physical and inorganic chemistry
1/359
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
360 Terms
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus
mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
isotope
atoms of the same element with the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons
relative atomic mass
the average mass of an atom compared to 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom
relative formula mass
the sun of the relative atomic masses of atoms in a molecule
relative molecular mass
the average mass of a molecule of an element or compound relative to 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom
avogadro’s number
6.022×10²³
stages of mass spectrometry
vaporisation, ionisation, acceleration, ion drift, detection
electron impact
bombarded with high energy electrons, forms M^+ ions
electrospray ionisation
sprayed through a hypodermic needle with large voltage, forms MH^+ ions
acceleration stage of tof
all ions are accelerated such that they have the same kinetic energy. ions are accelerated by a negatively charged acceleration plate. all have same kinetic energy
ion drift
lighter ions travel faster and meet the detector first. heavier ions travel slower
detection stage of tof
ions hit the detector and gain an electron. the more abundant a particular ion, the greater the current generated
avogadros number meaning
the number of ions present in a sample with a mass equal to its relative formula mass
mass of one ion equation
mass = relative isotopic mass x 10^-3 / 6.022×10²³
kinetic energy equation
KE = ½mv²
velocity equation simple
v= d/t
velocity equation combing kinetic energy
v = √m/2KE
tof comparing different isotopes equations
mv = mv
m/t² = m/t²
calculation for max number of electrons in energy level
2n² where n is the energy level
number of orbitals in the s subshell
1
shape of s orbital
spherical
number of orbitals in p subshell
3
shape of p orbital
dumbbell shaped
number of orbitals in d subshell
5
number of orbitals in f subshell
7
the Aufbau principle
electrons always fill up the lowest energy subshell first
hund’s rule
electrons will always go into empty orbitals before pairing because they repel each other
the Pauli exclusion principle
there is a maximum of two electrons with opposite spin in one orbital
electronic configuration of copper
[Ar] 4s^1 3d^10
electronic configuration of chromium
[Ar] 4s^1 3d^5
isoelectronic
atoms or ions of different elements that have the same electronic configuration
are 4s or 3d electrons lost first?
4s because it is a higher energy level
enthalpy change of 1st ionisation energy
when 1 mole of gaseous atoms lose 1 mole of electrons to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
factors that affect ionisation energy
atomic radius - greater distance - less attraction
nuclear charge - greater charge - greater attraction
electron shielding - greater shielding - less attraction
trend in ionisation energy down the group
greater radius - loses electrons more easily
greater charge - more attraction
more shielding - less attraction
trend in ionisation energy across a period
smaller radius - greater attraction
greater charge - more attraction
same shielding - neutral effect
number of moles equation
n = mass / Mr
empirical formula
simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound
percentage yield
how much product was produced compared to the expected amount
reasons for percentage yield of less than 100%
impure reactants
reversible reaction
side reactions
loss of mass during transfer
percentage yield calculation
(actual yield / theoretical yield) x 100
atom economy
the measure of the amount of useful products in relation to the reactants
atom economy calcualtation
(total mass of useful products / total mass of reactants) x 100
number of moles calculation with liquids
n = cv
ideal gas equation
PV = nRT
assumptions made for ideal gas equation to work
all the particles are perfect spheres
there are no attractive forces between the particles
all collisions between particles are elastic so kinetic energy stays the same
ionic bonding
the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
factors that determine strength of an ionic bond
ionic radius - smaller radius - stronger
ionic charge - greater charge - stronger
covalent bond
the electrostatic force of attraction between a pair of shared electrons and a positive nucleus
factor that determines the strength of a covalent bond
bond length - larger atoms - longer bonds- weaker
dative covalent bond
one atom supplies both electrons to form a covalent bond
conditions for a dative covalent bond to form
one atom must have a vacant orbital
another atom must have a lone pair of electrons
dimer
when two of the same small molecule join together to form a larger molecule via dative covalent bonding
metallic bonding
the electrostatic force of attraction between positive metal ions and a sea of delocalised electrons
factors that affect the strength of metallic bonds
ionic radius
ionic charge
valence shell electron pair repulsion theory
bonding pairs repel other bonding pairs equally and as much as possible
lone pairs repel other lone pairs equally and as much as possible
lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs
way to find base shape of molecule
valence electrons of central atom + number of bonds formed all divided by 2
bond angles with lone pairs
take 2.5 degrees away for every lone pair
polar bonds
ionic character of covalent bonds
electronegativity
the ability of an atom to withdraw electron density towards itself in a covalent bond
factors affecting electronegativity
nuclear charge
atomic radius
trend in electronegativity across a period
nuclear charge increases
atomic radius decreases
—> greater electronegativity
trend in electronegativity down a group
atomic radius increases
nuclear charge increases
—> lower electronegativity
most electronegative atom
fluorine
requirement for ionic bonds with covalent character
a polarising cation - small highly charged cations which distort the shape of the anion
a polarisable anion - large anions
van der waal’s forces
electron movement in first molecule induces a dipole in another, resulting to a temporary attraction between d+ on one molecule and d- on another
factors that determine the strength of van der Waal’s forces
size of the molecule - greater size - greater imf
shape of the molecule - branched chains don’t pack as closely together - lower imf
factors that determine the presence of dipole-dipole interactions
presence of electronegative atoms resulting in polar bonds
shape of the molecule - the distribution of charge must be asymmetric
the molecule must have an overall dipole moment
order of increasing strength of intermolecular forces
van der Waal’s forces
dipole-dipole interactions
hydrogen bonds
factors for hydrogen bonds to occur
a hydrogen atom must be directly bonded to one of the most electronegative elements eg. F, N, or O
the electronegative element must have a lone pair of electrons
way to draw hydrogen bonds
show all lone pairs of electrons
show all partial charges
linear arrangement of covalent bond and hydrogen bond
periodicity
the study of trends shown by the elements which repeat themselves in each period of the periodic table
oxidation
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
reducing agent
(itself is oxidised) loses electrons
oxidising agent
(itself is reduced) gains electrons / oxidises another atom or ion
neutral compound oxidation state
equals 0

name and bond angle of this shape
name: linear
bond angle: 180
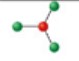
name and bond angle of the shape
name: trigonal planar
bond angle: 120
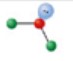
name and bond angle of this shape
name: bent
bond angle: 117.5
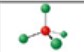
name and bond angle of this shape
name: tetrahedral
bond angles: 109.5
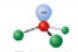
name and bond angle of this shape
name: trigonal pyramidal
bond angle: 107
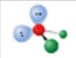
name and bond angle of this shape
name: bent
bond angle: 104.5
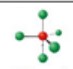
name and bond angles of this shape
name: trigonal bipyramidal
bond angle: 90,120
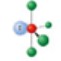
name and bond angles of this shape
name: sawhorse or seesaw
bond angles: 87.5, 117.5
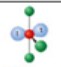
name and bond angles of this shape
name: T shaped
bond angles: 90
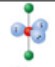
name and bond angles of this shape
name: linear
bond angle: 180
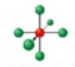
name and bond angles of this shape
name: octahedral
bond angles: 90
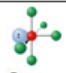
name and bond angles of this shape
name: square pyramidal
bond angles: 87.5
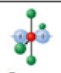
name and bond angles of this shape
name: square planar
bond angles: 90
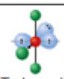
name and bond angles of this shape
name: T shape
bond angle: 87.5
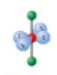
name and bond angles of this shape
name: linear
bond angle: 180
Exothermic reaction
Releases energy to the surroundings
energy of the products is less than the reactants
Characterised by an increase in temperature
Bond formation is exothermic
Endothermic reaction
Absorbs energy from the surroundings
energy of the products is greater than the reactants
Characterised by a decrease in temperature
Bond breaking is endothermic
Enthalpy change (delta H)
Heat change at constant pressure
Standard conditions (°)
298K, 100kPa, 1.00 moldm-3
Standard enthalpy change of formation
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its constituent elements with all reactants and products in standard states under standard conditions
Standard enthalpy change of combustion
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen with all reactants and products in standard states under standard conditions
Mean bond enthalpy
The enthalpy change required to break 1 mole of a covalent bond in gas phase, averaged over a range of compounds