Week 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
René Descartes
laid the foundation for rationalism
2
New cards
rationalism
the principle that some kinds of knowledge are innate, and others can be acquired through reasoning, independent of experience
3
New cards
John Locke and David Hume
We learn by association
empiricism
empiricism
4
New cards
Tabula rasa
analogy ==Locke== used to describe how our mind begins as a blank sheet on which life experiences write our reality (==“blank slate”==)
5
New cards
empiricism
the principle that knowledge is acquired only through experience
6
New cards
Immanuel Kant
we have no knowledge of reality, rather our mind forms appearances of reality
7
New cards
paradigm shift
a fundamental change in the prevailing model or theoretical orientation
^^Thomas Kuhn^^
^^Thomas Kuhn^^
8
New cards
personal knowledge, mass media, official state knowledge, theoretical knowledge
Factors that shape public perceptions of crime
9
New cards
net widening
process in which new sentencing options increase instead of reduce control over offenders' lives
\
Brian MacLean
\
Brian MacLean
10
New cards
vicarious reinforcement
learning through observing someone else being reinforced for that behaviour
11
New cards
moral panic
widespread exaggerated public concern over issues associated with morality (e.g., prostitution, pornography)
12
New cards
conflict theory
a theoretical perspective that views crime as a natural product of a society that promotes competition and, hence, social and economic disparity
13
New cards
left-realism
a theoretical perspective that aims to better understand the implication of crime control policies rather than the causes of crime
\
^^Jock Young^^
\
^^Jock Young^^
14
New cards
police, judicial system, corrections system
3 Primary Sources of Official Data
15
New cards
juristat
a regular publication of the canadian centre for justice statistics, considered the most authoritative source of criminal justice statistics in canda
16
New cards
reliability
the likelihood that an observed relationship between two or more variables can or will be observed in a consistent manner
17
New cards
validity
the likelihood that the relationships observed and measured are real
18
New cards
sampling
the process of selecting a group of research subjects who are representative of the entire population under investigation
19
New cards
random error
and error in data collection that occurs because of an intervening variable that could not have been forseen
20
New cards
systematic error
an error in data collection that the researcher has been able to anticipate and account for
21
New cards
crime funnel
a metaphor referring to the decreasing number of crimes processed at successive levels of the justice system, from law enforcement, through the courts, to corrections
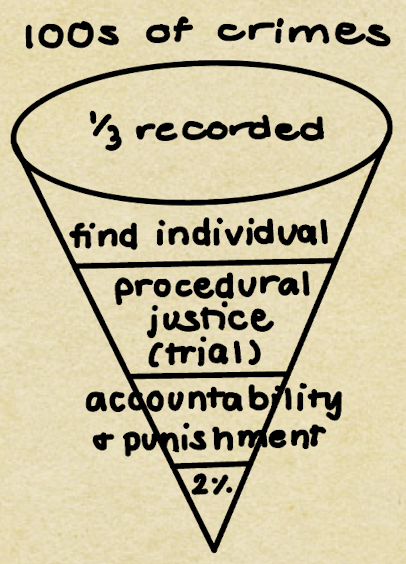
22
New cards
descriptive
statistics gathered by official sources are primarily (descriptive or explanatory)
23
New cards
The Research Cycle
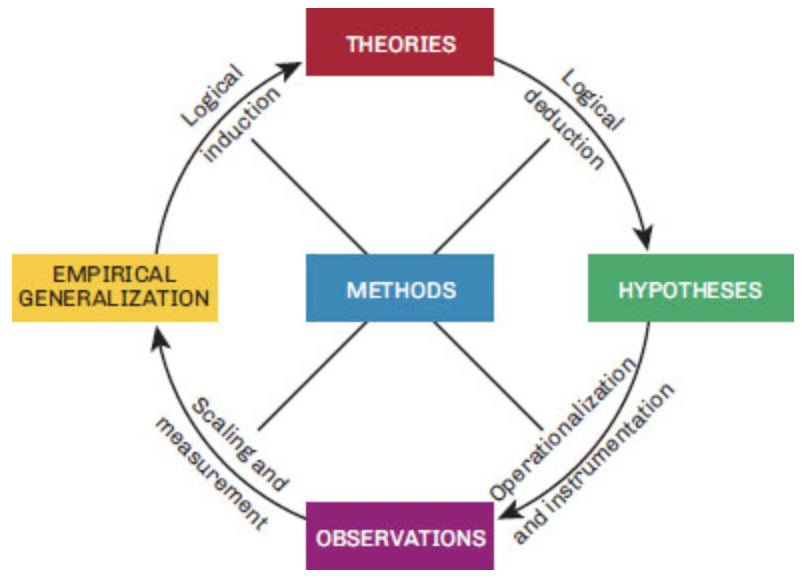
24
New cards
Personal Knowledge, Mass Media, Official State Knowledge, Theoretical Knowledge
4 Factors that Shape Public Perceptions of Crime
25
New cards
operationalization
defining criminological concepts or phenomena in such a way that they can be observed and measured scientifically
26
New cards
crime data
the information collected to measure the frequency and severity of criminal events
27
New cards
description, explanation, evaluation, risk assessment, prediction
5 Key Purposes of Crime Data
28
New cards
Kim Rossmo
developed a ==computer-mapping== technique known as ==*geographic profiling*==, which is used to ==predict== where various categories of offenders live or work, based on crime-site information focuses on spatial behaviour (where)
29
New cards
false positive
an incorrect test result, showing the presence of a condition that does not exist
\
^^John Monahan^^
\
^^John Monahan^^
30
New cards
lies, damned lies, statistics
3 kinds of lies
31
New cards
dark figure of crime
crime that goes undetected, unreported, or unrecorded, and is not included in official sources
32
New cards
uniform crime reporting (UCR)
a system providing a continuous historical record of crime and traffic statistics reported by every police agency in Canada since 1962
33
New cards
canadian centre for justice statistics (CCJS)
the agency responsible for collecting and compiling crime data on a wide range of criminological and criminal justice topics. opened in 1981
34
New cards
Crime Severity Index (CSI)
created by Statistics Canada as a measure of police-reported crime that would address the limitations of the traditional crime rate
35
New cards
summary offences, indictable offences, and hybrid offences
3 Categories of Police Crime Statistics
36
New cards
summary offence
carry a maximum penalty of six months in jail and/or a fine not exceeding $5,000 (unless a different penalty is specified).
37
New cards
indictable offence
carry a maximum penalty of life imprisonment and no maximum fine
38
New cards
Hybrid offence
consist of crimes such as impaired driving and theft under $5,000, which the Crown may choose to prosecute as either summary or indictable.
39
New cards
correctional statistics
data on people being held in federal and provincial corrections facilities, including age, sex, offence and prior convictions
40
New cards
media coverage, the dark figure of crime, changes in recording procedures
factors affecting crime data
41
New cards
Ezzat Fattah
noted the dark figure of crime (portion of the crime that goes undetected, unreported, or unrecorded)
42
New cards
changes in the number of police enforcers, police/court administrators, legal definition of crime, population base, and public reporting patterns (CUVS & GSS)
4 changes in recording procedures
43
New cards
(number of reported crimes / total population) x 100
Crime Rate Formula
44
New cards
canadian urban victimization survey (CUVS)
the first major attempt to survey canadians who had been victims of crime, conducted in the 1980s
45
New cards
general social suvery (GSS)
a statics canada survey used to regularly gather data on social trends and to provide information on specific policy issues of current or emerging interest (e.g., social support, health and well-being, victimization)
46
New cards
victimization survey
a data collection technique used to gather ==unofficial information from victims== of crime on incidents that have usually occurred within a predefined period of time
47
New cards
victimization data (from recipient of offence), self reported data (from the offender), and observational methods
sources of unofficial crime data
48
New cards
unofficial crime data
crime data not collected by official criminal justice agencies, including self-report studies, victimization surveys, and field observation data, usually used to elucidate existing official data and verify the validity of official sources
49
New cards
precursors, transactions, and aftermath
3 Stages to Describing a Criminal Event
50
New cards
self-report studies
survey in which individuals are asked to voluntarily disclose whether they have ever committed an offence. such unofficial crime data can shed light on undetected and under-reported types of crime (e.g., youth crime, fentanyl use, sexual assault, and robbery)
51
New cards
test-retest reliability
a method for determining the reliability of a test by comparing a test taker's scores on the same test taken on separate occasions
52
New cards
field research
research done in natural, real-life settings outside the laboratory
53
New cards
qualitative research
research designed to study characteristics that cannot be measured or counted
54
New cards
Max Weber
german sociologist who said that individuals interpret their own actions and the actions and reactions of others
55
New cards
verstehen
sociologist ==max weber=='s term for the effort to understand an event by ==placing oneself in the participant's situation== and trying to see it through his or her eyes
\
german for ==understanding==
\
german for ==understanding==
56
New cards
activity, dynamics of participants and their interrelationships, and setting
3 Levels where observation enables data collection
57
New cards
Tearoom Trade
Study by sociologist Laud Humphreys of ==men who engage in homosexual behaviour in public facilities==, including subsequent later interviews in their homes after recording their license plate numbers
\
widely cited in discussions of the need for informed consent to research.
\
widely cited in discussions of the need for informed consent to research.
58
New cards
never harm participants, ensure that participation is voluntary, maintain anonymity and confidentiality, be honest
Basic Guidelines to Minimize Potential Negative Impacts on Subjects
59
New cards
triangulation
the ==use of multiple data sources or research methods== to investigate a topic, with the goal of producing more reliable findings. it enables criminologists to illuminate the dark figure of crime
60
New cards
correlation (direct correlation)
a statistical relationship between two or more variables
61
New cards
positive correlation
a direct correlation in which an increase in one variable is associated with an increase in the other variable
62
New cards
negative correlation
a direct correlation in which an increase in one variable is associated with a decrease in the other variable
63
New cards
causal
the existence of a direct correlation does not imply a \_____________ relationship
64
New cards
causality
the idea that one event is the result of one or more other events
65
New cards
hypothesis
an idea or assertion about a phenomenon, a situation, or a relationship between variables that a researcher sets out to prove or disprove
66
New cards
discovery, demonstration, refutation, and replication
four basic aims of researchers
67
New cards
restorative justice
a sentencing model that emphasizes restitution and community participation, aimed at reintegrating offenders back into their communiti