DM1605 Mani
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Electronics
Last updated 10:40 PM on 5/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
The electrical force or ‘pressure’ that causes current to flow in a circuit
What is voltage?
2
New cards
Volts (V)
What are the units for voltage?
3
New cards
The movement of electrical charge, the flow of electrons through the electronic circuit
What is current?
4
New cards
From positive to negative voltages
Which way does current flow?
5
New cards
Amperes (Amps, A)
What are the units for current?
6
New cards
Causes an opposition to the flow of current in a circuit
What is resistance?
7
New cards
Controls the amount of voltage and current in a circuit
What does resistance control?
8
New cards
Ohms (Ω)
What are the units for resistance?
9
New cards
Ohm’s Law
What describes the relationship between current, voltage and resistance?
10
New cards
V=IxR
What is the equation for Ohm’s law
11
New cards
V is the voltage between two points ( measured in Volts)
In Ohm’s Law, what does the V stand for?
12
New cards
I is the current flowing along a path between those two points (measured in amperes)
In Ohm’s Law, what does the I stand for?
13
New cards
R is the resistance of that path (measured in Ohms)
In Ohm’s Law, what does the R stand for?
14
New cards
Volts=Amps x Ohms
What two units do you multiply to find volts
15
New cards
The sum of the currents flowing into the node is equal to the sum of the currents flowing out of the node
What is Kirchoff’s first law?
16
New cards
Where a current must take a single path, going through one component and then the other in a series
What is a series circuit?
17
New cards
A circuit in which the current splits and takes two parallel paths at the same time
What is a parallel circuit?
18
New cards
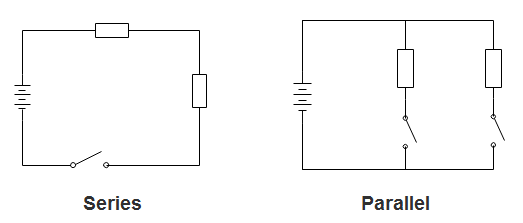
Draw out a parallel and series circuit
19
New cards
Joules (J)
What is the unit for energy?
20
New cards
Voltage
What is potential difference?
21
New cards
Volts, V
or
Energy per charge, joules per coulomb, J C^-1
or
Energy per charge, joules per coulomb, J C^-1
What the unit for voltage?
22
New cards
amps, A
or
charge per second, coulombs per second, C s^−1
or
charge per second, coulombs per second, C s^−1
What is the unit for current?
23
New cards
watts, W
or
energy per second, joules per second, J s^−1
or
energy per second, joules per second, J s^−1
What is the unit for power?
24
New cards
Power=voltage x current
What is the equation for power?
25
New cards
Ohms (Ω)
What is the unit for resistance?
26
New cards
Resistance= voltage/ current
What is the equation for resistance?
27
New cards
A device designed specifically to have a constant resistance
What is a resistor?
28
New cards
They store electrical energy and can be used like a temporary battery
maintain power supply while batteries are being charged
maintain power supply while batteries are being charged
What are capacitors?
29
New cards
They conducts current in one direction and are used to convert AC power to DC power in a diode bridge
What are diodes?
30
New cards
A semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power
low operating voltages
typically found embedded in integrated circuits
low operating voltages
typically found embedded in integrated circuits
What is a transistor?
31
New cards
A circuit in which all or some of the circuit elements are electrically interconnected so that they are considered to be indivisible
They are carriers that are soldered onto a pcb
They are carriers that are soldered onto a pcb
What’s an integrated circuit
32
New cards
3 x 10^8m/s
What is the value of speed of light?
33
New cards
2\.45 x 10^9 Hz
What is the value of microwave frequency?
34
New cards
1\.6 x 10^-19C
What is the value of a charge on an electron?
35
New cards
m
length
length
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the meter?
36
New cards
kg
mass
mass
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the kilogram?
37
New cards
s
time
time
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the second?
38
New cards
A
electric current
electric current
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the ampere?
39
New cards
K
temperature
temperature
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the Kelvin?
40
New cards
cd
luminous intensity
luminous intensity
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the candela?
41
New cards
mol
amount of substance
amount of substance
What is the unit symbol and quantity of the mole?
42
New cards
k
10^3
10^3
What is the symbol and factor of Kilo?
43
New cards
M
10^6
10^6
What is the symbol and factor of mega?
44
New cards
G
10^9
10^9
What is the symbol and factor of giga?
45
New cards
T
10^12
10^12
What is the symbol and factor of tera?
46
New cards
P
10^15
10^15
What is the symbol and factor of peta?
47
New cards
m
10^-3
10^-3
What is the symbol and factor of milli?
48
New cards
µ
10^-6
10^-6
What is the symbol and factor of micro?
49
New cards
n
10^-9
10^-9
What is the symbol and factor of nano?
50
New cards
p
10^-12
10^-12
What is the symbol and factor of pico?
51
New cards
f
10^-15
10^-15
What is the symbol and factor of femto?
52
New cards
A dense, central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons
What is an atom?
53
New cards
A mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons
Except for a hydrogen atom which only has one proton
Except for a hydrogen atom which only has one proton
What does the nucleus contain?
54
New cards
positive
What charge does a proton have?
55
New cards
Negative
What charge does an electron have?
56
New cards
Neutral
What charge does a neutral have?
57
New cards
Coulombs
C
C
What is electric charge measured in?
58
New cards
A fixed voltage that can be used to power an electronic device or an electrical system
What is a dc voltage source?
59
New cards
Batteries (chemical)
Generators (Electromechanical)
Power supplies (rectification from ac sources)
Generators (Electromechanical)
Power supplies (rectification from ac sources)
What are the three dc voltage sources?
60
New cards
Negative to positive
What direction do electrons flow in current?
61
New cards
The rate of charge transport
What does current describe
62
New cards
I=Q / T
What is the calculation for current?
63
New cards
Coulombs
C
C
What is the unit for charge?
64
New cards
Materials that allow a large number of free electrons to flow with very little voltage applied
What is a conductor?
65
New cards
copper
gold
aluminium
gold
aluminium
Examples of a conductor?
66
New cards
Materials that have very few free or no electrons and therefore does not allow current flow
What is an insulator?
67
New cards
Plastics
Wood
Rubber
Wood
Rubber
Examples of insulators?
68
New cards
A specific group of elements that exhibit characteristics between those of insulators and those of conductors
What are semi-conductors?
69
New cards
Silicon
Sulfur
Sulfur
Examples of semiconductors?
70
New cards
A longer wire has a higher resistance
In resistance, what is length, l?
71
New cards
A thicker wire has a lower resistance
In resistance, what is cross-sectional, A?
72
New cards
A value that quantifies how strong a material opposes the flow of electrons, the higher the resistivity, the higher the resistance
In resistance, what is resistivity, p?
73
New cards
R= pl/A
What is the resistance of a prism?
74
New cards
A higher temp causes the ions in the metal to vibrate more making it harder for electrons to move through the metal
How does temperature effect resistance?
75
New cards
A measure of how well a material conducts electricity
What is conductance?
76
New cards
G=1/R
What is the equation of conductance?
77
New cards
G,
measured in siemens, (S)
measured in siemens, (S)
What is the unit of resistance?
78
New cards
Carbon film
Metal film
Metal-oxide film
Thin/thick film
Wire wound
Metal film
Metal-oxide film
Thin/thick film
Wire wound
Name the 5 types of resistors?
79
New cards
A potentiometer
What is another word for a variable resistors?
80
New cards
\-The resistance between the wiper arm and either terminal can be from 0 0hms up to the full resistance value
\-The sum of the two resistances between the wiper arm and each outside terminal is equal to the full rated resistance of the potentiometer
\-The sum of the two resistances between the wiper arm and each outside terminal is equal to the full rated resistance of the potentiometer
How does a potentiometer work?
81
New cards
Rac= Rab + Rbc
Full rated resistance of a potentiometer equation?
82
New cards
A two terminal electrical component
Stores energy in the form of electrostatic charge
Stores energy in the form of electrostatic charge
What is a capacitor?
83
New cards
C=Q/V
\
C=capacitance
Q=Charge
V=Voltage
\
C=capacitance
Q=Charge
V=Voltage
What is the equation of capacitance?
84
New cards
Farad (F)
What is the unit of capacitance?
85
New cards
It charges up
electrons are pushed onto one plate and repelled from the other
when fully charged the capacitor stores charge Q
electrons are pushed onto one plate and repelled from the other
when fully charged the capacitor stores charge Q
What happens when a dc voltage is applied to a capacitor?
86
New cards
The capacitor discharges
What happens to the capacitor when voltage is removed and the charge flows back around the circuit?
87
New cards
Two conductive plates separated by a dielectric (insulator)
What does a common capacitor consist of?
88
New cards
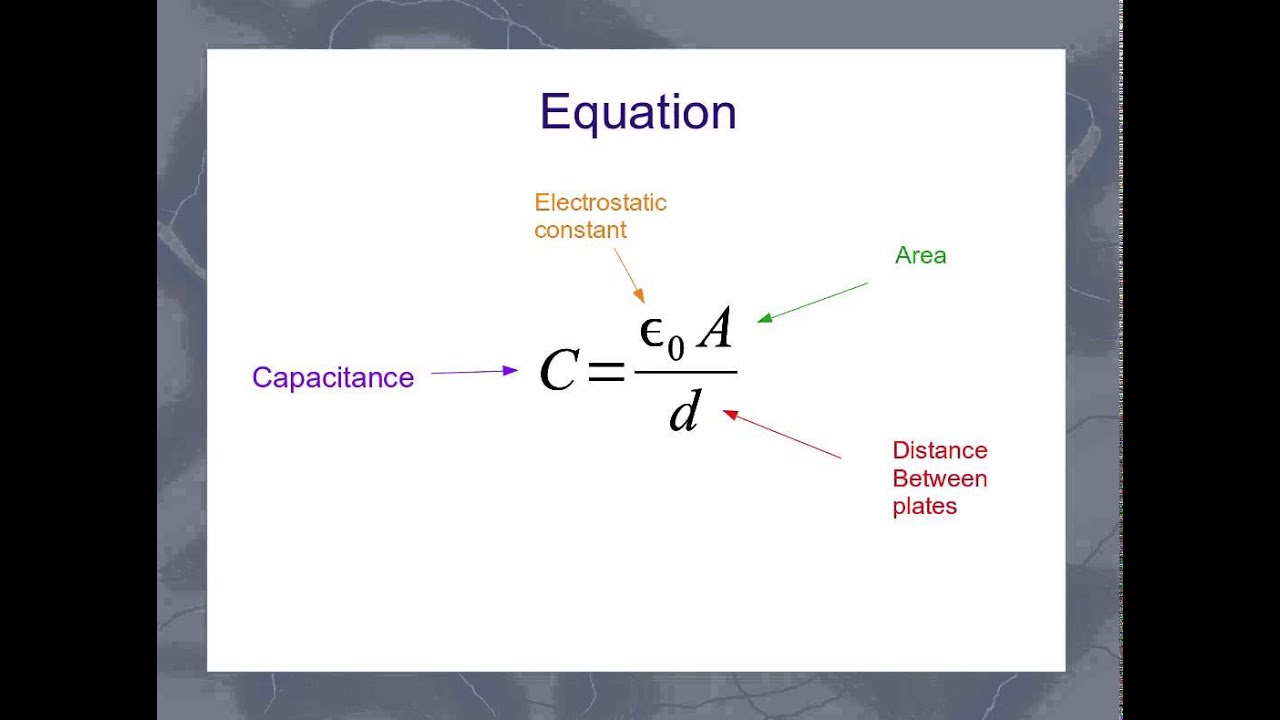
What is the equation of capacitance?
89
New cards
\-Ceramic
\-Electrolyric
\-Electrolyric
What are the two types of capacitors?
90
New cards
A passive electrical component that stores energy in the form of a magnetic field
It consists of a wire loop or coil
It consists of a wire loop or coil
What is an inductor?
91
New cards
Henry (H)
What is the unit of inductance?
92
New cards
An inductor
coil
ferromagnetic core to improve magnetic field strength
act like a permanent bar magnet with north and south poles
an example of an electro-magnet
coil
ferromagnetic core to improve magnetic field strength
act like a permanent bar magnet with north and south poles
an example of an electro-magnet
What is a Solenoid?
93
New cards
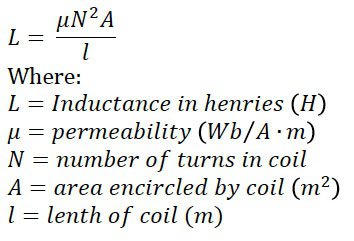
What is the inductance of a solenoid?
94
New cards
Used to change the voltage to a higher or lower without changing the power
What is a transformer?
95
New cards
To increase the voltage
From power stations to grid
From power stations to grid
What are step up transformers for?
96
New cards
To decrease the voltage
From grid to residential area
From grid to residential area
What are step down transformers for?
97
New cards
AC voltage
converted into magnetic flux in primary coil
Magnetic flux is converted into current again in secondary coil
converted into magnetic flux in primary coil
Magnetic flux is converted into current again in secondary coil
Do Transformers work with DC or AC voltage?
98
New cards
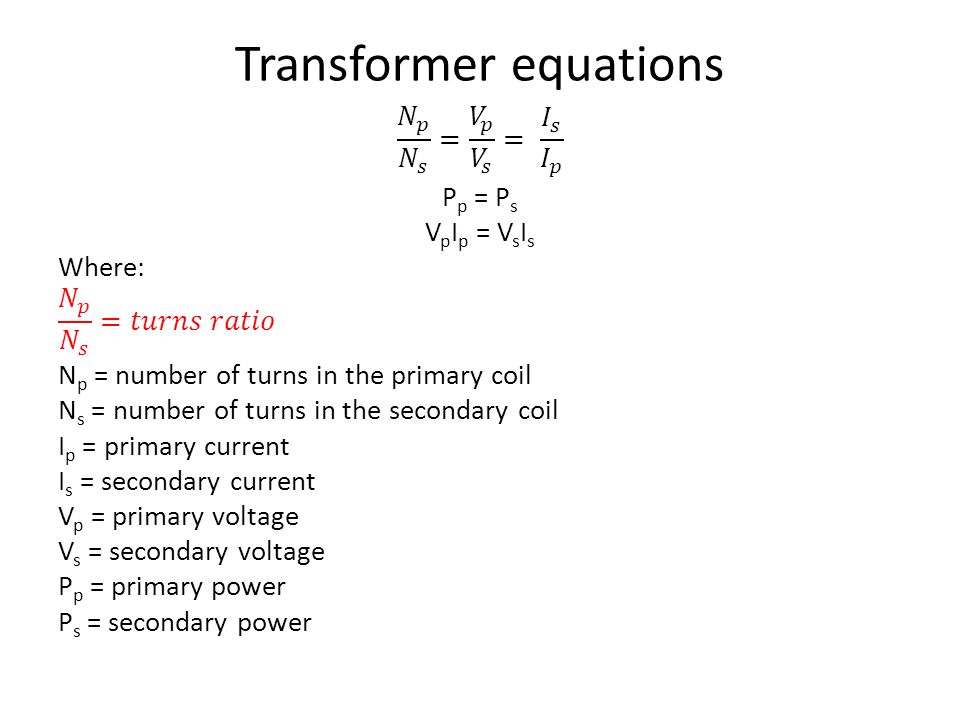
Transformer equations?
99
New cards
Magnetization and demagnetization of core (usually iron) will not be perfect. This is known as Hysteresis and some portion electrical energy will be consumed
What is hysteresis loss in a transformer?
100
New cards
Due to Stray fluxes link with the mechanical structure and winding conductors, an e.m.f will be induced which is not useful and hence considered as loss.
What is Eddy current loss in transformer?