Evidences & Symbols of Chemical Reactions - 1st Sem Chemistry
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Physical charge
A change in physical properties where there is no formation of a new substance.
Chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances. Also known as chemical reaction.
Reactants
A starting substance in a chemical reaction.
Products
The different substances produced by a chemical reaction.
Phase change
A change from one state to another without a change in chemical composition.
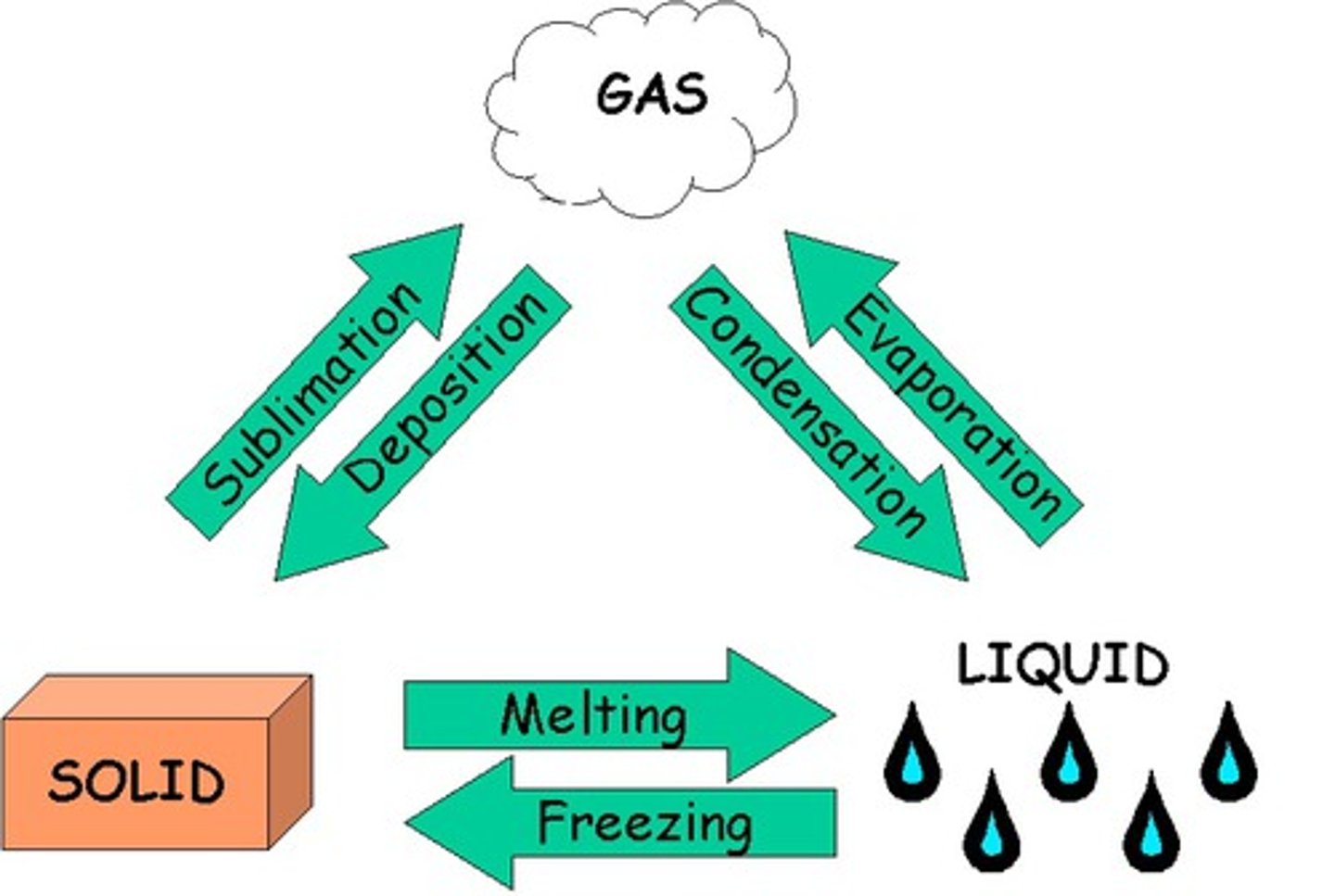
Production or absorption of heat and light; Evolution of gas; Formation of precipitate; Change in temperature/color; Production of mechanical energy; Production of sound
Enumerate seven (7) evidences of chemical reaction:
Production or absorption of heat
Formation of sparks or flame or light.
Exothermic
Warming the surrounding.
Endothermic
Cooling the surrounding.
Evolution of gas
Formation of bubbles.
Formation to precipitate
Insoluble (cannot be dissolved) solid is formed.
Word equation
An equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words.
+
Written between symbols and/or formulas of reactants or products.
→
"Yields," separates reactants from products.
⇌
Used in place of → for reversible reactions.
(s); (l); (g)
Designates a reactant or product in the solid state, liquid state, or gaseous state; placed after the formula.
(aq)
Designates an aqueous solution; the substance is dissolved in water; placed after the formula.
Δ
→
/
heat
→
Indicates that heat is supplied to the reaction.
Pt
→
A formula written above or below the yields sign indicates its use as a catalyst (in this example, platinum).
H₂, N₂, O₂, F₂, Cl₂, Br₂, I₂
Enumerate seven (7) diatomic molecules:
CₙH₂ₙ+2
State the formula for fuel (alkanes), where n = any integer:
Methane
CH₄
Ethane
C₂H₆
Propane
C₃H₈
Butane
C₄H₁₀
Pentane
C₅H₁₂
Hexane
C₆H₁₄
Heptane
C₇H₁₆
Octane
C₈H₁₈
Nonane
C₉H₂₀
Decane
C₁₀H₂₂