Biology 1407- Chapter 30: Protostome Animals
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Lophophore
Crest of ciliated, hollow tentacles around the mouth.
Lophotrochozoans
Trochophore
Larval form that moves by beating a wheel-like band of cilia.
Lophotrochozoans
Protonephridia
Simple excretory structures that filter waste and maintain osmotic balance.
Proto-: First
-nephr: Kidney
Phylum Platyhelminthes ("flat worms")
Gastrovascular cavity
Digestive system branched to deliver nutrients directly to cells via diffusion.
Scolex
Anterior end in tapeworms that has suckers to adhere to intestinal lining of hosts.
Class Cestoda
Proglottids
Body sections composed entirely of sex organs
Class Cestoda
Alimentary canal
Digestive tube that extends from the mouth to the anus
Phylum Rotifera- rotifers
(wheel-bearing)
Corona
"Crown" of cilia create water current for feeding
Phylum Rotifera- rotifers
(wheel-bearing)
Mastax
Muscular and jawed organ that breaks the food into smaller particles, unique to rotifers.
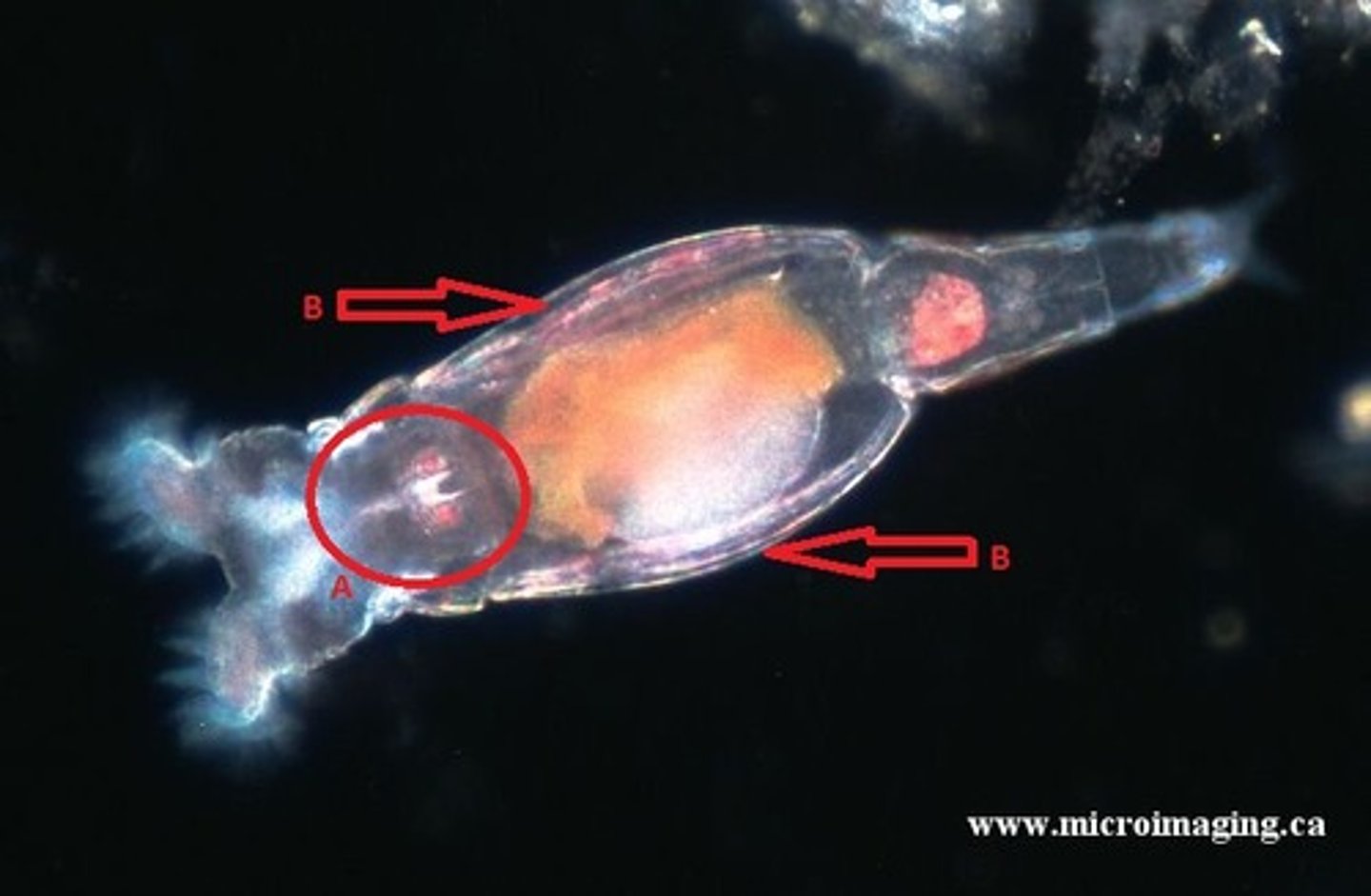
Parthenogenetic
Population exists entirely of females that produce more females from unfertilized eggs
Phylum Rotifera- rotifers
(wheel-bearing)
Parapodia
Paddle-like appendages that assist aquatic annelids in locomotion.
Phylum Annelida ("rings")
Class Polychaeta ("many bristles")
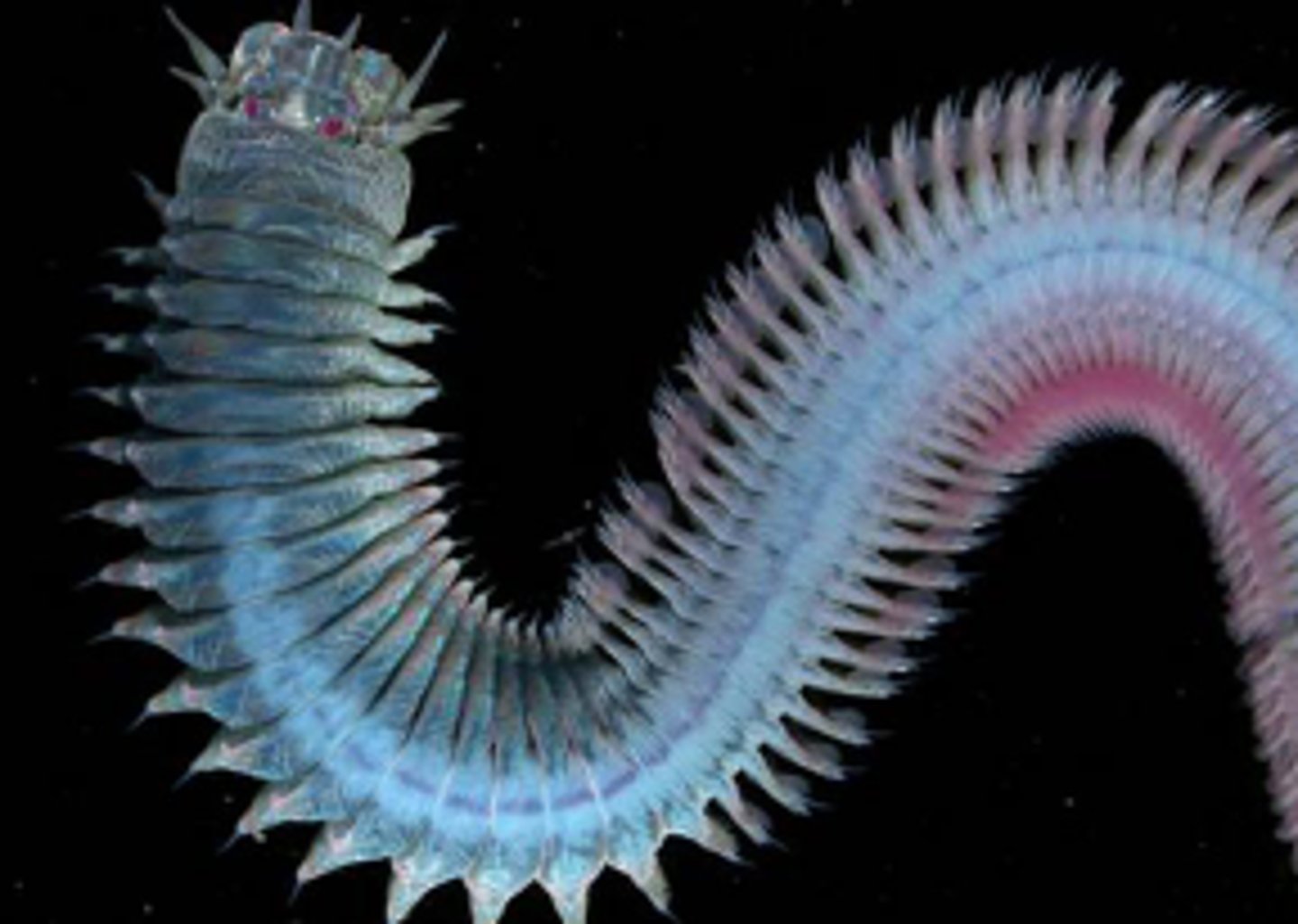

Chaetae
Bristle-like chitinous projections
("bristle")
Open Circulation
Hemolymph, or body fluid, leaves vessels of system, percolates between cells and tissues, then flows back into system to be pumped out again by a heart.
Example: Insects, spiders, mollusks
Closed Circulation
Blood is contained within a continuous system of vessels and pumped by a heart
Example: Humans and other mammals, birds, reptiles, fish
Foot
Muscular mode of locomotion in mollusks
Visceral Mass (Phylum Mollusca)
Heart, digestive, excretory, and reproductive organs.
Mantle (Phylum Mollusca)
Fold and tissue that drapes over visceral mass and secretes calcium carbonate shell.
Mantle cavity (Mollusca)
Fluid-filled chamber that houses gills, anus, excretory pores.
Radula
Strap-like organ used to rasp and scrape up food particles
Torsion (Class Gastropoda)
Visceral mass rotates 180 degrees causing anus and mantle cavity to rest above head.
Phylum Mollusca
What are ammonites?
Fossil cephalopods that were dominant marine invertebrate predators for hundreds of millions of years.
When did ammonites go extinct?
In the Cretaceous along with dinosaurs.
To which phylum do ammonites belong?
Phylum Mollusca.
Cuticle
Tough exterior that Ecdysozoans secrete
Ecdysis (molting)
Process of shedding off cuticle.
Ecdysozoans
Chelicerae
Claw-like feeding appendages in chelicerates.
Pincers or fangs that grasp rather than chew.
Mandibles (Myriapods)
Pair of antennae and three pairs of appendages modified as mouthparts.
Myriapods
(many feet).
e.g., Millipedes and centipedes.
Carapace (Crustaceans)
Hardened cuticle that covers head and thorax.
What is incomplete metamorphosis?
A type of development in which nymphs resemble adults but are smaller and lack wings.
What do nymphs do during incomplete metamorphosis?
They go through a series of molts until they reach full size.
What is complete metamorphosis also known as?
Holometabolous
What are the larval stages in complete metamorphosis specialized for?
Eating and growing
What aspects differ between larval and adult stages in complete metamorphosis?
Morphology, food, habitat
Give an example of complete metamorphosis.
Caterpillar to butterfly.
Undergo pupal stage to reach adulthood.