Cell Communication
4.8(6)
Card Sorting
1/24
Last updated 11:40 PM on 11/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
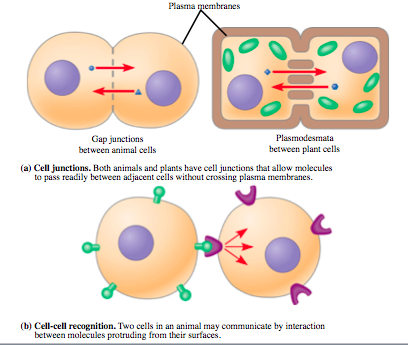
direct contact
cell communication via direct contact; examples of this type of cell communication include plasmodesmata, gap junctions and immune cell activity
2
New cards
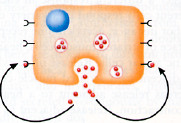
autocrine signaling
the target cell is also the secreting cell
3
New cards
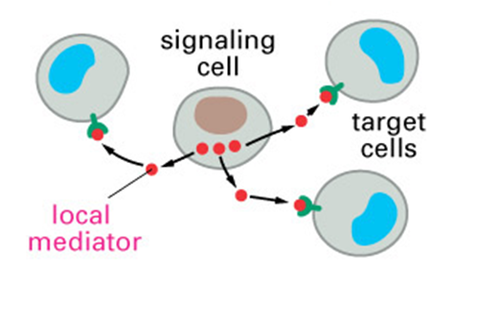
local regulators
A chemical messenger that influences cells nearby
4
New cards
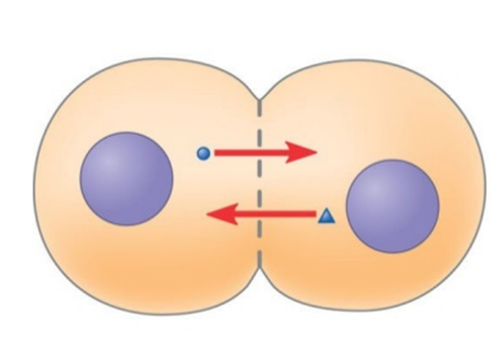
gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells, holes in cell membranes
5
New cards
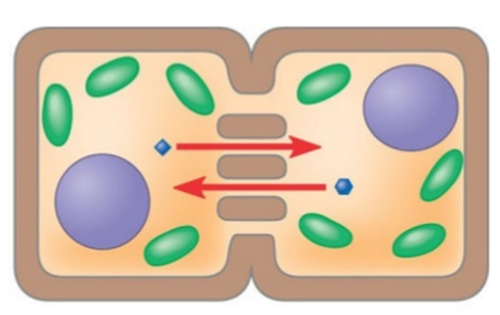
plasmodesmata
An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect adjacent cells
6
New cards
reception
A target cell's ability to detect a signal molecule coming from outside the cell; stage 1 in cell signalling .
7
New cards
response
The cell's reaction to a chemical messenger.
8
New cards
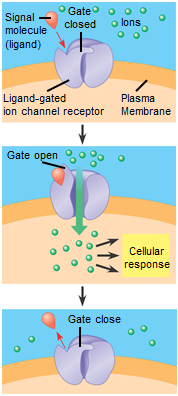
ligand
A molecular messenger that binds to specific receptors on, or within, the cell. It is not chemically altered.
9
New cards
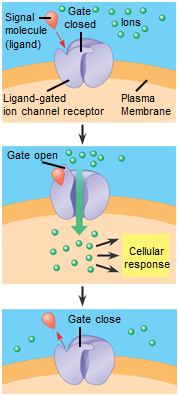
receptors
Molecules (often proteins) that detect specific ligands in their internal or external environment.
10
New cards
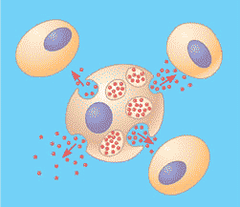
paracrine signalling
type of cell communication in which chemical messengers are detected by nearby cells
11
New cards
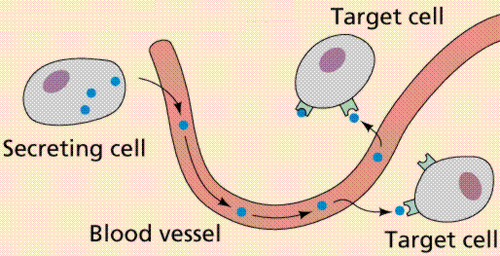
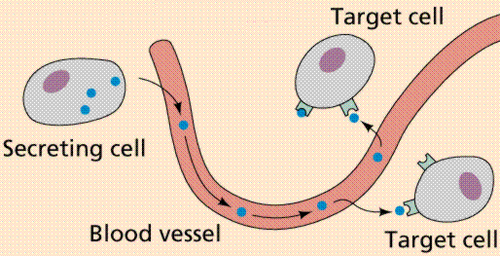
endocrine signalling
long distance signaling that uses hormones as ligands that travel through the blood
12
New cards
hormones
Chemical messengers manufactured endocrine glands & travel through the bloodstream to distant target cells
13
New cards
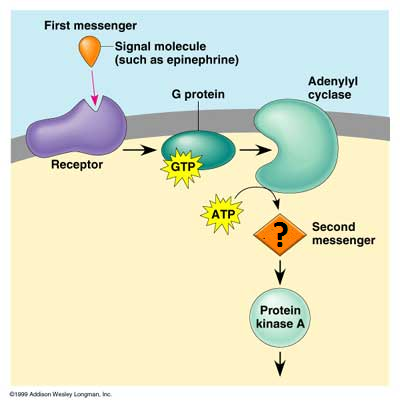
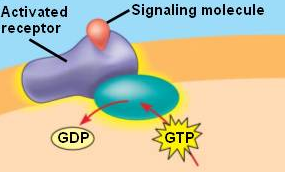
G-protein coupled receptors
A special class of membrane receptors with an associated GTP binding protein; this receptor involves dissociation and GTP hydrolysis
14
New cards
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
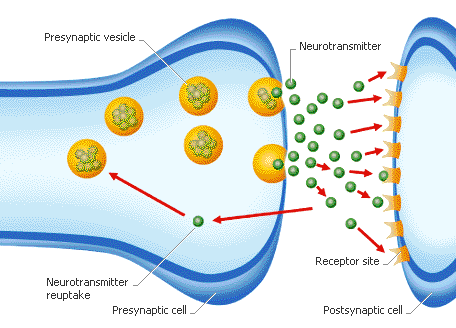
15
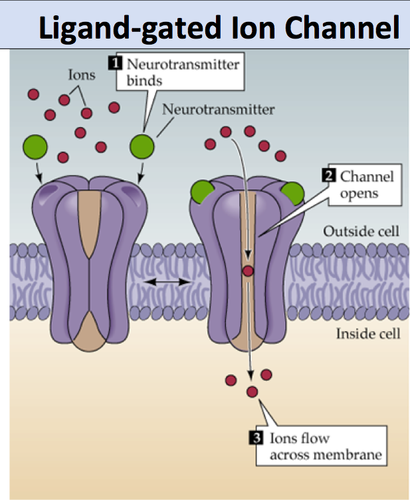
New cards
ligand-gated ion channel
Type of membrane receptor that has a region that can act as a "gate" when the receptor changes shape.
16
New cards
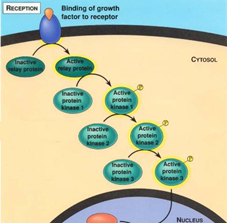
transduction
The transfer of the signal from the cell membrane resulting in a change in cell activity; stage 2 in cell signalling.
17
New cards
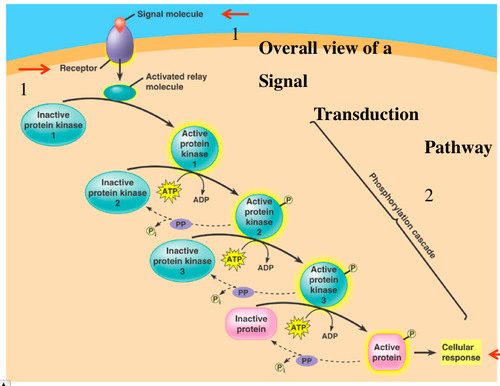
phosphorylation cascade
A series of enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation reactions commonly used in signal transduction pathways to amplify and convey a signal inward from the plasma membrane.
18
New cards
secondary messenger
A small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecule or ion, such as calcium ion or cyclic AMP, that relays a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signal received by a signal receptor protein.
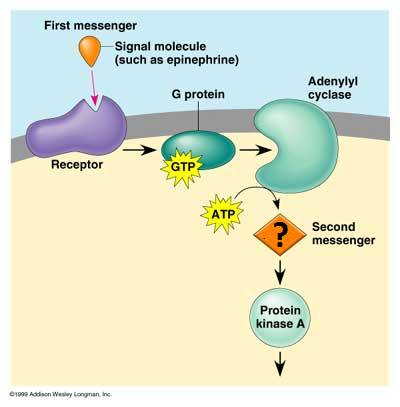
19
New cards
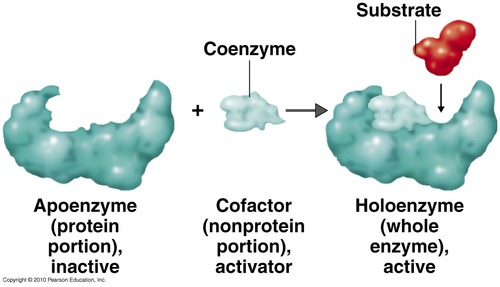
Cofactors
Organic molecules (not proteins) that assist in the normal functioning of enzymes (Zinc)
20
New cards
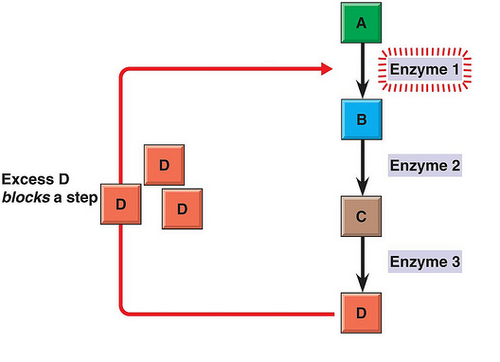
feedback inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
21
New cards
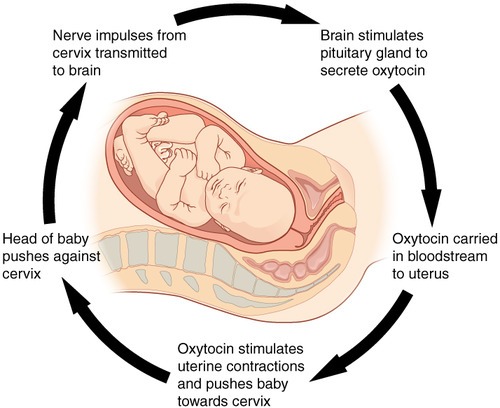
positive feedback loop
Causes a system to change further in the same direction.
22
New cards
negative feedback loop
A feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving
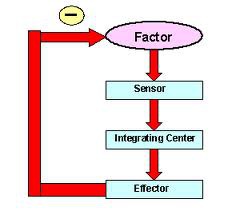
23
New cards
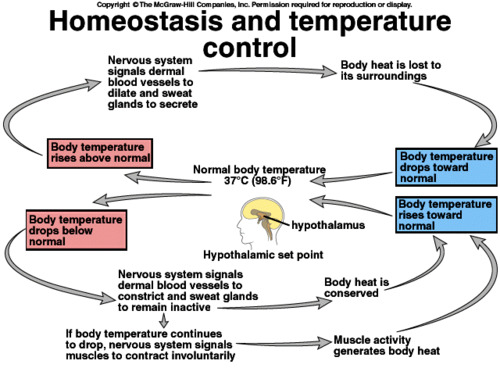
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
24
New cards
Kinases
Enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to acceptor molecules.
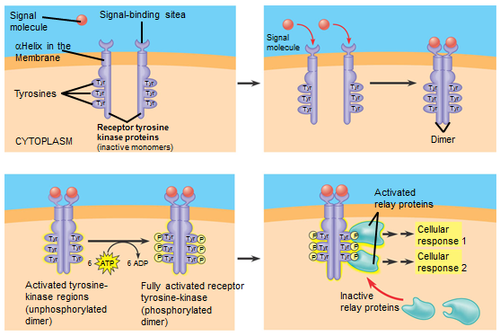
25
New cards
secondary messengers
Intermediate chemicals that help transduce a chemical signal