module 5 - petrology & economic geology ⛏️👷♂️🚧
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fmlfmlfml
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Concentration factor
The number of times the metal must be concentrated from the average crustal abundance to reach the cut off grade (the lowest economic ore grade for mining)
Concentration factor calculation
cut off grade (%) / average crustal abundance (%)
Average crustal abundance
The amount of metal in the crust of the Earth if it were all evenly spread throughout the crust
Ore
a rock or minerals which can be mined for metal extraction.
Many minerals contain metals but not all will be ores as it may be too expensive or difficult to extract the metal from the mineral
Internal processes
Igneous + metamorphic
Surface processes
Sedimentary + weathering
Resource
A useful and valuable natural material
The total quantity of metal in the world which may in the future become economic to mine
Mineral resource
Can be a metallic, non-metallic or industrial mineral
Reserves
The amount of the resource that can be extracted at a profit using existing technology
Consumption
Is the quantity of a metal being used
Ore
The rock containing valuable metal(s) that is economic to mine
Ore deposit
Accumulation of metal that maybe economic to mine
Ore mineral
A mineral containing valuable metal(s)
Gangue mineral
A low value waste mineral
e.g. quartz, calcite, pyrites and barytes
Grade
The concentration of valuable mineral within an ore
Cut-off grade
The grade below which it is uneconomical to mine
What controls the cut-off grade?
Value of the metal | The more valuable the metal the lower the cut off grade |
Demand | The higher the demand for the metal , the more valuable and the lower its cut off grade |
Abundance | If they are useful scarce metals will have a lower cut-off grade |
Size of the deposit | Large deposits will be economic to mine at lower cut off grades than smaller deposits |
Cost of mining and extraction | If it is costly to mine and extract a metal then the cut off grade will be higher |
Cut-off grade can be calculated by rearranging the concentration factor formula:
Average crustal abundance
X
Minimum concentration factor to be economic
Spoil
waste material brought up during the course of an excavation or a dredging or mining operation.
Secondary enrichment
Occurs when metals are leached from surface rocks and precipitated just below the water table
Not an ore forming process but an ore concentrating process
Very important for increasing the grade of otherwise uneconomic copper deposits
Leaching
Where elements are dissolved from rocks and carried downwards in solution
Gossan
An insoluble cap of iron oxides at the surface
Oxidising
Describes oxygen rich conditions, allowing elements to combine with oxygen to form oxides
Reducing
Describes oxygen poor anoxic / anaerobic conditions
Enriched Deposit
A zone of high grade ore just below the water table, formed by secondary enrichment
Porphyry
A large igneous intrusion below a volcano with a porphyritic texture
Porphyritic
An igneous rock w/ large crystals, called phenocrysts, surrounded by a matrix of smaller crystals or glass, called the groundmass
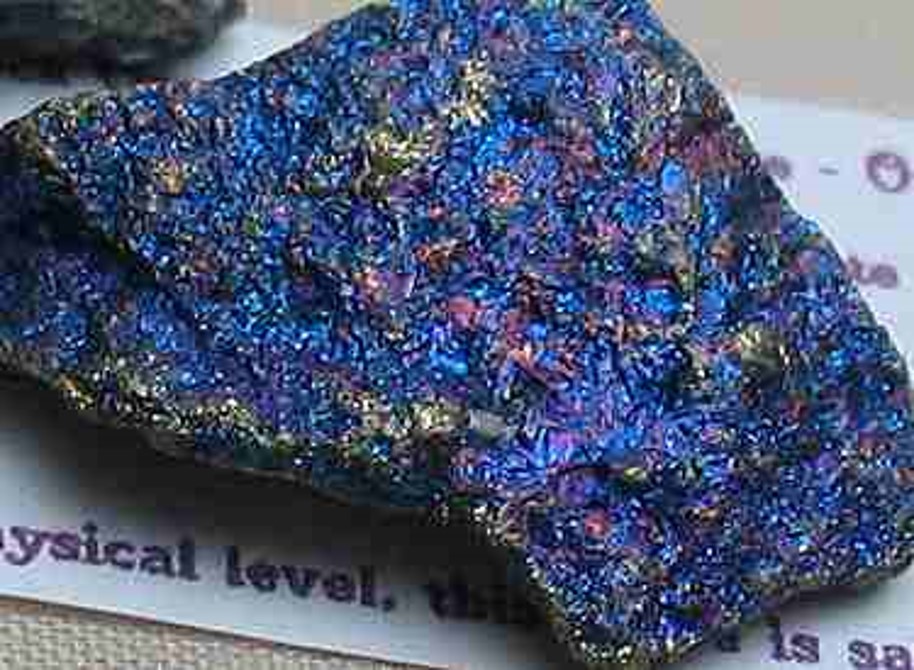

Chalcopyrite
Copper sulfide/The main ore mineral for copper

Malachite

Azurite

Chalcocite
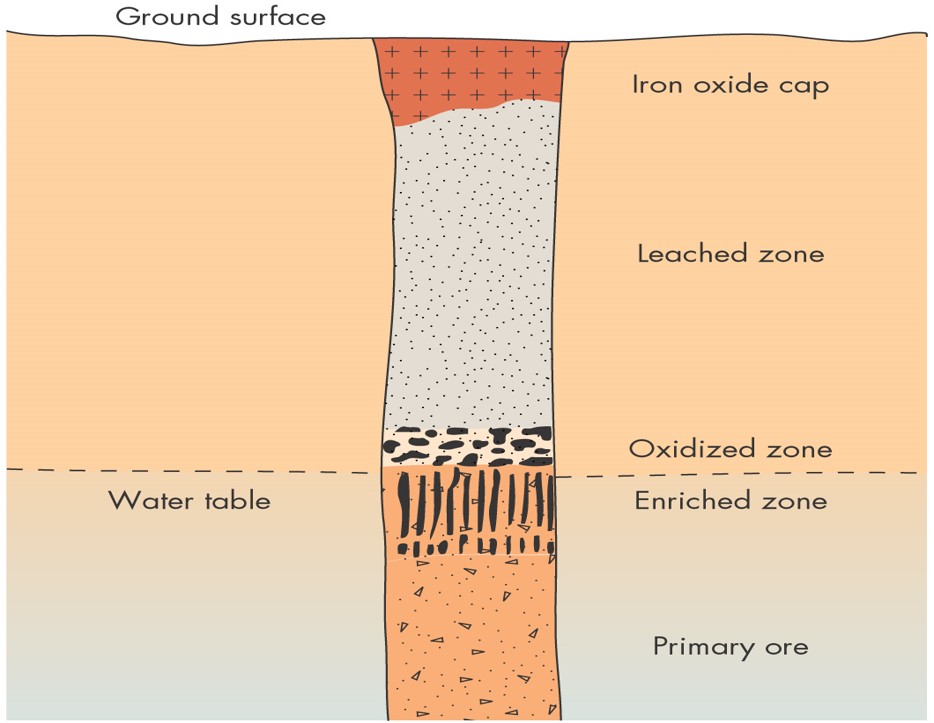
Above the water table…
Rainwater infiltrates into the exposed copper deposit and percolates downwards through the pore spaces
In the zone of oxidation ____ the water table, chemical reactions change insoluble copper sulfides such as chalcopyrite into soluble copper sulfates
The copper sulfates are dissolved, taken into solution and carried downwards by the groundwater
A barren, leached zone is left near the surface covered by an insoluble iron oxide capping called a gossan
Gossans are of no economic value but are useful exploration targets as they may indicate ores deposits underneath
Below the water table…