asynchronous week 2: overview of basic nutrition pt 1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
describe energy within nutritional context
the ability to do work. energy released by burning food (as heat) which raises water temp. 1kcal = amount of energy required to raise 1kg water 1 degrees celcius
identify and describe 3 energy requiring process of human body
basal metabolism: energy required to maintain normal body functions while rest
physical activity: energy required for muscular work
dietary thermogenesis: energy used to ingest and digest food
explain the difference between “digestion“ and “absorption“ of nutrients
digestion: food=substances that can be absorbed by body and done through mechanical process like chewing or chemical process like enzymes
absorption: nutrients and other substances transferred from the digestive system into body fluids for transport through body
define and describe carbohydrates and the significance of carbohydrate consumption
simple sugars
complex carbohydrates (starch)
fibre
we need it for energy (our body can only use one simple sugar which is glucose)
adequate intake prevents protein breakdown for energy
provides taste and sweeteness
___of the world’s food energy is provided by maize, rice and wheat
60%
define famine foods + strengths and limitations
it is a complex carbohydrate. foods that would otherwise be inedible but are eaten during times of extreme food scarcity
dont provide energy & upset stomach
helps people to care and prepare food together, sense of community
define and describe protein
structural component to all living matter, involved in almost every biological process in the body.
structural: red blood cells
functional: lactase, breaking down and transporting
limiting amino acid
the amino acid in an incomplete protein that is present in the least amount relative to the requirement for that amino acid
lysine is the limiting amino acid in cereal grains (not enough)
complete protein
contails all essential amino acids in amounts needed to support body
derived from animals
incomplete protein
are deficient in one or more essential amino acids
derived from plants
complementary proteins
a protein that is incomplete on its own but becomes complete when combined with another protein source with complimentary amino acid content
identify 4 functions of protein
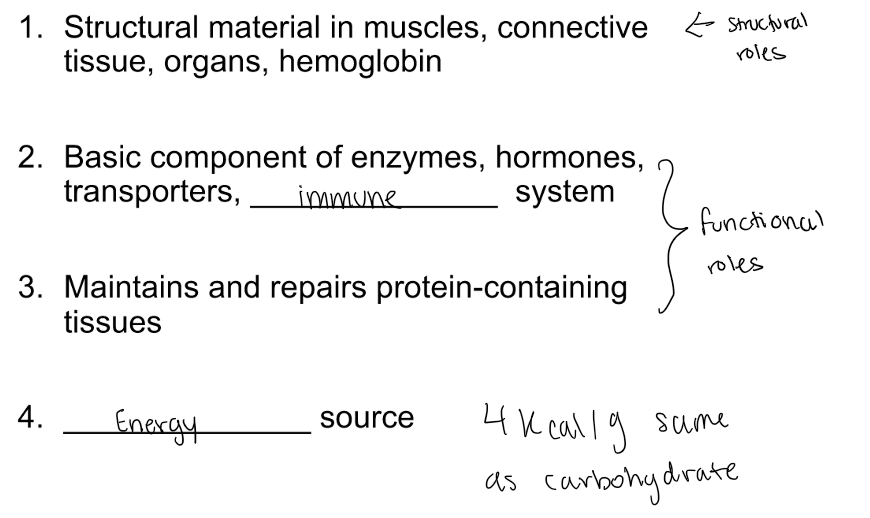
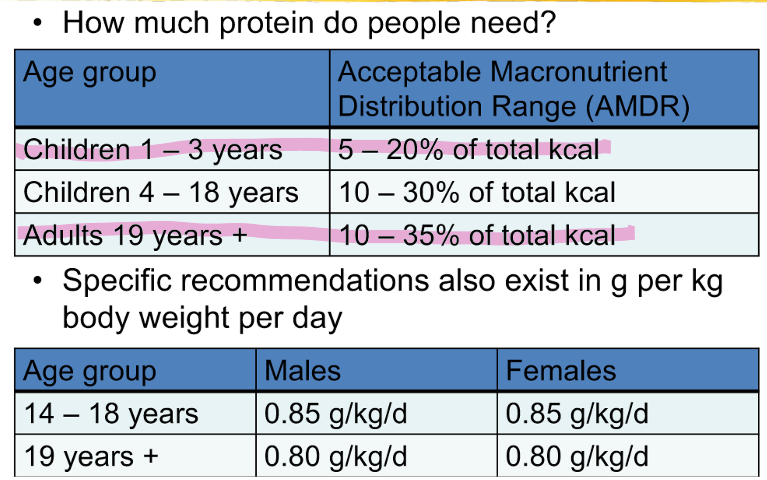
summarize protein requirements and comment on the likelihood of a plant based diet providing sufficient protein (quality and quantity)
soy is a complete protein and is plant based: tofu, edame
identify some consequences of inadequate or excessive protein intake
too little protein= multiple nutrient deficiencies
too much protein= over 45% will cause nausea, weakness, diarrhea and death
define fat, its functions
lipids= fat, oils, cholesterol, triglycerides
not water soluble
1g of fat = 9kcal of energy
Functions
concentrated energy source
carries essential fatty acids, fat soluble vitamins (D,E,A,K)
flavour, fullness
cell membranes, vitamin D, sex hormones
what’s the difference between triglycerides, saturated, and unsaturated fat
triglycerides
glycerol + 3 fatty acids (saturated or unsaturated)
used by cells for energy and tissue maintenance
most of our fat intake
saturated
solid at room temp, found in animal products
carbon atoms attached to as many hydrogen atoms as possible
unsaturated
fewer than max hydrogens
at least one double bond (monosaturated)
more than 1 double bond (polyunsaturated)
liquid at room temp
what are two polyunsaturated fats
linoleic acid (omega6) alpha-linolenic acid (omega3)
identify the AMDR’s for carbohydrate, protein, and fat for adults and children 1-3 years of age
adults: 20-35% of total kcal
children 1-3 years: 30-40% of total kcal
use those values to asses dietary intakes
higher fat intake associated with LOWER risk of mortality whereas carbohydrate intake associated with HIGHER risk of mortality