Part 8 - Introduction to Organic Reactions, Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Organic reactions:
A + B → AB
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
a. Addition
Organic reactions:
AB → A + B
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
b. Elimination
Organic reactions:
AB + CD → AD + CB
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
c. Substitution
Organic reactions:
Isomer 1 → Isomer 2
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
d. Rearrangement
Reagent is only present in which type of reaction?
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
e. a and b
f. a and c
f. a and c
Usually involve increase number of double bonds.
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
b. Elimination
Usually involve decrease number of double bonds.
a. Addition
b. Elimination
c. Substitution
d. Rearrangement
a. Addition
Type of reagents.
a. Electrophile
b. Nucleophile
c. Radical
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Electron poor type of reagent.
a. Electrophile
b. Nucleophile
c. Radical
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
a. Electrophile
Electron rich type of reagent.
a. Electrophile
b. Nucleophile
c. Radical
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
b. Nucleophile
Formed from homolytic cleavage in the presence of UV resulting to equally shared electron between the products.
a. Electrophile
b. Nucleophile
c. Radical
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
c. Radical
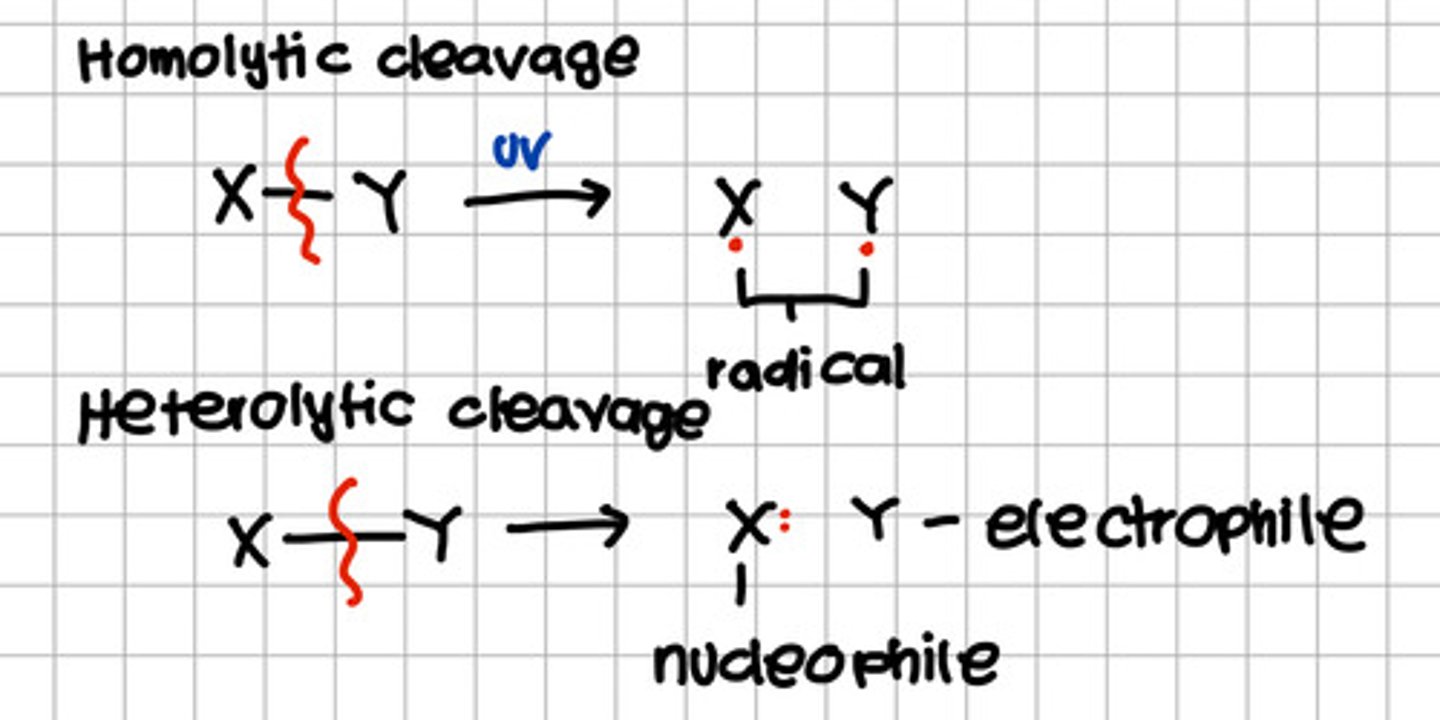
Formed from heterolytic cleavage wherein one product received both electrons the other do not.
a. Electrophile
b. Nucleophile
c. Radical
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Electrophile - does not received any electron
Nucleophile - received both electrons
Oxidation
a. Addition of oxygen
b. Addition of bond to O
c. Removal of hydrogen
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. all
f. All
Dehydrogenation
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
a. Oxidation
Hydrogenation
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
b. Reduction
Paraffins
a. Alkanes
b. Alkenes
c. Alkynes
a. Alkanes
Olefins
a. Alkanes
b. Alkenes
c. Alkynes
b. Alkenes
Acetylenes
a. Alkanes
b. Alkenes
c. Alkynes
c. Alkynes
Properties of hydrocarbons.
a. Water insoluble
b. Has relatively low boiling point
c. Ha relatively low melting point
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Reaction of alkanes.
a. Combustion
b. Halogenation
c. Both
d. None
c. Both
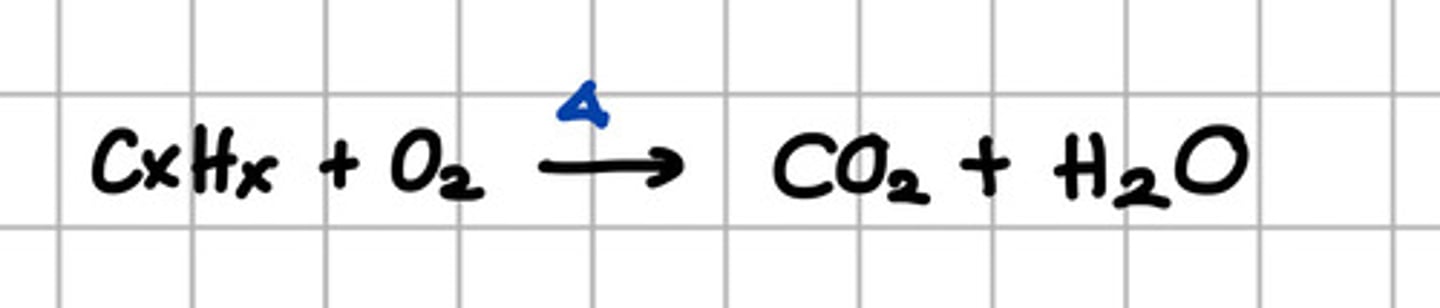
Product of complete combustion of alkane.
I. CO2
II. H2O
III. CO
IV. C
a. I, II, III, IV
b. I, II, III
c. I, II,
d. III, IV
c. I, II
Mechanism of reaction of alkenes.
a. Electrophilic addition
b. Electrophilic elimination
c. Nucleophilic addition
d. Nucleophilic elimination
a. Electrophilic addition
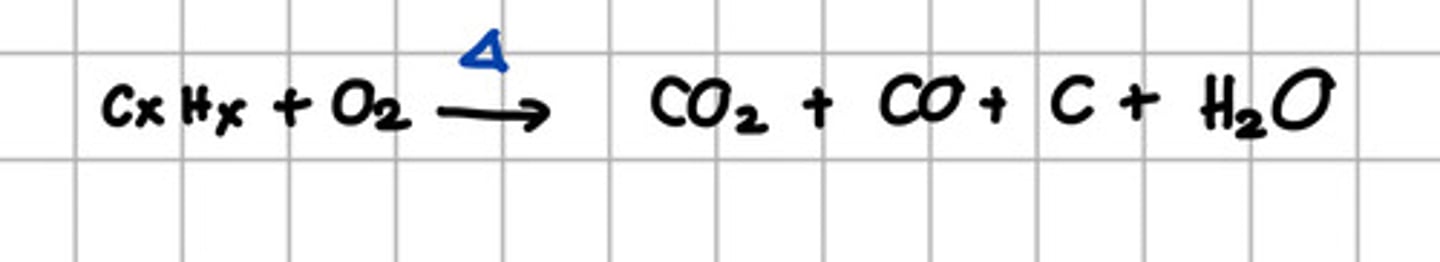
Product of incomplete combustion of alkane.
I. CO2
II. H2O
III. CO
IV. C
a. I, II, III, IV
b. I, II, III
c. I, II,
d. III, IV
a. I, II, III, IV
Catalyst for hydrogenation of alkene.
a. Pd
b. H+
c. Tetrahydrofuran
d. NaOH
e. H2O2
a. Pd
Product of incomplete combustion of alkane known as soot.
a. CO2
b. H2O
c. CO
d. C
d. C
Catalyst for hydration of alkene.
a. Pd
b. H+
c. Tetrahydrofuran
d. NaOH
e. H2O2
b. H+
Consider a chain reaction which produce radical.
a. Complete combustion of alkane
b. Incomplete combustion of alkane
c. Halogenation of alkane
d. a and b
e. All
c. Halogenation of alkane - the only halogenation that produce radical
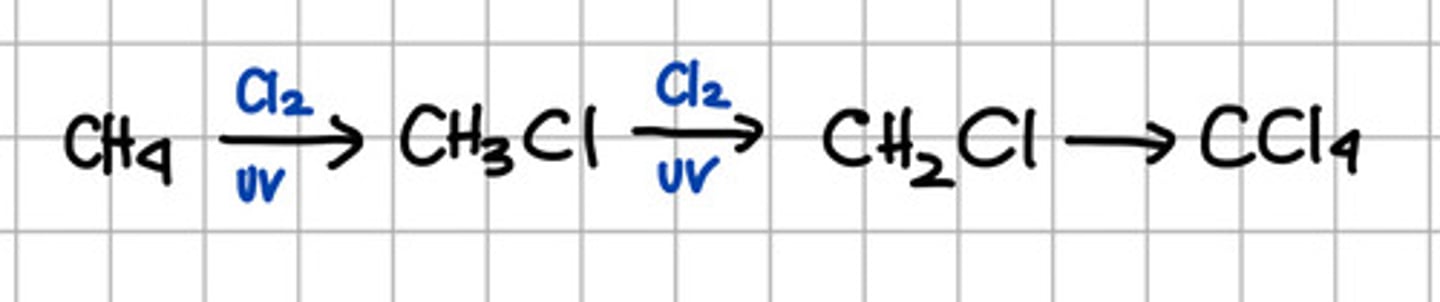
Catalyst for hydroboration-oxidation of alkene.
a. Tetrahydrofuran
b. NaOH
c. H2O2
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Catalyst for halogenation of alkanes.
a. Halogen group
b. UV
c. Strong acid
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
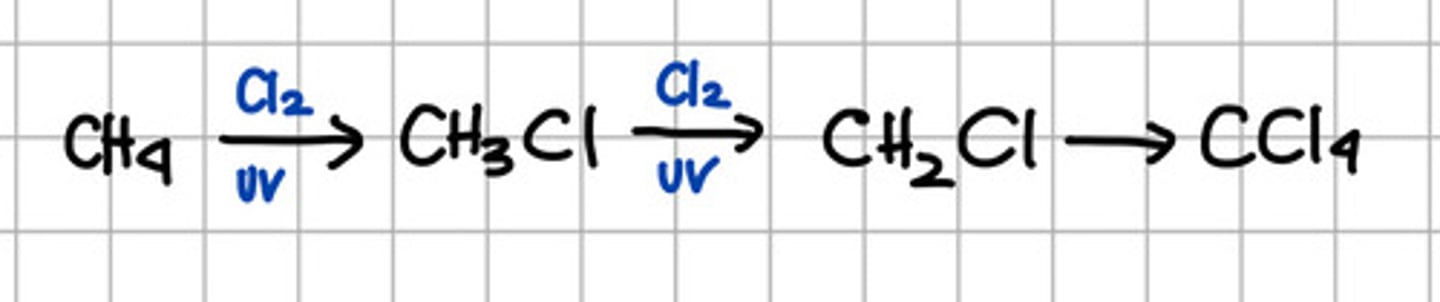
Insert reactions
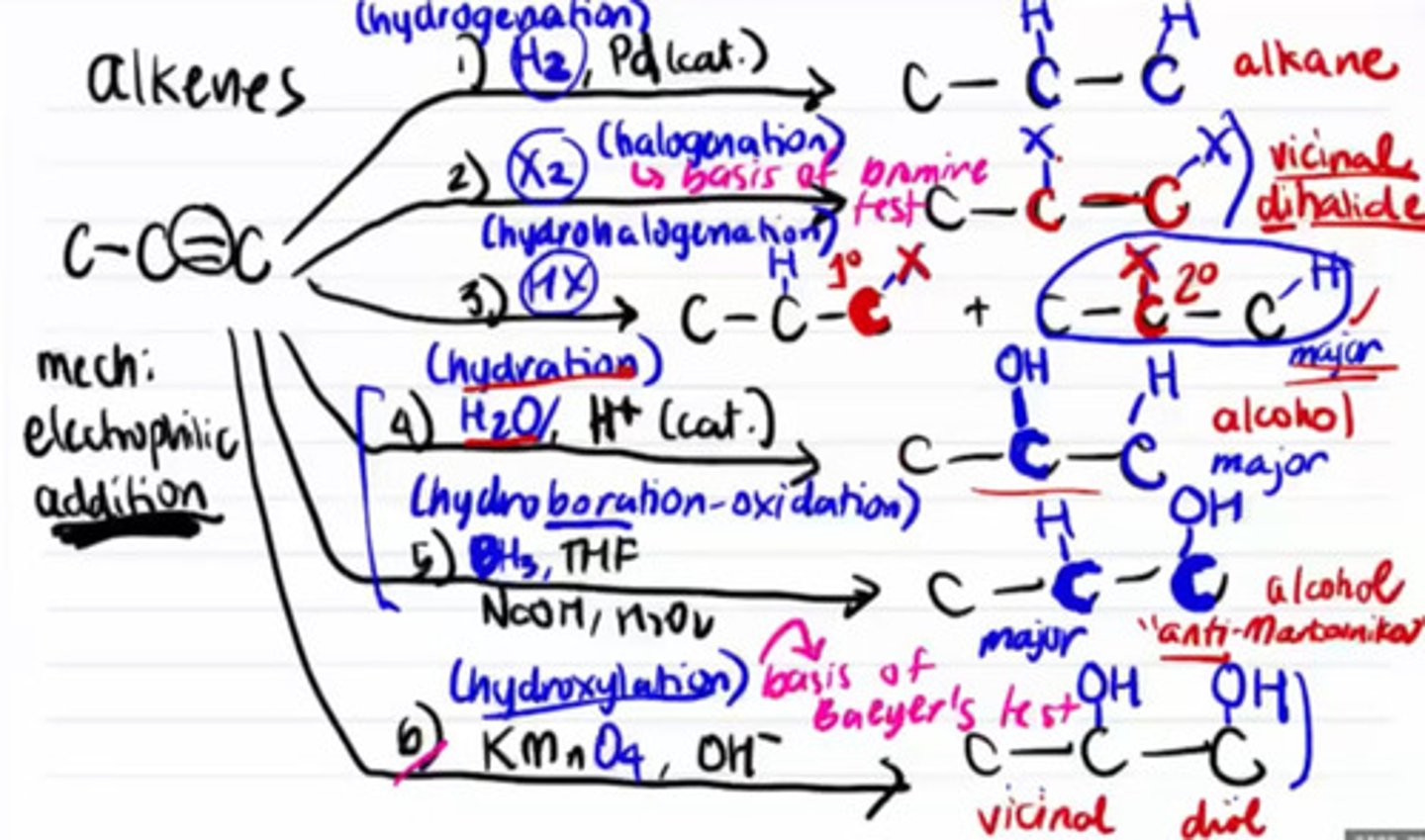
Product of hydrogenation of alkene.
a. Alkane
b. Vicinal dihalide
c. Alcohol
d. Vicinal diol
a. Alkane
Product of halogenation of alkene.
a. Alkane
b. Vicinal dihalide
c. Alcohol
d. Vicinal diol
b. Vicinal dihalide
Product of hydration of alkene.
a. Alkane
b. Vicinal dihalide
c. Alcohol
d. Vicinal diol
c. Alcohol
Product of hydroboration-oxidation of alkene.
a. Alkane
b. Vicinal dihalide
c. Alcohol
d. Vicinal diol
c. Alcohol
Product of hydroxylation of alkene.
a. Alkane
b. Vicinal dihalide
c. Alcohol
d. Vicinal diol
d. Vicinal diol
Reaction of alkane that is the basis of Bromine test.
a. Hydrogenation
b. Halogenation
c. Hydrohalogenation
d. Hydration
e. Hydroboration oxidation
f. Hydroxylation
b. Halogenation
Reaction of alkane that is the basis of Bayer's test.
a. Hydrogenation
b. Halogenation
c. Hydrohalogenation
d. Hydration
e. Hydroboration oxidation
f. Hydroxylation
f. Hydroxylation
Reaction of alkane that has anti-Markonikov product.
a. Hydrogenation
b. Halogenation
c. Hydrohalogenation
d. Hydration
e. Hydroboration oxidation
f. Hydroxylation
e. Hydroboration oxidation
In Markonikov's rule, substituents is on the carbon that will result the most stable compound.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Insert reaction
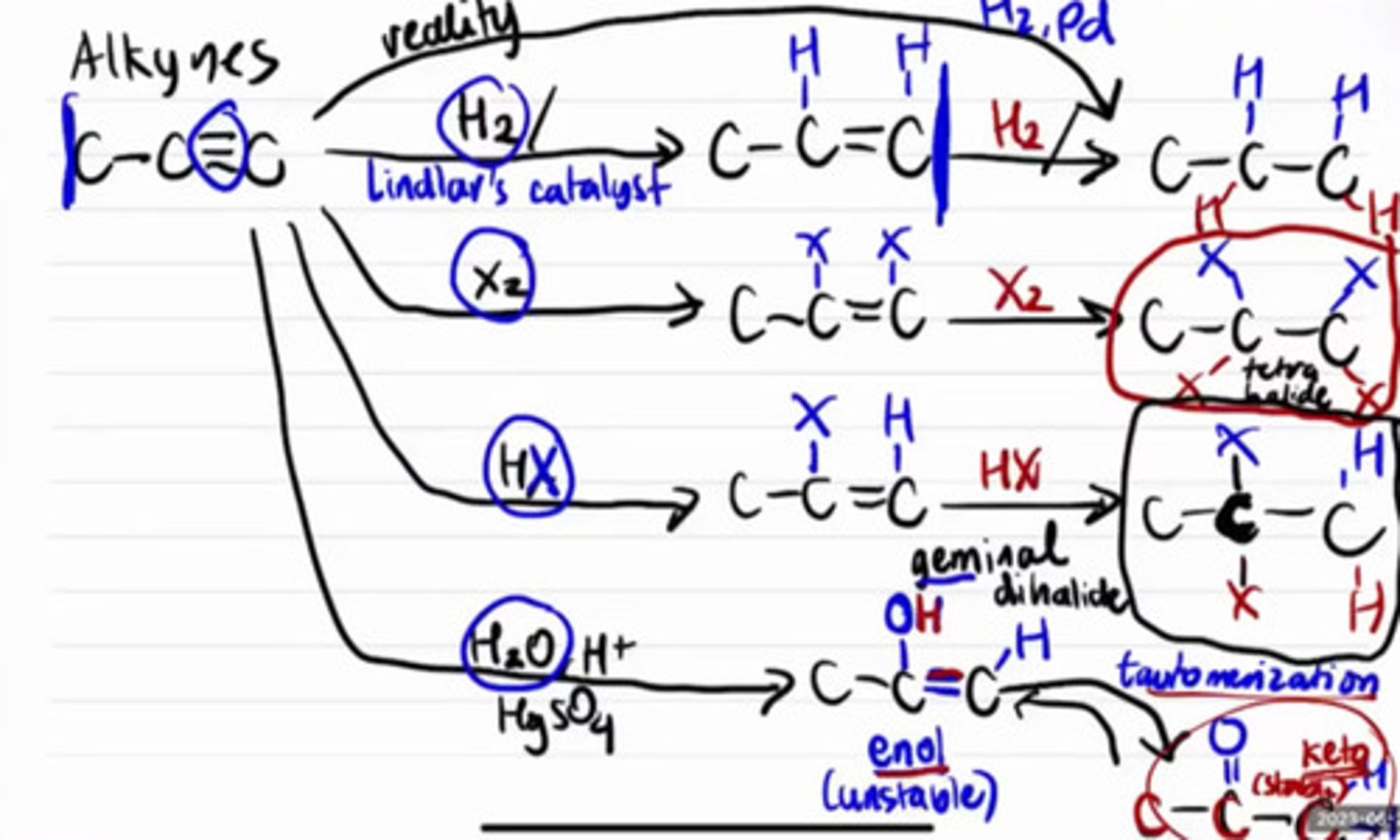
Reactions of alkyne that produce final product tetrahalide.
a. Hydrogenation
b. Halogenation
c. Hydrohalogenation
d. Hydration
b. Halogenation
Reactions of alkyne that produce final product geminal dihalide
a. Hydrogenation
b. Halogenation
c. Hydrohalogenation
d. Hydration
c. Hydrohalogenation
Reactions of alkyne that will produce ketone final product.
a. Hydrogenation
b. Halogenation
c. Hydrohalogenation
d. Hydration
d. Hydration
Catalyst to use if alkynes are only to be hydrogenated up to alkene form.
a. H2SO4
b. Lindlar's
c. Grignard
d. HgSO4
b. Lindlar's
Catalyst to use for hydration of alkynes.
a. H2SO4
b. Lindlar's
c. Grignard
d. HgSO4
d. HgSO4
Unstable nitial product of hydration of alkyne.
a. Enol
b. Ketone
c. Geminal dihalide
d. Tetrahalide
a. Enol
More stable final product of hydration of alkyne after tautomerization.
a. Enol
b. Ketone
c. Geminal dihalide
d. Tetrahalide
b. Ketone
Reduction
a. Removal of oxidation
b. Removal of bond to O
c. Additiom of hydrogen
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. all
f. All