FINAL
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What are the symptoms of thyroiditis?
Swelling
Tenderness
Diffusely enlarged
Palpable
Pain
How does thyroiditis appear on an US?
Diffusely enlarged gland
Slightly irregular echo pattern
Hypoechoic compared to adjacent muscles
Calcifications may occur after inflammation
What is the most common thyroid abnormality?
Nodular Thyroid Disease
What machine adjustments should be made for scanning the thyroid isthmus?
Decrease depth
Move focus to just below isthmus
What transducer is used for thyroid isthmus?
12-18 MHz
Linear
Which salivary gland most commonly has sialolithiasis?
Submandibular
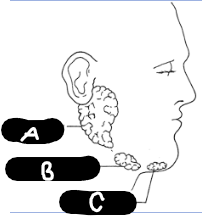
Salivary Gland Image
A = Parotid
B = Submandibular
C = Sublingual
What is the most common autoimmune disease of the salivary glands?
Sjogren’s
What is the palpable midline neck mass seen in children?
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
Who does Hashimoto’s affect the most?
Young or middle-aged females
What muscle is anterolateral to the thyroid?
Sternocleidomastoid
What muscle is posterolateral to the thyroid?
Longus Coli Muscle
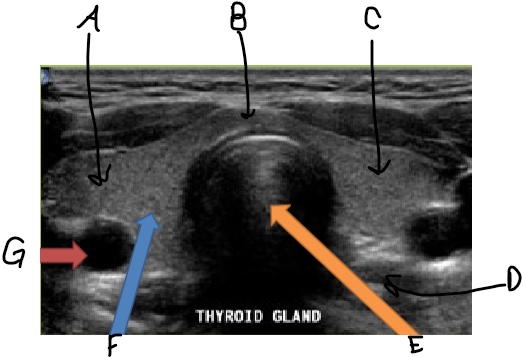
Transverse thyroid image
A = Right lobe
B = Isthmus
C = Left Lobe
D = Esophagus
E = Trachea
F = Thyroid
G = Carotid Artery
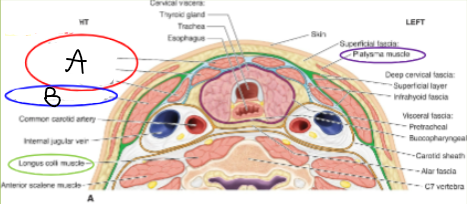
Muscles on US
A = Strap Muscles
B = Sternocleidomastoid
What is the strong deep penile fascia that is superficial to the tunica albuginea?
Buck’s fascia
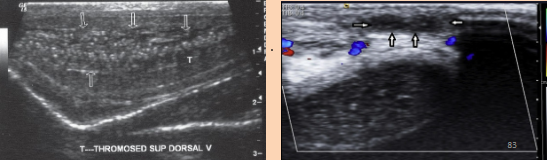
What is Mondor’s Disease?
Cord or string-like blood clot in superficial dorsal vein of penis
Beaded appearance
What is a palpated, well-demarcated, midline dorsum in the penis?
Peyronie’s Disease
What is the most common cause of erectile dysfunction?
Vasculogenic Impotence
What is Peyronie’s Disease?
Fibrosis of fibrous sheaths covering corpora cavernosa
Which way does the penis bend in someone with Peyronie’s Disease?
Bends TOWARDS diseased area
What are the symptoms of epididymitis?
Hypervascular testes
Slight fever
Heaviness
Tenderness
Which side of the body are varicoceles most common?
Left side
What does a tunica albuginea cyst look like?
Well circumscribed
Anechoic
2-5 mm
What is the tunica albuginea?
Dense, fibrous capsule covering testis
What do microcalcifications in a testicle mean?
Microlithiasis
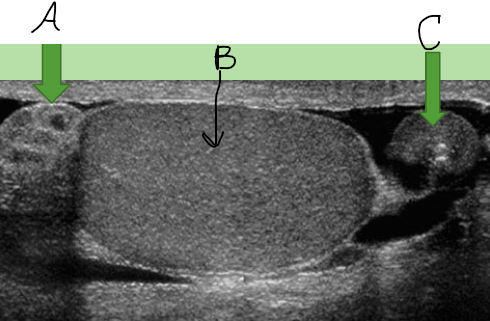
Image of testicle
A = Epi Head
B = Testes
C = Epi Tail
What does epi look like compared to testes on ultrasound?
Head = slightly more echogenic than testis
Body = slightly less echogenic than testes
Tail = thicker than epi head
What is the most common location for prostate carcinoma?
Peripheral zone of prostate
What is the normal range for PSA levels?
0.0-4.0 ng/ml
What is the cephalic portion of the prostate?
Base
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) originates in which area?
Transition Zone
Which mammography view shows if a lesion is in the superior or inferior aspect of the breast?
Medial-Lateral Oblique View
Which mammography view shows if a lesion is in the medial or lateral aspect of the breast?
Cranio-Caudad View
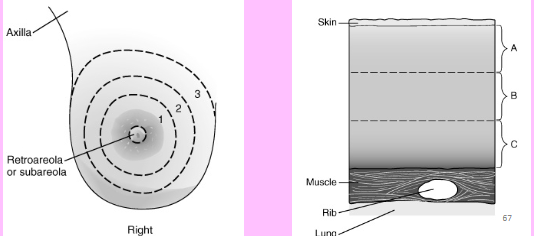
ABC and 123 method on breast
123 = inner, middle, outer
ABC = skin layer or depth
A mass is documented on breast ultrasound as being located at 6 o’clock 2A. What does 2A indicate?
Mid distance from nipple, close to skin
Under what conditions is increased transducer pressure not particularly helpful?
Performing Doppler
What correctly identifies the expected sonographic changes in breast tissue with age?
Amount of fatty tissue increases
Amount of fibroglandular tissue decreases
Fat within the premammary and retromammary regions will not increase in…
Women on hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
Which carcinoma is ultrasound often more affective at demonstrating than mammography?
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
When establishing correct gray scale and gain settings for sonographic breast imaging, all structures should be compared to the mid-level echogenicity of which structure?
Fat
The Rotter's nodes are part of what lymph node chain?
Axillary lymph node chain
What is the fremitus maneuver?
When Color Doppler is used to distinguish borders of a mass
The fremitus maneuver can be used to…
Better distinguish borders of a breast lesion
When a breast has metastatic tumors, are they more likely to be single or multiple?
Multiple
If the TCGs are decreased in the near-field of the image, what changes are seen?
Superficial tissues become darker
What is the step ladder sign?
Demonstrates INTRACAPSULAR silicone rupture
Multiple parallel linear and curvilinear echogenic lines within implant
What is the normal sonographic appearance of the periosteum?
Thin, echogenic line that runs parallel to the cortex of bone
What is compartment syndrome?
Compression of blood vessels and nerves causing cessation of blood flow to that compartment
What are the scan planes for MSK?
SAX
LAX
What is not associated with rotator cuff anatomy and therefore not evaluated in a shoulder ultrasound examination of the rotator cuff?
Triceps tendon
What is the appearance of a Baker’s cyst?
Cyst on back of knee
When performing a sonogram, what is the most commonly seen pathology of the knee?
Baker's cyst
What is the sonographic appearance of a normal bursa?
Small hypoechoic flat sac containing a small amount of normal fluid with a hyperechoic wall and peribursal fat
What is defined as a closed connective and synovial sac that normally contains a small amount of fluid and facilitates the gliding of one MSK structure on another?
Bursa
Be sure to use light transducer pressure when scanning through the… to avoid causing…
Anterior Fontanelle
Bradycardia
What scanning technique uses an abundance of gel to avoid using pressure?
Floating Technique
The anterior fontanelle becomes progressively smaller and closes completely at how many months of age?
15 months
Spinal sonography is useful in the normal infant until approximately how many months of age?
3 to 6 months
On a sonogram of a patient with a tethered cord, the conus medullaris will terminate at or below the level of which vertebral body?
L3
What is the best transducer routinely used to evaluate the neonatal spine?
Linear
In which of the following maneuvers does the examiner attempt to push the femoral head out of the socket when performing a neonatal hip sonogram?
Barlow’s maneuver
Which scanning plane allows for assessment of the femoral head coverage with respect to how well it is contained in the acetabulum?
Coronal Neutral
A 2-year-old patient presents with a low-grade fever and has recently had an upper respiratory infection. She has started refusing to bear weight on her right hip. What is the MOST likely diagnosis?
Transient Synovitis
What is the normal value of the alpha angle when assessing the neonatal hip for DDH?
> 60 degrees
What is the impression of the hip if the alpha angle measures 40 degrees?
Type III hip, dislocated
What is a terminal myelocystocele?
CSD abnormality
Large, fluid-filled mass in lumbar region
Central canal widens and directly communicates with fluid-filled sac
What is an abnormal dilation of the terminal
ventricle which communicates with the central spinal cord canal?
Terminal myelocystocele
What is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain?
Epididymitis
Microlithiasis is associated with an…
Increased risk of malignancy
List three (3) sonographic features consistent with acute epididymitis.
Enlarged epididymis
Hypoechoic epididymis
Hypervascularity
List three (3) possible causes for an increased PSA.
BPH
Carcinoma
Increasing age
Which of the following is the MOST sensitive indicator of the presence of prostate cancer?
Increased prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
A 35-year-old postpartum women presents for a breast ultrasound reporting having breast tenderness and breast edema. The sonographer notices that the skin of the affected breast appears red and thickened. Sonography reveals a superficial tubular structure with a beaded appearance.
1. What is the most likely diagnosis?
2. This pathology is most commonly associated with what specific structure?
Mondor's Disease
Lateral thoracic vein