mains electricity
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what is mains electricity
Mains electricity is the electricity generated by power stations and transported around the country through the National Grid
when do people connect to mains
Everyone connects to the mains when plugging in an appliance such as a phone charger or kettle
what kind of current is mains electricity?
Mains electricity is an alternating current (a.c.) supply
what is the frequency and p.d of domestic electricity supply in the uk
In the UK, the domestic electricity supply has a frequency of 50 Hz and a potential difference of about 230 V
what does a 50Hz frequency mean?
A frequency of 50 Hz means the direction of the current changes back and forth 50 times every second
what does it mean for mains electricity to be an alternating current?
Mains electricity, being an alternating current, does not have positive and negative sides to the power source
what are the positive and negative of the circuit?
The equivalent to positive and negative are called live and neutral and these form either end of the electrical circuit
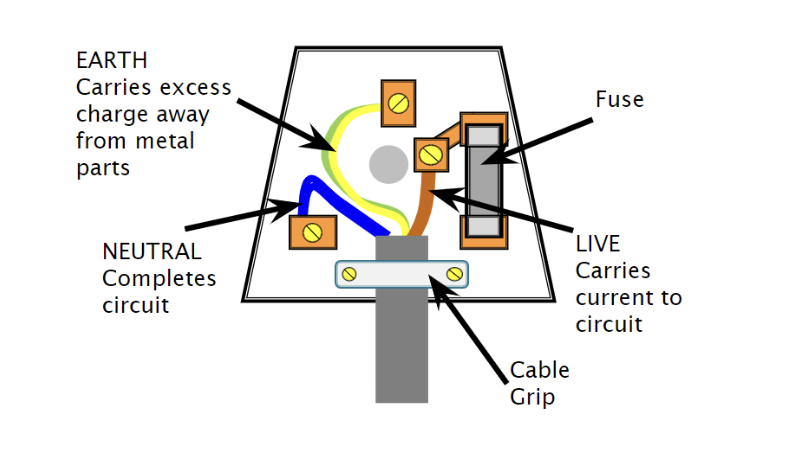
what are the purposes of live, neutral and earth wires?
The live and neutral wires deliver the electricity to the device. The Earth wire is purely for safety
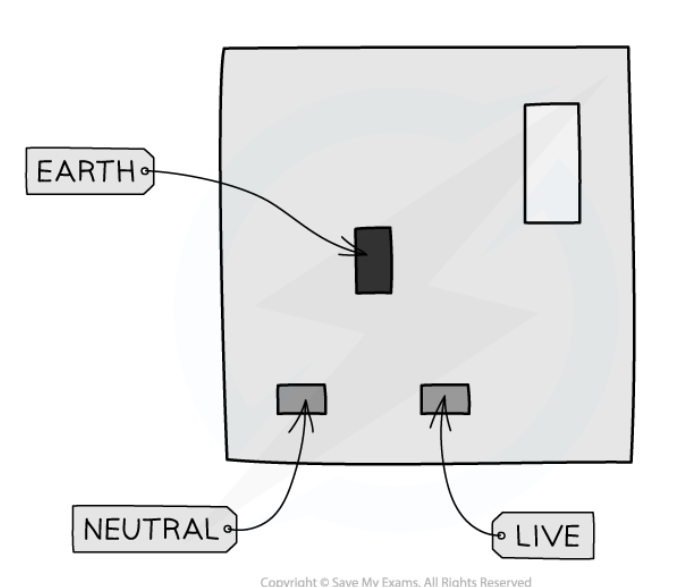
what does electricity have to pass through to get to the house
Electricity entering the house must first pass through the
consumer unit (the fuse box and meter).
how can the mains be isolated?
● Separate ‘spurs’ link some fittings to the mains, so they can
be isolated.
● This is known as a ring circuit, and it is also used for
lighting circuits.
what connects the plug to the appliance?
A length of flex connects the plug to the appliance. This
is made using three smaller wires, which are colour-coded.
why are thicker wires used to carry larger currents?
Thicker wires are used to carry larger currents; this is because a large current will transfer more thermal energy.
why are the inner strands of wire made from copper?
thicker copper strands will reduce the resistance (reducing energy loss)
why is a thicker plastic casing provided?
a thicker plastic casing is provided to keep the user safe.