Cell Biology EXAM 1
1/280
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
281 Terms
A genetic disease in which patients age so rapidly they die in their second decade of life from advanced atherosclerosis, which is typically a disease of the elderly
Progeria
2 important functions of nucleus:
Nuclear transport (import vs export)
Role of nuclear lamins in membrane assembly/disassembly
by studying Progeria, we could expect to learn more about:
aging and cardiovascular disease (structure/function of nucleus)
what are some things that can pass through the nuclear ring via diffusion?
tiny things (nutrients, vitamins, hormones, steroid hormones, small peptide hormones)
what connects chromatin to the nuclear membrane?
nuclear lamins (type of IF)
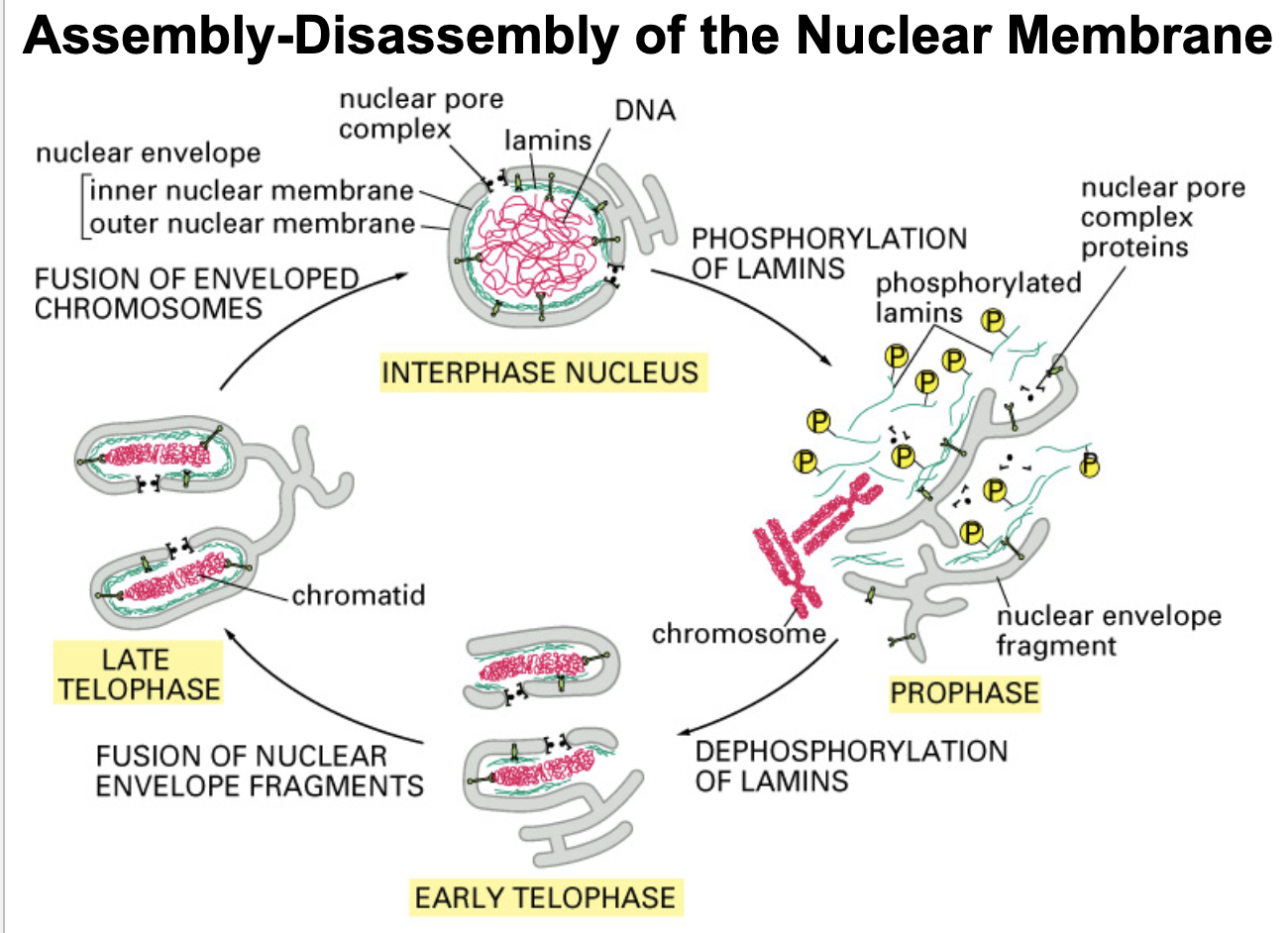
during interphase, nuclear lamins are _______
dephosphorylated
what initiates the beginning of mitosis?
lamin phosphorylation (done by kinase)
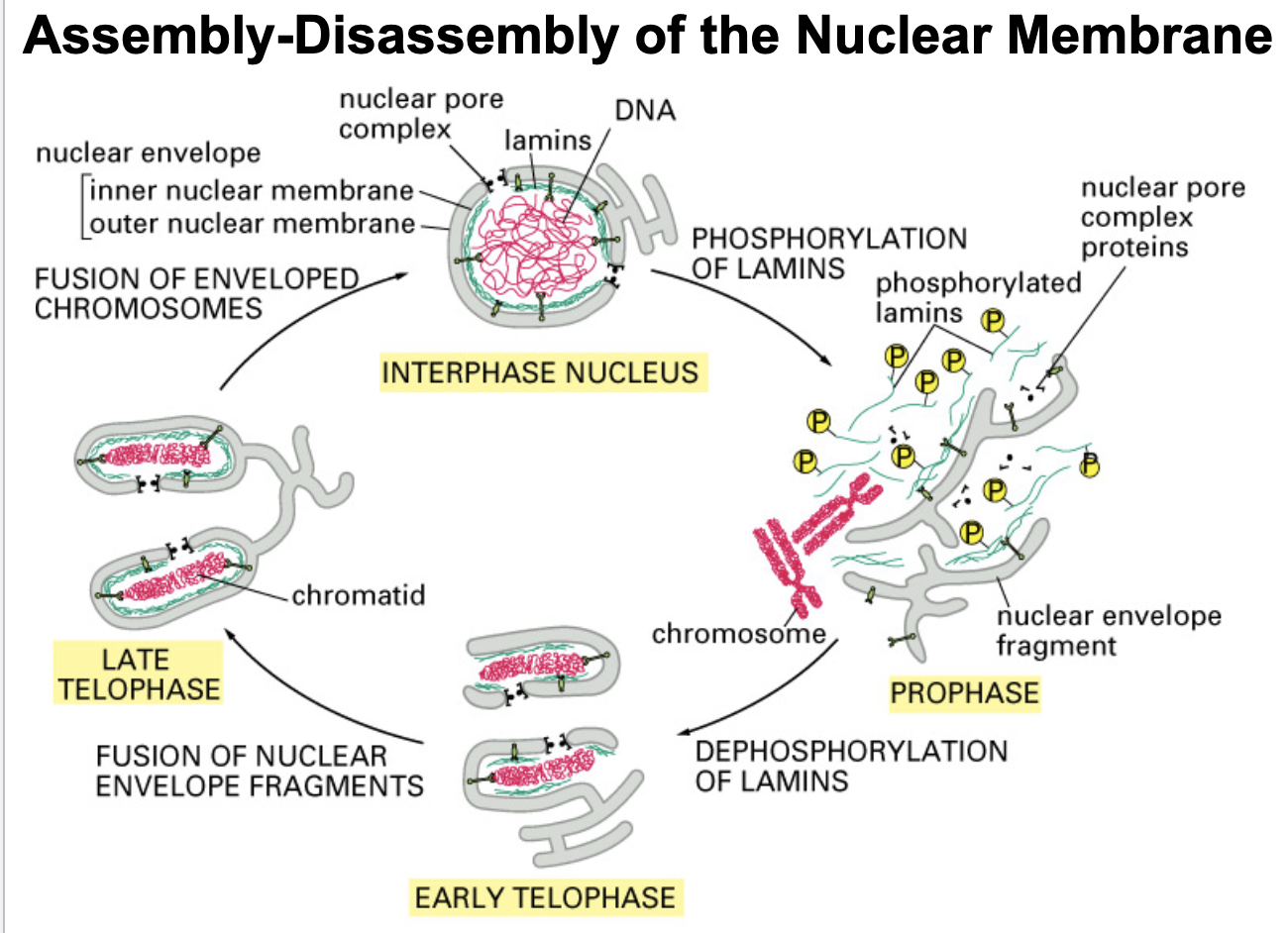
what allows/ initiates the condensation of chromosomes in preparation to replicate?
lamin phosphorylation
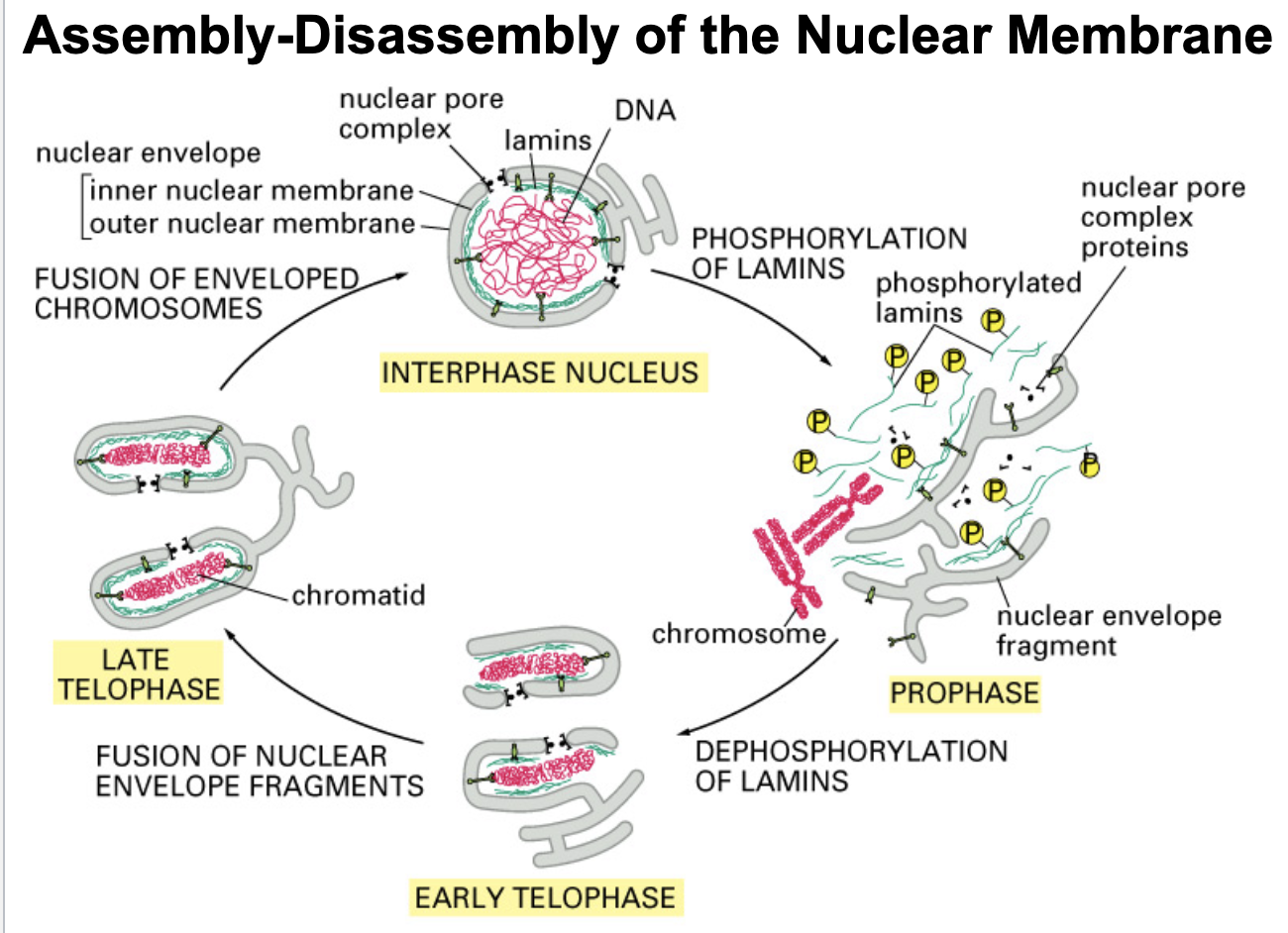
During interphase, when the nuclear envelope is intact, lamins are in the _________ state
dephosphorylated
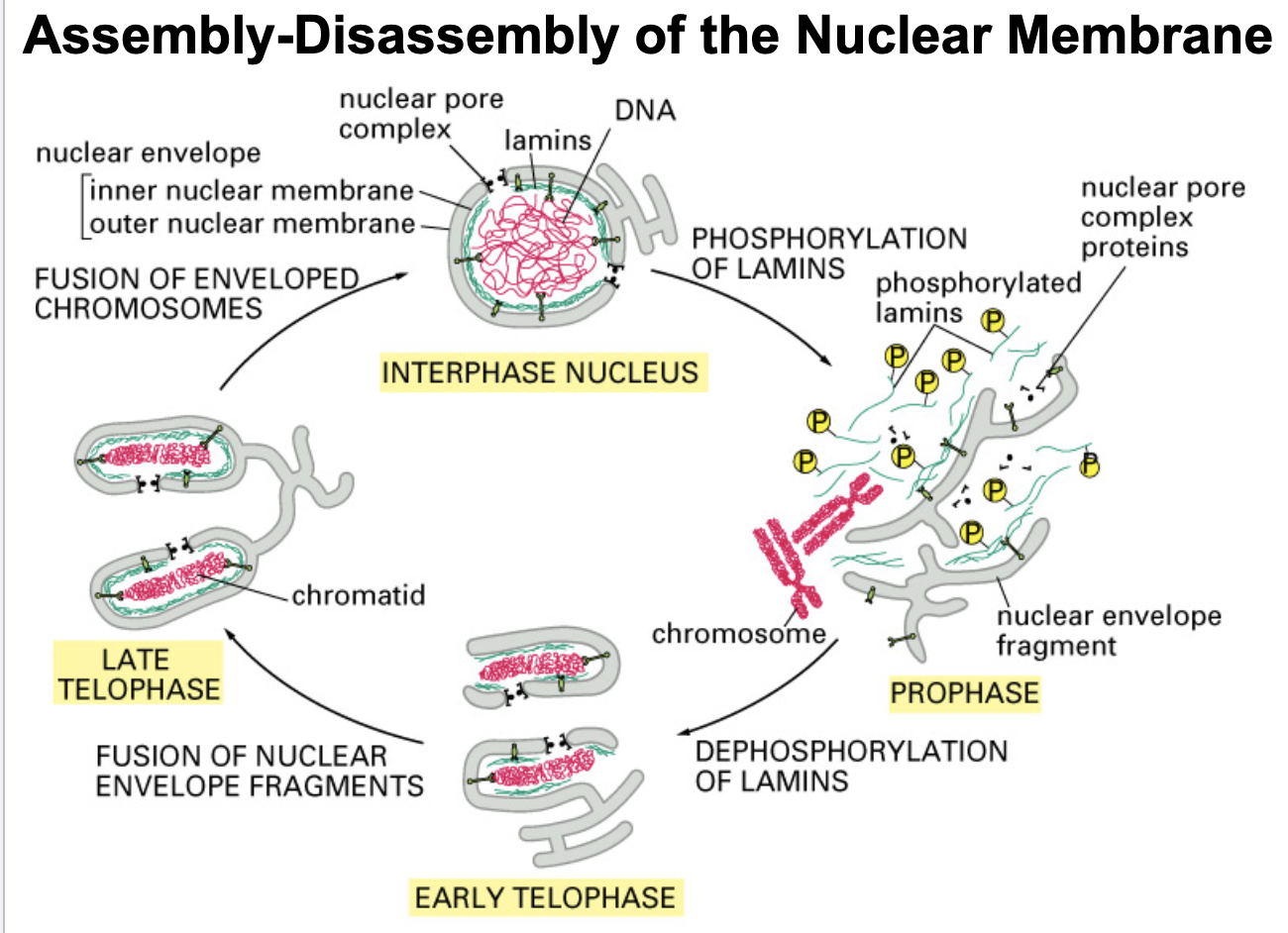
Early in mitosis, lamins are ________ causing the chromatin-nuclear membrane connection to break, thus beginning the process of nuclear membrane disassembly
phosphorylated
Cargo smaller than ____ kDa can enter nucleus via diffusion through nuclear pores
5-10
Cargo smaller than 5-10 kDa can enter nucleus via diffusion through nuclear pores, but larger cargo must be _______ transported through nuclear pores
actively
which part of the nuclear pore opens/closes but can’t keep really small things out?
nuclear ring
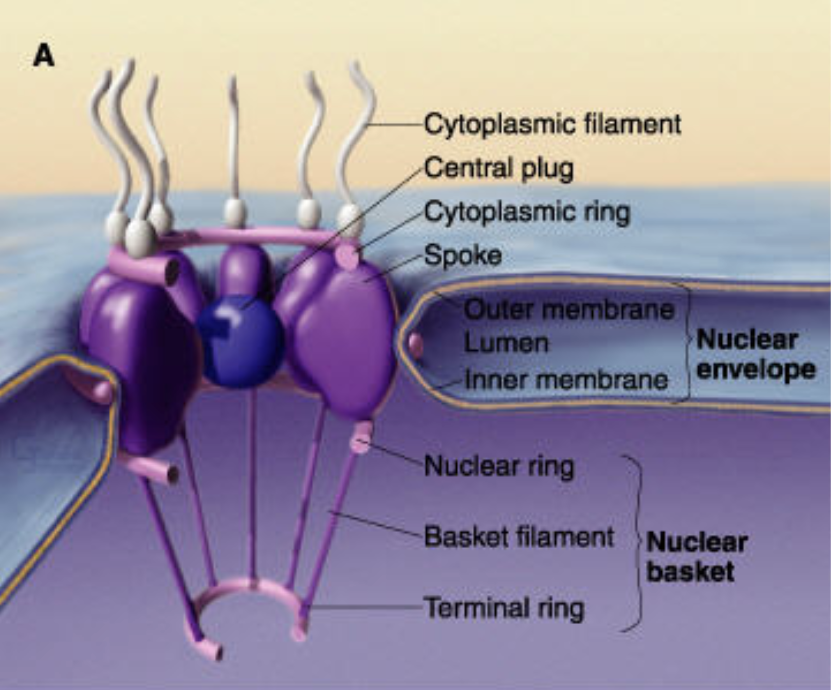
what are importins?
chaperone proteins that escort newly synthesized proteins with an NLS to the nuclear pore
Chaperone proteins bind to _______ on cargo and escort cargo into nuclear pore
nuclear localization signals (NLS)
proteins and ribonucleo-protein complexes destined for export have Nuclear Export Signals that are recognized by _______
exportins
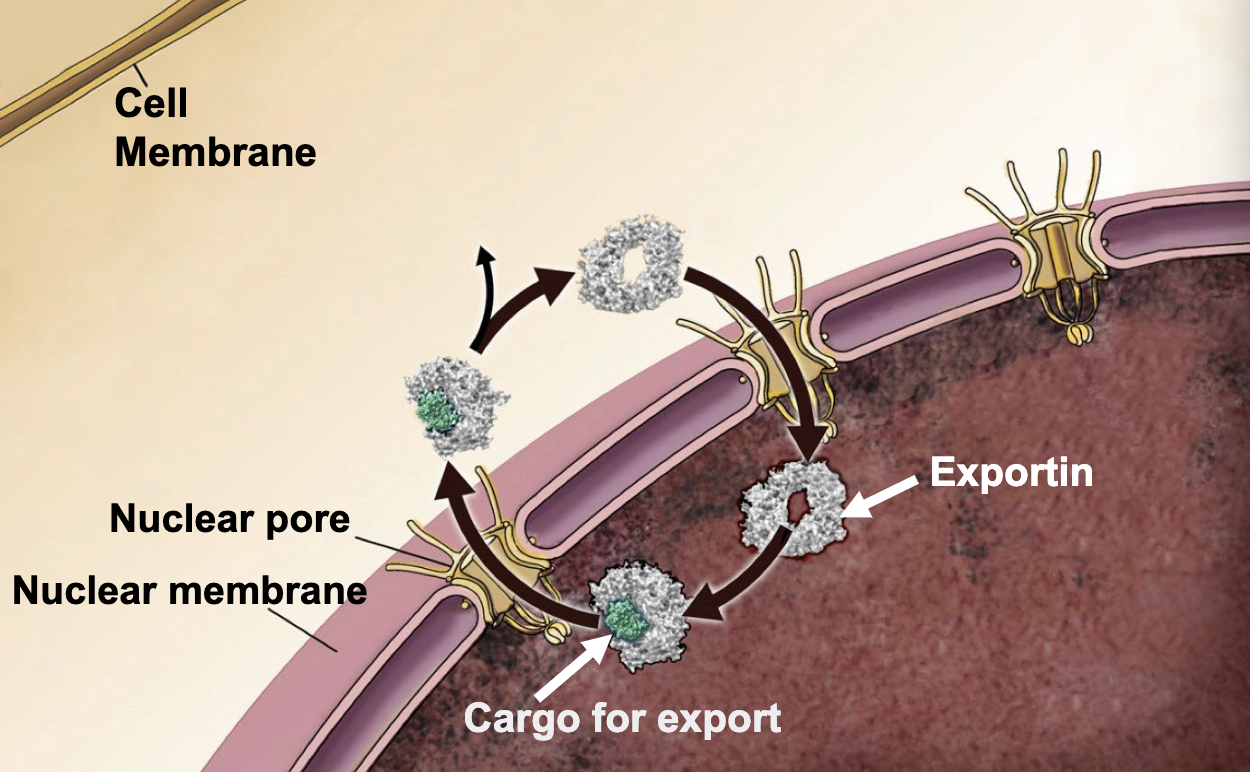
proteins and ribonucleo-protein complexes destined for export have __________ that are recognized by exportins
nuclear export signals (NES)
specializes in exporting tumor suppressors, apoptosis inducers, and anti-proliferative molecules that exert their normal biological activities via binding to DNA
exportin-1
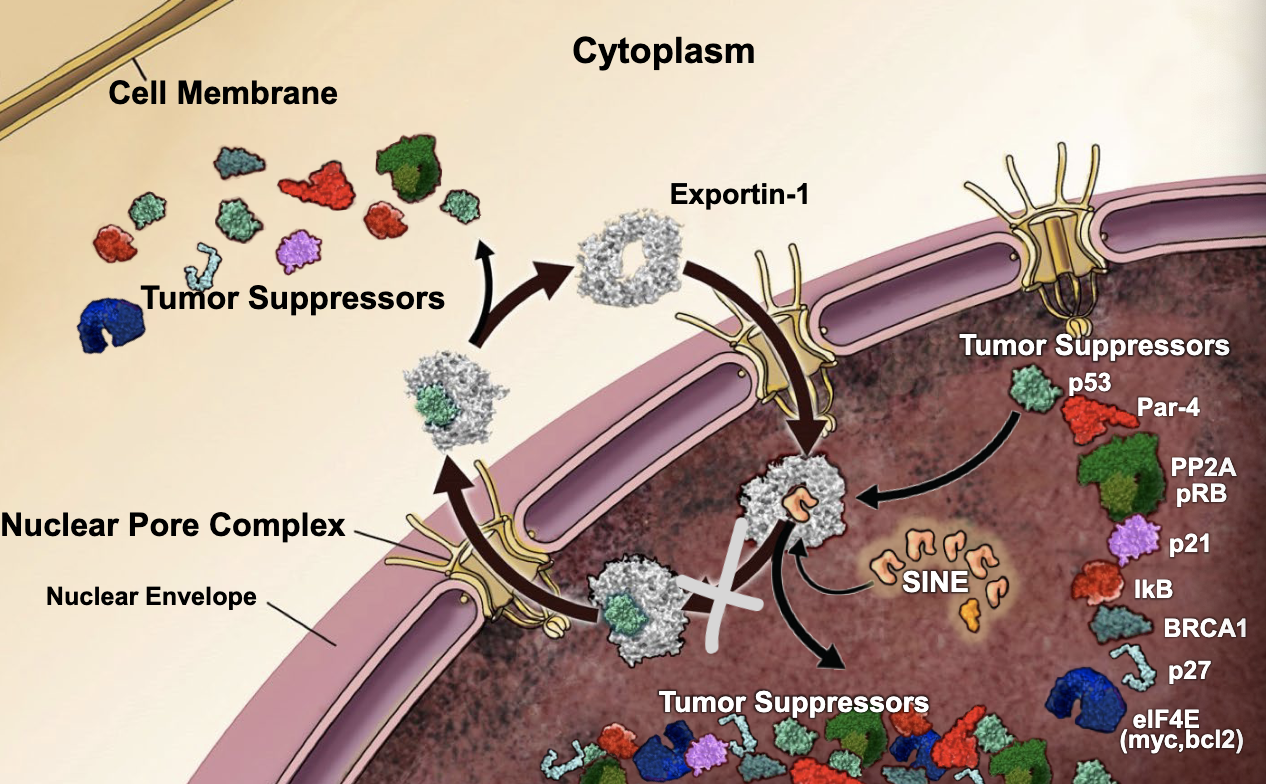
Cancer cells greatly over-express ________ resulting in a death of tumor suppressors, apoptosis inducers, and anti-proliferative molecules in the nucleus, which leads to excessive cell proliferation, ie, tumor growth
exportin-1
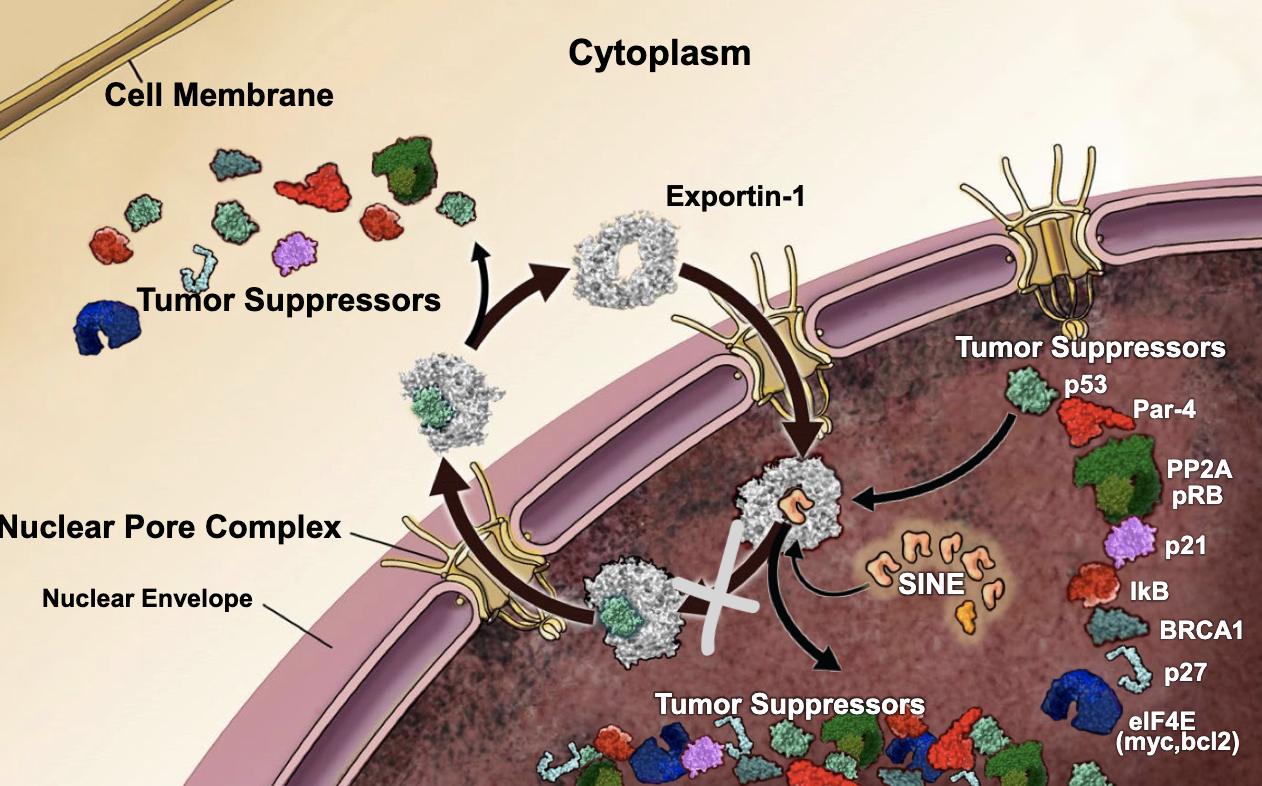
by targeting the exportin-1 protein to decrease its presence in the nucleus, you should see an _________ in tumor suppressors within the nucleus
increase
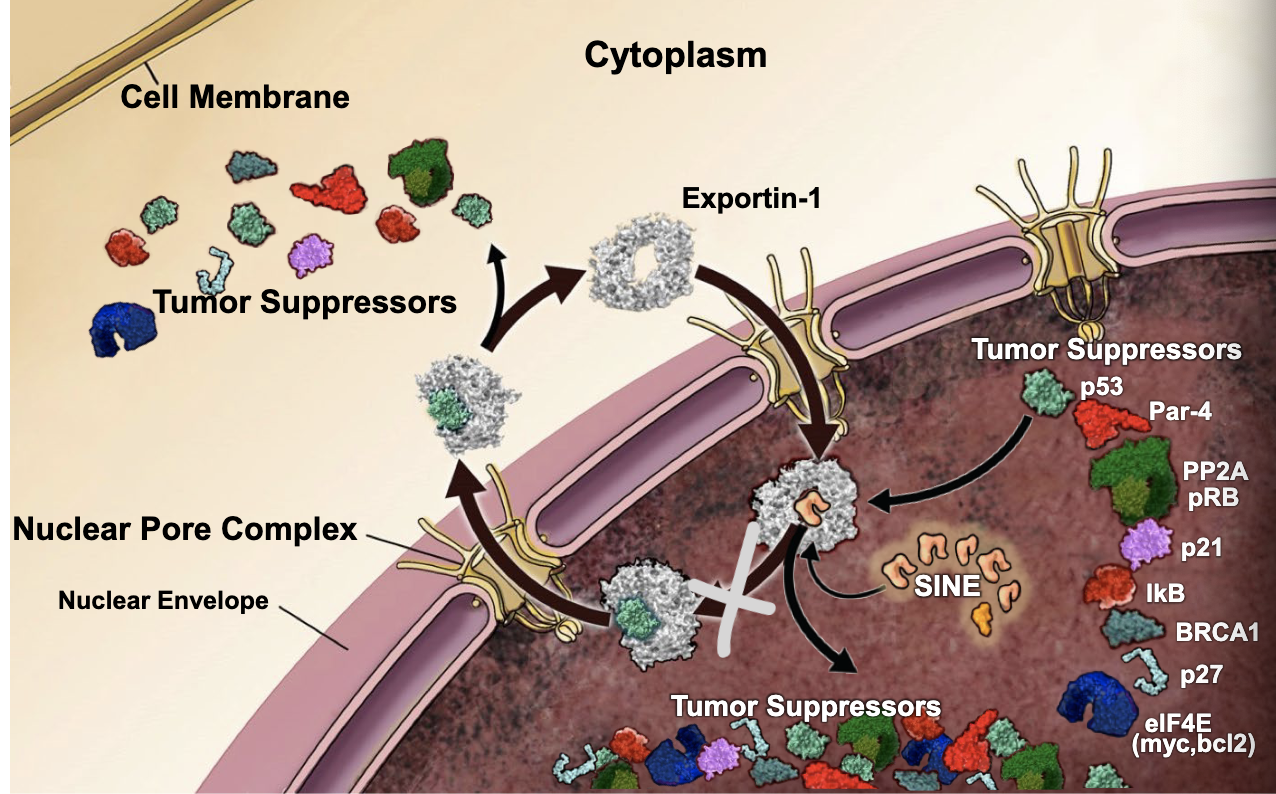
small molecules that block the pocket on exportin-1, thus keeping tumor suppressors in the nucleus:
selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINEs)
what type of disease is Progeria?
laminopathy
Huntington's Disease is caused by what change in normal nuclear transport?
nuclear import
what nuclear function does SINEs (anti-cancer drugs) attack?
nuclear export
what feature of the Huntingin fragments allow them to bypass the nuclear import regulation?
- phosphorylation
- size
- sequence
size
this disease is caused by small fragments of miss-folded protein entering the nuclear pores due to their small size and negatively affecting the cells nucleus
Huntington's disease
cytoplasmic protein Huntingtin is mutated via addition of multiple _________ residues
glutamine
what AA sequence is found in mutated repeats in the Huntingtin gene?
CAG
during gene testing, a patient is found to have many trinucleotide CAG repeats in the HTT gene. This is a diagnostic characteristic of what disease?
Huntington's disease
forms a strong network beneath nuclear membrane and connects nuclear membrane to chromatin
nuclear lamina (flexible but strong)
the nuclear lamina is made up of
3 proteins
most membranes contain roughly _____ % protein
50
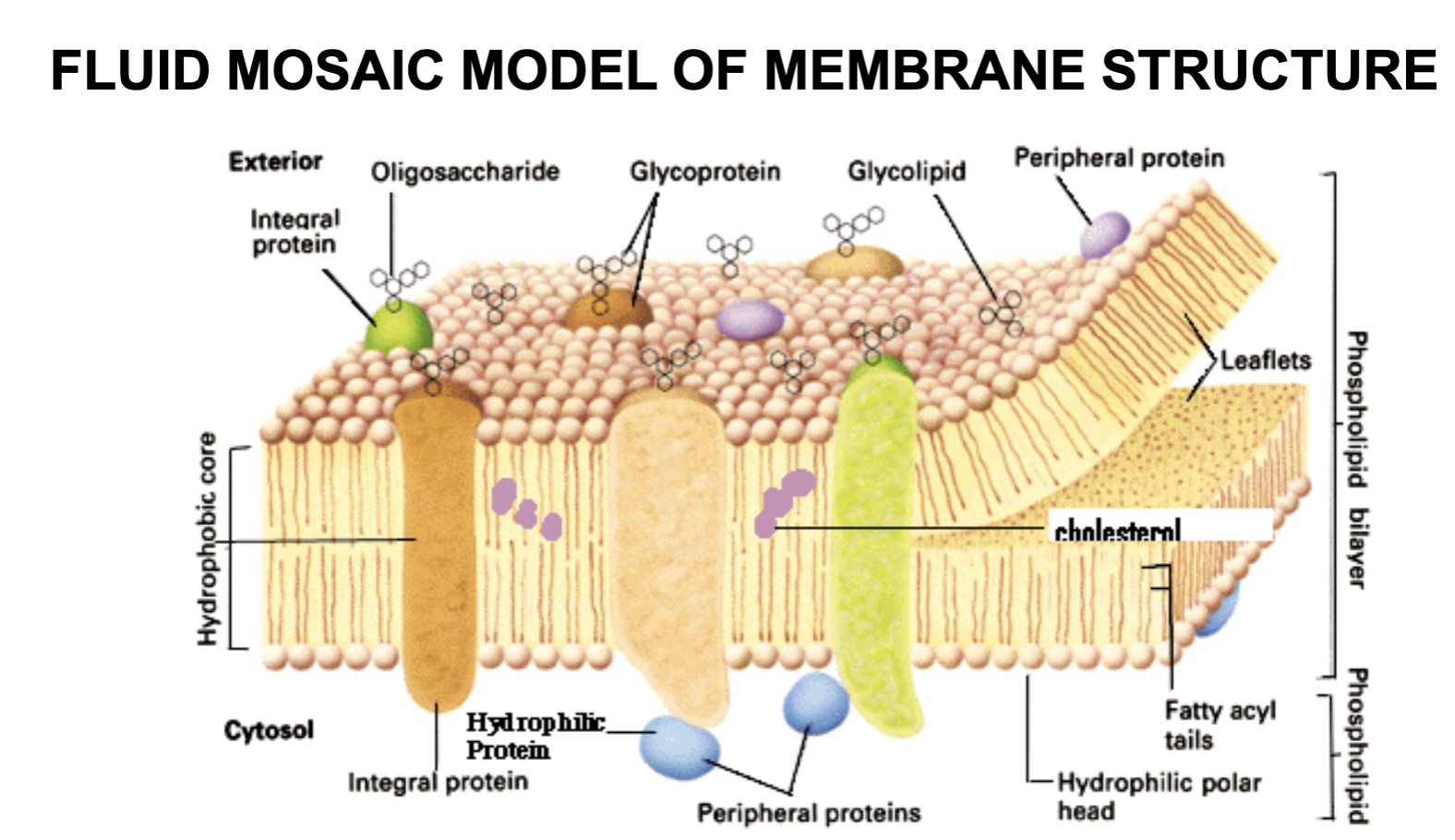
what are peripheral proteins on both sides of membrane that help anchor membrane and connect it to the matrix?
oligosaccharides
glycoproteins
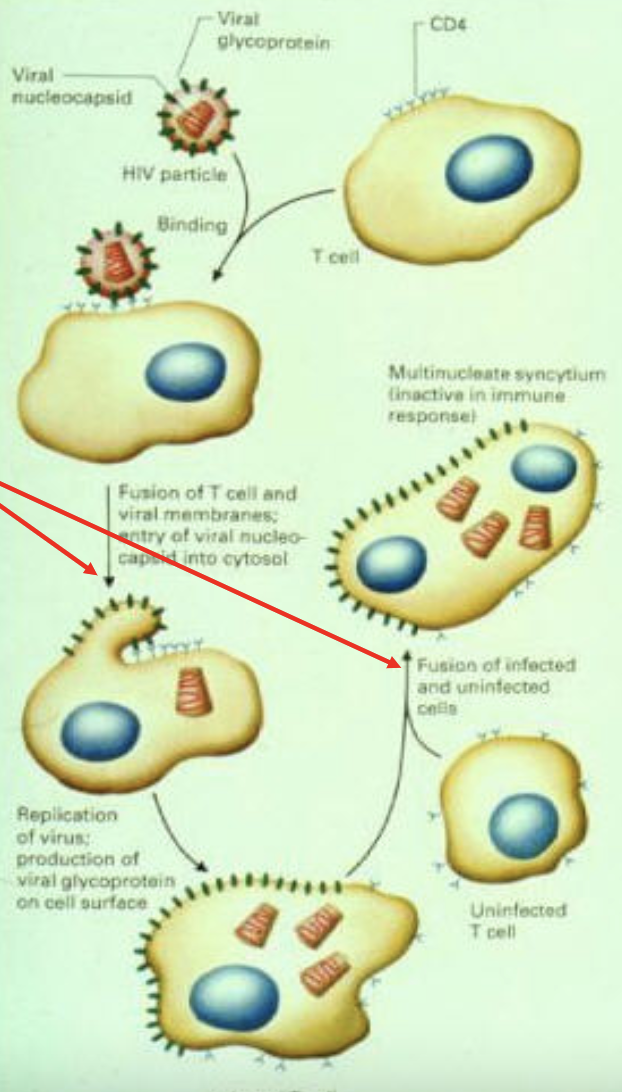
describe how HIV enters target cells via protein receptor interactions
HIV particle binds to receptors on target cell
Puts phospholipid membranes of HIV and target cell in close apposition (allows fusion)
Viral nucleocapsid can now enter cytosol of target cell
Virus is replicated and infected target cell can continue to fuse with other uninfected target cells to create multinucleate particle
what are the classes of membrane lipids?
phospholipids (most abundant)
sphingolipids
cholesterol
eicosanoid (least abundant)
what is the critical lipid component of the plasma membrane?
eicosanoids
most common form of pneumonia
mycoplasma pneumonia
mycoplasma pneumonia is also known as
walking pneumonia
mycoplasma pneumonia is a disease of altered
membrane fluidity
interaction of coccidial parasites with cell surface carbohydrates
coccidiosis
disease that’s transmitted via cat feces and can cause severe birth defects in offspring of infected pregnant women
toxoplasmosis
most membranes contain roughly _____ % fat
50
most membranes contain roughly _____ % carbohydrates
<10 (small amount)
the chemical composition of myelin membrane is mostly _______. why?
lipid
function of myeline sheath is to prevent signals jumping from one nerve to another. lipid does not conduct electricity.
the chemical composition of mitochondrial inner membrane is mostly _______. why?
protein
function of mitochondrial inner membrane is oxidative phosphorylation machinery is protein
phospholipid bilayer (cytoplasmic leaflet and extracellular leaflet)
Proteins embedded within membrane (transmembrane, some only part way through)
Peripheral proteins on both sides of membrane that help anchor membrane and connect to matrix
fluid mosaic model
t/f: lipids are Asymmetrically distributed across the plasma membrane
true
which lipid membrane is more fluid: inner or outer?
outer membrane
what are two key propertied of membrane lipids?
fluidity
fusogenicity
ability to spontaneously fuse (no energy requirement)
key property of membrane lipids
fusogenecity
prostaglandin PGE2 is a ________ that induces uterine contractions
eicosanoids
where are prostaglandins found?
Source: kidney, spleen, heart, platelet aggregation
where are thromboxanes found?
platelets
too many thromboxanes mean
clotting problems
where are leukotrienes found?
immune cells, epithelium
where are eicosanoids found?
- cytoplasm
- plasma membrane
- nucleoplasm
- ECM
plasma membrane
what eicosanoid induces uterine contractions?
PGE2
what eicosanoid induces vasodilation and bronchoconstriction in asthma and anaphylaxis:
leukotrienes
what eicosanoid induces platelet aggregation (first step in clotting) and vasoconstriction:
thromboxanes
what are the 3 classes of eicosanoids?
prostaglandins (PGE2)
thromboxanes
leukotrienes
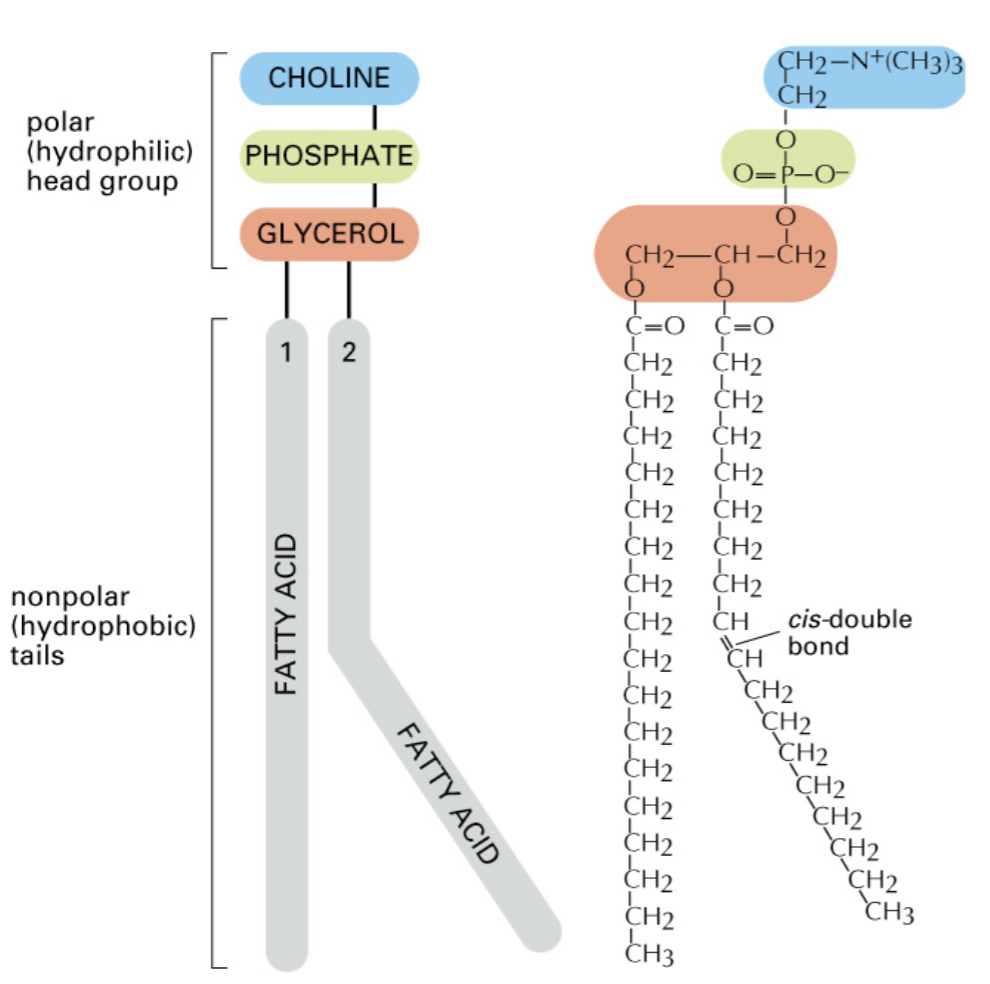
cis double bonds cause kinks in fatty acid chains, contributing to _______ of the membrane
fluidity (kink increases entropy, takes up more space)
unsaturated phospholipids have at least 1
cis-double bond (more fluid)
trans fats are bad because
trans-double bond = no kink
stiffens membrane
HIV and measles viruses takes advantage of the ______ property of phospholipids to enter the cell membrane
fusogenicity
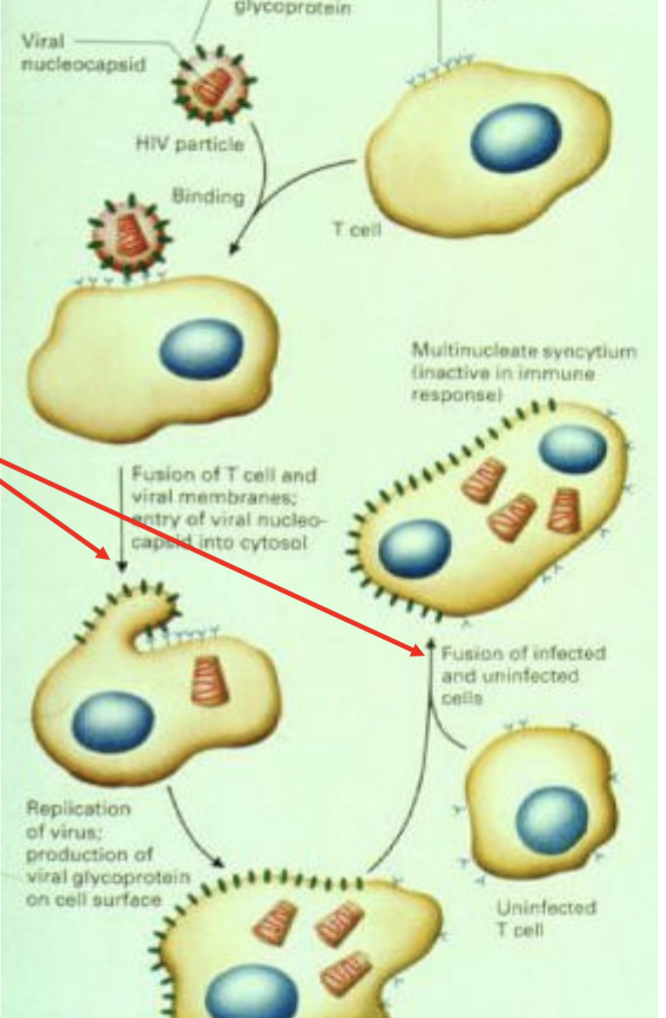
name two diseases that take advantage of the fusogenicity of the plasma membrane to infect the host:
HIV
measles
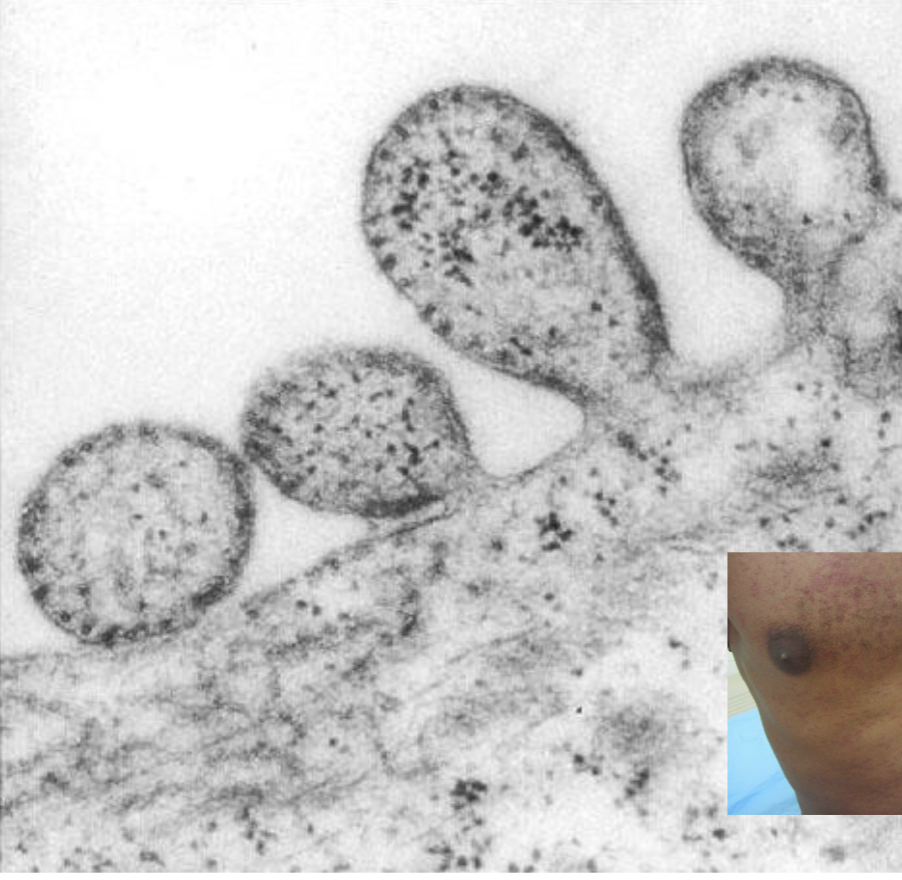
what is this?
measles virus
what is the difference between a sphingolipid and a phospholipid?
saturated fatty acid chains (stiff, trans-double bond)
the proliferation of mycoplasm pneumonia in respiratory cilia is due to the extraction of ________, causing the cilia to be overly fluid, limp over and become ultimately dysfinctional, no longer allowing them to remove mucus from repspiratory tract
cholesterol
t/f: sphingolipid lack fusogenicity, although the structure is similar to that of a phospholipid's. why?
true (2 straight-chain saturated fatty acids = rigid)
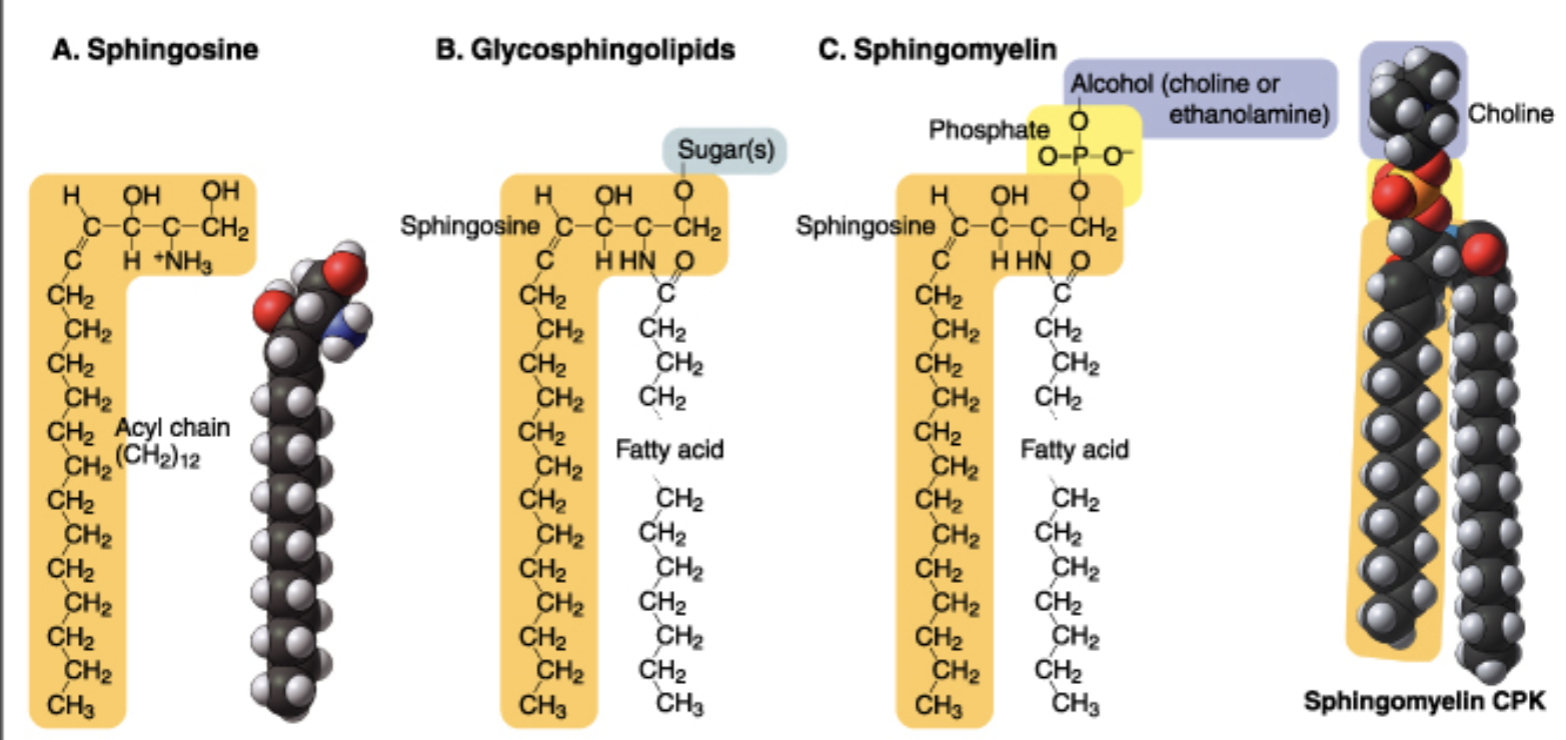
typical phospholipid/sphingolipid fatty acid chains are ___-___ carbons long
16-18
factors affecting membrane fluidity
double bonds
acyl chain length (short = more fluid, long = less fluid)
temperature (high = more fluid, low = less fluid)
cholesterol (high = less fluid, low = more fluid)
cilia needs (amount of cholesterol)
optimum amount of cholesterol (more/less is not better)
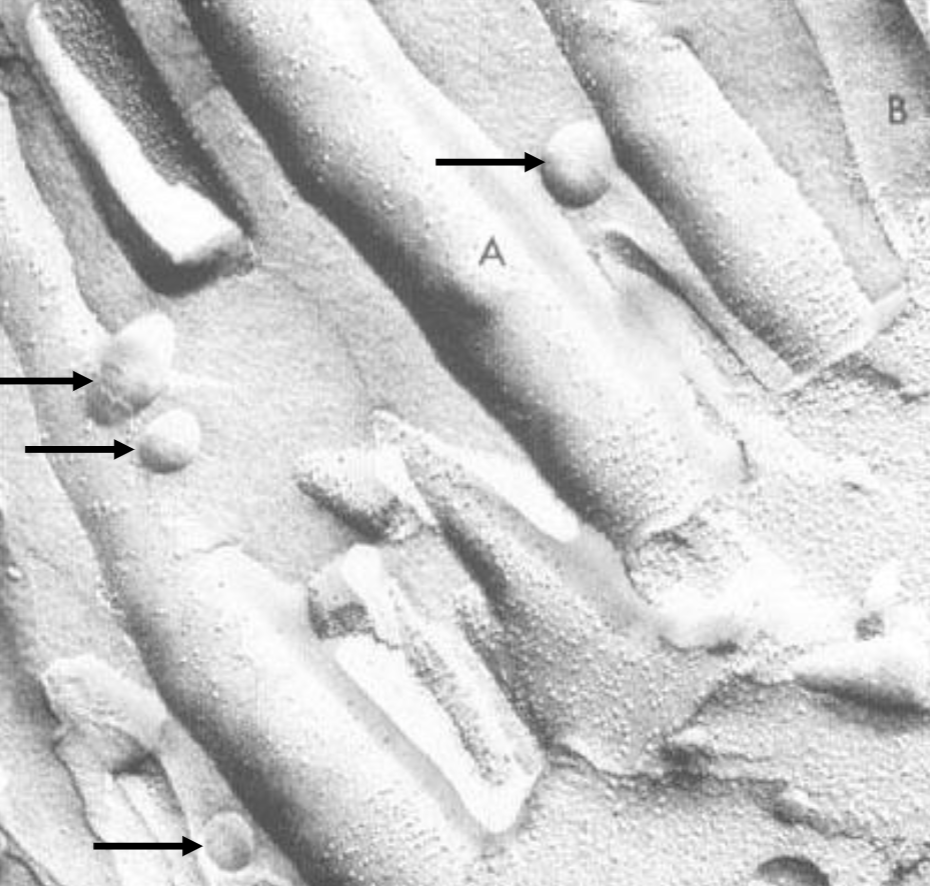
what is this?
mycrophilia attaching to base of respiratory cilia to suck out cholesterol
patients with Hunter's (Mucopolysaccharidosis IV (MPS IV)) disease exhibit a urinalysis with a high amount of:
GAGs
why is erythrocytes (RBCs) great model system for membrane studies?
easy to separate membranes (no nucleus, hypertonic solution bursts cells easily)
what is the most common LSD (lysosomal storage disease)?
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS)
what is the 1st LSD to be cured with enzyme replacement therapy?
Farby Disease
the accumulation of GAGs in the body may be a sign of that disease?
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS)
an increase in double bonds will ______ membrane fluidity
increase
a decrease in double bonds will ______ membrane fluidity
decrease
shorter acyl chain lengths will ______ membrane fluidity
increase
longer acyl chain lengths will ______ membrane fluidity
decrease
increase in temperature will ______ membrane fluidity
increase
decrease in temperature will ______ membrane fluidity
decrease
increase in cholesterol content will ______ membrane fluidity
decrease
decrease in cholesterol content will ______ membrane fluidity
increase
how many amino acids does it take to span the membrane?
20-25 aas
proteins may have # membrane-spanning segments
15+
transmembrane proteins have mostly ______ molecules
hydrophobic
mycoplasma can attach to the base of respiratory cilia and remove the cholestrol from the cilia causing dysfunction due to _________ fluidity
too much
what molecules contribute to determining blood types?
carbohydrates
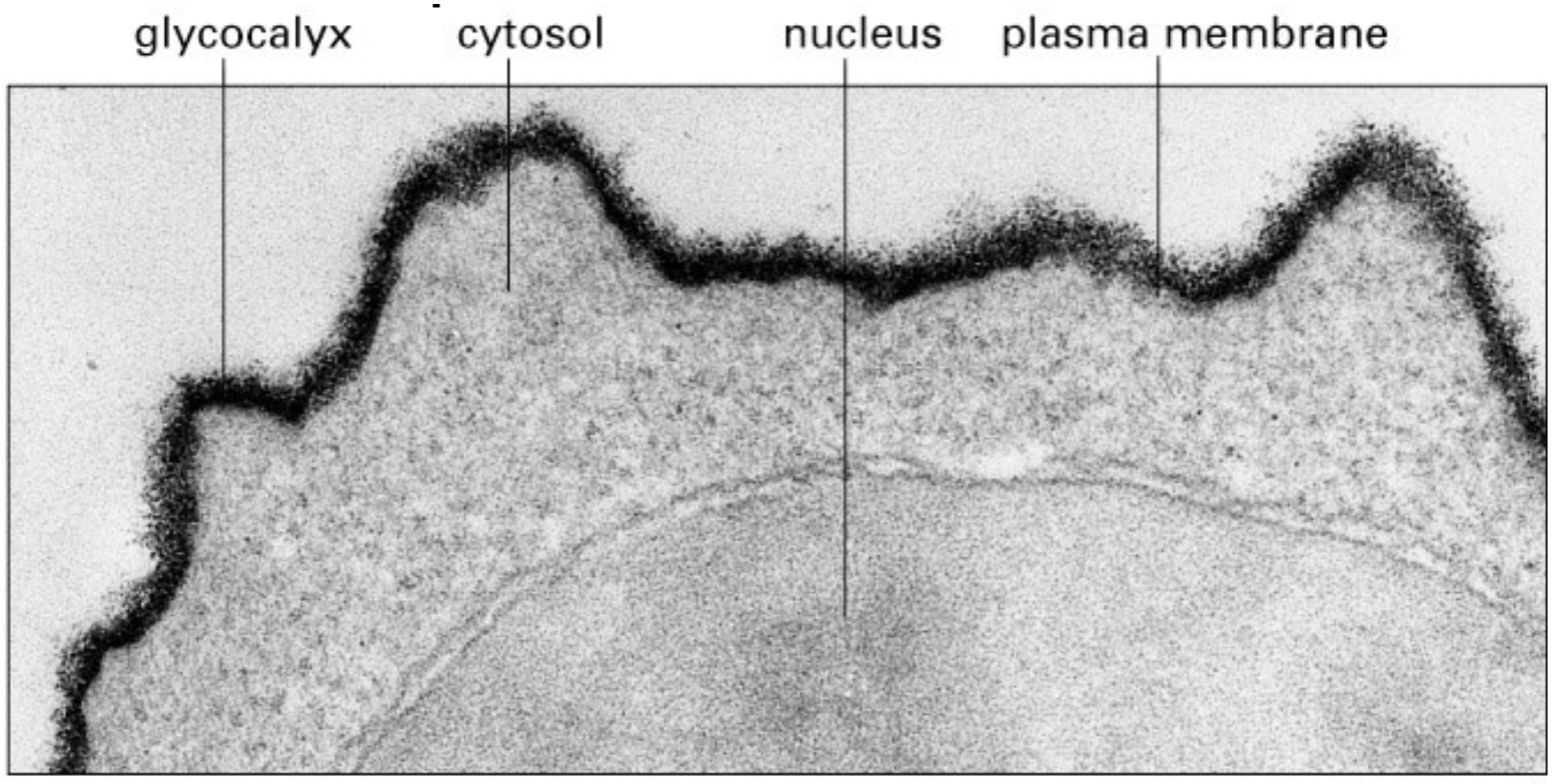
what molecules are used in pathogen recognition sites?
carbohydrates
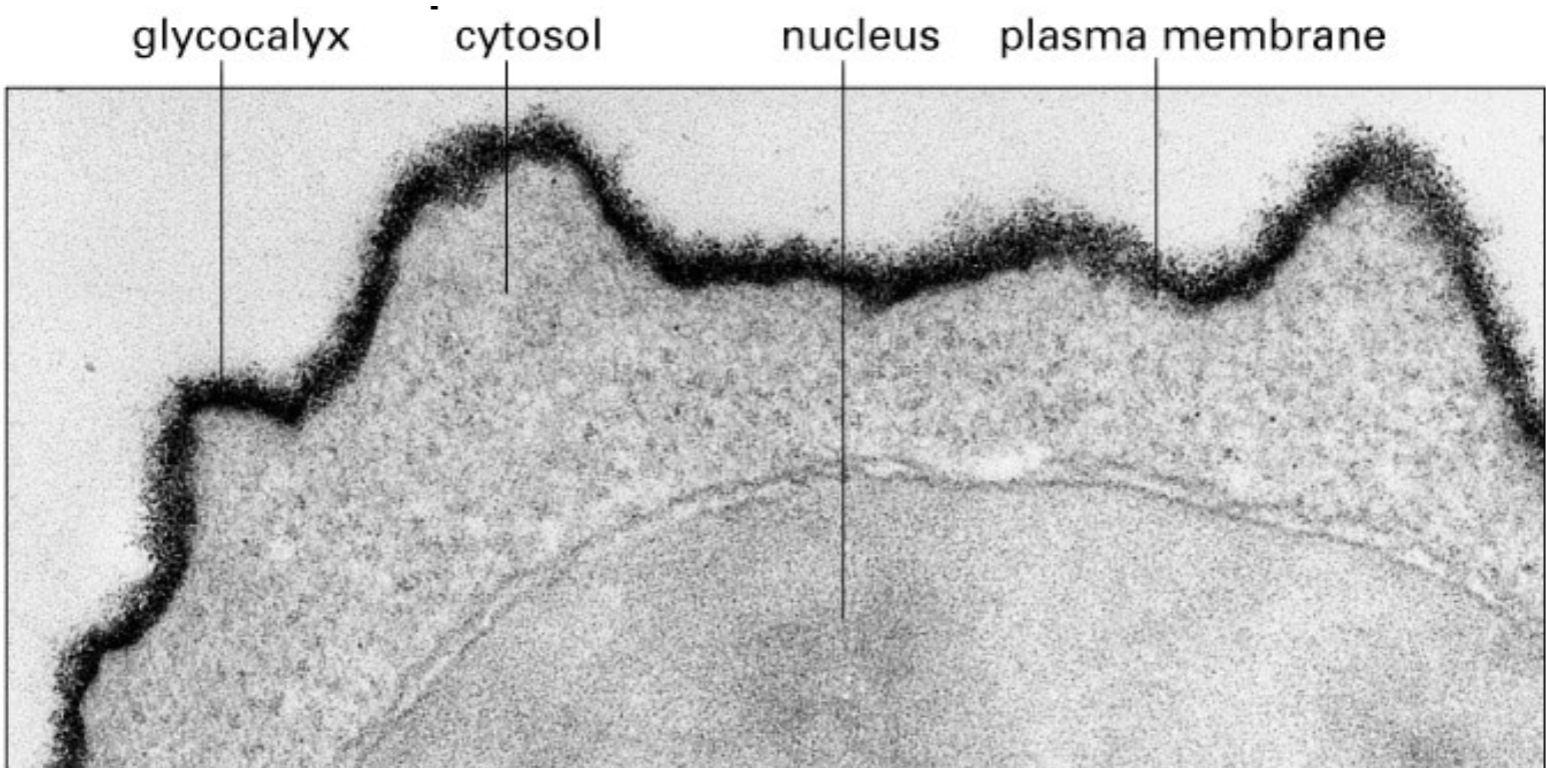
what molecules are used as reservoir for cytokines/growth factor?
carbohydrates (sequester or release these growth factors)
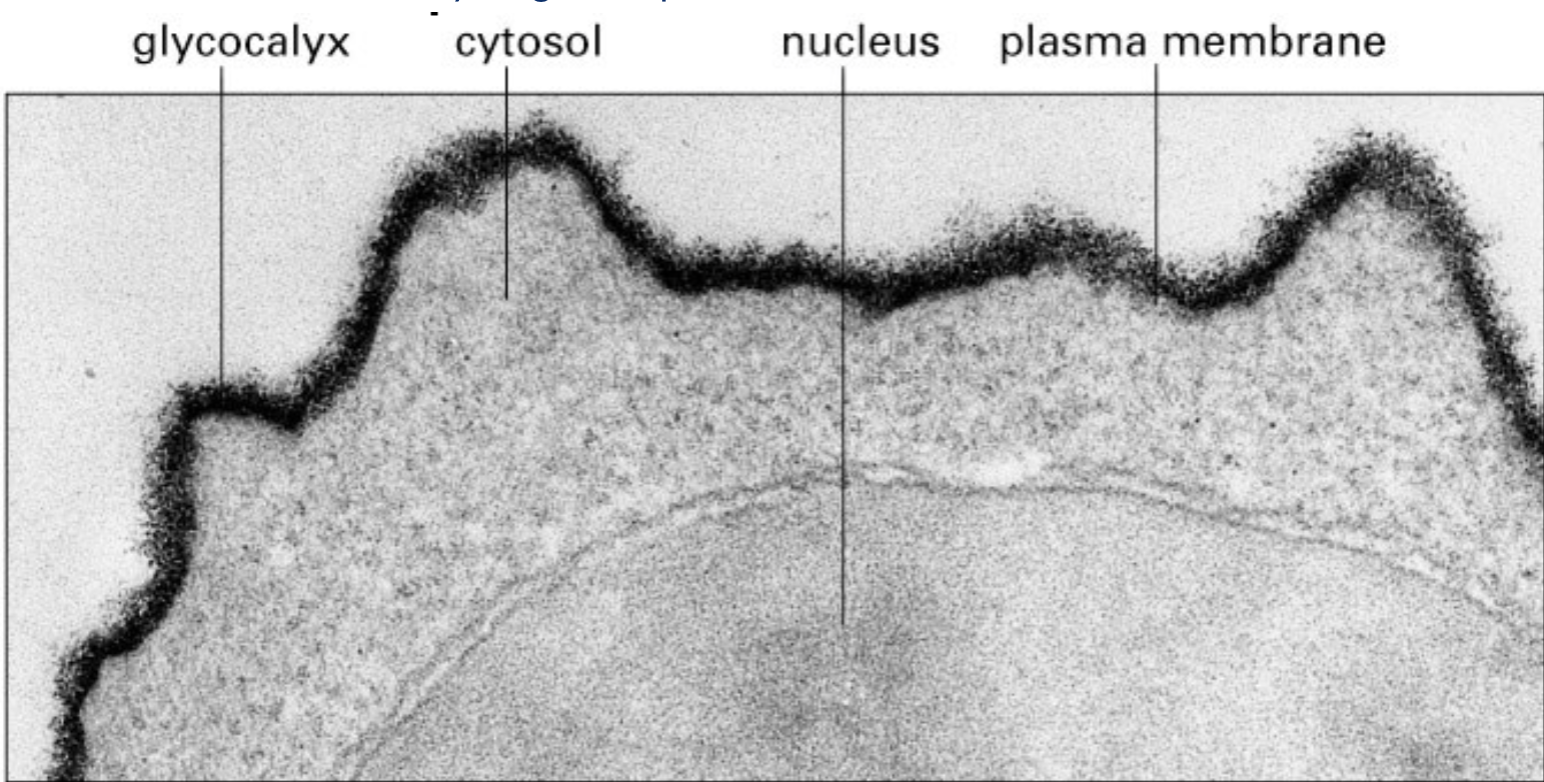
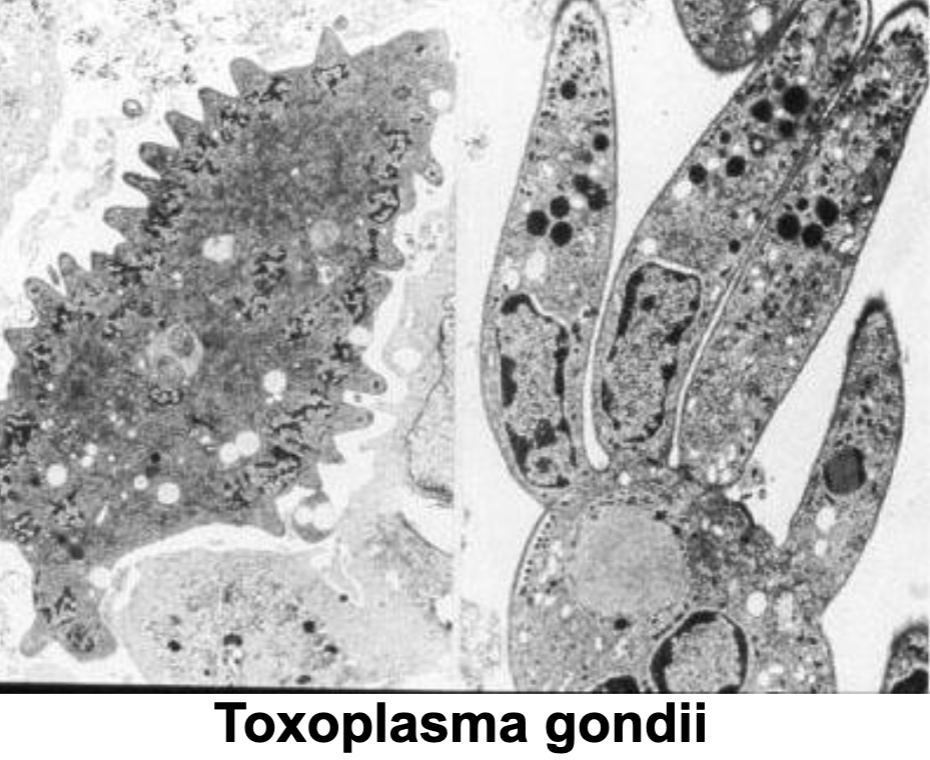
Toxoplasma gondii parasite works by entering the IG tract and recognizes specific __________ on intestinal epithelial cells to then invade and destroy cells
carbohydrates
If it's a bacteria or bigger it gets into cells via:
phagocytosis
rabies and influenza takes advantage of which transport mechanism?
receptor-mediated endocytosis
mesothelioma is caused by
defect in mitotic spindles (due to incorporation of asbestos fibers) blocking normal chromosome distribution
mesothelioma can lead to
aneuploidy, cancer
how to calculate pack-years?
#of packs smoked a day x # of years = pack-year
what is the dilemma facing mammalian cells?
needs such varying concentrations of different types of components inside vs outside the cell (eg. low sodium, but high potassium)