Christianity - Houses of Worship
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1st event
30-33 CE: death of Jesus Christ
2nd event
312: Constantine’s conversion
3rd event
313: Edict of Milan
4th event
325: Nicene Creed
5th event
380 CE: Christianity becomes state religion of the Empire
6th event
1054: East/West Schism
7th event
12th–13th c.: Rise of monastic orders
8th event
1517: Luther’s 95 Theses
9th event
1534: Church of England est.
10th event
1545–1563: Council of Trent
11th event
Late 18th-19th century: massive missionary movements to Africa, Asia, & the Americas
12th event
1962-65: Vatican II Council
Doctrine?
Trinitarian monotheism
What is Trinitarian monotheism
Christian doctrine that there is one God who exists as three co-equal and co-eternal persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit
altarpiece
work of art, typically a painting or sculpture, that is placed behind or above the altar in a Christian church to serve as a visual aid for worship and to decorate the spacebaptistery
baptistery
designated place for baptisms in a Christian church
basilica
honorific title given by the Pope to a church that stands out
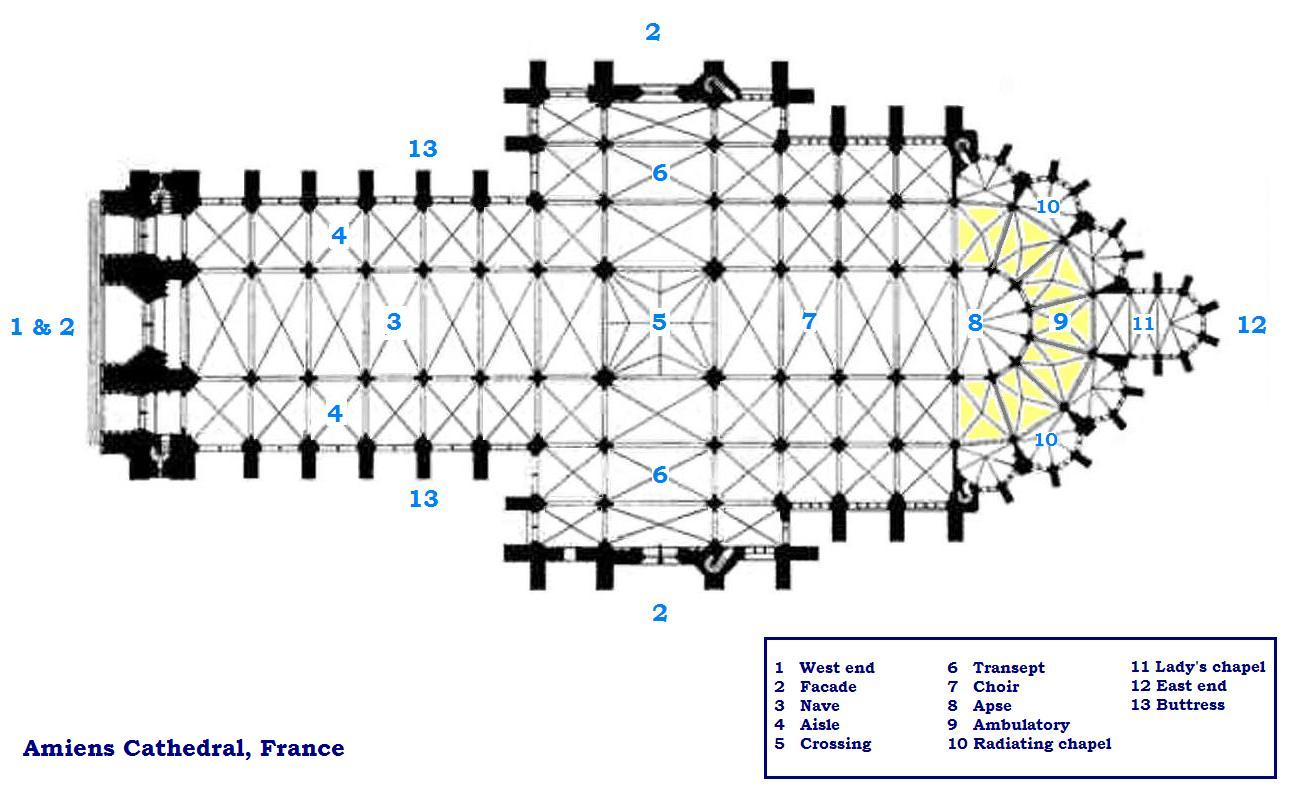
box pew
enclosed, private pew with wooden walls and a door - popular in protestant churches from 16th to 19th centuries
domus ecclesiae
private home in early Christian era that was adapted for communal Christian worship - popular before legalization of Christianity in 313 AD
Gothic
medieval European style of architecture with towering height, pointed arches, and large stained glass windows
Gothic Revival
architectural movement that revived medieval Gothic style and associated with Christianity
humanism
combines classical humanist ideals with Christian faith - advocating for human dignity, reason, and individual potential within a framework of Christian ideals
Iconostasis
wall of icons that separates the sanctuary from the nave of the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic churches
meetinghouse
a building used for religious gatherings, often associated for groups like quakers
megachurch
huge churches with large gatherings of sometimes a thousand people
mosaic
Mosaic law referring to the laws given to Moses by God
Art form of mosaic which is a metaphor for the Churches community
Plans: longitudinal & centralized
Longitudinal - a longitudinal plan is linear and elongated with a central axis (like a nave leading to an altar)
Centralized - centralized plan is symmetrical around a central point, often circular, square, or polygonal
Protestant Reformation
16th century religious movement that led to a split in Western Christianity, ending unity with Catholics
Renaissance
period of intellectual and artistic “rebirth” that significantly influenced Christianity by sparking a renewed focus on original scripture, leading to a more scholarly approach
rose window
circular design within the Christian faith refers to the infinite sphere of God and the endless nature of God’s love
stained glass
used to visually tell biblical stories, symbolize divine light, and inspire worshippers
Vatican II Council
major council that reformed the Catholic Churches approach to modern world - resulting in key changes and definitions in Christiantiy