LA 2 Honors Poetry Terms 2020
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Allusion
a reference to a historical or literary person, place, or event
Apostrophe
a figure of speech in which a person, abstract quality, or non-existent personage is directly addressed as though present

Hyperbole
a figure of speech in which conscious exaggeration is used for emphasis or humorous effect

Imagery
the use of vivid language to appeal to the senses of touch (tactile), sound (auditory), taste (gustatory), smell (olfactory), kinesthetic (movement), organic (bodily or emotional sensations), and sight (visual).
Metaphor
an indirect comparison between two unlike objects

Personification
a figure of speech in which an object, animal, or idea is given human characteristics (actions or feelings)

Simile
a direct comparison of two unlike objects which uses "like," "as," or "than" as the means of comparison

Synecdoche
a form of metaphor in which a part signifies the whole or the whole signifies the part (ex "El Dorado won" rather than El Dorado baseball, football, soccer, etc.)

Metonymy
the use of a linked term to stand in for an object. (ex: "The dish was delicious" vs. "The chicken, green beans and potatoes were delicious")

Connotation
a meaning or idea suggested by or associated with a word

Denotation
the literal meaning of a word

Sound Devices
help to add to the rhythm, musicality, and sound of a poem

Alliteration
the repetition of initial consonant sounds

Assonance
the repetition of vowel sounds within non-rhyming words

Consonance
the repetition of consonant sounds within and at the ends of words

End rhyme
words that rhyme at the ends of lines of poetry (can be further separated into male and female rhymes)

Iambic pentameter
a line of poetry made of five iambs (an unaccented syllable followed by an accented syllable), making the line 10 syllables long

Internal rhyme
words that rhyme within a single line of poetry
Onomatopoeia
the use of words that imitate sounds
Refrain
the repetition of words or phrases throughout a poem

Rhyme scheme
the pattern of end rhyme in a poem.
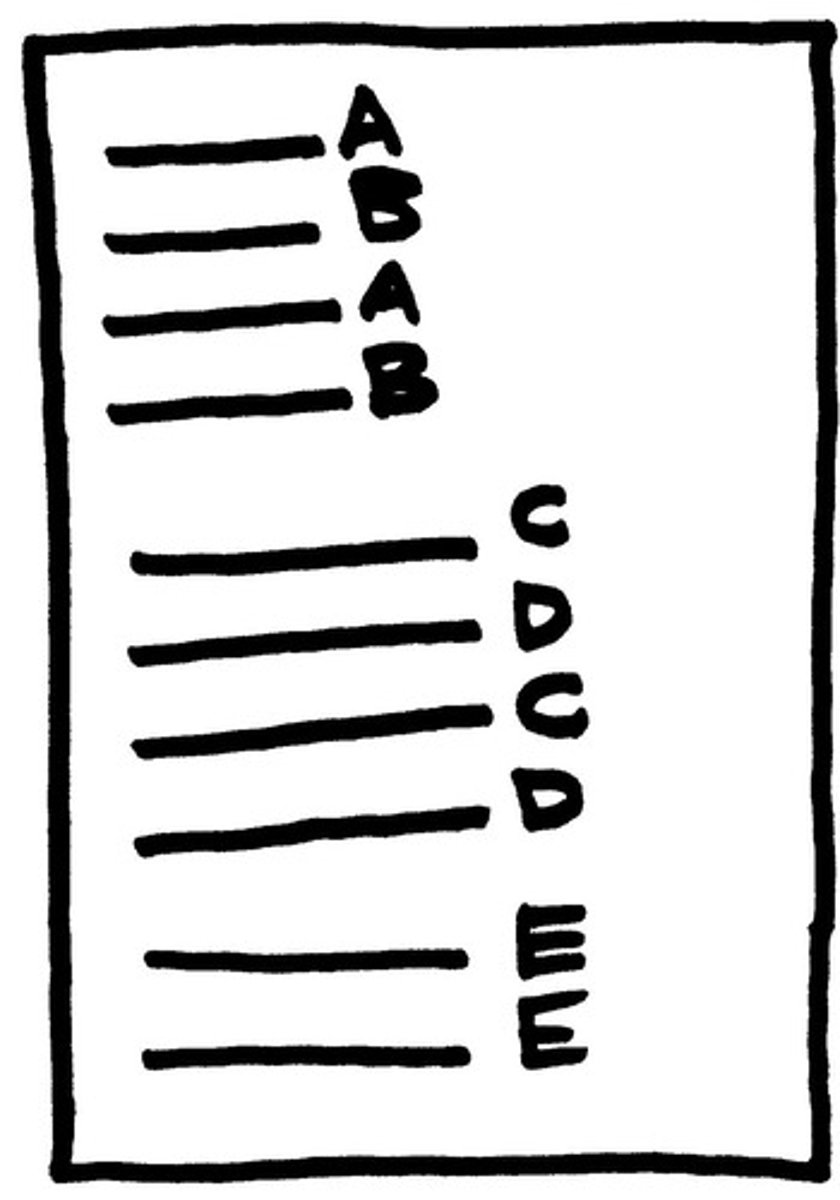
Alternating rhyme
rhyming in an ABAB pattern

Couplet
two rhyming lines

Blank verse
a poem in unrhymed iambic pentameter (Macbeth)
Dramatic monologue
a poem in which a single speaker addresses an unheard or absent listener

Free verse
a poem that does not follow regular patterns of rhyme, meter, or form

Lyric
a poem which focuses on the emotions, feelings, and/or observations of the author or speaker
Narrative
a poem that tells a story or event. Different types of narrative poems include the ballad or epic poetry

Sonnet
a fourteen-line poem, most often written in iambic pentameter and with a specific rhyme scheme. Types of sonnets include Shakespearian and Italian/Petracharan

Villanelle
a nineteen-line poem made up of five tercets followed by a quatrain. The rhyme scheme is ABA with the same end-rhyme for every first and last line of each tercet and the final two lines of the quatrain. Two of the lines are repeated: The first line of the first stanza is repeated as the last line of the second and fourth stanzas, and as the second-to-last line in the quatrain. The third line of the first stanza is repeated as the last line of the third and fifth stanzas, and as the last line in the quatrain.
Tercet
a three line stanza

Quatrain
a four line stanza (a standard form—there are names for the other forms too)

Speaker
the voice of the poem. The speaker of the poem is not necessarily the poet.
Tone
the attitude a writer takes toward a subject. Tone is reflected through language and details the writer includes in the work.

Mood
the feeling or atmosphere that the poet or writer creates for the reader. Mood is created by use of figurative language, word choice, sound, and rhythm.
