Carbohydrates
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Types of Carbohydrates Carbohydrate Food Sources and Guidelines for Intake Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates Glucose Regulation and Utilization in the Body Fiber – Types, Food Sources, Health Benefits, and Whole Versus Refined Grains Sugar: Food Sources, Health Implications, and Label-Reading Sugar Substitutes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What does the CHO abreviation for carbohydrates mean?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
What are the 2 subgroups of simple carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
3 Monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
what does gucose look like?
Picture
what sources contian glucose
Fruit
Vegetables -Corn
Honey
Syrup
Why is glucose important to plants? (2)
They make it directlu from photosynthesis to fuel all they do
They transform to other molecules
Why is glucose imporant to humans
The nervous system is not as good at using other sources of energy. (right away)
What does fructose look like?
Chem sturcture
What foods can fructose be found in?
Fruit
Vegetables- High fructose corn syrup
Why is fructose important to plants?
it is the sweetest carbohydrate, so it attracts insects and animals, which helps with reproduction
What does galactose look like?
chem form
what is galactose found in?
Can you usually find it by its self?
Milk, milk products
No, it is ussually in disaccaride form as lactose
what are the 3 Disaccharides,
what makes up each?
Maltose- Glucose + Glucose
Sucrose- Glucose + Fructose
Lactose- Glucose + Galactose
What foods are maltose found in?
Sprouted Grains
Fermentation???
Why is Maltose found in spouted grains?
Because sprouted grains contain a lot of starch, and when it starts to break down maltose is exposed
What food sources is sucrose found in?
Fruit
Vegetables
Maple Syrup
Honey
.
the benifit of surcose from vegetables to table sugar is the other nutrients it provides
WHat foods is Lactose found in?
Only found in milk and milk products
What are the 3 types of complex carbs?
Starch
Glycogen
Fiber
What are the 2 types of starches?
Amylose Linear
Amylopectin Branched
Lots of glucose
What food have starch?
Grains
Legumes
Nuts
Seeds- energy for later, sprout
Why is Glycogen important for animals?
Why is it branched?
Where is it stored?
storage of carbs to provide quick energy to body,
for the ability to be broken down faster
It is stored in the liver, and skeletal muscles- liver sends to all, muscles use their own
What is the make up of Fiber?
Network of glucose with hydrogen bonds
What is fiber found in?
Stocks of foods for protection
seeds
nuts
vegetables- Broccoli
Why is Fiber important to plants?
Cellulose is a strong barrier making up cell walls (structure and support)
What Carbs are found in Whole fruits like an apple?
Sucrose
Glucose
Fructose
Fiber
what carb do fruit juices lose?
Fiber, no peel
What carbs are found in non starchy vegetables?
Sucrose
Glucose
Fructose
Fiber
what carbohrate do starchy carbs contian like, potatoes, peas, and corn?
Starch
Fiber
Glucose
Fructose
sucrose
What Carbs do nonspouted grains like rice and oatmeal contain?
Sucrose
Fiber
what carbs are found in sprouted grains?
Starch
Maltose
Fiber
What carbs are found in dairy products
Lactose
What carbs are found in Beans and nuts?
Starch
fiber
What is the RDA for CHO and why?
130g
The minimum amount of glucose utilized by the brain
what is higher RDA or AMDR for carbohydrates
AMDR (45-65) unless less than 1100 calories/day
AI for fiber?
Do most people meet this goal?
14g/1000kcals
No U.S. is about half
Reccomendation of Added sugar (DGA)
Less than 10% of calores
What does the mouth do for the digestion of Carbohydrates?
Chewing mixes salivary amylase (from salivary glands) with food.
What does the stomach do for carbohydrate digestion?
MD Not much just churning
CD HCL disables salivary amylase
What does the small intestine do for the digestion of carboydrates?
Abdsorption?
Pancreatic Amylase breaks down starch into maltose and shorter chains of polysaccharides called oligosaccharides (3-10)
Enterocytes release
Maltase to break down Maltose
Lactase to break down Lactose
Sucrase to break down Sucrose
Monosaccharides are abosorbed by enterocytes(brush border) and brought to the blood stream,
The liver has to convert lactose and sucrose into glucose and put it back into the blood.
What does the Large intestine do to carbohydrates?
what does fermentation do to gut?
Fermentation of fiber from gut microbiome-
.
prucucing gas(bloating and flatuence) and short chain fatty acids which large intestine cells can use for energy
Whole foods= more fiber
What is the primary goal of carbohydrate digestion
turn polysaccharides into small enough pieces to be absorbed
where are alpha and beta cells found?
In the pabreas
which release hormones that influence the liver (blood sugar)
What does insulin do?
Hormone that makes cells uptake glucose
Decrease blood sugar
What does glucagon do?
hormone that makes liver break down glycogen, which releases glucose into the blood
What do sucrose rich foods do to blood sugar and insulin compaired to starch rich foods?
Higher peaks, lower crashes
Blood sugar and insulins relation is direct
What does insulin do at the cellular level?
Triggers the opening of glucose transporters on the surface of the cell, allowing glucose to enter the cell, subsequently decreasing blood glucose.
How could glucose be used in a cell?
If the cell needs energy right away. The cell can metabolize glucose with cellular respiration, producing ATP
If the cell does not need energy right away? If the cell is the liver or skel msucle cell then glucose is converted to glycogen. If other cell turned into fat.
How does the body reach homeostasis once their is low BS
Tell the brain to eat. BS inc
Pancrease released glucagon into blood, stimulates breakdown of glycogen releasing glucose into blood. BS in
Glucagon also stimulates glucogenesis, new glucose is made from amino acids in the liver and kidneys. BS inc
How do cells use glucose for energy?
Cellular respiration?
Glucuose (6C molec) is broken down into two Pyruvic Acid (3C molecule) via glycolysis
Pyruvate enters a mitochondrion of the cell, where it is converted into Acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA goes through Krebs, which is aerobic, it produces CO2 and High energy electron carriers NADH2 and FADH2
These high energy electron carriers go through electron transport chain to procude ATP (energy for the cell)
What happens when there is not enough glucose?
glucose can be very low when someone is fasting, starving eating low carb
Your cells will start to use two other macronutrients.
How does the body use protein as a glucose source?
The body will turn amino acids in the blood stream to glucose though glucogenesis in the liver (some kidneys).
Which can go through glycolosis and be used to make ATP. But if someone is starving they wont have free amino acids to use so the breakdown of muscle will occur to free up amino acids.
How does the body use Fat as an energy source?
You can break down fat into acetyl CoA in the liver which can go through the krebs cycle to producse ATP,
eventually liver Krebs will get tired.
Then Acytel CoA will be converted to compounds called Ketones or ketone bodies.
Which can be exported to other cells of the body and used for energy, (primarily the brain and muscle cells)
How do ketones help to preserve the protein in the muscle?
Ketones can be used by tissues of the body as energy instead of gluconeogenesis. Preserving muscle tissue. It takes about 3 days for the brain to adjust.
What is Ketosis?
Symptoms?
The accumulation of ketones in the blood.
Sweet breath, dry mouth, reduced appetite
What is Ketoacidosis?
to much accumilaton of ketons in the blood, to acidic
What is diabetes and what are the types?
Disease where the body isn’t able to regulate glood glucose levels
1- autoimune, body kills beta cells, not enough insulin produced to allow glucose to enter cells and receive energy or low BS
2- pancreas gets tired from producing so much insulin and starts to make less, not enough produced.
Gestational- develops during pregenacy 6% of pregnacnys- can cause to much fetal growth
Symptoms of type one diabetes
Weight loss and fatigue,
Glucose build up which increases urination and thirst
what age group is type one diabetes diagnosed
What percent of diabetes are type one?
childhood
5-10%
how is diabeties treated?
taking insulin following meals
How many US peiple have pre or diabetes?
who is it assoiatoed with?
100 million
fat people(abdominal obesity)
Problems from type 2 diabetes
Hypoglycemia,
heart, increasing the risk of heart disease
blood vessel, stroke
nerve damage, eye, blindness.
kidney failure,
Define Fiber
Non degestible carbs found in plans
What does soluble fiber do?
What are the types?
What are some food sources?
Dissolves in water, forms a viscous gel which slows digestion and absorption of glucose, which decreases BS spike speed.
Soluble fiber binds cholesterol to bile salts, which contain cholesterol.
it is very fermentable, so it is easily digested by the large intestine bacteria.
Pectins and gums are common types of soluble fibers,
Good Food sources include oat bran, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, peas, and some fruits and vegetables.
What do insoluble fibers do
What are they
What food
Some are fermentable by bacteria in the large intestine but to a lesser degree than soluble fibers. Insoluble fibers help prevent constipation, as they create a softer, bulkier stool that is easier to eliminate.
Lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose
Food sources include wheat bran, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
What types of foods are fibers found in.
All whole plant foods (including whole grains),
oatmeal, barley, rice, and wheat, beans, nuts, seeds, whole fruits, and vegetables.
When foods are refined what can happen to fiber and other nutrients?
Parts of the plant are removed, and some nutrients are lost.
Good choices of fiber?
Raspberries, dried chia seeds, Mixed vegetables, lentils, and black beans
How does fiber affect cardiovascular health?
Lowers_ risk of cardiovascular disease.
Higher fiber intake has been shown to improve blood lipids by reducing total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low density cholesterol (“bad cholesterol,” associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease), and increasing high density cholesterol (“good cholesterol,” associated with lower risk).
What does fiber do to diatabetes
Colorectal cancer
Body weight
slow spike of glucose decrease need of insulin
dec chance of colorectal cancer
helps maintian a healthy body weight
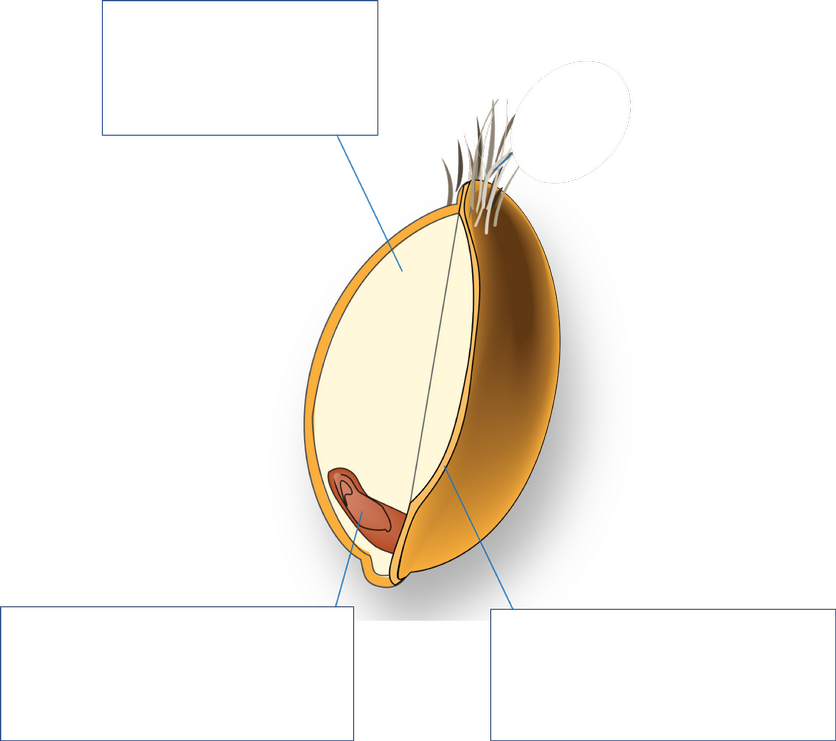
What is TOP, and what nutrients does it contain?
Endosperm
protein,
sm amt of vit,
min
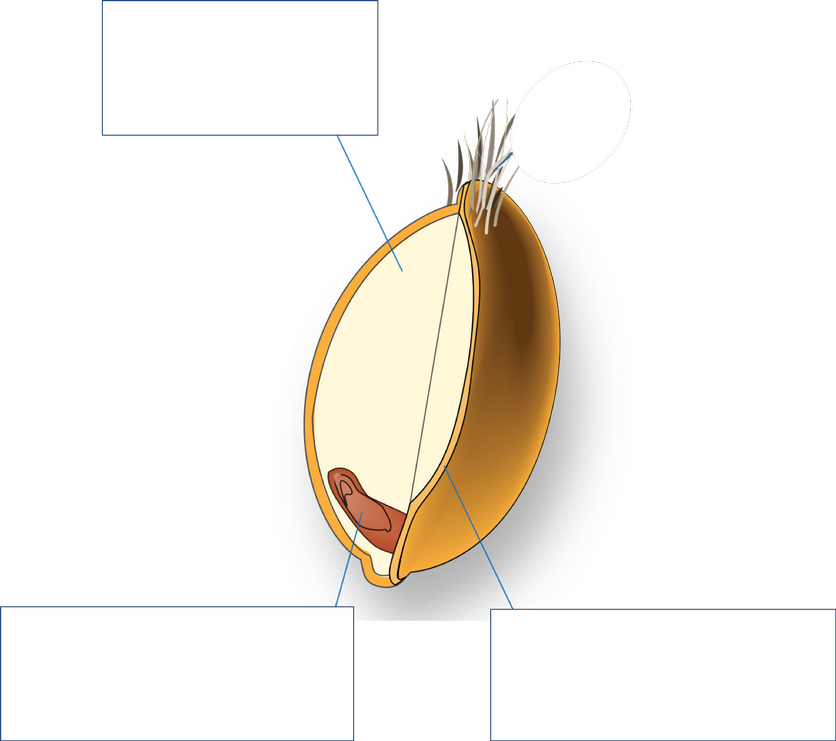
What is LEFT, and what nutrients does it contain? (5)
Germ,
B vit,
protein,
min: zinc magnesium,
Healthy fats
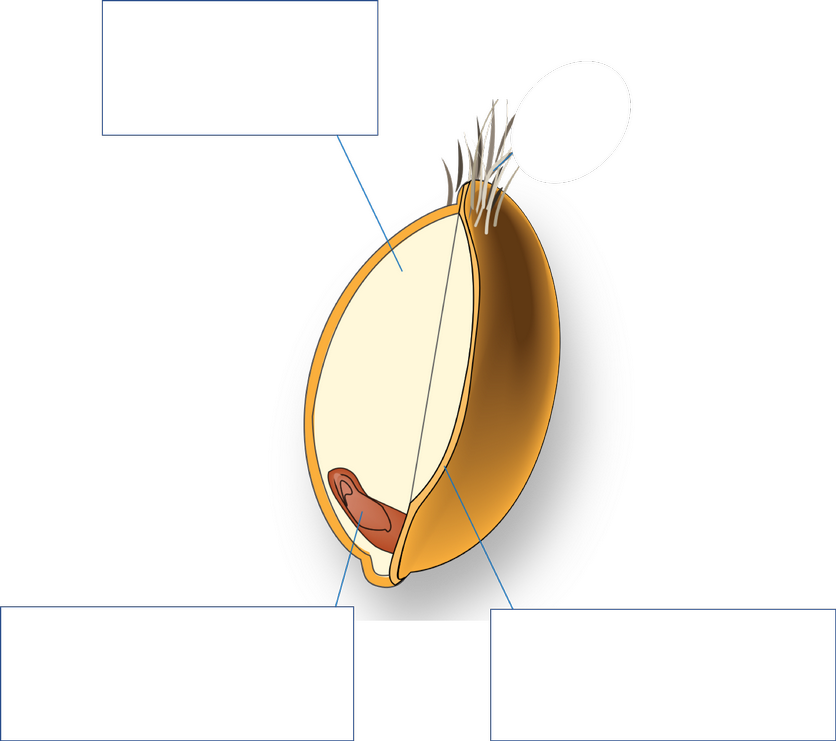
What is Right, and what nutrients does it contain? 3
Bran
antioxidants,
b vit,
fiber
How does the DGA define Whole grains?
Grains and grain products made from the entire seed, usually called the kernel which consists of the bran, germ, and endosperm.
If kernel has been modified it must contain similar proportions of each to be considered whole grain.
Usually has high fiber
EX of whole grain?
Barley, corn( whole cornmeal and popcorn), oats
What are refined grains? what parts removed?
Grains and grain products with the germ and bran removed, any grain that is not a whole grain product. Many are low fiber and enriched
Ex Refined grains
White rice, removed protein and lots of nutrients.
How can you identify whole grians when shopping?
Look at nutrition label, a whole grain should be listed first ex 100% wheat flour, should not be followed by enriched or refined
Some whole grains: wheat, barley, brown rice, buckwheat, corn, rye, oats, whild rice, less known varieties include teff, amaranth, millet, quinoa, black rice, black barley, and spelt
What foods have naturally occuring sugars?
what nutrients ussually come with them?
Ex apple
Fresh fruit, vegatables, and milk
Fiber, potassium, and vitamin C, calcium potassium, phosphorus, riboflavin.
Apple has 23g sugar but 5g fiber, vit C and potassium
75 percent of packeged foods in the US conaitn added sugar
What is the biggest sourse of sugar in american diet and how much added sugar do we consume?
Teaspoons to g of sugar
Soda
22-30 teaspoons 17% of calories
1 teaspoon 4g sugar
Benifits of eating less added sugar? 5 health
Lower risk of:
cardiovasciular disease,
obesity,
type 2 diabeties,
some cancers,
dental cavities(not just added sugar)
Why should we limit high fructose corn syrup?
What is a better option?
significant evidence that fructose corn syrup can be just as toxic as alcohol to the liver.
Honey or Maple syrup, other nutrients
Where should you look to find out if a food is high in sugar or not?
Nut label g added sugar
and ingreedeints are adding to added sugar?
What are sugar substitutes?
Artificial, Non nutrative, high intencity, low cal sweeteners
Ex of sugar Subs
-ame
S-
Monk-
• Acesulfame Potassium (Ace-K) 200x
• Advantame 20,000x
• Aspartame 200x
• Neotame 7000-13000
• Saccharin 200-700
• Sucralose 600x
• Luo Han Guo (monk fruit extracts) 100-150
• Stevia 200-400x
What are sugar alcohols? How differnet from sugar subs?
Ex
effects?
They are more like monosaccharides, but not as extreme as sugar subs.
Only partially digested. Ex 2kcal/g
Xythol, Erythrtol, Lactitol, mannitol, sorbitol
not good digestion, bloating, gas, and diareha
Can sugar subs help with weight loss?
Short and long term?
what might be a better stategy than using sugar subs?
short: yes cut out empty cals
Long: Association between artificial sweetners and bad health effects, like fatness
Using real sugar in moderation
What are emerging safty concers of high intensity sweetners?
Bacteria problems and glucose intolerance
Not cancer
Are natural sweetners better than artificial sweeteners?
No
cause gut becteria problems, metabolic helath issues, does not prove weight loss