NST Exam 4: Nucleotide Metabolism (Vitamins B9 and B12)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Purines
A and G
Pyrimidines
C, U, T
does purine production require high or low energy?
high
common precursor to de novo biosynthesis of AMP and GMP
IMP
what enzymes are allosterically inhibited by products of purine biosynthesis?
PRPS1, PPAT, IMPDH, ADSS2
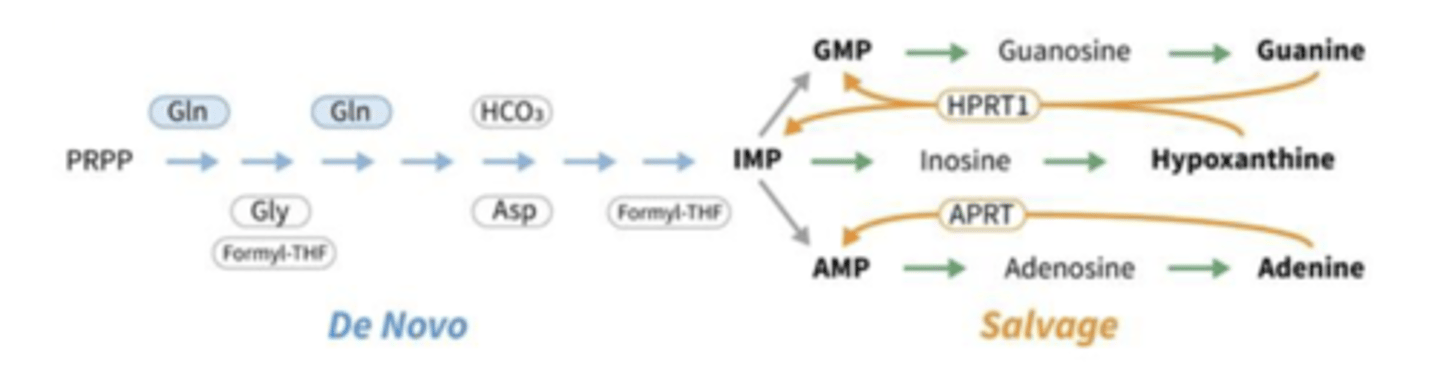
De novo purine synthesis
R5P --> PRPP by PRPP synthetase (adds 2P's)
add base (hypoxanthine) --> IMP by HGPRT
IMP converted to AMP and GMP
purinosome
giant complex that is proposed to hold de novo purine biosynthesis enzymes
what was noted about several enzymes in DNPB?
several enzymes are encoded on one polypeptide in different organisms ; ex. GART, PAICS, ATIC
What enzyme is shared between purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis pathways?
PRPS1; makes R5P --> PRPP
what enzymes are allosterically inhibited by products of pyrimidine biosynthesis?
PRPS1, CAD, UMPS, CTPS
starting product : purine synthesis
ribose-5-phosphate
starting product : pyrimidine synthesis
glutamine and ribose-5-phosphate
for purine and pyrimidine what gene encodes the first 3 reactions in one protein?
CAD
What does DHODH use in pyrimidine biosynthesis? what is the effect of this?
uses mitochondrial CoQ, so UMP biosynthesis requires mitochondrial respiration to recycle CoQH2 to CoQ
What happens when the nitrogen base is available outside the cell?
then the cell stops using de novo pathway and switch to salvage pathway where they add the nitrogen base to ribose
What makes all deoxyribonucleotide?
ribonucleotide reductase
ribonucleotide reductase
Contains two types of allosteric regulatory sites for activity and specificity. Converts ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides.
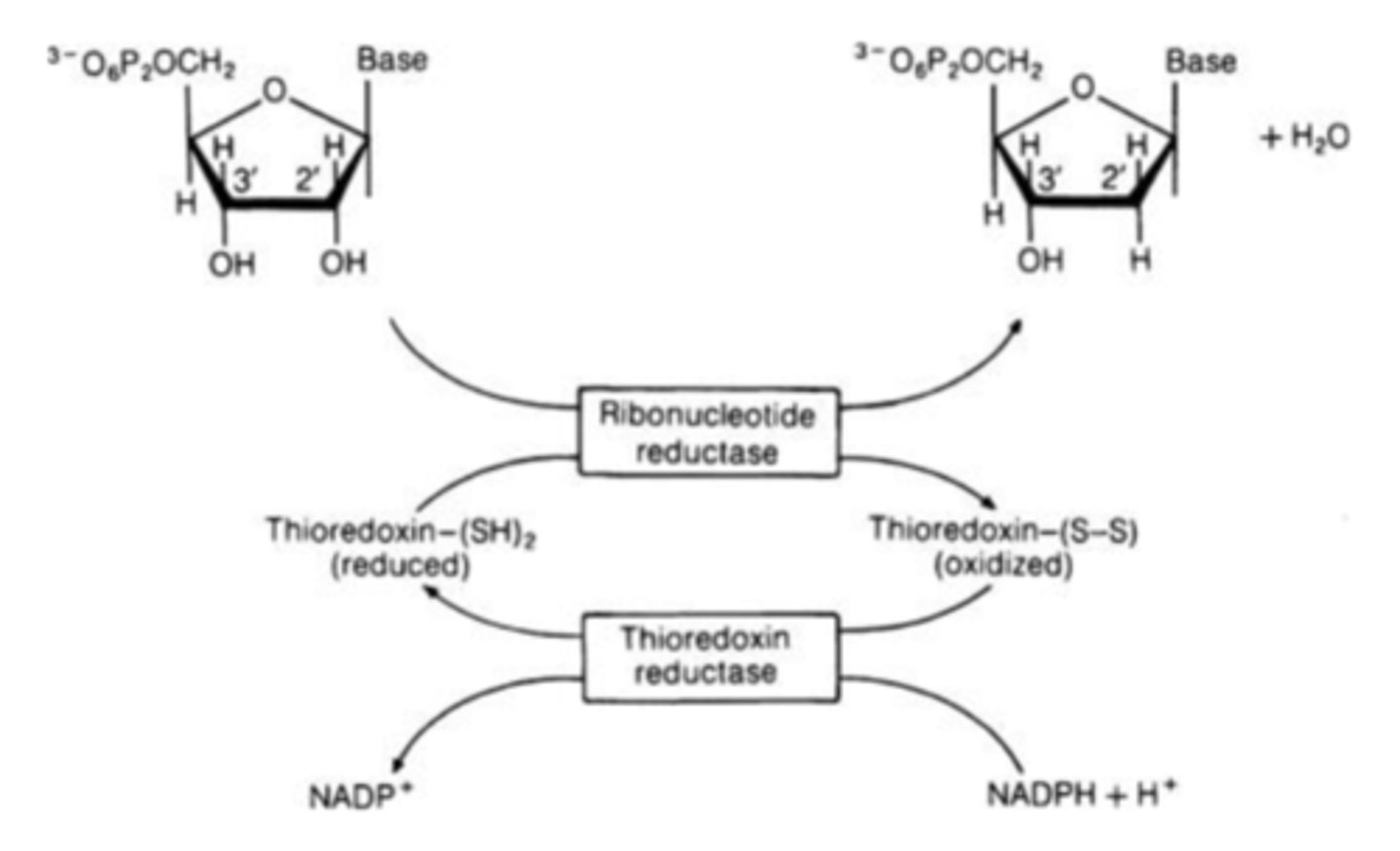
What regulates ribonucleotide reductase?
ATP, dATP, dGTP, dUTP, dCTP
who discovered folate/B9 and what was the context of this discovery?
Lucy Wills as a micronutrient in yeast extract (Wills factor) that can prevent macrocytic anemia in pregnant women; later purified from spinach
Folate deficiency causes what?
megaloblastic anemia with large and fewer red blood cells, which also have shorter lifespan
low folate is associated with an increased risk of ?
neural tube defects
- spina bifida
- anencephaly
spina bifida
spinal cord and/or fluid bulge through the back
anencephaly
brain and skull are underdeveloped
What was the enrichment level and aim when the addition of folic acid to enriched cereal grain products became mandatory in the US in 1998
enrichment level = 140ug/100g product
aim = increase intake by 80-130ug/day
How is folate processed inside the cell
reduced and polyglutamated inside the cells
two key players in folate absorption from the gut:
glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII) and Proton coupled folate transporter (PCFT)
Glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII)
brush border hydrolase that cleaves polyglutamate folate derivatives
Proton coupled folate transporter (PCFT)
primary intestinal folate transporter, also present in the liver
How can folate be polyglutamated?
via NADPH + H+ or ATP + folylpolyglutamate synthase
What allows folate transport across plasma membrane?
multiple drug resistance protein and reduced folate carrier protein (RFC)
What is the primary form of folate in the plasma? How does is circulate?
5-methyl THF (monoglutamate); circulates free or bound to albumin
What is folate a cofactor of?
participates in transfer of one-carbon units at formic acid, formaldehyde and methanol redox levels
Formaldehyde is ?
very toxic ; causes protein crosslinks, so its levels must be kept very low in cells
What are the three redox states of the carbon unit carried by folate?
Methanol, formaldehyde, and formic acid.
What cofactors are necessary for the interconversion of folate redox states?
NADPH for reduction to methanol and NADP for oxidation to formic acid.
What is the quantitatively most important reaction for one-carbon units to enter the folate pool?
The reaction with serine, catalyzed by Serine Transhydroxymethylase (SHMT), producing methylene tetrahydrofolate.
Which form of folate is used in all of the purine biosynthesis reactions?
N10-formyl-FH4 (formyl state).
Which amino acid is used to produce one-carbon units because it is easily made from glycolytic intermediates?
Serine.
What is the major consequence of the Thymidylate Synthase (TYMS) reaction on folate?
TYMS produces dihydrofolate (DHF) instead of tetrahydrofolate (THF).
What is the role of Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR) in the folate cycle?
DHFR recycles dihydrofolate back into active tetrahydrofolate using NADPH.
Why does B12 deficiency lead to functional folate deficiency?
Without Vitamin B12, the Methionine Synthase reaction cannot proceed, trapping folate as 5-methyl-THF.
How does folate metabolism differ between the cytosol and mitochondria?
Folate metabolism enzymes are compartmentalized; mitochondrial folate metabolism produces formyl-Methionine.
Which scientists pioneered the use of antifolate drugs for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)?
Sidney Farber and Yellapragada Subbarow
How did antifolate drugs affect the prognosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)?
They helped transform ALL from a universally fatal disease to one with a 90% plus cure rate.
What is the mechanism by which antifolates like Methotrexate preferentially target cancer cells?
Methotrexate inhibits Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR), collapsing the folate pool in highly proliferative cells.
Name an antibiotic that also targets Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR).
Trimethoprim
Besides DHFR, which other enzyme in nucleotide biosynthesis is a target for chemotherapy using drugs like 5-fluoro-dUMP?
Thymidylate Synthase (TYMS)
Who determined the complex structure of Vitamin B12 using X-ray crystallography?
Dorothy Hodgkin
What type of anemia is caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Pernicious anemia
What early, unconventional treatment was discovered for pernicious anemia?
Eating one pound of raw liver
Why is most pernicious anemia caused not by dietary deficiency but by malabsorption?
Most patients are unable to produce Intrinsic Factor (IF), a protein required for B12 absorption
How many enzyme reactions require Vitamin B12 in humans?
Only two
Name the two enzyme reactions in humans that require B12.
1. Methionine Synthase, 2. Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase
What is the purpose of Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase?
It converts propionyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA
What special chemical mechanism does B12 catalyze in the Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase reaction?
It initiates a radical-based rearrangement using a 5′-Deoxyadenosyl radical