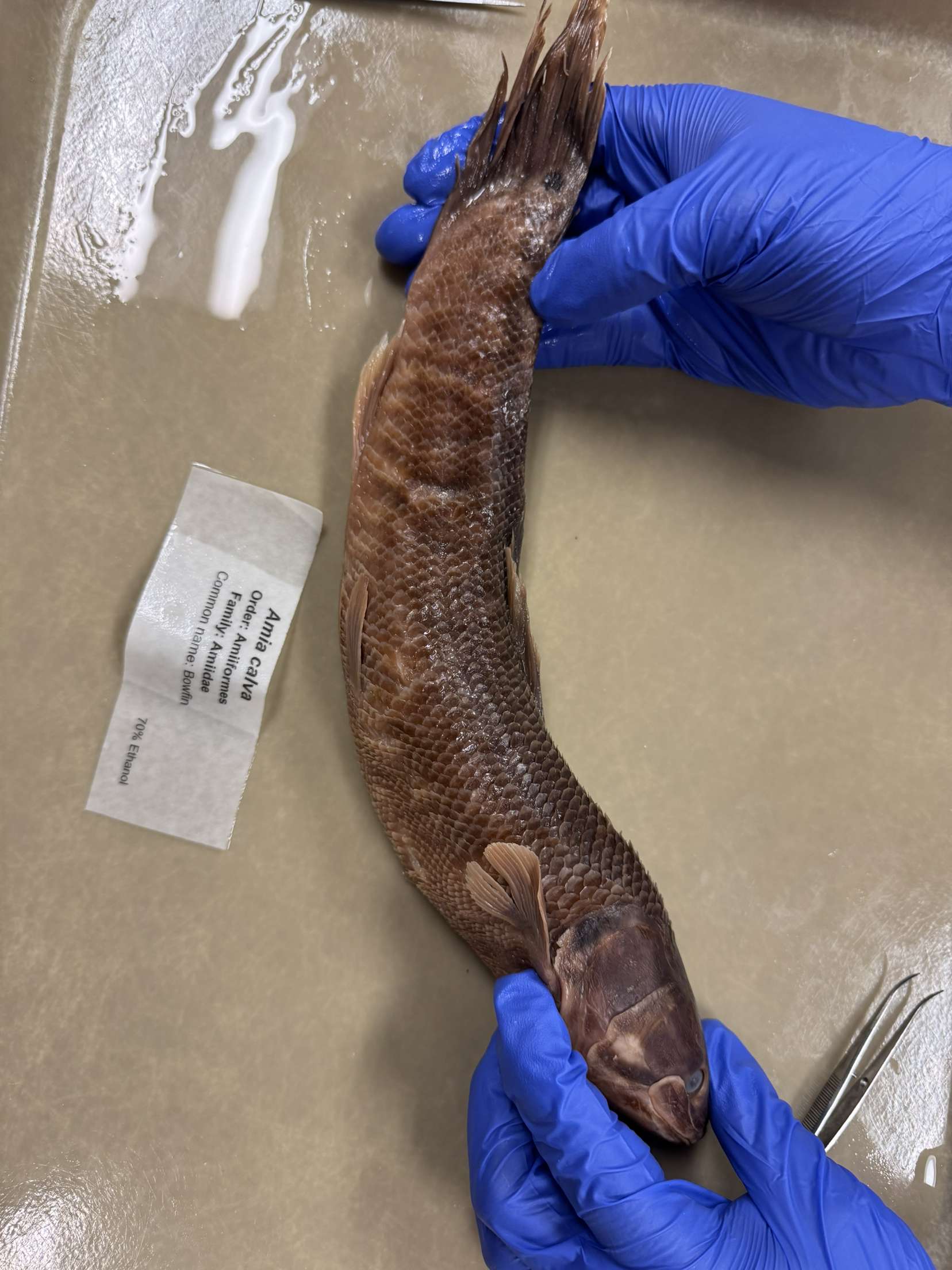

Amia calva
Bowfin
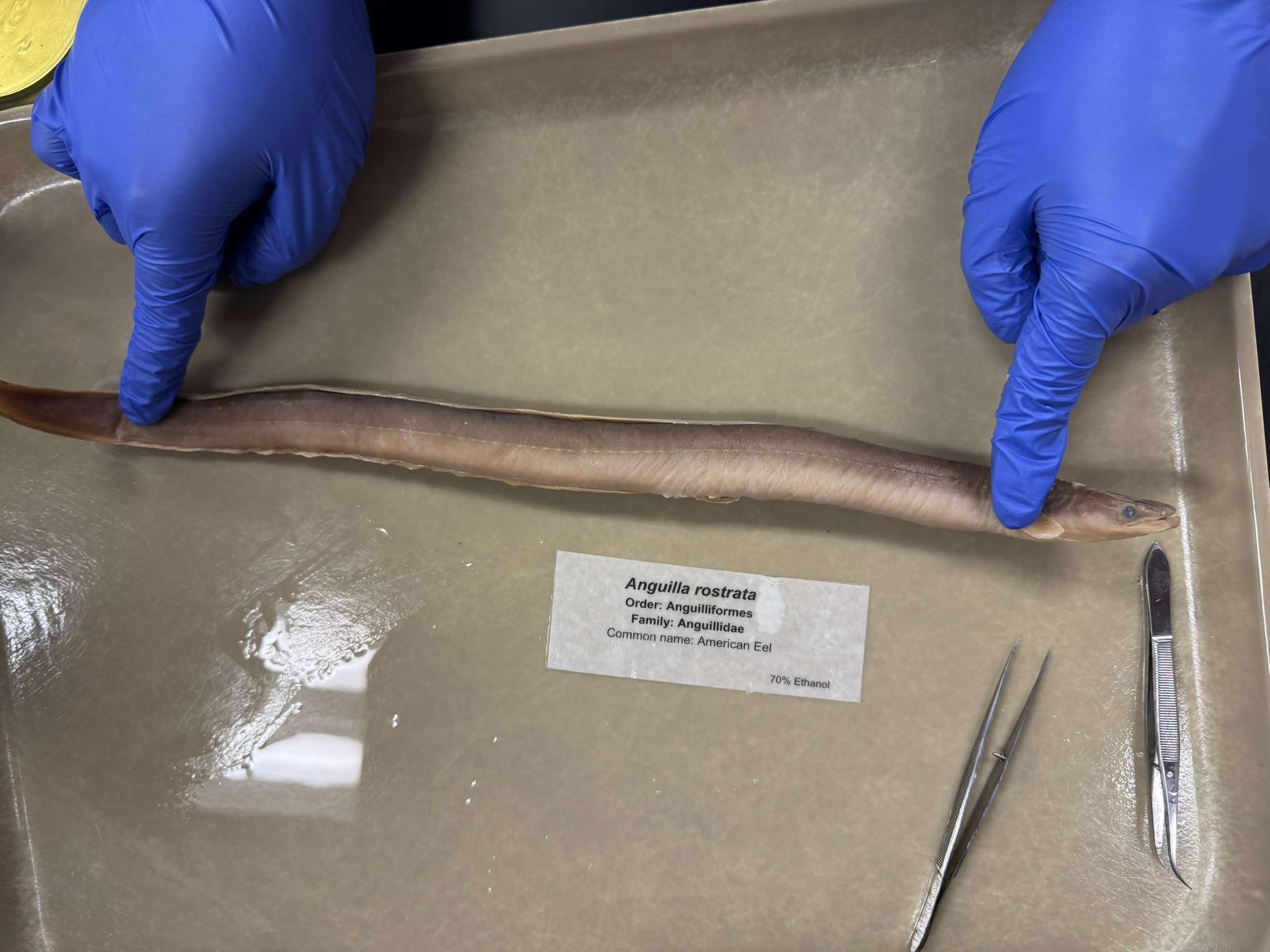
Anguilla rostrata
American Eel
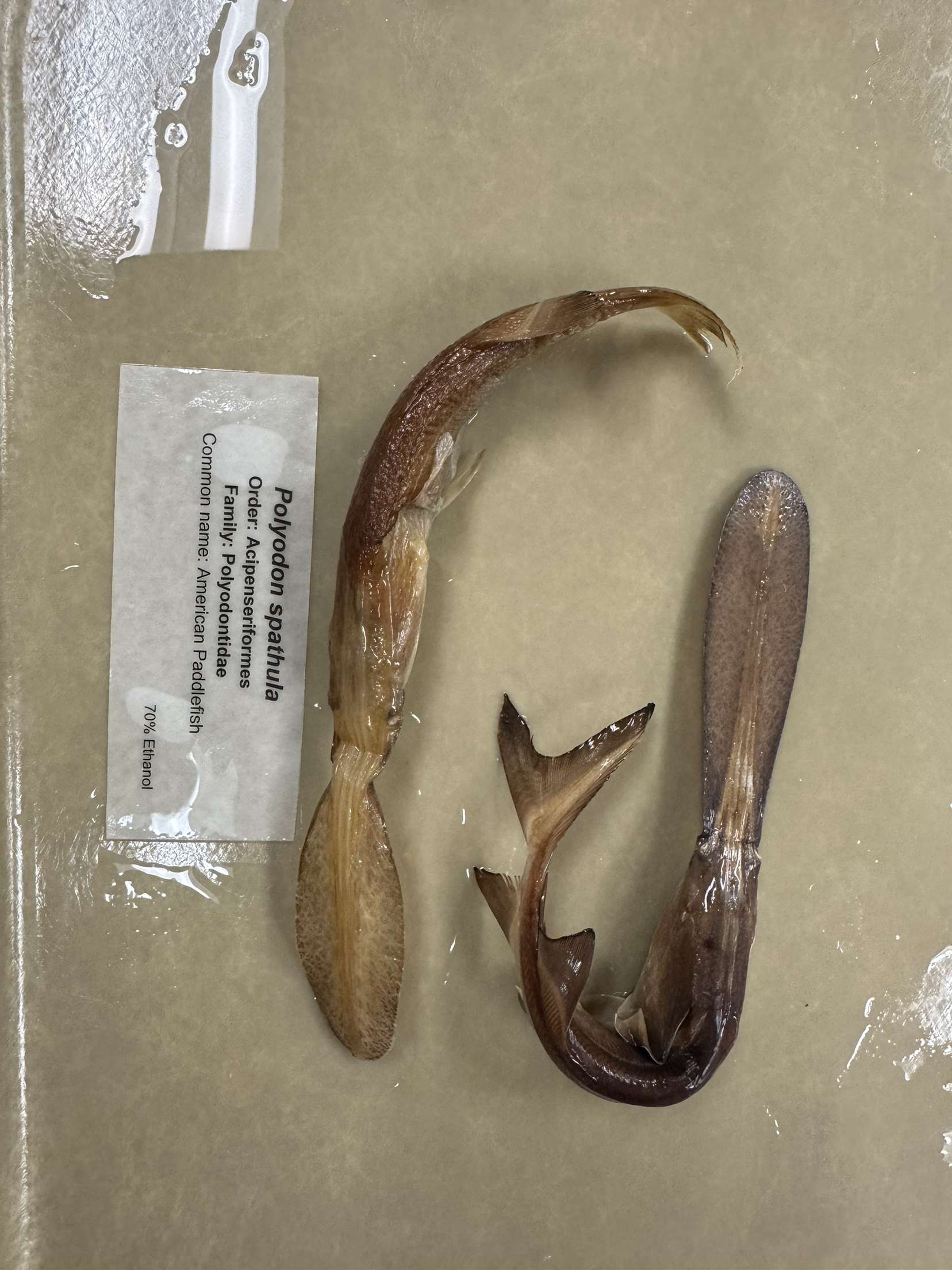

Polyodon spathula
American Paddlefish
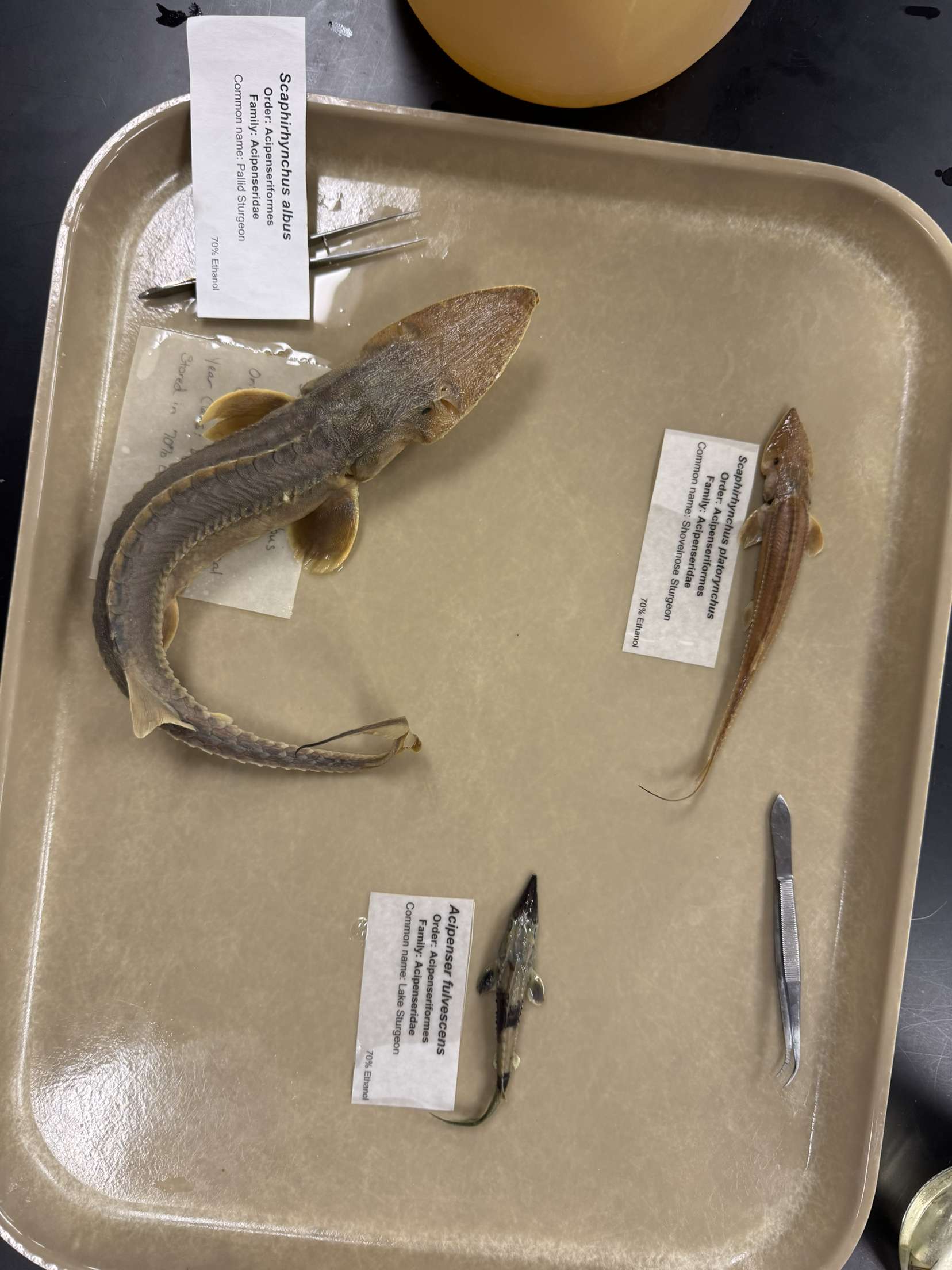

Acipenseriformes
Includes the sturgeons

Engraulidae
Anchovies
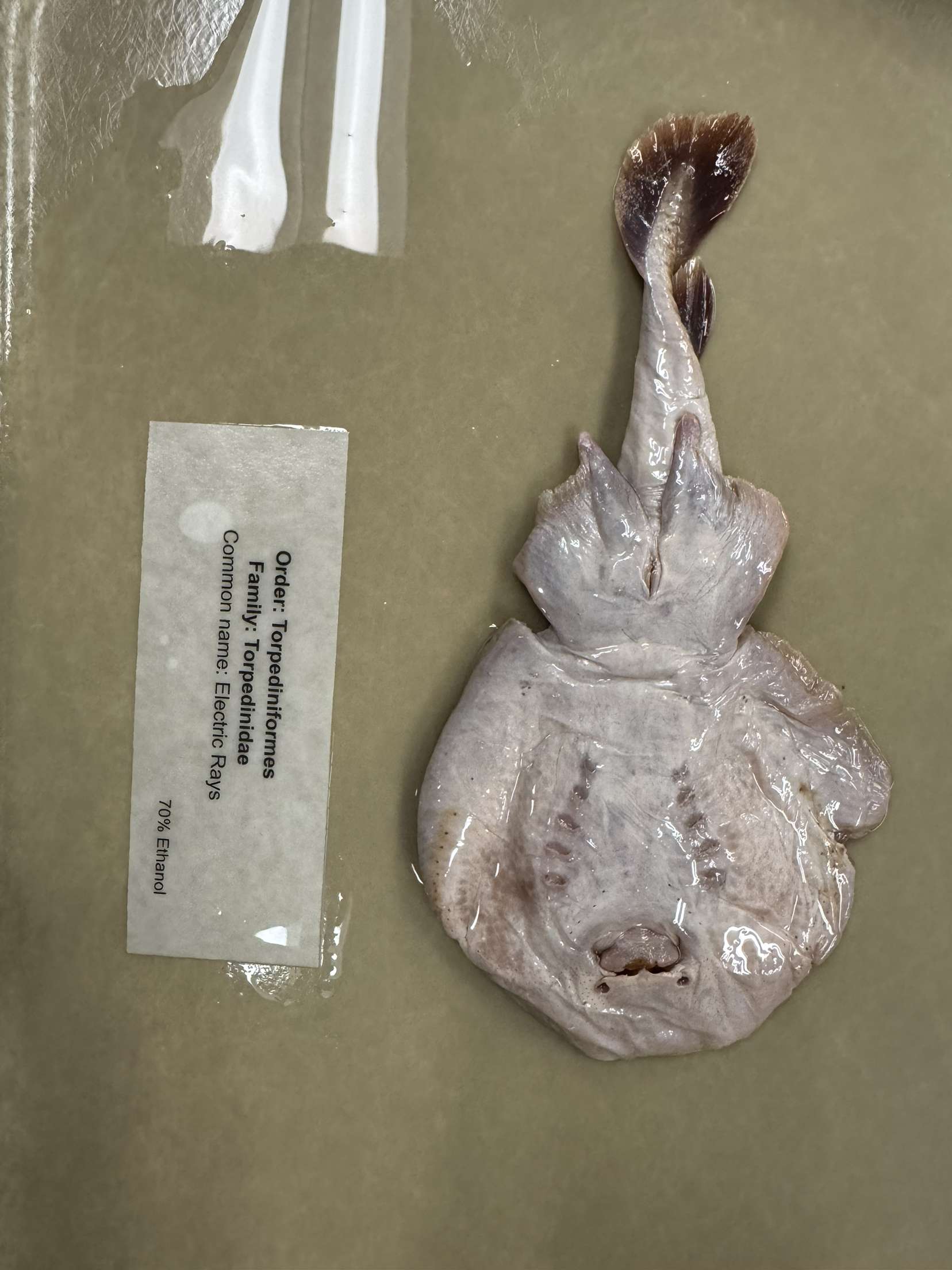
Torpediniformes
Electric Ray
Chondrichthyes
A class of fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, including sharks, rays, and chimaeras.
Actinopterygii
The class of ray-finned fish, which constitutes the largest class of vertebrates and includes most bony fish.
Ganoid scales
Thick, bony, non-overlapping scales composed of ganoine, typically found in primitive fish like gars and bowfins.
Cycloid scales
Thin, flexible, overlapping scales with a smooth posterior margin, characteristic of some teleost fish.
Ctenoid scales
Thin, flexible, overlapping scales with a toothed posterior margin, characteristic of many teleost fish.
Lateral line system
A system of sense organs in aquatic vertebrates used to detect movement and vibration in water.
Pectoral fins
Paired fins located on the side of a fish, homologous to forelimbs of tetrapods, used for steering.
Pelvic fins
Paired fins located ventrally on a fish, homologous to hindlimbs of tetrapods, used for stabilization.
Terminal Mouth
A mouth located at the very end of the snout, opening forward. This type is common in fish that feed directly in front of them, often in the water column.
Superior (Upturned) Mouth
A mouth that is angled upwards, with the lower jaw protruding beyond the upper jaw. This is characteristic of surface feeders, allowing them to easily catch prey from above.
Inferior (Subterminal) Mouth
A mouth located on the underside of the head, often with the upper jaw extending beyond the lower jaw. This type is adapted for bottom feeders that graze on the substrate.
Protrusible Mouth
A mouth that can be extended forward from the head, often forming a tube during feeding. This allows fish to quickly capture prey or filter feed by creating suction.