AP Psych: Brain Parts // Психология мозъка
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
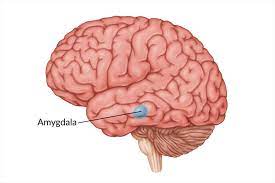
amygdala
part of the limbic system, related to fear and rage
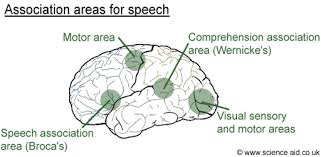
association areas
cortical areas involved in higher order functions like learning
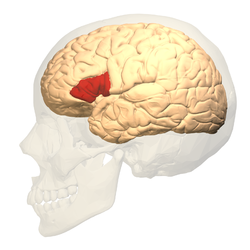
broca's area
in the left frontal lobe, specializes in language production
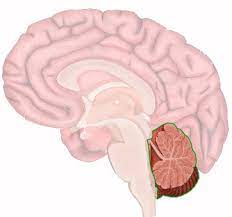
cerebellum
little brain, coordinates muscle movement and balance
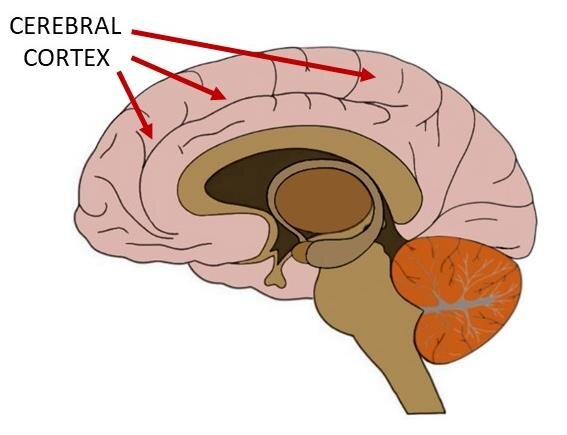
cerebral cortex
covering of the brain, responsible for information processing
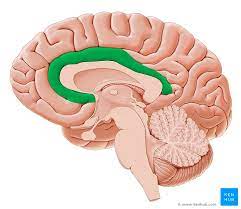
cingulate gyrus
coordinates emotions, sensory input; attending to own thoughts
convolution
one of several folds of the cerebral cortex
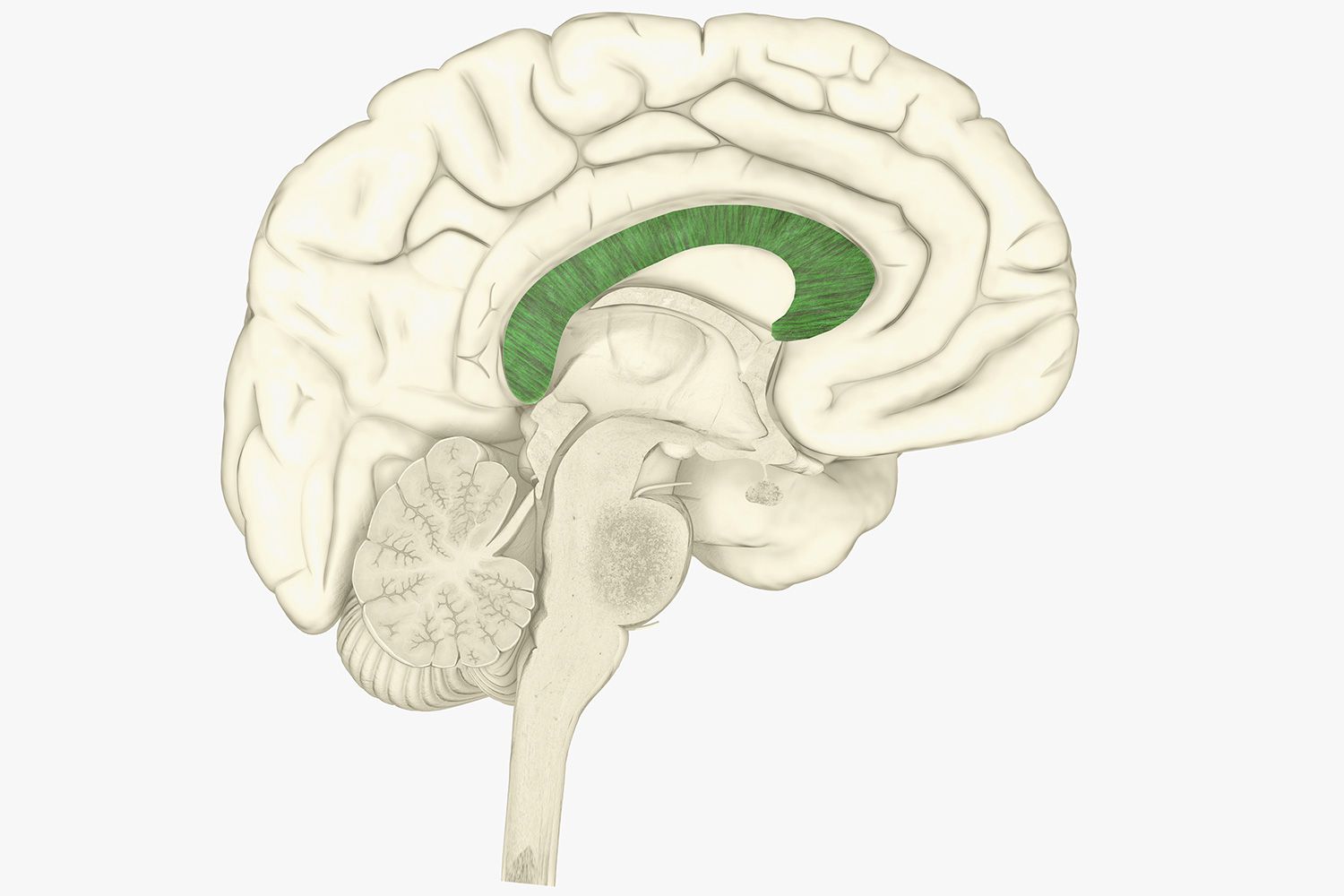
corpus callosum
band of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres
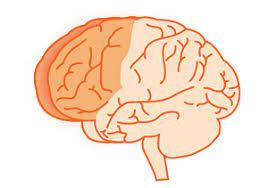
frontal lobes
involved in speaking, making plans, decision-making
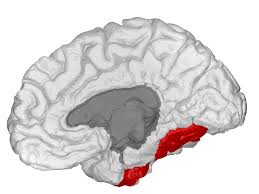
fusiform gyrus
face and number recognition
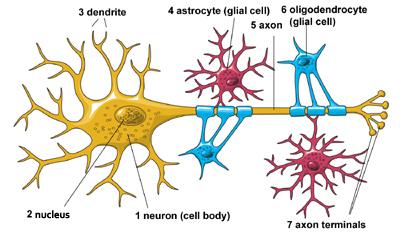
glial cells
cells that nourish, protect, and support neurons
gyrus
a folding out of the cerebral cortex
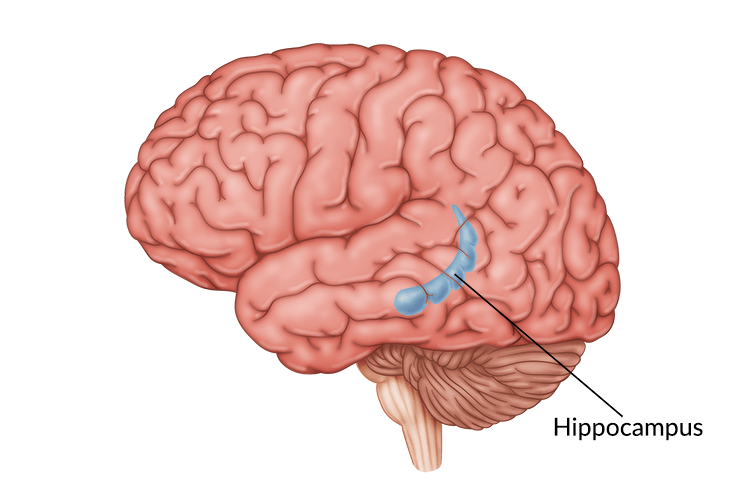
hippocampus
part of the limbic system, related to long term memory formation
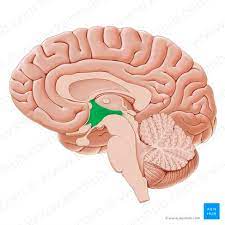
hypothalamus
part of the limbic system; contains hunger, thirst, pleasure centers
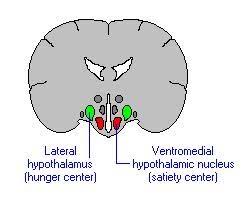
lateral hypothalamus
part of the hypothalamus known as the hunger center
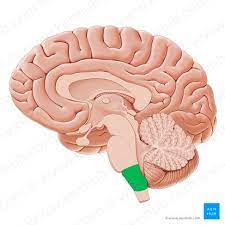
medulla (oblongata)
base of the brainstem controlling heart and breathing rates
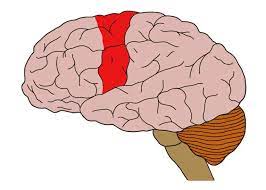
motor cortex
back of the front lobe, responsible for voluntary movement
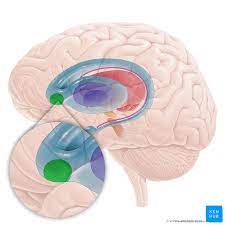
nucleus accumbens
part of the hypothalamus known as the pleasure center
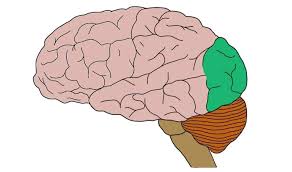
occipital lobes
include the visual processing centers
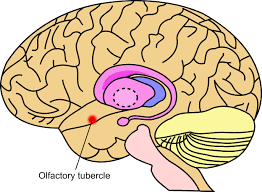
olfactory bulb
processes information related to taste and smell
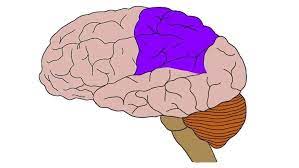
parietal lobes
includes the sensory cortex; responsible for tactile-processing
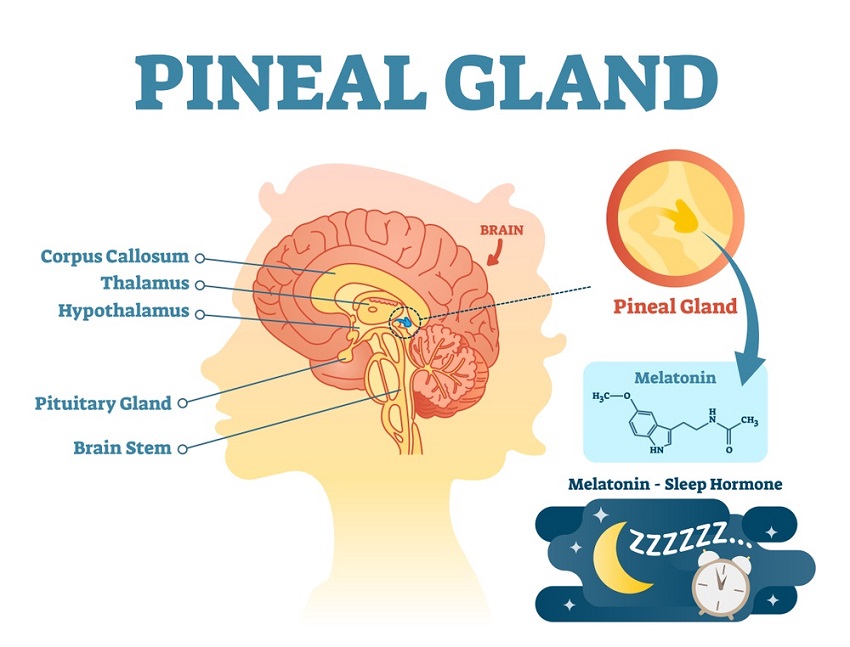
pineal gland
endocrine gland that produces melatonin, related to sleep
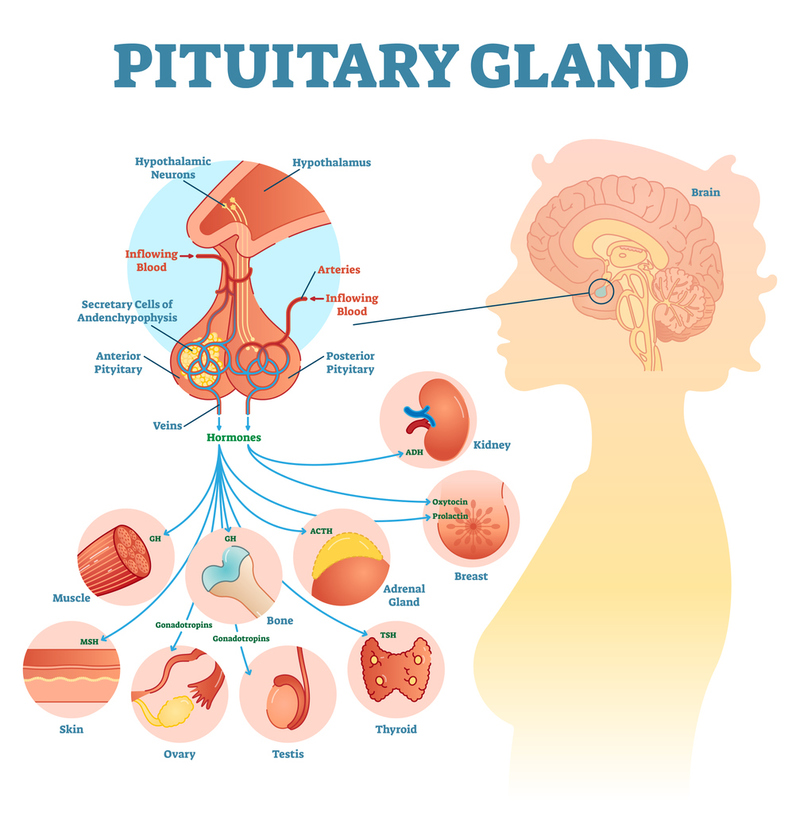
pituitary gland
regulates growth of the individual
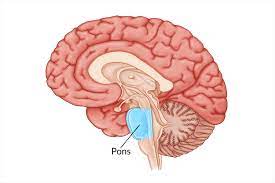
pons
connects forebrain to midbrain; controls facial expressions
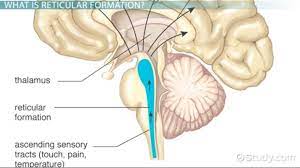
reticular formation
neural network of the pons regulating wakefulness, arousal
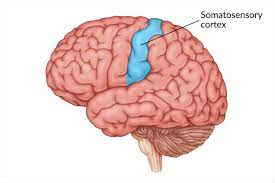
sensory cortex
front of the parietal lobe; processes bodily sensations
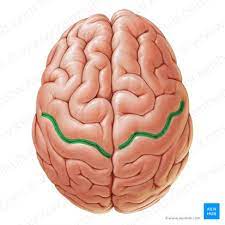
sulcus
a folding in of the cerebral cortex
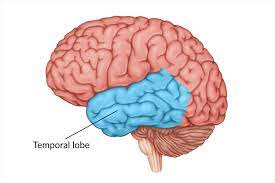
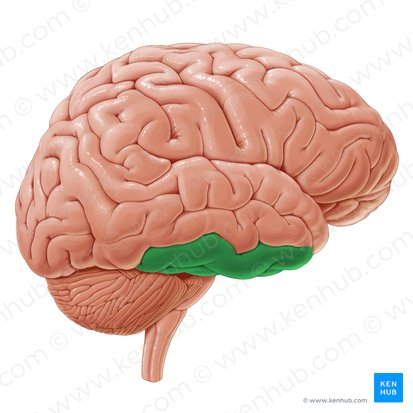
temporal lobes
includes the auditory processing center
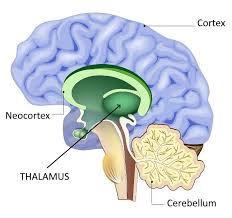
thalamus
brain's switchboard; sends messages to proper areas of the cortex
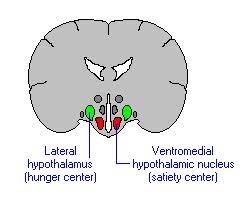
ventromedial hypothalamus
part of the hypothalamus known as the satiety center
wernicke's area
located in left hemisphere, interprets language, auditory information
acetylcholine
(nt) related to motor movement, associated with Alzheimer's disease
dopamine
(nt) related to alertness, motor movement, associated with schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease
endorphins
(nt) related to pain control; involved in addictions
gaba
(nt) inhibitory, associated with Huntington's, seizures
glutamate
(nt) involved in ltm and pain perception
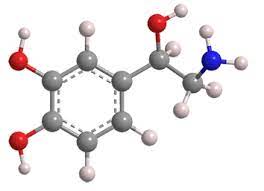
norepinephrine
(nt) affects arousal, wakefulness, learning, memory, and mood
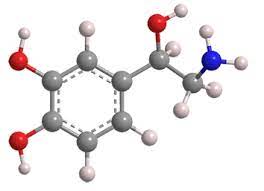
serotonin
(nt) related to arousal, mood, sleep, associated with anxiety, depression
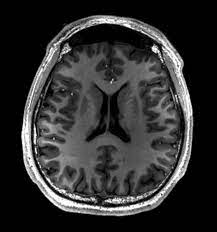
MRI
Medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the inside of the brain
(no radiation and clear images, fast, BUT no pacemakers (control heartbeat,) no metal, expensive)
Structure shown
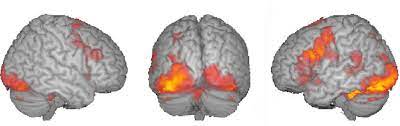
fMRI
It is a neuroimaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow
(no radiation and clear images, fast BUT no pacemakers (control heartbeat,) no metal, expensive)
Function shown
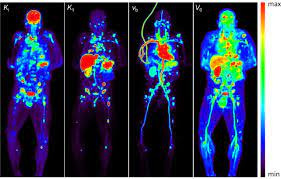
PET scan
Imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to detect activity in the body, helpful in diagnosing conditions like cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders.
(noninvasive, painless, short time, studies body function --> can diagnose, BUT radiation, expensive, images aren't as clear)
Function shown
CT scan
Medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body
(measures brain flow, noninvasive, painless, provides clear enough info. for surgeons before surgery, BUT radiation, not as great as MRI)
Structure shown
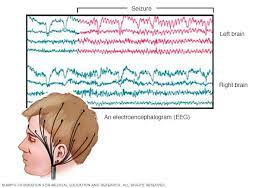
EEG scan
A diagnostic test that records electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp to detect abnormalities or patterns associated with various neurological conditions.
(noninvasive, painless, cheap, fast, BUT difficult to locate source of electrical activity, expensive)
Function shown
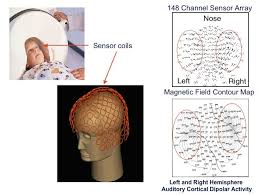
MEG scan
A non-invasive brain imaging technique that measures magnetic fields generated by neural activity, providing detailed insights into brain function.
(provides timing as well as spatial info. about brain activity, BUT very expensive, rare to find, and not as good as fMRI at localizing where brain activity is taking place)