RMA Week 4: experimental methods II
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what’s a within-subjects design?
aka repeated-measures, all participants receive all levels of the IV
what’s a between-subjects design?
aka independent groups, different groups of participants receive different levels of the IV
advantages of a between-subjects design
no order effects
some participants can only be between-subjects
naïve participants - no learning
disadvantages of a between-subjects design
lots of participants
characteristics may differ between groups
how to counteract disadvantages of between-subjects designs
random assignment to groups or participant characteristics matched in each group (but can’t account for every nuisance variable and variables can be related yet unmatchhable)
advantages of a within-subjects design
fewer participants required
reduced individual differences - confounding variables from each participant, and they’re used as ‘their own controls’
disadvantage of a within-subjects design
carryover effects - effect of one condition carries over to the next session
solution to carryover effects
order of conditions randomised/counterbalancing
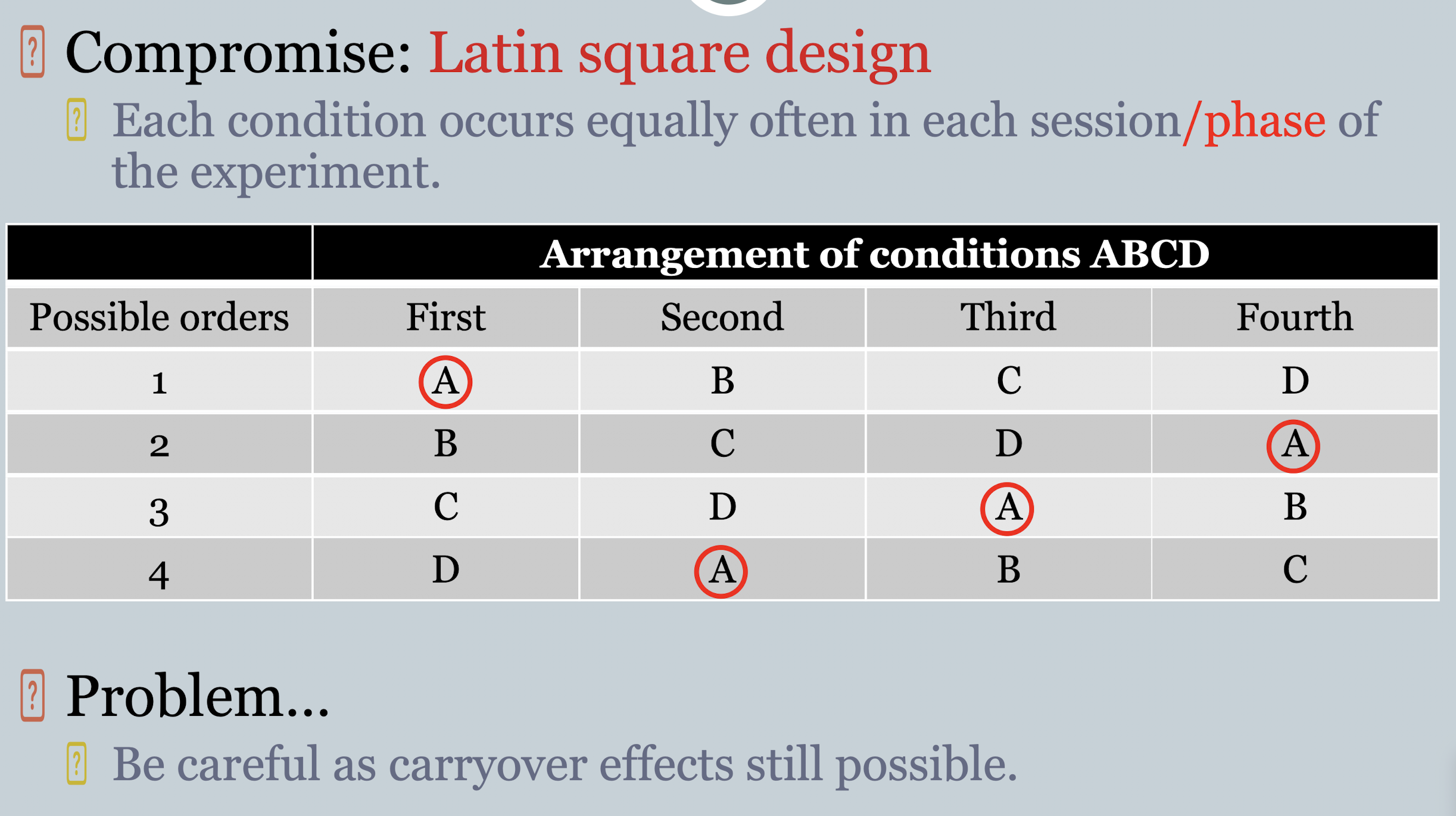
counterbalancing can be too complex with more conditions - e.g. 24 orders with 4 conditions… what’s the compromise?
latin square design - each condition occurs equally often in each phase of the experiment
what’s a quasi-experiment
when 1+ IV’s are selected - not manipulated - as impractical/impossible/unethical
advantages of quasi-experiments
you can examine variables that would be impossible to manipulate otherwise
can inform potential experiments (if ethical)
disadvantages of quasi-experiments
no strong conclusions about cause and effect
no manipulation leads to more confounding variables that can’t be removed
how can improvements be made to quasi-experiments?
matching participants
if treatment study: tests before and after treatment with pp as their own control
what’s a random sample
everybody (in the population) has an equal chance of being selected - usually practically different!
what’s a stratified sample and one advantage
random selection of each subgroup of the population. advantage: key groups in sample
what’s a quota sample
representative sample that meets quotas/targets e.g. 50% males and females: ‘semi-randomised’
state the aim of psycho-physiological measurements
testing the effect of psychological variables on physiological processes
name three examples of psycho-physiological measurements
muscle activity
eye movements/eye blink rate
brain imaging/neurophysiological measures