BIO 130 Final Exam
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
1
New cards
Electrically charged particle due to loss of electron
Cation
2
New cards
Electrically charged particles due to the gain of an electron
Anion
3
New cards
Neutral subatomic particle
Neutron
4
New cards
Smallest particle of an element that retains its properties
Atom
5
New cards
Isotopes differ from each other only in the number of electrons the atom contains.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
6
New cards
A chemical bond is an energy relationship between outer (valence) electrons of neighboring atoms.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
7
New cards
If atom X has an atomic number of 74 it would have which of the following?
A) 37 protons and 37 neutrons
B) 74 protons
C) 37 protons and 37 electrons
D) 37 electrons
A) 37 protons and 37 neutrons
B) 74 protons
C) 37 protons and 37 electrons
D) 37 electrons
74 protons
8
New cards
Atoms that are bonded with an electronegativity difference of 0-0.4 are generally considered to be _______.
A) Negatively charged compounds
B) Non-polar covalent compounds
C) Polar-covalent compounds
D) Ionic compounds
A) Negatively charged compounds
B) Non-polar covalent compounds
C) Polar-covalent compounds
D) Ionic compounds
Non-polar covalent compounds
9
New cards
Which of the following describes a chemical bond that involves sharing of pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule?
A) A cation
B) A covalent bond
C) A ion
D) An ionic bond
A) A cation
B) A covalent bond
C) A ion
D) An ionic bond
A covalent bond
10
New cards
The four elements that make up about 96% of your body are______.
A) Sodium, potassium, hydrogen, oxygen
B) Nitrogen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium
C) Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
D) Carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, calcium
A) Sodium, potassium, hydrogen, oxygen
B) Nitrogen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium
C) Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
D) Carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, calcium
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
11
New cards
An atom with three valence electrons may have a total of _______ electrons.
A) 17
B) 13
C) 8
D) 3
A) 17
B) 13
C) 8
D) 3
13
12
New cards
A(n) ________ bond means that two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms.
A) Triple bond
B) Single Bond
C) Double Bond
D) Ionic bond
A) Triple bond
B) Single Bond
C) Double Bond
D) Ionic bond
Double bond
13
New cards
A polar covalent bond ______.
A) Has equal attraction of the electron pair between the bonded atoms
B) Has unequal attraction of the electron pair between the bonded atoms
A) Has equal attraction of the electron pair between the bonded atoms
B) Has unequal attraction of the electron pair between the bonded atoms
Has equal attraction of the electron pair between the bonded atoms
14
New cards
The lower the pH, the higher the hydrogen ion concentration.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
15
New cards
Weak acids can act as chemical buffering systems for the body because they only partially dissociate.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
16
New cards
Buffers resist abrupt and large changes in the pH of the body by releasing or binding hydrogen ions.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
17
New cards
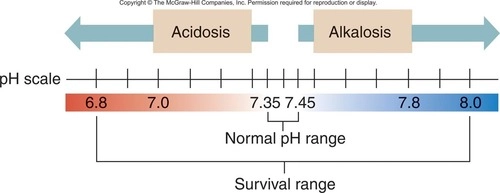
The normal pH of blood is 7.00-7.25
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
18
New cards
The acidity of a solution reflects the concentration of free hydrogen ions in the solution.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
19
New cards
Which statement best describes a pH indicator?
A) Changes color when exposed to different levels of OH-
B) Changes color when exposed to different levels of weak acids
C) Changes color when exposed to different levels of weak bases
D) Changes color when exposed to different levels of H+
A) Changes color when exposed to different levels of OH-
B) Changes color when exposed to different levels of weak acids
C) Changes color when exposed to different levels of weak bases
D) Changes color when exposed to different levels of H+
Changes color when exposed to different levels of H+
20
New cards
In water, a substance that ionizes completely in solution is called a ______.
A) semiconductor
B) strong electrolyte
C) non electrolyte
D) weak electrolyte
E) non conductor
A) semiconductor
B) strong electrolyte
C) non electrolyte
D) weak electrolyte
E) non conductor
strong electrolyte
21
New cards
______ atoms attract electrons very strongly.
A) Electropositive
B) Electroneutral
C) Electronegative
D) Electrostable
A) Electropositive
B) Electroneutral
C) Electronegative
D) Electrostable
Electronegative
22
New cards
Which of the following is a neutralization reaction?
A) HCl + NaOH --> NaCl + H2O
B) NH3 + H+ --> NH4+2
C) HCl --> H+ + Cl-
D) NaOH --> Na+ + OH-
A) HCl + NaOH --> NaCl + H2O
B) NH3 + H+ --> NH4+2
C) HCl --> H+ + Cl-
D) NaOH --> Na+ + OH-
HCl + NaOH --> NaCl + H2O
23
New cards
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The pH of blood is slightly basic
B) The more hydrogen ions in a solution, the more acidic the solution
C) When acids and bases are mixed, they react with each other to form water and a salt
D) When the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the hydroxyl ion concentration also decreases
A) The pH of blood is slightly basic
B) The more hydrogen ions in a solution, the more acidic the solution
C) When acids and bases are mixed, they react with each other to form water and a salt
D) When the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the hydroxyl ion concentration also decreases
When the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the hydroxyl ion concentration also decreases
24
New cards
A falling blood pH and a rising partial pressure of carbon dioxide due to pneumonia or emphysema indicates ______.
A) metabolic acidosis
B) respiratory alkalosis
C) metabolic alkalosis
D) respiratory acidosis
A) metabolic acidosis
B) respiratory alkalosis
C) metabolic alkalosis
D) respiratory acidosis
respiratory acidosis
25
New cards
A mixture is prepared by dissolving 2 g of KCl in 100 ml of H2O. In this mixture, H2O is the ______.
A) solution
B) solute
C) solvent
D) solid
E) ionic compound
A) solution
B) solute
C) solvent
D) solid
E) ionic compound
solvent
26
New cards
The single most important blood buffer system is the bicarbonate buffer system.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
27
New cards
______ are proton acceptors and decrease the concentration of H+ ions in solution.
Buffers
28
New cards
Weak acids paired with weak bases can be used to ______ pH
Balance
29
New cards
It is the high number of ______ bonds that attract water molecules to each other and polar solutes in solution.
Hydrogen
30
New cards
A ______ is a layer of water molecules enveloping dissolved solutes in solution.
Hydration layer
31
New cards
______ is the water volume found inside every cell in the human body.
Intracellular fluid (ICF)
32
New cards
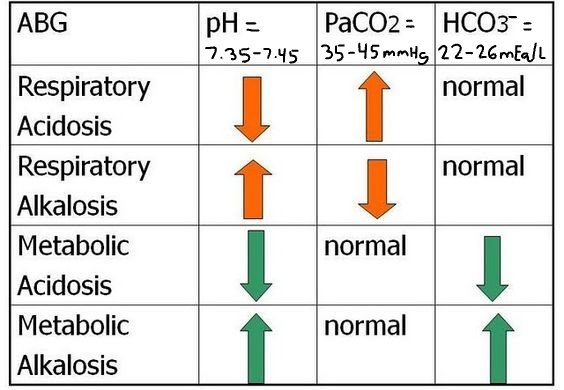
Patient #1 ABG Results: pH= 7.2, Pco2= 57 mmHg, HCO3-=25 mEq/L
A) uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
C) uncompensated metabolic acidosis
D) uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
A) uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
C) uncompensated metabolic acidosis
D) uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
uncompensated respiratory acidosis
33
New cards
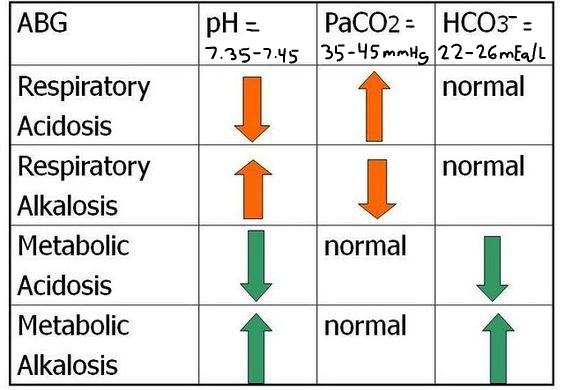
Patient #2 ABG Results: pH= 7.49, Pco2= 37 mmHg, HCO3-=29 mEq/L
A) partially compensated respiratory alkalosis
B) partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
C) uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
D) uncompensated respiratory acidosis
A) partially compensated respiratory alkalosis
B) partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
C) uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
D) uncompensated respiratory acidosis
uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
34
New cards
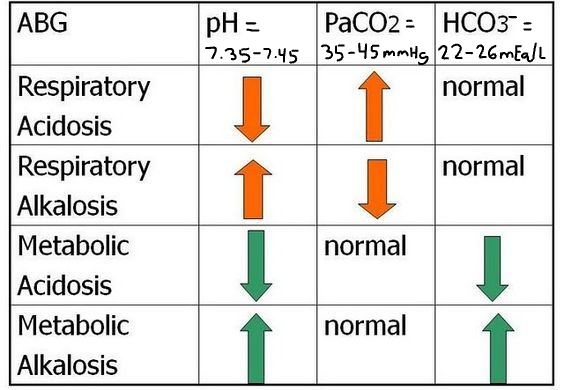
Patient #3 ABG Results: pH= 7.54, Pco2= 49 mmHg, HCO3-= 32 mEq/L
A) uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) partially compensated respiratory alkalosis
C) uncompensated metabolic acidosis
D) partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
A) uncompensated respiratory acidosis
B) partially compensated respiratory alkalosis
C) uncompensated metabolic acidosis
D) partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
partially compensated metabolic alkalosis
35
New cards
Amino acids that are not synthesized in the body and must be obtained from the diet are referred to as ______.
A) imcomplete
B) polar
C) complete
D) nonpolar
E) essential
A) imcomplete
B) polar
C) complete
D) nonpolar
E) essential
Essential
36
New cards
Purines are small, single-ring nitrogen-containing bases.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
37
New cards
Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscles of humans in the form of ______.
A) amylose
B) glycogen
C) starch
D) cholesterol
A) amylose
B) glycogen
C) starch
D) cholesterol
Glycogen
38
New cards
A carbonyl group consists of ______.
A) carbon and oxygen attached by a single bond
B) carbon and oxygen attached by a double bond
C) a carbon-oxygen-carbon attached by single bonds
D) a carbon-oxygen-hydrogen attached by single bonds
E) carbon and oxygen attached by triple bonds
A) carbon and oxygen attached by a single bond
B) carbon and oxygen attached by a double bond
C) a carbon-oxygen-carbon attached by single bonds
D) a carbon-oxygen-hydrogen attached by single bonds
E) carbon and oxygen attached by triple bonds
carbon and oxygen attached by a double bond
39
New cards
Select the most correct statement regarding nucleic acids.
A) DNA is a long, double-stranded molecule made up of A, T, G, and C bases
B) RNA is a long, single-stranded molecule made up of the bases A, T, G, and C
C) Three forms exist: DNA, RNA, tDNA
D) DNA is found exclusively in the cytoplasm of the cell
A) DNA is a long, double-stranded molecule made up of A, T, G, and C bases
B) RNA is a long, single-stranded molecule made up of the bases A, T, G, and C
C) Three forms exist: DNA, RNA, tDNA
D) DNA is found exclusively in the cytoplasm of the cell
DNA is a long, double-stranded molecule made up of A, T, G, and C bases
40
New cards
Compounds that have the same molecular formula, but different structural arrangements of atoms are called ______.
A) isotopes
B) isomers
C) isometrics
D) isozymes
E) indicators
A) isotopes
B) isomers
C) isometrics
D) isozymes
E) indicators
Isomers
41
New cards
Phospholipids can interact with other lipids and water because they contain ______.
A) glycerol
B) cholesterol
C) double bonds
D) saturated fatty acids
E) polar regions and nonpolar regions
A) glycerol
B) cholesterol
C) double bonds
D) saturated fatty acids
E) polar regions and nonpolar regions
Polar regions and nonpolar regions
42
New cards
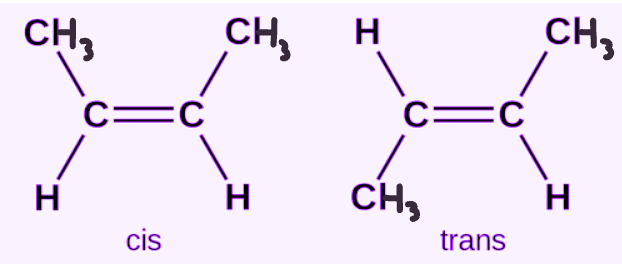
What type of isomer is this show in the image?
Cis-trans isomer
43
New cards
The sugar also known as dextrose, and blood sugar is ______.
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) glucose
D) lactose
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) glucose
D) lactose
Glucose
44
New cards
In the L- isomer of a monosaccharide, the OH- group farthest from the carbonyl is written
A) on the left
B) on the right
C) on the top
D) on the bottom
A) on the left
B) on the right
C) on the top
D) on the bottom
on the left
45
New cards
______ is the basis of steroid hormones and vitamin D and may contribute to clogged arteries when increased levels form plaques.
A) Carbohydrates
B) Triglycerides
C) Prostaglandins
D) Cholesterol
A) Carbohydrates
B) Triglycerides
C) Prostaglandins
D) Cholesterol
Cholesterol
46
New cards
A clear blue color in a Benedict’s test indicates the presence of aldehyde groups.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
47
New cards
Which of the following is involved in tertiary protein structure?
A) interactions between two different polypeptides
B) alpha helix
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) beta-pleated sheets
A) interactions between two different polypeptides
B) alpha helix
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) beta-pleated sheets
Hydrophobic interactions
48
New cards
Which of the following is not true of proteins?
A) They may be denatured or coagulated by heat or acidity
B) Their function depends n their three-dimensional shape
C) They have both functional and structural roles in the body
D) They appear to be the molecular carriers of genetic information
A) They may be denatured or coagulated by heat or acidity
B) Their function depends n their three-dimensional shape
C) They have both functional and structural roles in the body
D) They appear to be the molecular carriers of genetic information
They appear to be the molecular carriers of genetic information
49
New cards
Which of the following is involved in primary protein structure?
A) peptide bonds
B) salt bridges
C) hydrogen bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
A) peptide bonds
B) salt bridges
C) hydrogen bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
Peptide bonds
50
New cards
A red blood cell will undergo crenation in ______.
A) hypertonic solution
B) hypotonic solution
C) isotonic solution
A) hypertonic solution
B) hypotonic solution
C) isotonic solution
Hypertonic solution
51
New cards
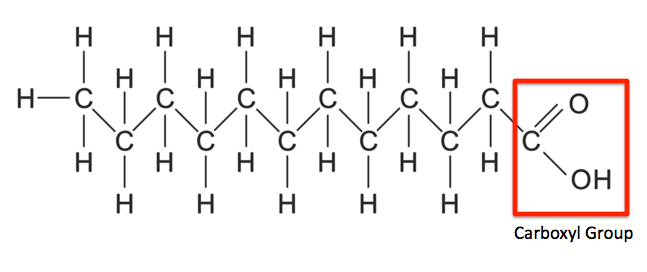
This structure represents a saturated fatty acid.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
52
New cards
Denaturation of a protein ______.
A) changes the primary structure of a protein
B) disrupts the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein
C) is always reversible
D) can only occur in a protein with quaternary structure
A) changes the primary structure of a protein
B) disrupts the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein
C) is always reversible
D) can only occur in a protein with quaternary structure
disrupts the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein
53
New cards
A monosaccharide that consists of 5 carbon atoms, one of which is a ketone group, is classified as a(n) ______.
A) aldopentose
B) ketotetrose
C) ketopentose
D) aldohexose
A) aldopentose
B) ketotetrose
C) ketopentose
D) aldohexose
Ketopentose
54
New cards
The carbon atoms in a saturated hydrocarbons ______.
A) contain at least one double bond
B) contain a benzene ring
C) contain both a double and a triple bond
D) have only single bonds
E) contain at least one triple bond
A) contain at least one double bond
B) contain a benzene ring
C) contain both a double and a triple bond
D) have only single bonds
E) contain at least one triple bond
Have only single bonds
55
New cards
Introns are the only regions in genes that contain information for building proteins.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
56
New cards
The alpha helix of a protein is held together by ______ between two distant amino acids in a polypeptide.
A) double covalent bonds
B) disulfide bridges
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) hydrogen bonds
A) double covalent bonds
B) disulfide bridges
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds
57
New cards
In a disaccharide, two monosaccharides are joined by what kind of bond?
A) double
B) glycosidic
C) dehydration
D) peptide
A) double
B) glycosidic
C) dehydration
D) peptide
Glycosidic
58
New cards
A gene can best be defined as ______.
A) a three-base triplet that specifies a particular amino acid
B) a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for synthesizing a polypeptide chain
C) an RNA messenger that codes for a particular polypeptide
D) noncoding segments of DNA up to 100,000 nucleotides long
A) a three-base triplet that specifies a particular amino acid
B) a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for synthesizing a polypeptide chain
C) an RNA messenger that codes for a particular polypeptide
D) noncoding segments of DNA up to 100,000 nucleotides long
a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for synthesizing a polypeptide chain
59
New cards
In the process known as osmosis, __ moves through a semipermeable membrane into an area of ____ concentration.
A) solute, lower solute
B) solvent, lower solute
C) solvent, higher solvent
D) solvent, lower solvent
E) solute, higher solute
A) solute, lower solute
B) solvent, lower solute
C) solvent, higher solvent
D) solvent, lower solvent
E) solute, higher solute
Solvent, lower solvent
60
New cards
Which statement is false?
A) All lipids contain fatty acids
B) Lipids are found in the cell membrane
C) Lipids are soluble in organic solvents
D) There are many different types of lipids
E) Some hormones are lipids
A) All lipids contain fatty acids
B) Lipids are found in the cell membrane
C) Lipids are soluble in organic solvents
D) There are many different types of lipids
E) Some hormones are lipids
All lipids contain fatty acids
61
New cards
Galactose is a ______.
A) disaccharide
B) trisaccharide
C) monosaccharide
D) polysaccharide
A) disaccharide
B) trisaccharide
C) monosaccharide
D) polysaccharide
Monosaccharide
62
New cards
The structural formulas of all amino acids are the same except for the ______.
A) alpha carbon
B) ammonium group
C) carboxylate group
D) R goup
A) alpha carbon
B) ammonium group
C) carboxylate group
D) R goup
R group
63
New cards
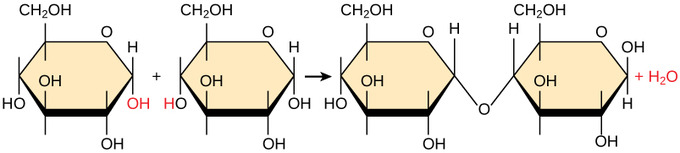
What specific type of reaction is depicted in the image?
Dehydration synthesis
64
New cards
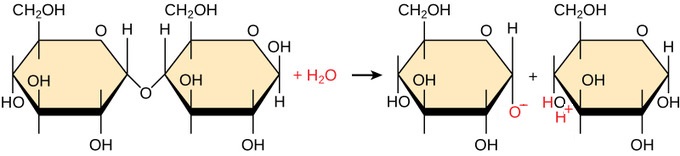
What specific type of reaction is depicted in the image?
Hydrolysis
65
New cards
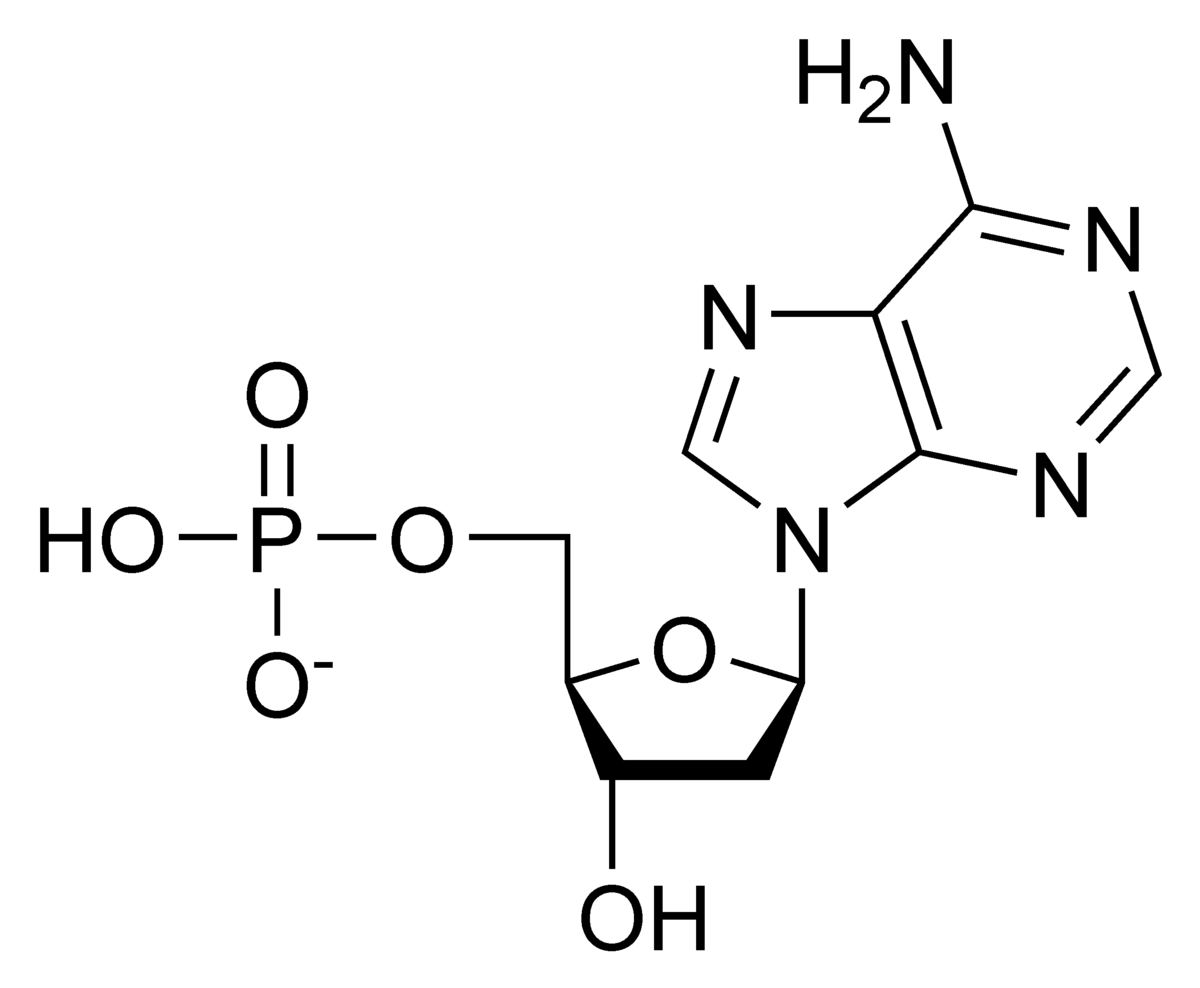
Identify each part of the nucleotide (from left to right).
Is this a DNA or RNA nucleotide?
Is this a DNA or RNA nucleotide?
Phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base. This is a DNA nucleotide.
66
New cards
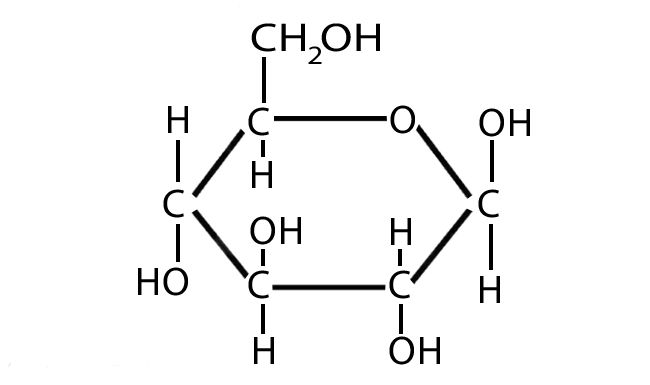
What best describes this organic molecule?
Monosaccharide
67
New cards
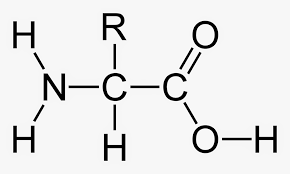
What best describes this organic molecule?
Amino acid
68
New cards
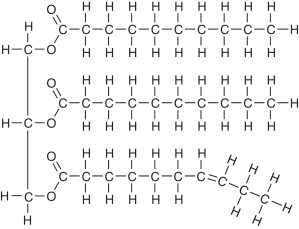
What best describes this organic molecule?
Triglyceride
69
New cards
One DNA triplet codes for one amino acid.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
70
New cards
Active transport uses ATP to move particles from high to low particles.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
71
New cards
DNA transcription is another word for DNA replication.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
72
New cards
Polyribosomes produce multiple copies of that same protein.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
73
New cards
Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
74
New cards
Editing and capping of the mRNA takes place in the cytoplasm.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
75
New cards
Proteins are not involved in determining the chemical and physical nature of cells.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
76
New cards
Transcription cannot begin until the RNA polymerase binds and unwinds the DNA double helix.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
True
77
New cards
New tRNA molecules enter the ribosomes and dock at the P site.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
78
New cards
Translation takes place in the nucleus of the cell.
A) True
B) False
A) True
B) False
False
79
New cards
The RNA responsible for bringing the amino acids to the ribosome for protein formation is ______.
A) mRNA
B) ssRNA
C) tRNA
D) rRNA
A) mRNA
B) ssRNA
C) tRNA
D) rRNA
tRNA
80
New cards
An enzyme’s ____ binds a(n) ____ and forms a(n) ____.
A) substrate, enzyme-substrate, active site
B) active site, substrate, enzyme-substrate complex
C) product, substrate, active site
D) catalyst, active site, substrate
A) substrate, enzyme-substrate, active site
B) active site, substrate, enzyme-substrate complex
C) product, substrate, active site
D) catalyst, active site, substrate
active site, substrate, enzyme-substrate complex
81
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding integral proteins is false?
A) They have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
B) They are firmly inserted into the plasma membrane
C) They are loosely attached to the intra- or extracellular surface of plasma membrane
D) They can function as transport proteins, enzymes, or receptors
A) They have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
B) They are firmly inserted into the plasma membrane
C) They are loosely attached to the intra- or extracellular surface of plasma membrane
D) They can function as transport proteins, enzymes, or receptors
They are loosely attached to the intra- or extracellular surface of plasma membrane
82
New cards
Which of the following is the correct order of events on Transcription?
A) DNA synthesis, mRNA synthesis, mRNA processing
B) Initiation, Elongation, Termination
C) Elongation, Processing, Migration
D) Initiation, Termination, Elongation
A) DNA synthesis, mRNA synthesis, mRNA processing
B) Initiation, Elongation, Termination
C) Elongation, Processing, Migration
D) Initiation, Termination, Elongation
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
83
New cards
If the nucleotide or base sequence of the DNA strand used as a template for messenger RNA synthesis is ACGTT, they what would be the sequence of bases in the corresponding mRNA?
A) ACGTT
B) GUACC
C) TGCAA
D) UGCAA
A) ACGTT
B) GUACC
C) TGCAA
D) UGCAA
UGCAA
84
New cards
_____ is the diffusion of a solvent through a _____ membrane from a _____ solution into a more _____ one.
A) Osmosis, permeable, concentrated, dilute
B) Osmosis, selectively permeable, dilute, concentrated
C) Active transport, hydrophilic, hypotonic, hypertonic
D) Active transport, hydrophobic, hypertonic, hypotonic
A) Osmosis, permeable, concentrated, dilute
B) Osmosis, selectively permeable, dilute, concentrated
C) Active transport, hydrophilic, hypotonic, hypertonic
D) Active transport, hydrophobic, hypertonic, hypotonic
Osmosis, selectively permeable, dilute, concentrated
85
New cards
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Catabolic reactions form large molecules from smaller molecules
B) Anabolic reactions reduce complex structures to simpler structures
C) Catabolic reactions absorb energy
D) Anabolic reactions form large molecules from smaller molecules
A) Catabolic reactions form large molecules from smaller molecules
B) Anabolic reactions reduce complex structures to simpler structures
C) Catabolic reactions absorb energy
D) Anabolic reactions form large molecules from smaller molecules
Anabolic reactions form large molecules from smaller molecules
86
New cards
Starting at the gene, select the correct sequence of nucleotide information during protein sunthesis.
A) anticodon, triplet, codon
B) triplet, codon, anticodon
C) triplet, codon, amino acid
D) codon, triplet, anticodon
A) anticodon, triplet, codon
B) triplet, codon, anticodon
C) triplet, codon, amino acid
D) codon, triplet, anticodon
Triplet, codon, anticodon
87
New cards
Once the transcription termination sequence has been reached the ______ and the pre-mRNA are released.
RNA polymerase
88
New cards
______ is located outside cells and includes blood plasma and interstitial fluid.
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
89
New cards
______ involves the passive movement of particles through channels or membrane carrier proteins.
Facilitated diffusion
90
New cards
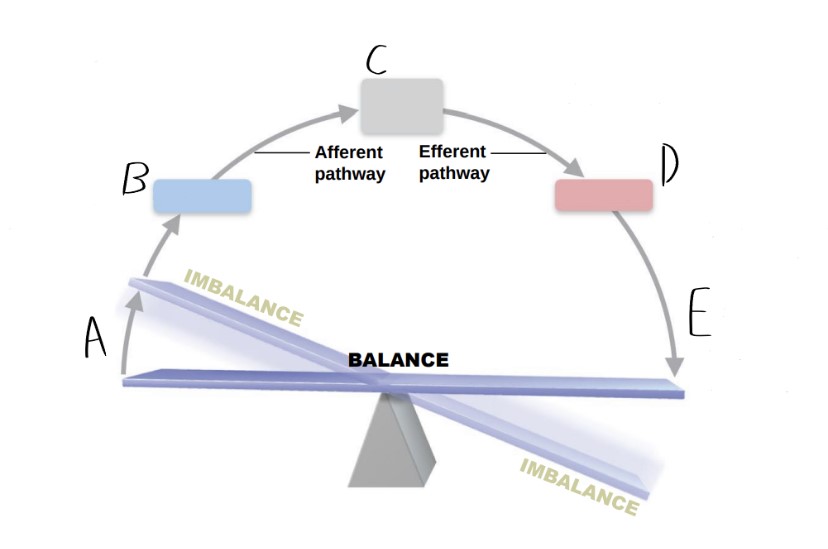
Label each letter with the correct term.
A) Stimulus B) Receptor C) Input/afferent pathway D) Output/efferent pathway E) Response
91
New cards
______ prevents substrates from fitting into enzyme active sites.
Inhibitors
92
New cards
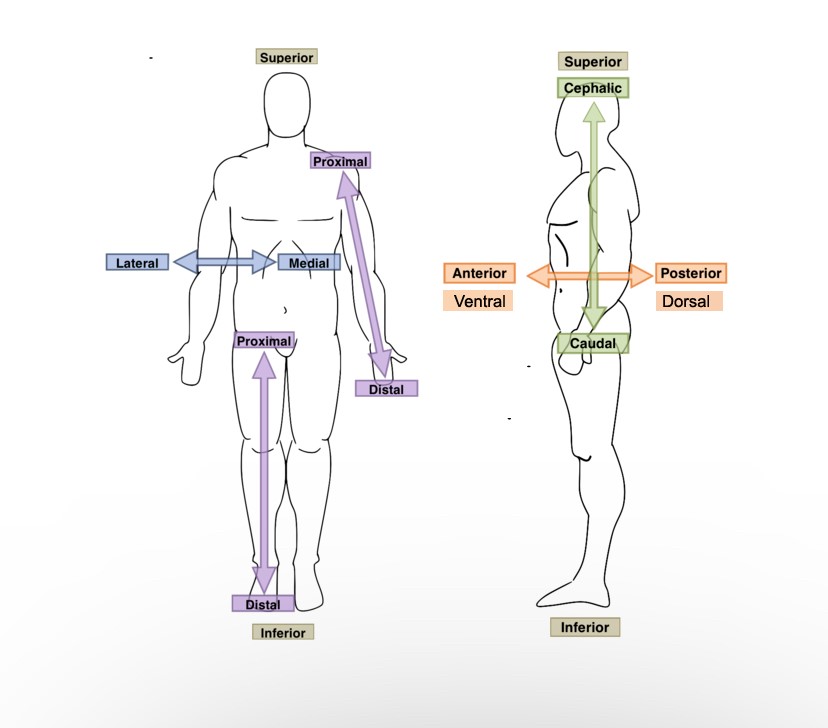
The fingers are ______ to the wrist.
Distal
93
New cards
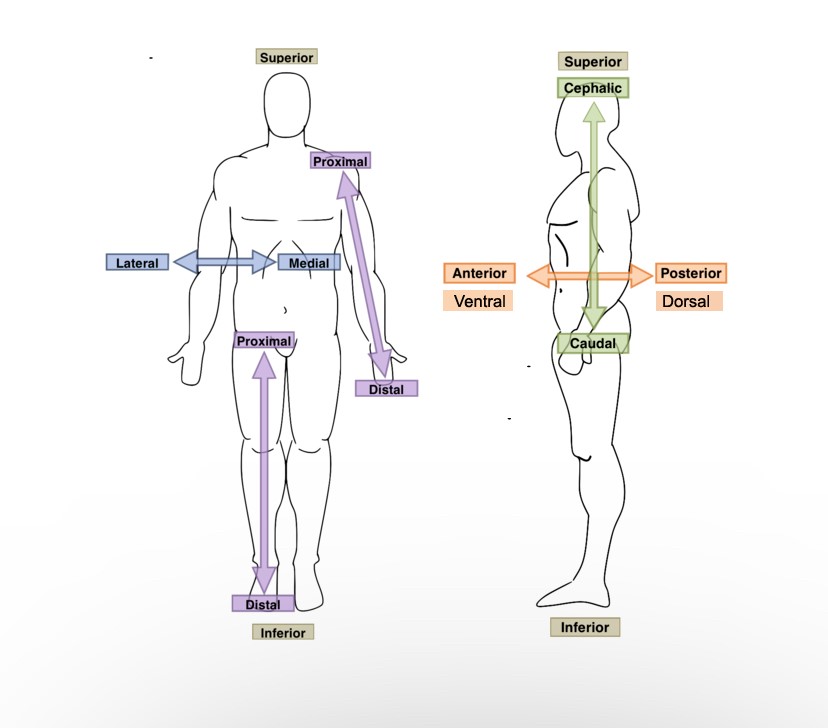
The bridge of the nose is ______ to the left eye.
Medial
94
New cards
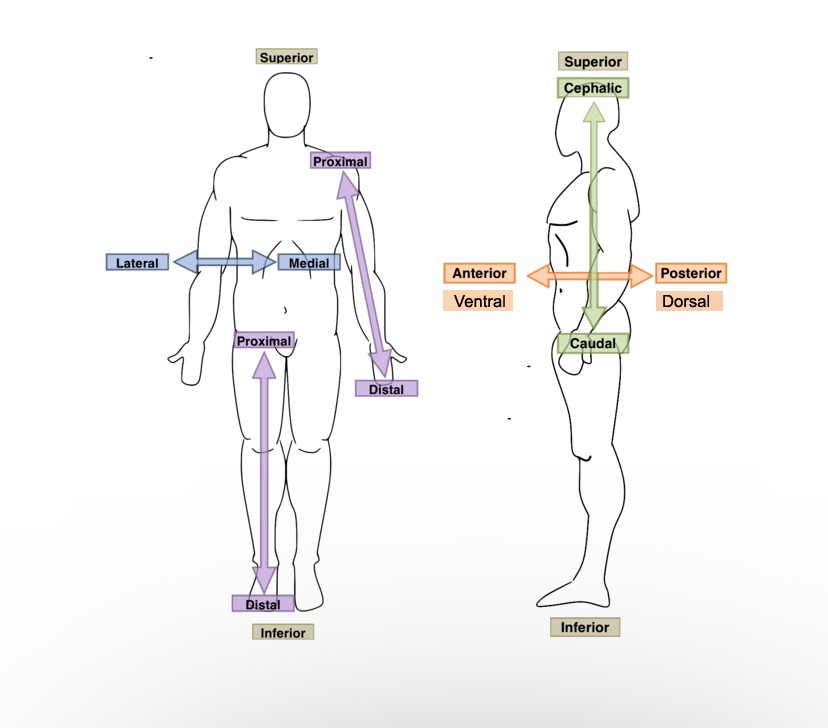
The stomach is ______ to the spine.
Ventral
95
New cards
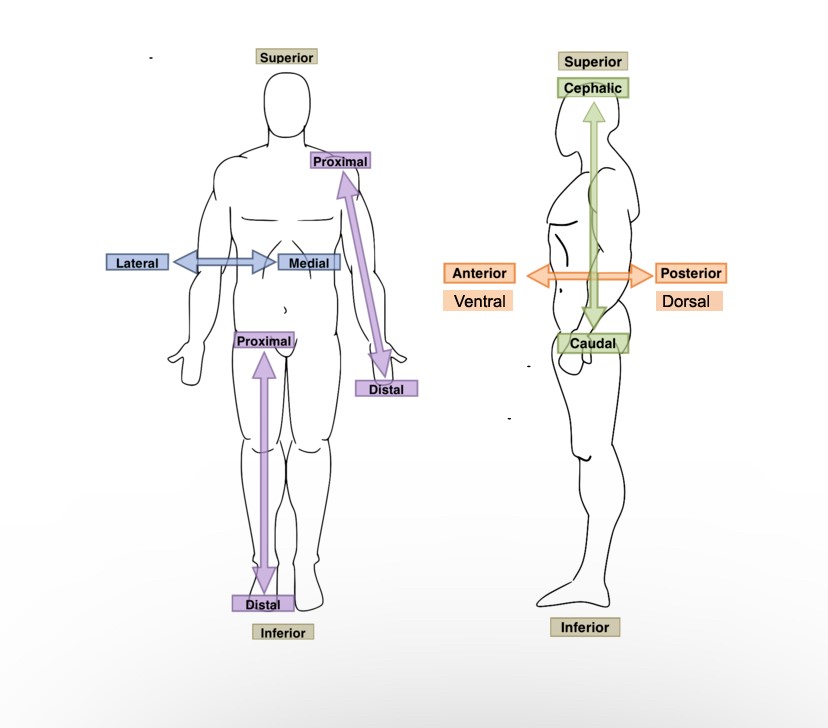
The lungs are ______ to the heart.
Lateral
96
New cards
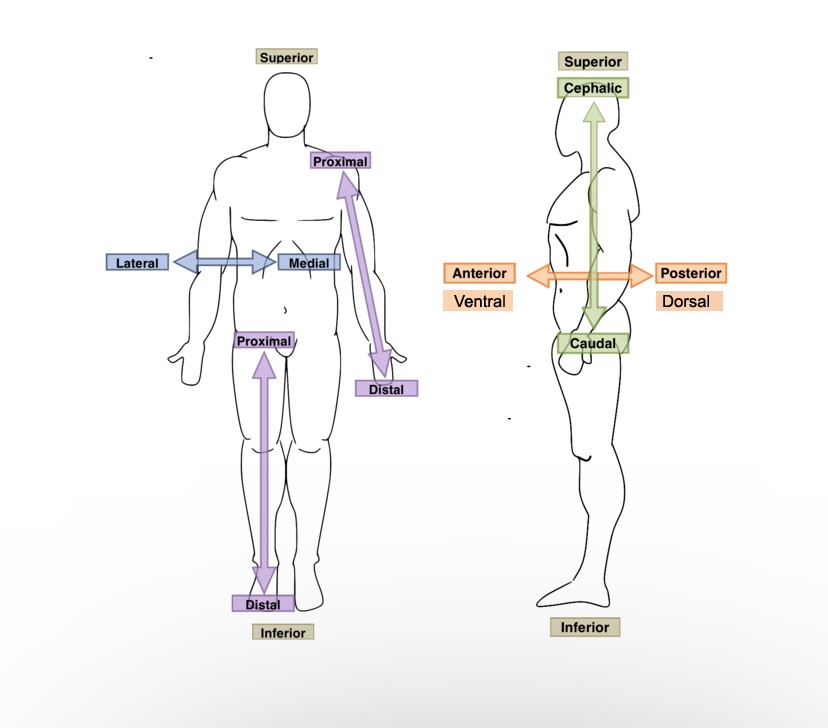
The upper arm is ______ to the forearm.
Proximal
97
New cards
What is the main, general purpose of negative feedback?
A) to keep the body’s blood sugar level high
B) to maintain homeostasis
C) to regulate excretion via the kidneys
D) to control body movement
A) to keep the body’s blood sugar level high
B) to maintain homeostasis
C) to regulate excretion via the kidneys
D) to control body movement
To maintain homeostasis
98
New cards
A good example of a positive feedback mechanism would be ______.
A) enhancement of labor contractions
B) blood calcium level regulation
C) regulating glucose levels in the blood
D) body temperature regulation
A) enhancement of labor contractions
B) blood calcium level regulation
C) regulating glucose levels in the blood
D) body temperature regulation
Enhancement of labor contractions
99
New cards
What is a vertical section through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior regions called?
A) transverse
B) median
C) frontal
D) sagittal
A) transverse
B) median
C) frontal
D) sagittal
Frontal
100
New cards
The parietal pleura would represent a serous membrane ______.
A) covering individual lungs
B) lining the thoracic cavity
C) lining the abdominal cavity
D) covering the heart
A) covering individual lungs
B) lining the thoracic cavity
C) lining the abdominal cavity
D) covering the heart
Lining the thoracic cavity