NRES 251 EXAM 4 (FINAl)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
When H2O molecules are in a strict orderly structure which phase state is water in?
Solid
Which of the following can cause a waterbody to have a dissolved oxygen percent saturation that is less than 100%?
Excessive respiration or decomposition
Which nutrient tends to be the dominant limiting nutrient in saltwater ecosystems?
Nitrogen
Precipitation in the phosphorus cycle is best described as which of the following?
When free dissolved cations such as calcium create a solid species with orthophosphate and settle in the sediments
What is the most common source of chloride contamination in surface waters of the northern latitude regions of the United States?
Road salts
Which of the following is NOT true regarding Contaminants of Emerging Concern?
Because all of these compounds have been recently invented we are not sure of their behavior
Mineralization or ammonification will release which form of nitrogen?
Ammonium
Why is denitrification beneficial from a human perspective?
It removes nitrate from waterbodies which is a human health and ecological conern
Which of the following best describes the Haber-Bosch process?
This allows humans to industrially fix nitrogen out of the atmosphere
What does phosphorus have a high affinity for?
Polyvalent cations such as calcium, iron, and aluminum
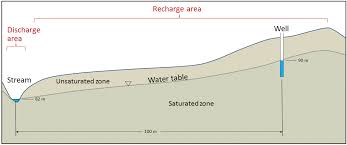
The line that represents the division between the unsaturated and saturated zone in the soil profile is what?
Water table
In the cone of depression, what is the distance between the pumping well and the furthest extent away from the well that you still observe a decline in the water table called?
Radius of influence
What is needed for an actively flowing Artesian well to occur on the landscape?
For the well to be in a confined aquifer and for the potentiometric surface to be above the well casing
Which of the following is true about the groundwater that is located deeper in the aquifer?
It fell on the ground further way from the location you are located at
In Darcy's Law (Q=s⋅K⋅A) what does s refer to?
Hydraulic gradient
What will result in a larger Hydraulic conductivity?
Material with large pore spaces
In the scenario below which direction is groundwater moving?
Groundwater is discharging into the stream
Based on the image below what is the hydraulic gradient between the two wells?
0.012 ft/ft

Based on the image below which direction is groundwater flowing?
Right to left

Based on the image below and knowing that the hydraulic conductivity for this aquifer is 150 ft/day and the porosity is 0.35, determine the seepage velocity of the groundwater
5.1 ft/day

How are riffle, run, pool sequences beneficial to stream ecosystems?
These locations provide diverse and valuable habitat for organisms
On a meander (or bend) in a stream channel which of the following is true?
Deposition occurs on the inside bend while erosion occurs on the outside of the bend
Which of the following is NOT a reason why floodplains are valuable?
They are important for treating wastewater
If a lake is considered oligotrophic which of the following would be true?
It has low primary production most likely due to low nutrients
What is the name of the lake zone in the image below?
Metalimnion
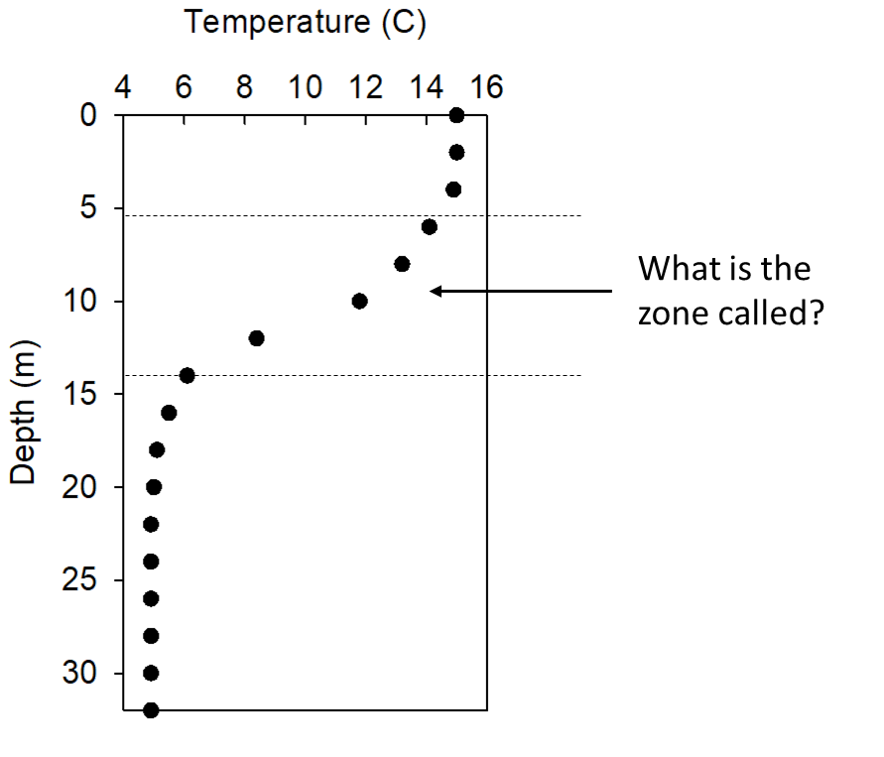
A deep lake that stratifies is prone to low dissolved conditions under which conditions?
When it is eutrophic, during stratification, and only in the hypolimnion
Which of the following best describes how shallow ponds can use aerators to help combat low dissolved oxygen?
They disrupt ice formation during winter and help add additional dissolved oxygen throughout the year
Which of the following is NOT a required characteristic for a piece of land to be considered a wetland?
Anaerobic bacteria capable of generating methane gas
Why are wetlands good at carbon storage?
Dead plant material is stored in the soil because decomposition is slowed down
Which reaction in the nitrogen cycle occurs readily in wetlands and help remove a contaminant in drinking water?
Denitrification
How do we measure groundwater elevation in the field?
using a water level meter or piezometer, often in conjunction with a well or borehole
Determine which direction groundwater flows
flows from high to low hydraulic head very slowly (3 ft3 day-1 in Portage County)
Darcy’s Law
discovered that the flow of water flowing through a pipe was dependent on 3 things – Hydraulic head of water at each end and the length of the pipe (hydraulic gradient) – The medium (sand vs. clay) that filled the pipe (hydraulic conductivity) – The diameter of the pipe (cross sectional area)
-Q = s · K · A – s (hydraulic gradient)
proper structures commonly observed in groundwater
-dissolved minerals, metals, and even some naturally occurring contaminants like radioactive compounds, iron, and chloride.
-Human activities can also introduce contaminants like pesticides, fertilizers
Unique structure and properties of H2O
2 hydrogen molecules and oxygen, can be found in all states of matter, creates one slight positive and negative charge (dipolar), attracted to other water molecules (cohesion) and other surfaces (adhesion)
Describe all the specific properties of water that make it unique
-Highest specific heat
capacities of substances of
Earth
– Difficult to warm or cool a
large body
– Requires a lot of energy for
freezing (latent heat of fusion)
or boiling (latent heat of
vaporization
-act as an acid and a base
—universal solvent
– pH of pure is 7
Describe the variables commonly used to assess water quality
-Turbidity – how well light can
penetrate the water
– Influenced by either erosion or
phytoplankton (algae)
– TSS – total suspended solids
(mg L-1)
– Turbidity Meter – scatter of
light in water (NTU’s)
– Secchi Depth – clarity of a
standard object at depth in a
lake
Bioassessment
the process of evaluating the biological condition of a waterbody, like a river or lake, using biological surveys and measurements of the living organisms present
Eutrophication
increase in organic matter (typically N or P) that results in DO depletion
Describe all the ecological and anthropogenic concerns regarding excessive algal growth in aquatic ecosystems
1. River outflow carries nitrate and/or phosphorus laden water
2. Nitrate/phosphorus and sunlight stimulate algal growth
3. Algae die and float to the bottom of the bay
4. Microbes colonize the dead algae
5. The microbes decompose the algae and consume O2
Nitrate – NO3-
• Highly mobile → leaches into groundwater, common
form of inorganic fertilizer, human health concern
Nitrite – NO2-
Unstable form of nitrogen → never in high abundance
and usually indicates reactions are taking place
Ammonium – NH4+ or Ammonia – NH3
Ionized form more common, tends to sorb to soil
colloids, potential form of inorganic fertilizer, more
common form with manure applications
haber-bosch
the industrial method for producing ammonia (NH3) by reacting nitrogen (N2) from the air with hydrogen (H2) under high pressure and temperature, typically using an iron-based catalyst
Nitrification
aerobic while
denitrification → anaerobic
(two different ecosystems)
Phosphorus
strong affinity for
polyvalent cations: Ca2+, Mg2+, Al3+, and Fe3+ and clay
Phosphorus Cycle
Weathering and release
behavior of phosphorus compounds in the water/soil environment
reacts with clay, iron and aluminum compounds in the soil, and is converted readily to less available forms by the process of phosphorus fixation
How have humans altered the global phosphorus cycle
phosphate mining and use in fertilizers, which leads to increased phosphorus in soils and runoff into aquatic ecosystems. This has resulted in accelerated phosphorus loading to freshwaters, causing eutrophication and impairing water quality and aquatic biodiversity
Floodplain Habitat
-Connected during high flow
-Moist conditions during base flow
In-Stream Habitat
-Undercut Banks
-Riffle-Run-Pool Sequences
-Substrate
Riffle
-pollution intolerant
-low predation (Caddisflies, darters,
etc.)
How does dissolved oxygen fluctuate in streams?
-Warmer water holds less oxygen than cooler water
-Faster-flowing streams have increasing DO
-Aquatic plants and algae produce oxygen
-Decomposition of organic matter lowers DO levels
Describe the function that floodplains provide
floodwater storage and conveyance, natural flood and erosion control, water quality maintenance, groundwater recharge, and habitat for wildlife and fish
Flood pulse
helps maintain genetic and species diversity in the floodplain ecosystem, and it brings in oxygen to help fauna and decomposition. The flood pulse also increases yields by increasing the surface area of water and showers the land with river biota
seasonal stratification in temperate zone lakes
the process where lakes develop distinct, stable layers of water based on temperature and density, primarily due to seasonal changes in temperature. This stratification typically occurs from late spring through early fall, with a summer pattern of three distinct layers: the epilimnion (warm, upper layer), the thermocline/metalimnion (a zone of rapid temperature change), and the hypolimnion (cold, deeper layer)