The Special Senses - Eye, Ear and Nose
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for reviewing lecture notes on special senses - eye, ear, and nose.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
General senses receptors
Temperature, pain, touch, stretch, and pressure.
Special senses receptors
Gustation, olfaction, vision, equilibrium, and audition.
External ear structures
Auricle, external auditory meatus, tympanic membrane.
Middle ear structures
Tympanic cavity, auditory ossicles (Malleus, Incus, and Stapes).
Inner ear (Labyrinth) structures
Cochlea and other structures associated with equilibrium.
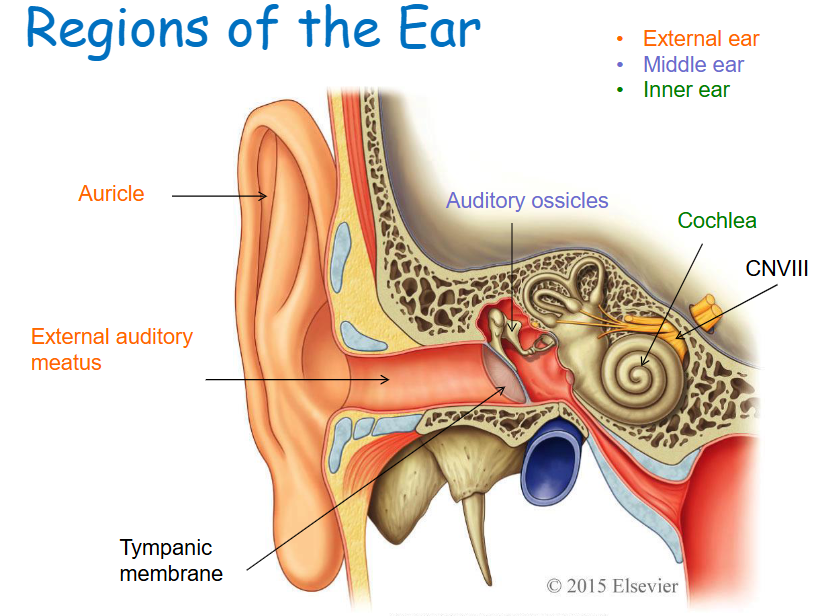
Auricle
Skin covered, funnel-shaped, elastic cartilage-supported structure.
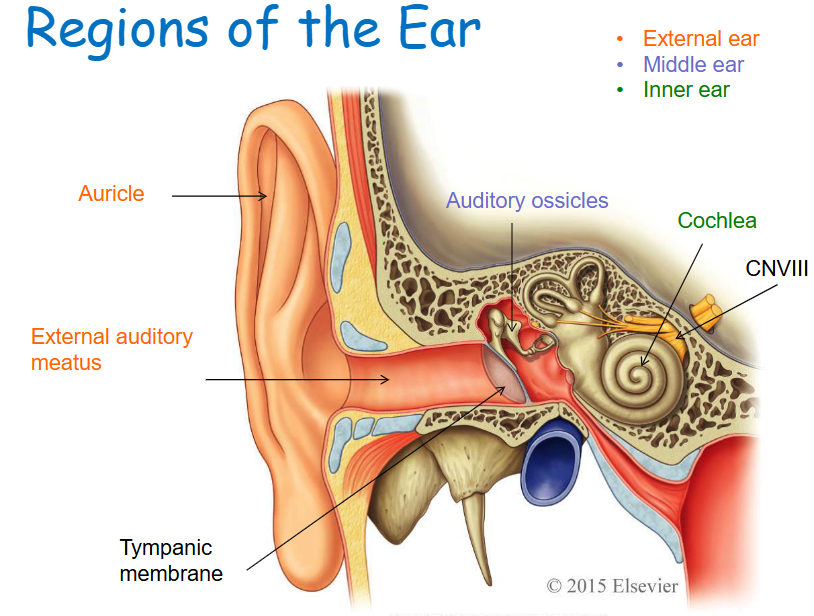
External acoustic meatus
Bony tube leading to the tympanic membrane (eardrum).
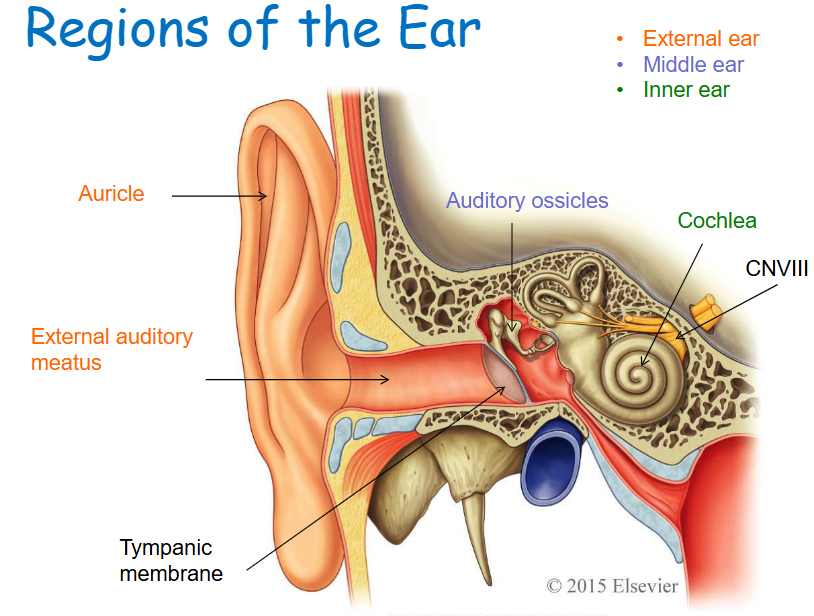
Tympanic cavity
Air-filled cavity containing the auditory ossicles.
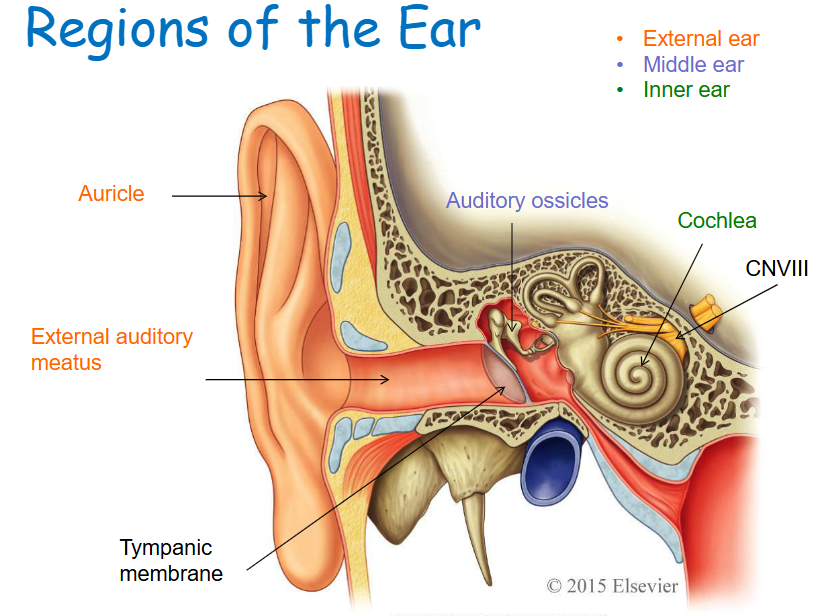
Auditory ossicles
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
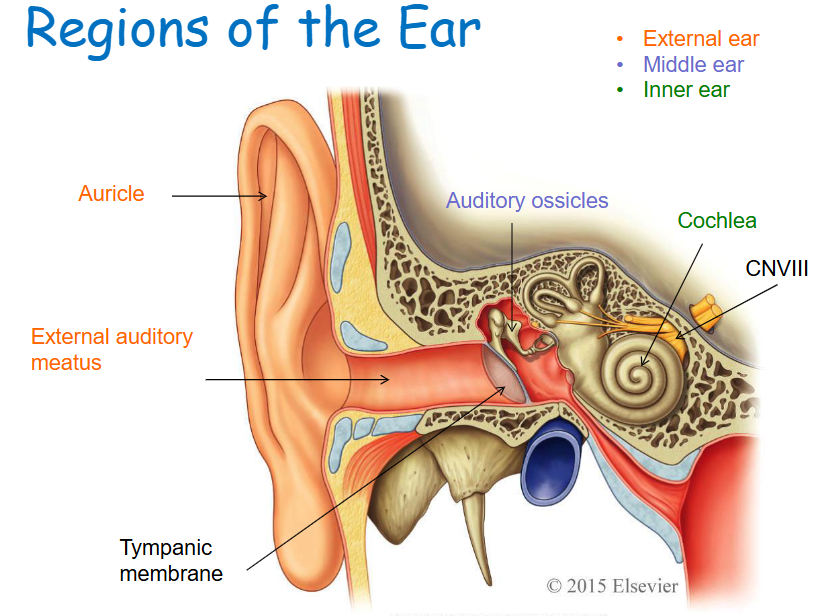
Tympanic membrane
Partitioning the external and middle ear, an epithelial sheet
Auditory ossicles function
Amplify and transmit sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
Oval window function
Responsible for transmitting vibrations to the fluid of the inner ear and hearing receptors.
Inner ear
Houses specialized sensory apparatus for balance and hearing.
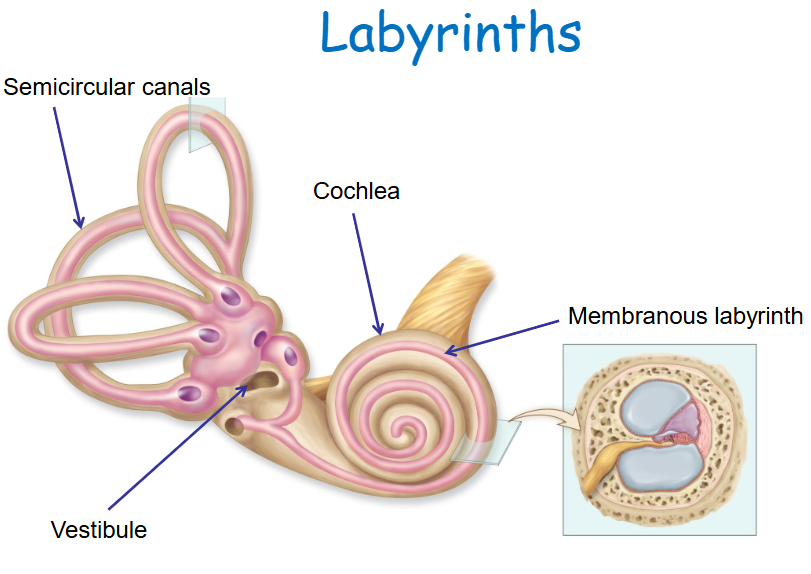
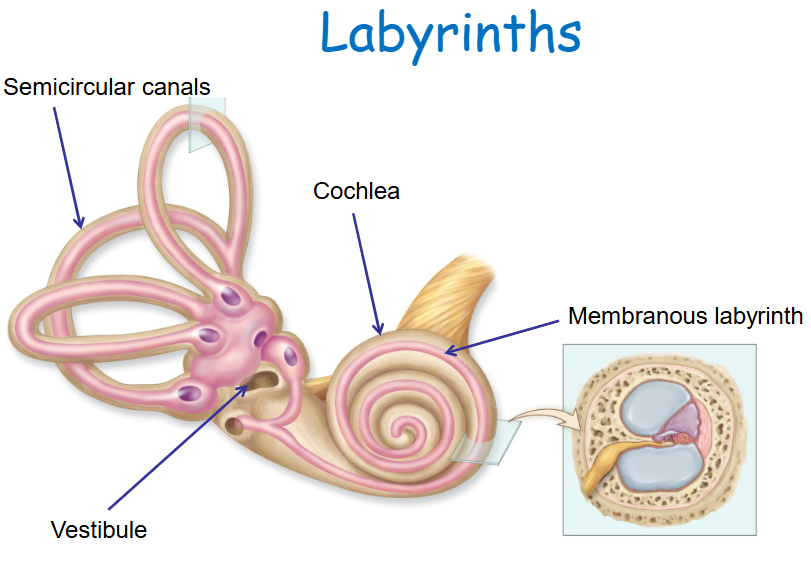
Bony labyrinth divisions
Semicircular canals, vestibule, and cochlea.
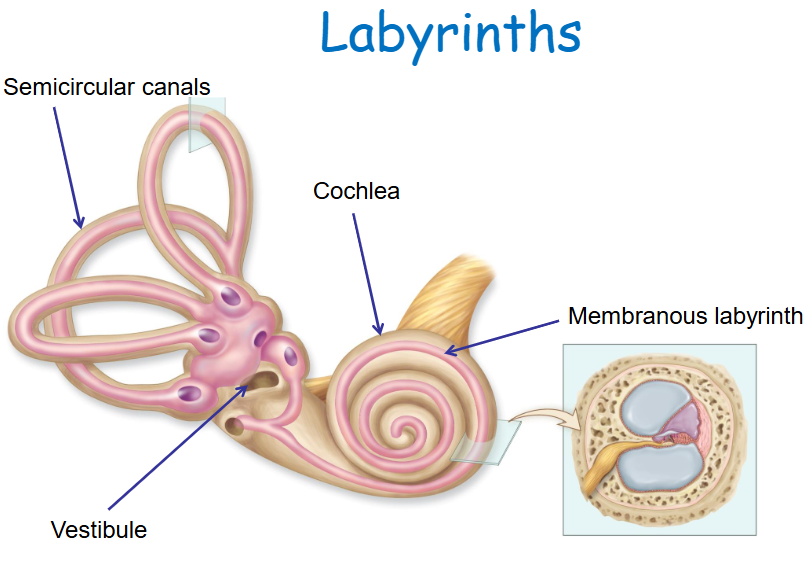
Membranous labyrinth
Fluid-filled tubes and spaces within the bony labyrinth.
Bony labyrinth
Lined with periosteum and contains perilymph.
Epithelial membranous labyrinth
Contains endolymph.
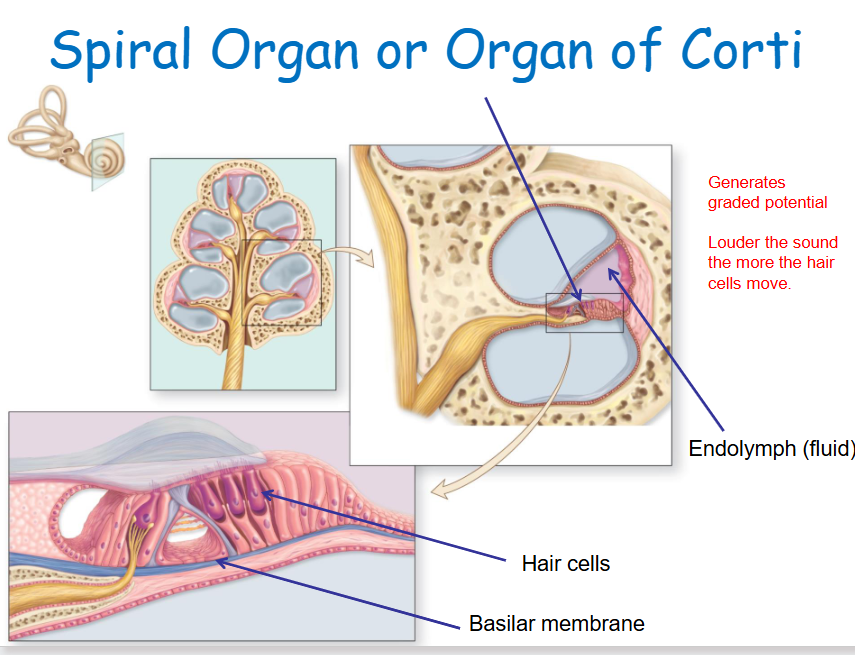
Spiral organ (Organ of Corti)
Contains hair cells that detect movement of surrounding membranes.
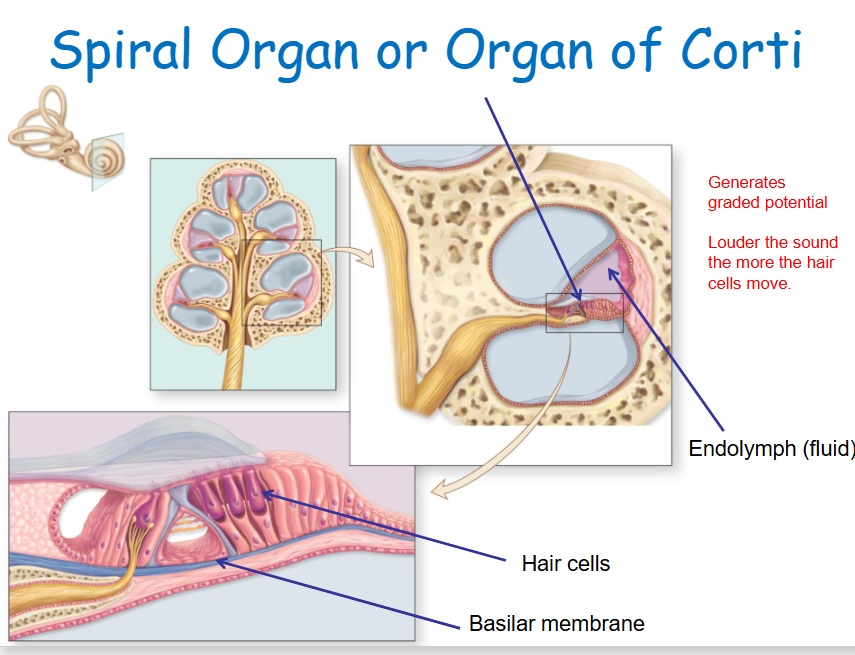
Organ of Corti function
Specialized sensory epithelium that transduces sound vibrations into neural signals.
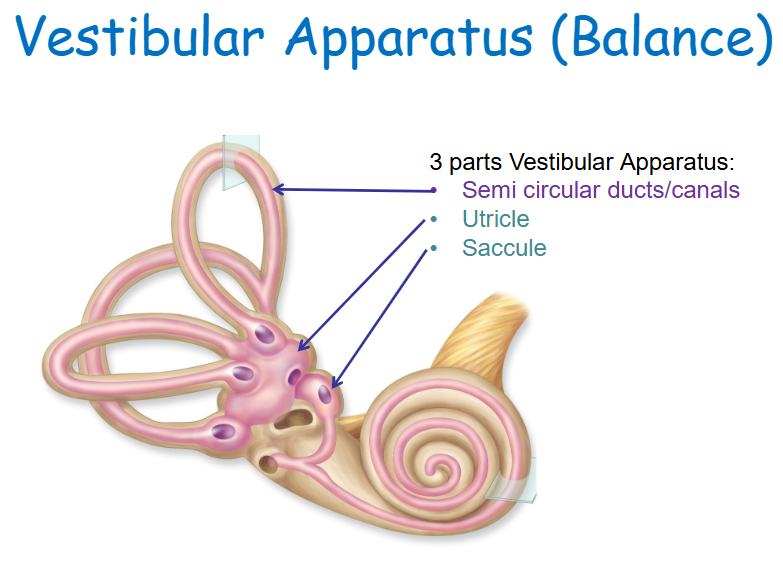
Balance - 3 parts
Vestibular Apparatus: Semicircular ducts/canals, Utricle, Saccule
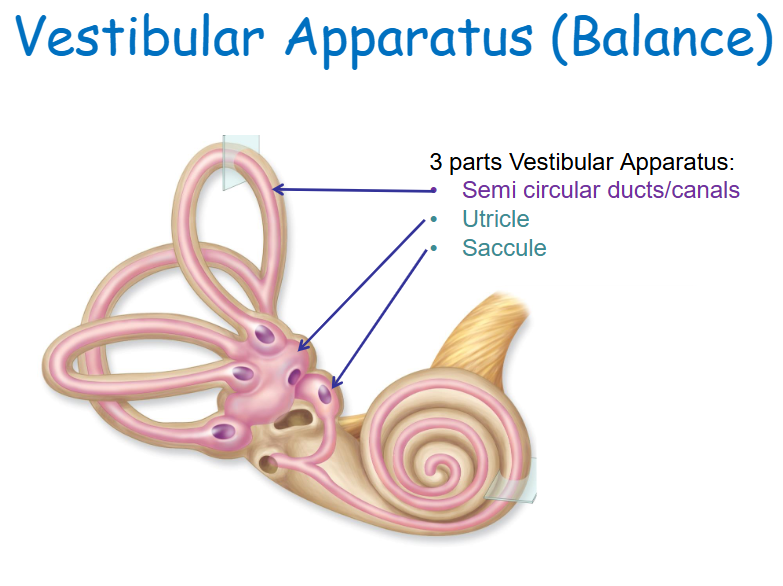
Utricle and Saccule
Two sacs within the vestibule connected by a small duct.
Maculae function
Provide sensory information on the position of the head in space. (Static equilibrium)
Hair cells
Sensory receptors for both equilibrium and hearing.
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Carry nerve impulses from the ear to the brain.
Auditory pathway destinations
Brainstem, thalamus, cerebellum, and auditory cortex of the temporal lobe.
What are the 2 classes of receptors?
1. general senses receptors—temperature, pain, touch, stretch, and pressure
2. special senses receptors—gustation, olfaction vision, equilibrium, and audition
What is the external ear comprised of?
primarily composed of the skin covered, cartilaginous
structure called the auricle
What are some of the components of the middle ear?
air filled tympanic cavity; bony walled
a connection through to the nasopharynx but is normally
closed
What are the auditory ossicles?
Auditory ossicles (three smallest bones in the body) located here that amplify and transmit sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
Where is the inner ear located and where are some of the components?
Located in spaces within the petrous portion of the temporal bone
In the inner ear are specialised sensory apparatus for the sensations of balance and hearing -these are connected to the middle ear by areas the oval and round window
What is the bony labyrinth composed of?
A set of cavities in the petrous part of the temporal bone
Divided into three parts: semicircular canals, vestibule, and cochlea
Lined with periosteum and filled with perilymph
What is the Membranous labyrinth composed of?
A series of epithelial sacs and tubes located within the bony labyrinth
Filled with endolymph
Houses receptors for hearing and equilibrium
Where are hearing organs housed?
In the cochlea of the inner ear.
When the cochlea is cut in half/ cross section you can see it has a number of canals of the membranous labyrinth. What is it called?
cochlea duct
Frequency and intensity are measured (low frequency sounds travel
further along the cochlear duct)
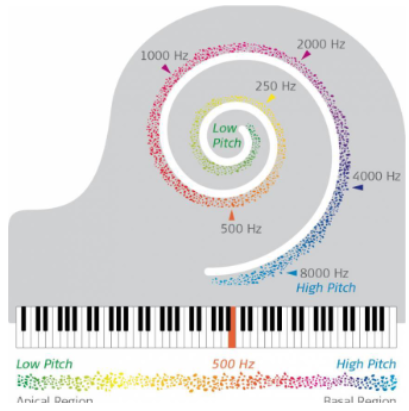
Summarise some of the components of the spiral organ
Summary – The Spiral Organ (Organ of Corti):
Located within the cochlea, between the membranes of the cochlear canals
Contains hair cells that detect membrane movement
Sound waves hitting the tympanic membrane create pressure waves in the cochlear fluid, which distort membranes
The organ of Corti (spiral organ) is a specialised sensory epithelium that converts these vibrations into neural signals for hearing
What are the 2 sacs called in the vestibule of a membranous labyrinth?
the utricle and the saccule, which are connected by a small duct
What are the 3 semicircular canals that project superiorly and posteriorly from the vestibule.
The anterior, posterior, and lateral semicircular canals, which are involved in balance and spatial orientation.
What are the 3 semicircular canals innervated by?
cranial nerve VIII Vestibulocochlear
What do maculae provide?
The maculae provide sensory information on the position of
the head in space.
What happens when stereocilia is bent?
As the stereocilia is bent, the amount of NT released changes.
What do the utricle and saccule contain?
The sensory epithelium lining the two maculae (utricle and saccule)
contains hair cells and supporting cells
What are hair cells for?
Hair cells are sensory receptors for both equilibrium and hearing.
On the apical surface how many microvilli do they have and what are they called?
On their apical surface, they contain more than 50 stiff microvilli called stereocilia and one long cilium called a kinocilium
What happens when stereocilia and kinocilium are bent?
When the stereocilia and kinocilium are bent, this translates into
electrical activity sent to the brain via the vestibular nerve.
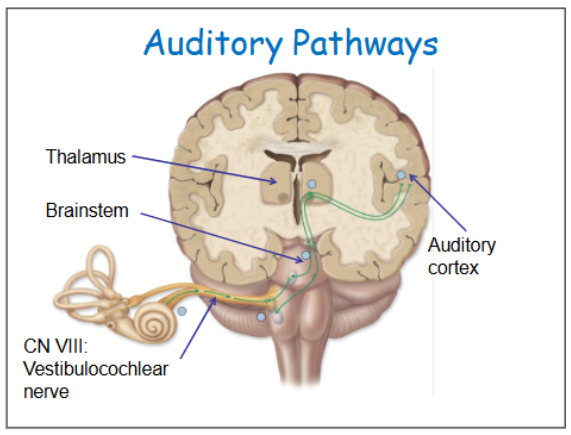
Look at the diagram of the auditory pathways
What happens when stereocilia on hair cells is bent?
Bending of stereocilia on hair cells produces a nerve impulse
During auditory pathways what cranial nerve carries the nerve impulse?
Nerve impulse is carried via the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
What are the auditory neural pathways?
Summary – Auditory Neural Pathway:
Sensory axons from the ear travel to the brainstem
They synapse with secondary neurons, which project to:
Other parts of the brainstem
The thalamus
The cerebellum
And finally, the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe, where sound is consciously perceived