3.3 carbohydrates
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what molecules make up carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
Examples of monosaccharides
Glucose, galactose, fructose
Glucose + glucose → make what
Maltose
Glucose + fructose → make what
Sucrose
Glucose + galactose → make what
Lactose
What are polysaccharides
Two or more monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds, branched/unbranched
Examples of polysaccharides
Starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin
How to form glycosidic bonds
Condensation reaction
How to break glycosidic bond
Hydrolysis reaction
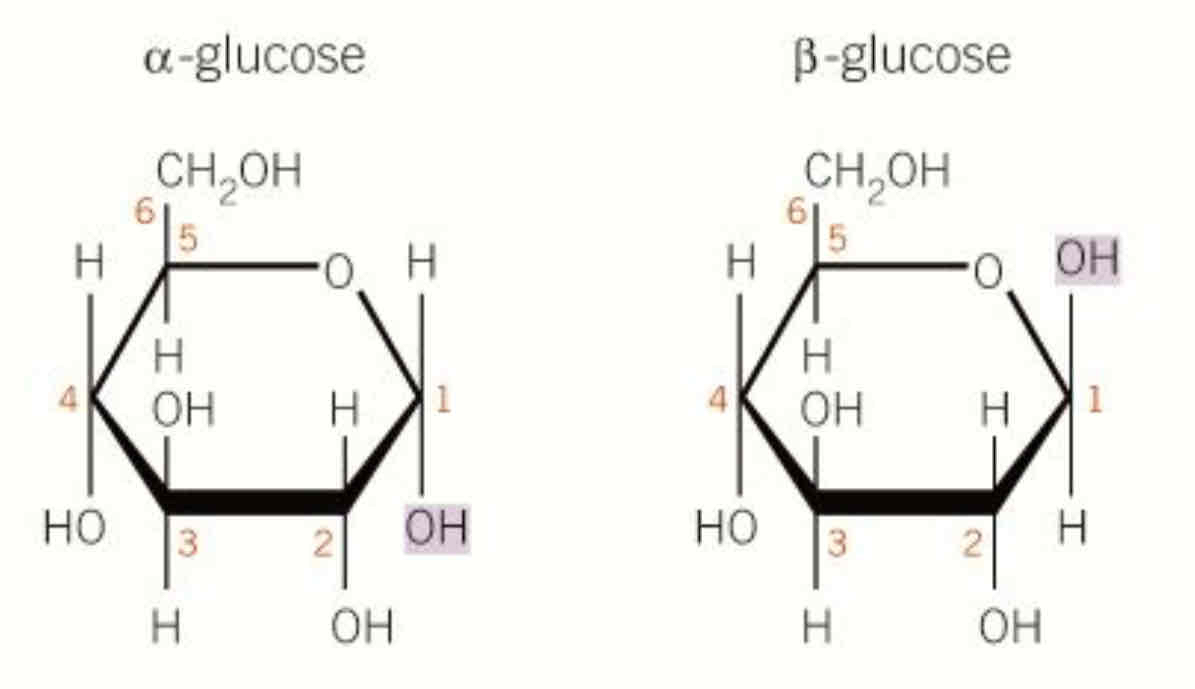
what is the difference of α-glucose and β-glucose
in a glucose OH is down b is up
Functions of starch
Main energy storage material in plants
stored in seeds
broken down into glucose when need more energy,
act as source of food for humans and animals
Features of starch
Does not change the osmotic balance
insoluble in water
made of amylopectin and amylose (both alpha-glucose)
Features of amylopectin
Highly branched chain
enzymes can easily access glycosidic bonds, can be quickly released when needed
1-4 glycosidic bonds but also 1-6 glycosidic bond (branch) approximately every 25 glucose subunits
Features of amylose
Linear chain, helical structure
amylose strands can pack closely together
good for storage
form 1-4 glycosidic bonds (a-glucose), less soluble
Function of glycogen
Highly branched molecule (similar to amylopectin)
highly branched structure glucose can released fast
difference between hexose and pentose sugar
glucose = hexose sugar (6 carbons in structure) ribose = pentose sugar (5 carbons in structure)
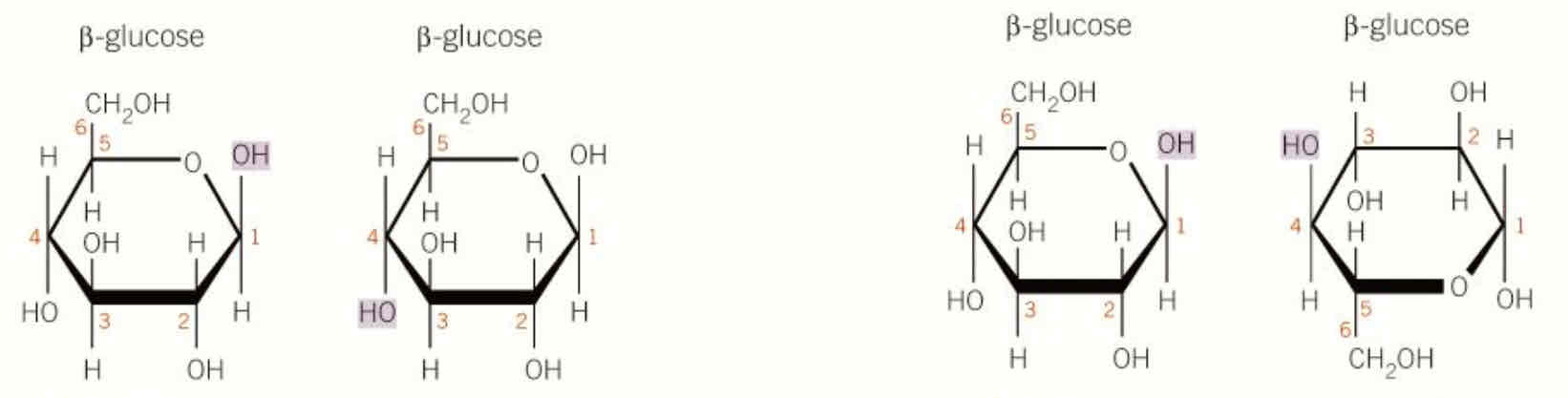
how is cellulose formed
b glucose unable to join like a glucose since OH groups are too far, so alternate b glucose molecule turn upside down
unable to form branches or coil
use of cellulose
make h bonds with each other form microfibrils, join together make macrofibrils
join make fibres, strong and insoluble, used to make cell walls
very hard to break down into monomers, forms the fibre necessary for healthy digestive system
example of a reducing sugar
glucose
example of a non-reducing sugar
sucrose