Chapter 4 physiology
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon
what elements make up 96% of the human body?
carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins
what are the 4 major compounds that make up human life?
they lack carbon
key quality of inorganic compounds
salts, minerals, water, acids, bases, ions
key inorganic compounds
organic compounds
which is typically larger? organic or inorganic compounds?
organic compounds
a compound disolves in water which means it is…?
inorganic compounds
a compound dissociates in water which means it is….?
cell membrane
communication and boundary for the cell with selective permeability
cytosol
fluid portion of cytoplasm
cytoplasm
cytosol containing organelles
cytosol
metabolism occurs here
growth, repair, DNA continuity, forms tissues
function of somatic cell division?
tissues
a group of similar cells functioning together
histology
study of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve
what are the 4 types of tissues
covers exposed surfaces and lines internal passageways and forms glands
function of epithelial tissues
carcinoma
epithelial tissue that has become cancerous
epithelial tissue
avascular tissue
epithelial tissue
tissue that is excellent at regeneration
epithelial tissue
tissue that is subject to mechanical stress
cell adhesion molecules
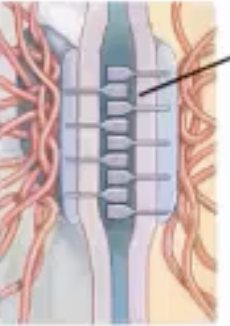
type of transmembrane protein
hemidesmosomes
proteins that hold tissue to basement membrane
secretion and absorption
function of simple epithelium tissues
simple squamous epithelium
what tissue lines the pericardium (lungs)
simple cuboidal epithelium
what tissue lines the kidney tubule for urine secretion?
simple columnar
what tissue lines your intestine for nutrient absorption
for protection from trauma and wear and tear and stretching
what is the function of stratified epithelial tissue
stratified squamous epithelium
what tissue lines the vaginal canal?
stratified cuboidal epithelium
what tissue lines the milk ducts in the breast?
stratified columnar epithelium
what tissue lines the throat for protection?
stratified transitional epithelium
what tissue lines the urinary bladder for stretch and protection?
sweeping / cleaning and moving fluids along a surface
function of psuedostratified epithelium
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
what tissue lines the respiratory tract?
endocrine glandular epithelium
release secretions directly into the blood without the use of ducts
endocrine glandular epithelium
exocrine glandular epithelium
exocrine glandular epithelium
secretes non-hormones to the tissues of the body using ducts
connects structures together
fills internal spaces
transports materials
stores energy
forms internal support
what are the functions of connective tissue
sarcoma
when non-epithelial tissue becomes cancerous
connective tissue
what is the most abundant tissue in the body
connective tissue
very vascular tissue
connective tissue
not easily regenerated tissue
ground substance
the “glue” that holds the connective tissue together
ground substance and protein fibers
what make up the matrix of connective tissues?
extracellular
is the matrix of connective tissue intracellular or extracellular?
adipose
areolar
reticular
what are the 3 loose connective tissues?
regular
irregular
elastic
what are the 3 dense connective tissues?
hyaline
elastic
fibrous
what are the 3 cartilage types of connective tissue?
fibroblasts
what type of cells are in the loose and dense connective tissue
chondrocytes
waht type of cell makes up cartilage?
osteocyte
what cell type is in bone
white cell
red cell
platelets
what cells make up blood
white blood cells (lymphocytes)
what type of blood cells are in lymph?
hyalauronic acid
what is the ground substance in loose and dense connective tissue?
chondroitan sulfate
what ground substance is in cartilage
mineral salt crystals
what ground substance is in bone?
water (plasma)
what is the ground substance in blood? and lymph?
around organs
where is areolar tissue found in the body?
stores fat as triglycerides, and insulates
function of adipose tissue
internal support for organs
function of reticular tissue
tendons and ligaments
what does dense regular tissue make up?
forms fasciae and membranes
what does dense irregular tissue make in the body
lung and in the aorta
where is elastic connective tissue found?
lacunae
where chondrocytes sit in their cartilage
hyaline cartilage
cartilage that is flexible and makes up joints
fibrous cartilage
shock absorbing tissue in discs
elastic cartilage
cartilage that bends and is resilient in the outer ear
defense, transport, and clotting
functions of blood
movement and thermogenesis
function of muscle tissue
vascular
parallel arranged cells
limited regeneration
characteristics of muscle tissue
muscle hypertrophy
muscle cells increase in size not number
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
order of somatic cell division
division of germinative cells (stem cells) located near the basement membrane
how is epithelial tissue replaced?
osteosarcoma
name of bone cancer
chondrosarcoma
name of cartilage cancer
smooth, skeletal, and cardiac
what are the 3 types of muscle
carries electrical signals from one part of the body to the next
function of nervous tissue