Applied Biochemistry - RNA Structure, Synthesis, and Processing
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What are the three major types of RNA in the process protein synthesis?
rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA
What is ncRNA?
Non-coding RNA
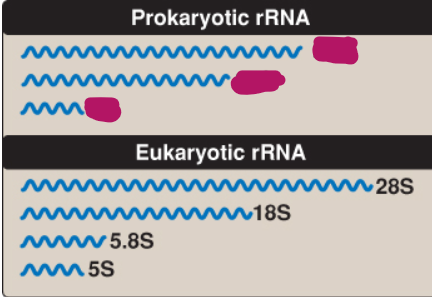
What is the size of prokaryotic rRNA?
5S, 16S, 23S
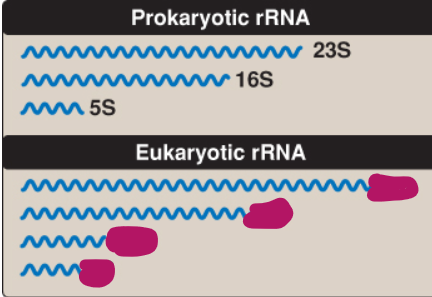
What is the size of eukaryotic rRNA?
5S, 5.8S, 18S, 28S
What is rRNA?
Ribosomal RNA
How much of the total cell RNA is rRNA?
80%
What is a ribozyme?
RNA with catalytic activity
What is the smallest type of RNA?
tRNA
What percentage of total cell RNA is made up of tRNA?
15%
Which type of RNA contain a high percentage of unusual/modified bases?
tRNA
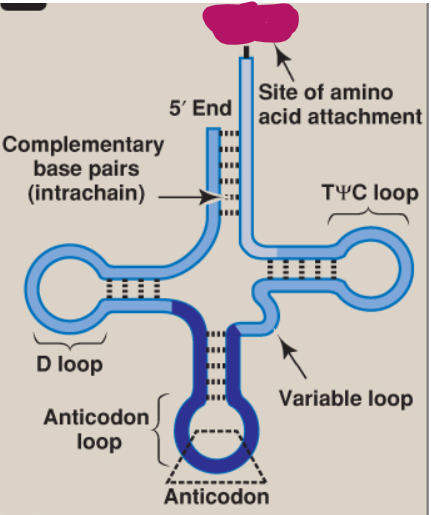
What is this part of tRNA?
3’-End CCA
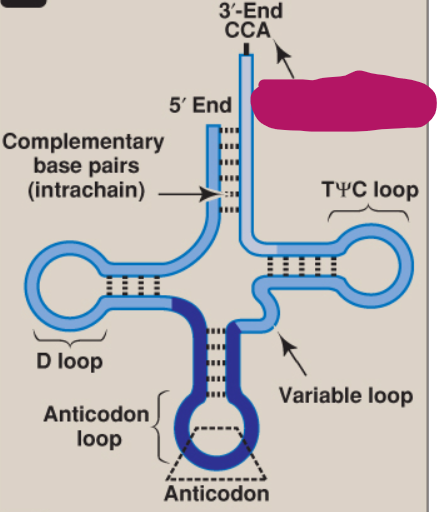
What is this part of tRNA?
Site of amino acid attachment
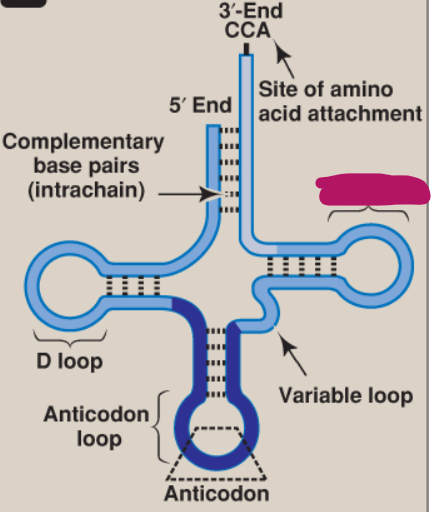
What is this part of tRNA?
TΨC loop
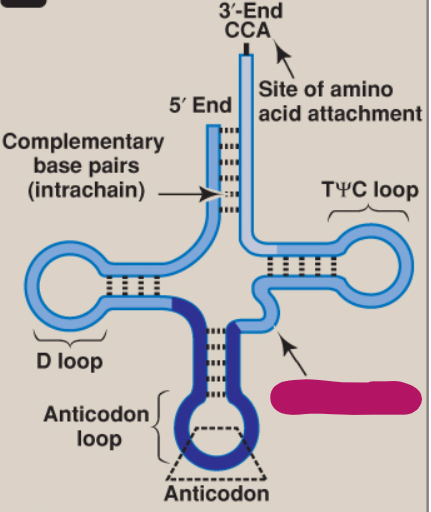
What is this part of tRNA?
Variable loop
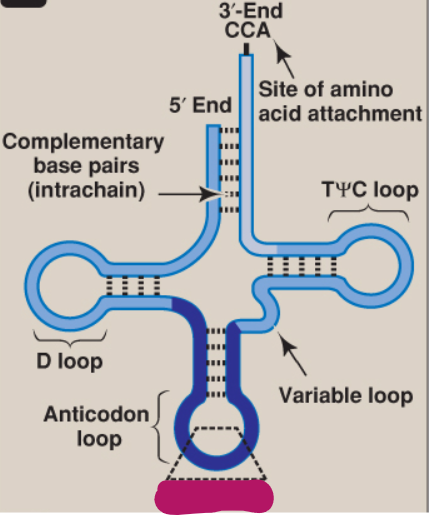
What is this part of tRNA?
Anticodon
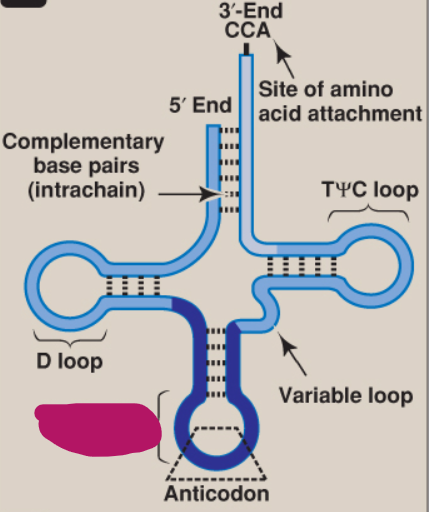
What is this part of tRNA?
Anticodon loop
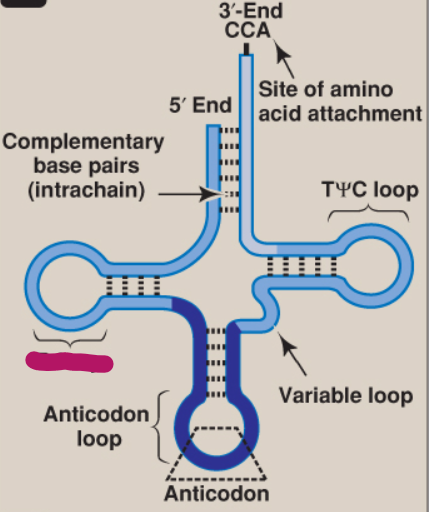
What is this part of tRNA?
D loop
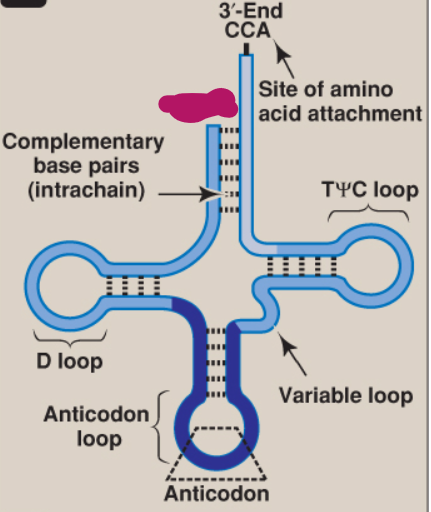
What is this part of tRNA?
Complementary base pairs
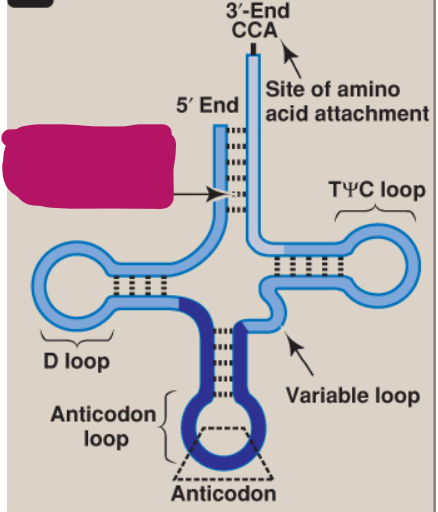
What is this part of tRNA?
5’ end
What diseases are associated with a mutation in lysine tRNA?
Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers (MERRF) and mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS)
What disease is associated with mutations in leucine tRNA?
Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS)
What is MERRF?
A disorder that affects skeletal muscle structure and function (myopathy)
What is MELAS?
A disorder that affects the brain, nervous system, and muscles
What percentage of total cell RNA is made up of mRNA?
5%
What is mRNA?
Messenger RNA
What is the function of mRNA?
Coding RNA that carries genetic information from DNA for use in protein synthesis
What is the name of an mRNA that carries information from more than one gene?
Polycistronic
Where is polycistronic mRNA found?
Prokaryotes, mitochondria, some viruses, and chloroplasts
What is the name of mRNA that carries information from only one gene?
Monocistronic
Where is monocistronic mRNA found?
Eukaryotes
What is the S in the measurement of rRNA?
the Svedberg unit for sedimentation rate
What are the sizes of rRNA species encoded by miochondrial DNA?
12S and 16S
How many types of tRNA molecules are there?
At least one type for each of the 20 amino acids
What is the structure of tRNA?
Cloverleaf
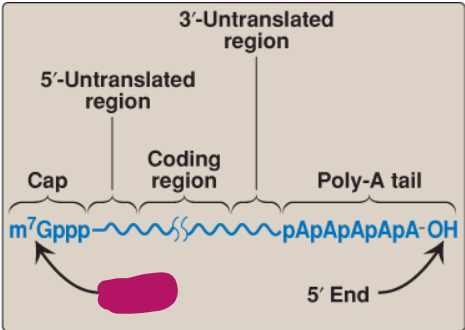
Label this part of mRNA.
5’ end
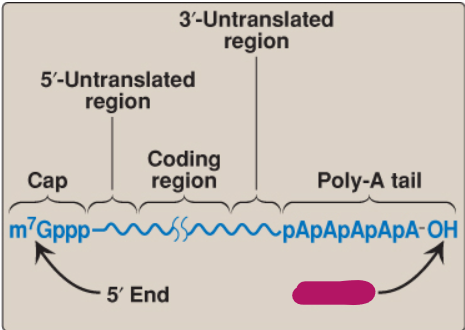
Label this part of mRNA.
5’ end
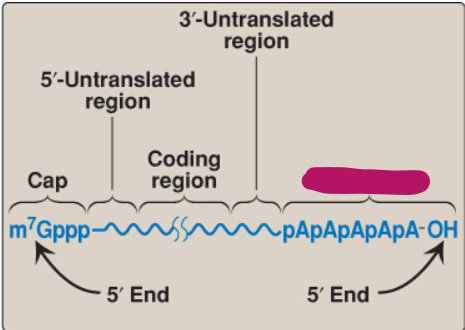
Label this part of mRNA.
Poly-A tail
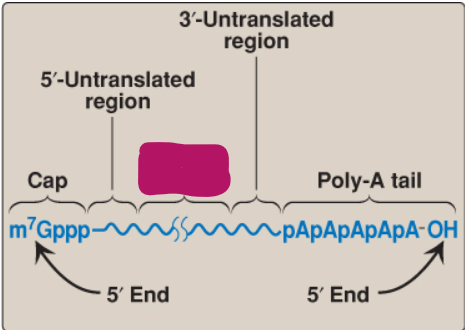
Label this part of mRNA.
3’-Untranslated region
Label this part of mRNA.
Coding region
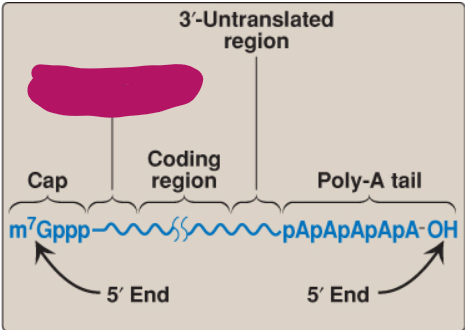
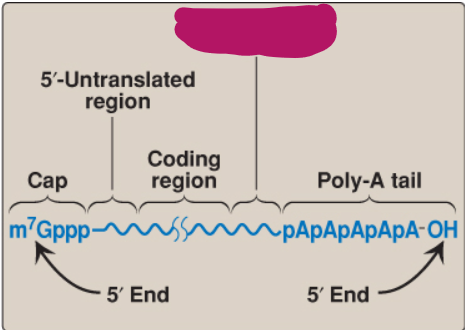
Label this part of mRNA.
5’-Untranslated region
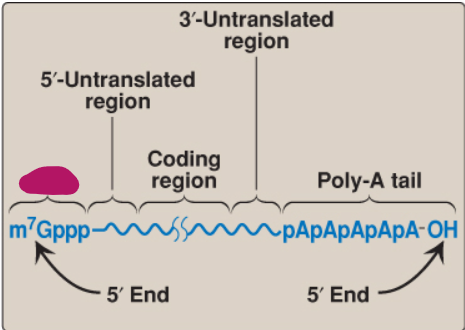
Label this part of mRNA.
Cap
What is RNA polymerase?
A multisubunit enzyme that recognizes the promoter region at the beginning of DNA to be transcribed and makes an RNA copy
In what direction is RNA synthesized?
5’→ 3’
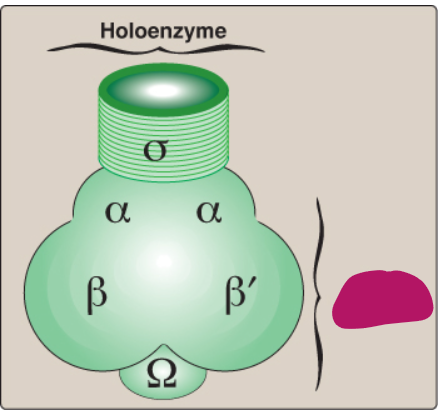
Label this section of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Holoenzyme
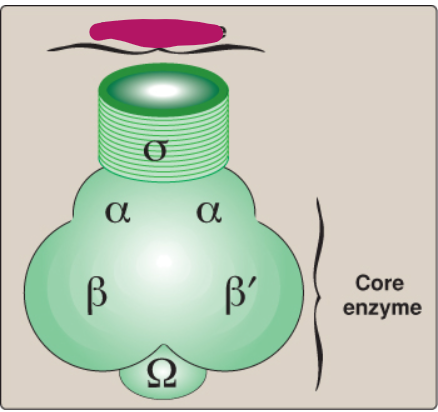
Label this section of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Core enzyme
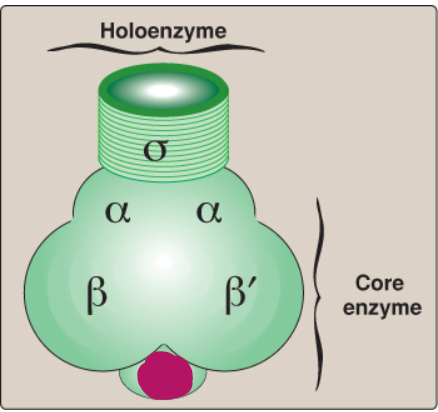
Label this section of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Omega
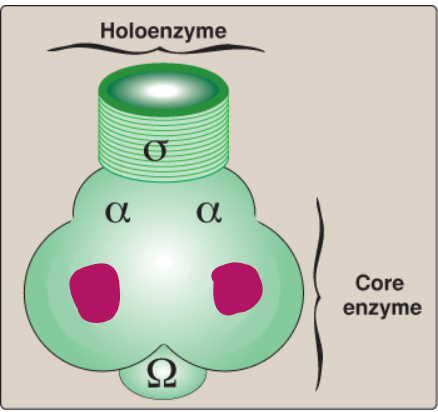
Label this section of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Beta and beta prime
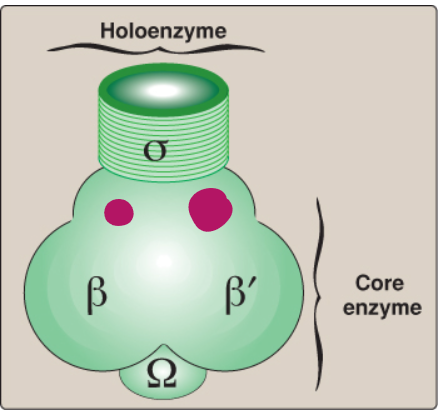
Label this section of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Alpha
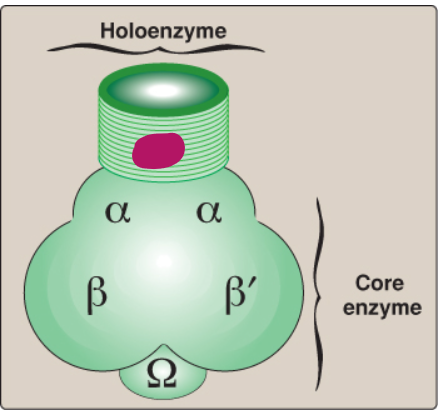
Label this section of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Sigma
What components make up the core enzyme of RNA pol?
Alpha, beta, and omega
What component makes up the RNA pol holoenzyme?
Sigma
Which part of the core enzyme is required for enzyme assembly?
Alpha and omega
Which part of the core enzyme is required for template binding?
Beta prime
Which part of the core enzyme is required for 5’→ 3’ polymerase activity?
Beta
What part of the core enzyme of RNA pol lacks specificity?
The core enzyme
What is the function of the holoenzyme of RNA pol?
Recognizing promoter regions on DNA
What are the three phases of transcription?
Initiation, elongation, and termination
What happens in the initiation of transcription?
The RNA pol holoenzyme binds to the promoter region of DNA.
What are consensus sequences?
Calculated sequences of the most frequent residues at certain positions
What is the -35 sequence?
The initial point of contact for the holoenzyme, about 35 bases to the left of the start of transcription
What is the pribnow box?
A consensus sequence at -10 which is the site of melting/unwinding of a short stretch of DNA to make a transcription bubble
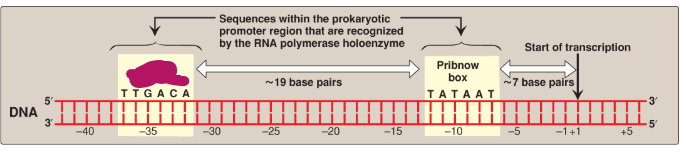
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
-35 sequence
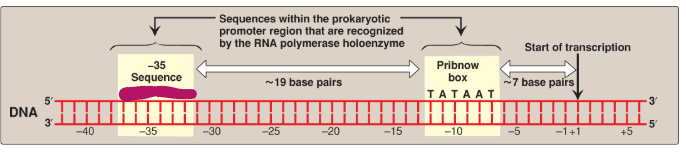
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
TTGACA
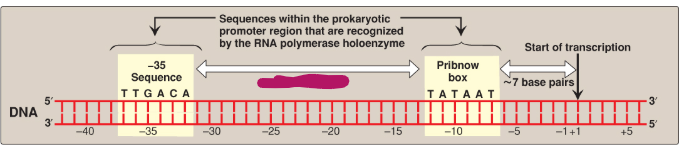
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
~19 base pairs
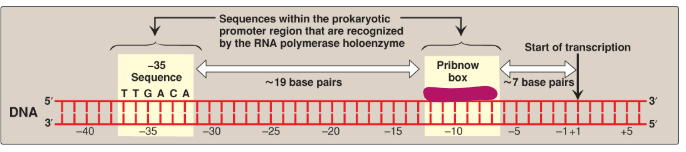
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
TATAAT
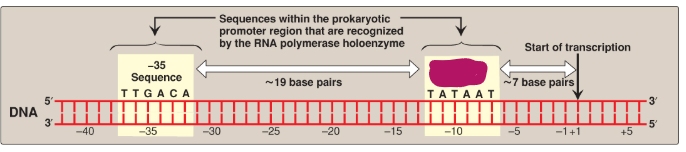
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
Pribnow box
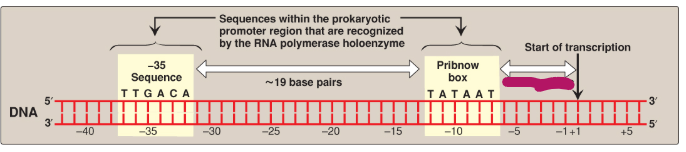
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
~7 base pairs
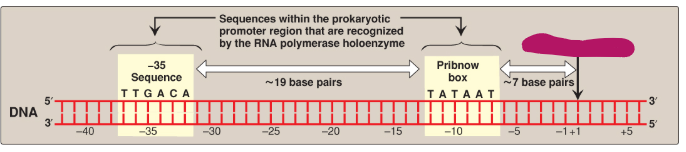
Label this section of the prokaryotic promoter region.
Start of transcription
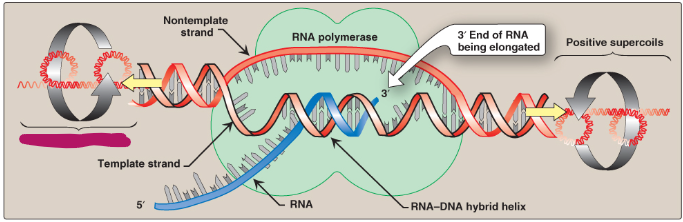
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
Negative supercoils
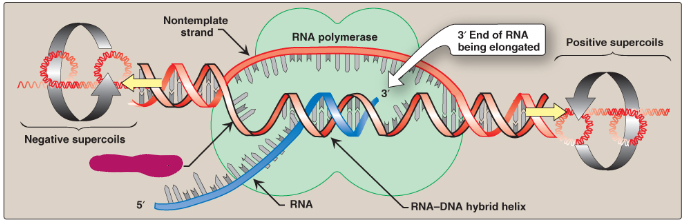
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
Template strand
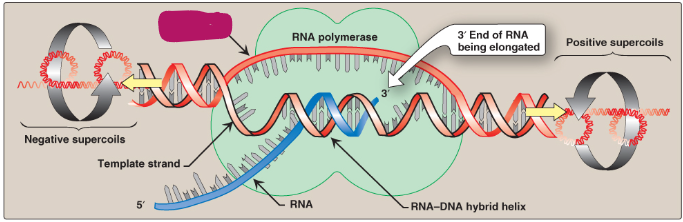
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
Nontemplate strand
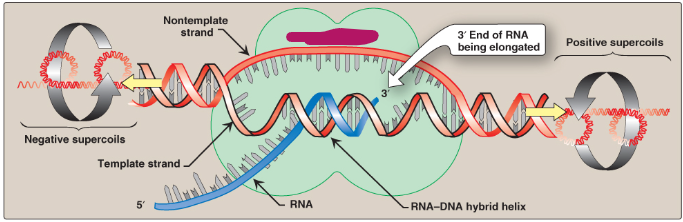
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
RNA polymerase
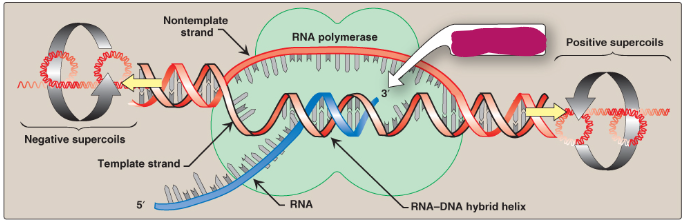
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
3’ end of RNA being elongated
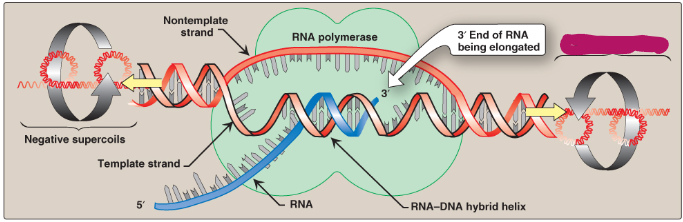
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
Positive supercoils
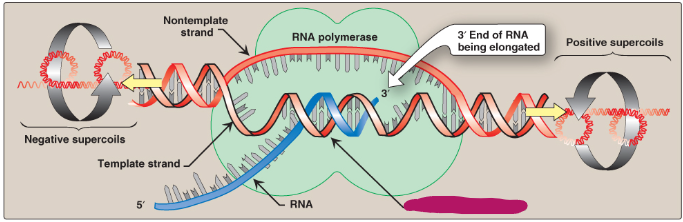
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
RNA-DNA hybrid helix
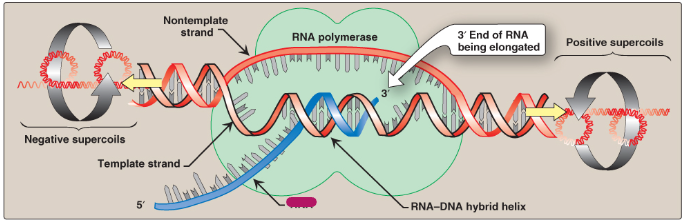
Label this section of the transcription bubble.
RNA
What happens in the elongation phase of protein synthesis?
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA sequences longer than 10 nucleotides in length. The core enzyme moves along the template strand acting as its own sliding clamp. 5’ → 3’ direction
What makes RNA pol different from DNA pol?
RNA pol does not require a primer and does not have 3’→ 5’ exonuclease domain, therefore more errors