2.3 - Supply and PES (Price Elasticity of Supply)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Define supply.
The quantity of a good / service that producers are willing and able to provide at each price level in a given time period.
Define the Law of Supply.
For most goods / services, quantity supplied varies positively with price.
As prices fall, quantity supplied _____. As prices rise, quantity supplied _____. More supply when prices are higher means ____ profits are likely to be earned. Higher __________ costs as output increases results in ______ prices needed to cover costs.
falls, rises, more, production, higher
The supply curve slopes ________ due to the ________ relationship between _____ and ________.
upwards, positive, price, quantity
Define individual supply.
The supply of a good or service by an individual producer.
Define market supply.
The total supply of a good / service as a result of adding together all individual producer supplies.
Movement along the supply curve is caused by a change in _____ and by no other factor. Price changes lead to a movement — or —— the curve. A price increase leads to a movement __ the curve, leading to an _________ in supply. A price ________ leads to a movement ____ the curve, leading to a contraction in ______.
price, up, down, up, expansion, decrease, down, supply
An outward shift is caused by an ________ in supply. An ______ shift is caused by a decrease in supply.
increase, inward
If demand _____, producers see an opportunity to sell more - and at higher ______ - so they increase ______, shifting the supply curve ________. If demand _____, the opposite happens, so the ______ curve shifts _______.
rises, prices, supply, outwards, falls, supply, inwards
What is the mnemonic for factors that cause a shift in the supply curve? What does it stand for? Explain each one.
PINTSWC
productivity - higher productivity increases supply with lower costs of production (outward shift)
Indirect taxes - higher indirect taxes causes costs of production to rise, leading to fall in supply (inward shift)
Number of producers - more producers in the market causes supply to increase (outward shift)
Technology - new / improved technology increases productivity, lowers costs of production, and increases output / supply (outward shift)
Subsidies - government subsidies lower costs of production, increasing supply (outward shift)
Weather - poor weather causes agricultural products’ supply to fall (inward shift)
Costs of production and government regulations - higher production costs causes supply to fall (inward shift). Government regulations often cause production costs to rise, leading to falls in supply (inward shift).
Define PES.
Measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price.
What is the formula for PES?
PES = (%change in quantity supplied / %change in price)
Define inelastic PES.
When the %change in quantity supplied is less than the %change in price.
Define elastic PES.
When the %change in quantity supplied is more than the %change in price.
If a business can respond to changing ______ quickly and/or efficiently, the business has price _______ supply. This creates an ______ sloping ______ curve with a _______ gradient. If the business struggles to lower / increase supply to price changes, the business has price _________ supply. The supply curve will have a _____ gradient.
prices, elastic, upward, supply, shallow, inelastic, steep
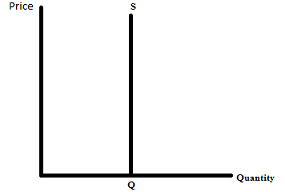
For perfectly inelastic supply:
what is the PES value
Explanation
Graph
0
Quantity supplied is entirely unresponsive to a change in price
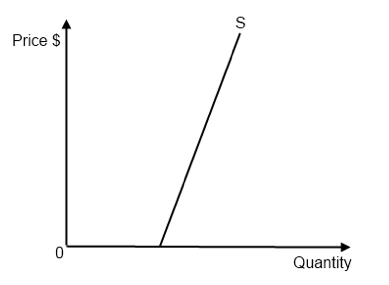
For inelastic supply:
what is the PES range
Explanation
Graph
0 to 1
Quantity supplied changes by a lower rate than a change in price
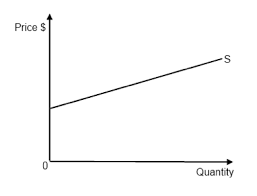
For unitary elastic supply:
what is the PES value
Explanation
Graph
1
Quantity supplied changes at the same rate as a change in price
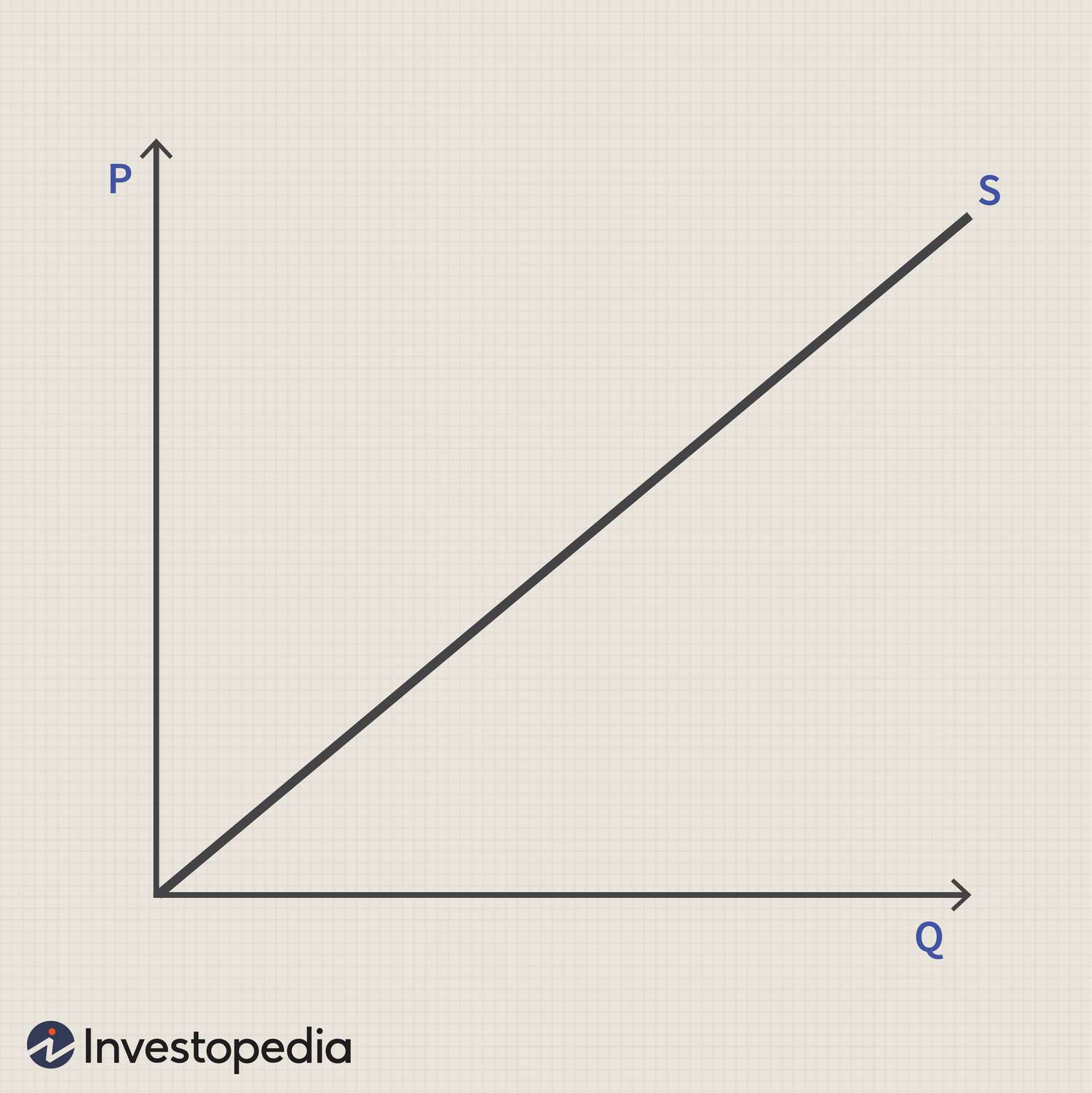
For elastic supply:
what is the PES range
Explanation
Graph
1 to infinity
Quantity supplied changes at a greater rate than a change in price
For perfectly elastic supply:
what is the PES value
Explanation
Graph
infinity
Quantity supplied is infinite at one price, but falls to zero if price changes

What is the mnemonic for factors affecting the PES of a product? What does it stand for? Explain each one.
PSSST
production lags - if product takes long time to manufacture, e.g. crops, then they will be unresponsive to price changes; product has more price inelastic supply
Spare capacity - if a firm is underutilising its resources, they can easily increase capacity if price increases, therefore increasing supply; product has more price elastic supply
Stock levels and work in progress - if a firm has low stock levels, won’t be able to respond to price changes; product has more price inelastic supply
Substitutability of factors of production - if a firm can easily move factors of production between product lines, it can respond to price changes; product has more price elastic supply
Time period - in short time, firms are unable to change production processes quickly; product has more price inelastic supply.
Most consumers don’t have the means to _________ PES but it still affects them. _________ PES = more difficult for consumer to purchase more of product without paying much higher price.
calculate, inelastic
_______ PES may be better for producers - can easily _______ to _____ changes.
Elastic, respond, price