PMIS
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Project Management Information Systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
3 Types of Data
Basic Data
Performance Data
Documented Data
Basic Data
Initial activity database and project baseline plans
Performance Data
Represents actual outcome of the planned activity on a given date
processed by project monitoring centre to analyze its variances from basic and documented data to retrieve information required for decision making
Documented Data
Standard data that are referred to for business transaction purposes
Information management
implies management of data and documents, and communication of processed information to appropriate persons for making decisions
Information
What the human mind has perceived to be of use for making decisions after analyzing data
Schematic Diagram of a Control Process
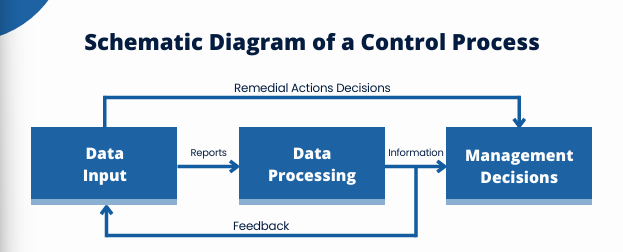
Project Management Information System (PMIS)
attempts to economically collect the right data and documents in the correct form through appropriate means, at the right time and place.
Management of PMIS involves following processes
Database Structure Development Process
Performance Data Reporting Process
Information Retrieval Process
Information Communication Process
Document Management Process
Tools and Outcome of Database Structure Development Process
Data structuring and codification methodology
Work package, activity, resources and cost code dictionaries, baselines
Tools and Outcome of Performance Data Reporting Process
Data change reports
Changes from baseline, updated data
Tools and Outcome of Information Retrieval Process
PM software support
Monitored information, what-if analysis, remedial options
Tools and Outcome of Information Communication Process
PMIS reporting, feedback and information communication tools
Decisions to control changes, information communication
Tools and Outcome of Document Management Process
Document procurement, storage and updating methodology
Updating documents with changes from planned path
INFORMATION CHARACTERISTICS
The information quality shows the degree of accuracy with which the reality is represented.
The information must be reliable, comprehensive, error free, precise, clear, consistent and understandable by those who need it
is useful if it is available on time and it should be comprehensive one highlighting the critical factors.
The information should be economical enough to support the situation that warrants a decision.
The information should be adequate, excess information costs money and causes overload, while insufficient information can frustrate the decision makers efforts.
The information furnished to a manager should be relevant to his area of responsibility and what he needs to know.
2 Types of Information Needs
Stakeholder Information Needs
Functional Managers and Executives Information Needs
Stakeholder Information Needs
clients, corporate, architects, suppliers and consultants
Functional Managers and Executives Information Needs
planning/information manager, technical manager, cost and finance manager
contract manager, materials manager, plant and equipment manager
personnel manager and executives
2 Classifications for Sources of Information
Internal Sources
External Sources
Internal Sources
formal and informal reports by project team and study of standard documents
External Sources
diverse
Project Phases
Marketing
Estimating
Contracting
Design
Functional Managers and Executives
External Environments
Sources of In formation for Marketing
Govt policy, research publications, commercial journals, industry magazines, academic journals
Sources of In formation for Estimating
Construction cost indices, websites
Sources of In formation for Contracting
Contractors, govt and public sector agencies, contracting and construction related publications
Sources of In formation for Design
Architect and engineering associates, consultants
Sources of In formation for Functional Managers and Executives
Project reports, output performance, internal benchmarks, professional bodies
Sources of In formation for External Environments
Builders and consultant associations, web enabled electronic libraries, NBC and construction specifications
IT SUPPORT IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
started from 1970
Widely used for processing data electronically and communicating information in all forms including text data, graphics, voice, chat, documentation storage and combination of these.
Main benefits of IT
speedy manipulation of data and real-time information distribution to distant geographical locations. Removal of redundant information
Typical Software Applications for Low
Word processing,
spreadsheets,
accounting,
finance,
database
Typical Software Applications for Medium
Estimating,
scheduling,
simple designs,
specifications,
quantity take-off
Typical Software Applications for High
CADD,
automated information retrieval using project management software,
communication and documentation management
Typical Software Applications for Advanced
Expert systems, decision support system, artificial intelligence, 3D modelling computer-integrated building design, robots
SYSTEM COMPUTERISATION PROBLEMS
Acquiring a computerized system is a time-consuming process
It is necessary that the functional requirements of the computerized system be crystalline at the feasibility stage.
The supplier should be chosen after a thorough scrutiny
Scrutinize the system carefully before purchasing.
The last 10% of installation and commissioning is usually tricky and time consuming.
If the system does not function properly in the beginning, it does not account for failure.
Job training on the installed system will instill confidence. A detailed study of manuals may reveal extra facilities which the trainee may not have though of earlier.
The PMBOK Guide– 5th Edition defines a Project Management Information System (PMIS) as:
-An information system consisting of the tools and techniques used to gather, integrate, and disseminate the outputs of project management processes.
-It is used to support all aspects of the project from initiating through closing and can include both manual and automated systems
PMIS
A standardized software system and process utilized to efficiently manage construction project-related workflows.
typically a computer-driven system to aid a project manager in the development of the project.
can calculate schedules, costs, expectations, and likely results
to automate, organize, and provide control of the project management processes
are system tools and techniques used in project management to deliver information
used by upper and lower management to communicate with each other
Configuration management
an approach for tracking all approved changes, versions of project plans, blueprints, software numbering, and sequencing.
Tracks:
Functional and physical characteristics of the project deliverables
Control, track, and manage any changes to the project deliverables
Track any changes within the project
Allow the project management team to audit the project deliverables to confirm conformance to defined criteria for acceptance
budget framework such as estimating costs.
During the planning process, project managers use PMIS for
the project management team collects information into one database
At the execution of the project management goals
to review the goals to check if the tasks were accomplished. Then, it is used to create a final report of the project.
During the close of the project, the Project Management Information System is used
MICROSOFT PROJECT (MS PROJECT)
-dominates PM software systems
-carries its own database and is compatible with SQL Server or Oracle databases
PROJECT SCHEDULER
-works with an SQL database and is MS Office compatible.
-information from multiple projects or sub-projects can be merged or consolidated to reveal company wide resource utilization
WELCOM
has three software products: Open Plan, Cobra, and Spider
TRAKKER
offers a variety of interesting products including tools for risk management activity-based costing, earned value management as well as the usual planning, budgeting, and tracking tools
PRIMAVERA
offers four software products
SureTrak Project Manager
This software enables modeling and scheduling of simultaneous projects of up to 10,000 activities per project
Activities can be inserted or rearranged on Gantt charts and PERT charts with a mouse click.
Primavera Project Planner
This program provides for unlimited projects, up to 100,000 activities per project, concurrent, multiuser accessibility, and scheduling options similar to SureTrak
It can create fragments of networks to store for later use as templates or building blocks for creating other project plans.
Primavera Expedition Contract Control Software
This software assists in change management and tracking of contracts and purchase orders.
It enables users to view the latest submittals and schedule changes from P3 or SureTrak in real time.
Webster for Primavera
This software provides access to the project database, timecard activities, and project information from SureTrak and P3.
Team members can see assignments and can report accomplishments and time needed to complete assignments
Components of PMIS
Hardware
Software
Operators
Procedures
Hardware
Electronics and electro-mechanical equipment used in computerised data processing system.
Software
-Operating procedures and instructions in a computerised system
-undergoes constant improvements at a fast pace
Operators
Computer operators, system analysts, programmers, data preparation, personnel, information system management, data administrators, etc
Procedures
Exist in physical form– manual or instruction booklet and construction method statement
Codification
Codes transform the data into some set of predetermined string of characters by using alphabets, numeral, symbols or a combination of these.
Code for Sub-Project Robotics Automated Production System
AS
Code for Sub-Project New Conveyor System
CS
Code for Sub-Project Office Building Addition
BA
Activity identification code (ID)
is a unique code that identifies the activity.
Base Preparation Work Package
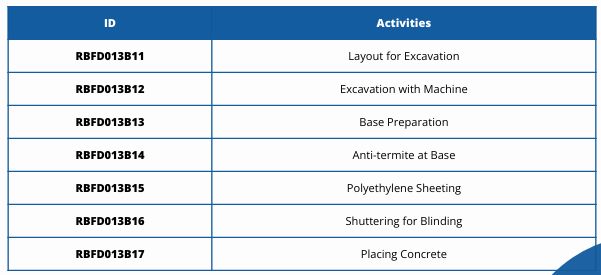
RBFD
Residential Building FOundation
013
Building Module Location Number
B
represents the Base Preparation Work Package
11 to 17
are the serial number of activities
Resources Code Dictionary
The physical resources needed for the work to be performed in a project include manpower, material and machinery
cost accountant
is responsible for the cost management information system of the project and the accounts for all the costs.
Open Plan
has advanced scheduling and modeling tools for resource management
Cobra
a cost-management tool designed to manage and analyze budgets, earned value, and forecasts
Spider
a multiuser, multi project web-based tool for viewing and updating project data from Open Plan user Web browsers
WEB-BASED PMIS
-especially helpful in situations where project team members are located at different sites
-immediate availability of project information, efficiency and accessibility for communicating with workers, ease of learning and usage, and reliability and currency of information because it is entered and communicated in real time
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Codes
a most valuable tool as it enables the project manager to manage the project successfully.